Abstract
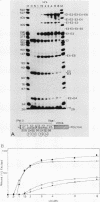
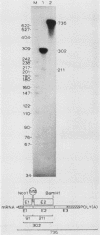
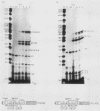
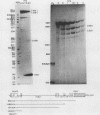
We analyzed the in vitro splicing pathways of three multi-intervening-sequence (IVS) pre-mRNAs: human beta-globin, which contains two IVSs (K. M. Lang, V. L. van Santen, and R. A. Spritz, EMBO J. 4:1991-1996, 1985); rat alpha-lactalbumin, which contains three IVSs; and murine interleukin-3, which contains four IVSs. We found that there are highly preferred pathways of IVS removal from these multi-IVS pre-mRNAs in vitro. The three IVSs of rat alpha-lactalbumin pre-mRNA were excised sequentially from 5' to 3'; in most molecules, IVS1 was removed first, followed by IVS2 and finally by IVS3. The splicing pathway of interleukin-3 pre-mRNA in vitro was more complex. The four IVSs were excised in a highly preferred temporal order, but the order was not strictly sequential or directional. In most molecules, IVS1 and IVS4 were removed first, either simultaneously or in rapid succession. Subsequently, IVS2 was excised, followed by IVS3. The observed splicing pathways apparently resulted from differences in lag times and maximum excision rates of the different IVSs. We detected no exon skipping during splicing of these transcripts in vitro. These observations have implication for proposed models of splice site selection.
Full text
PDF
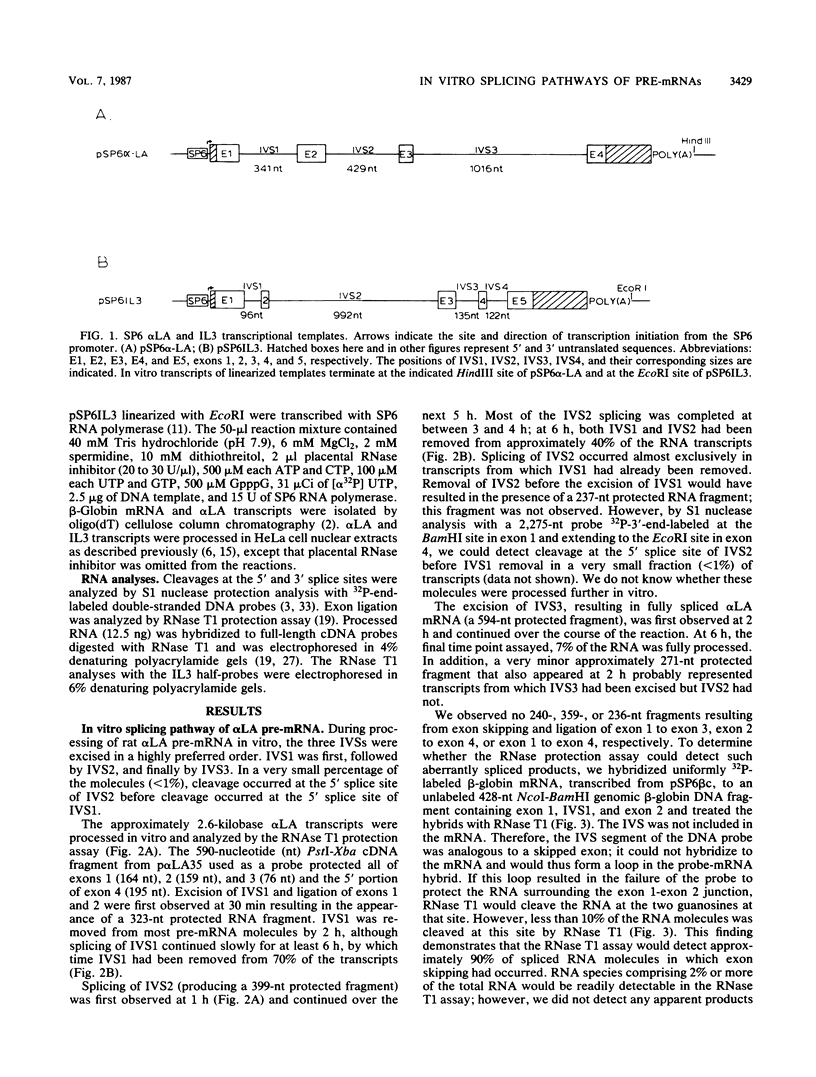
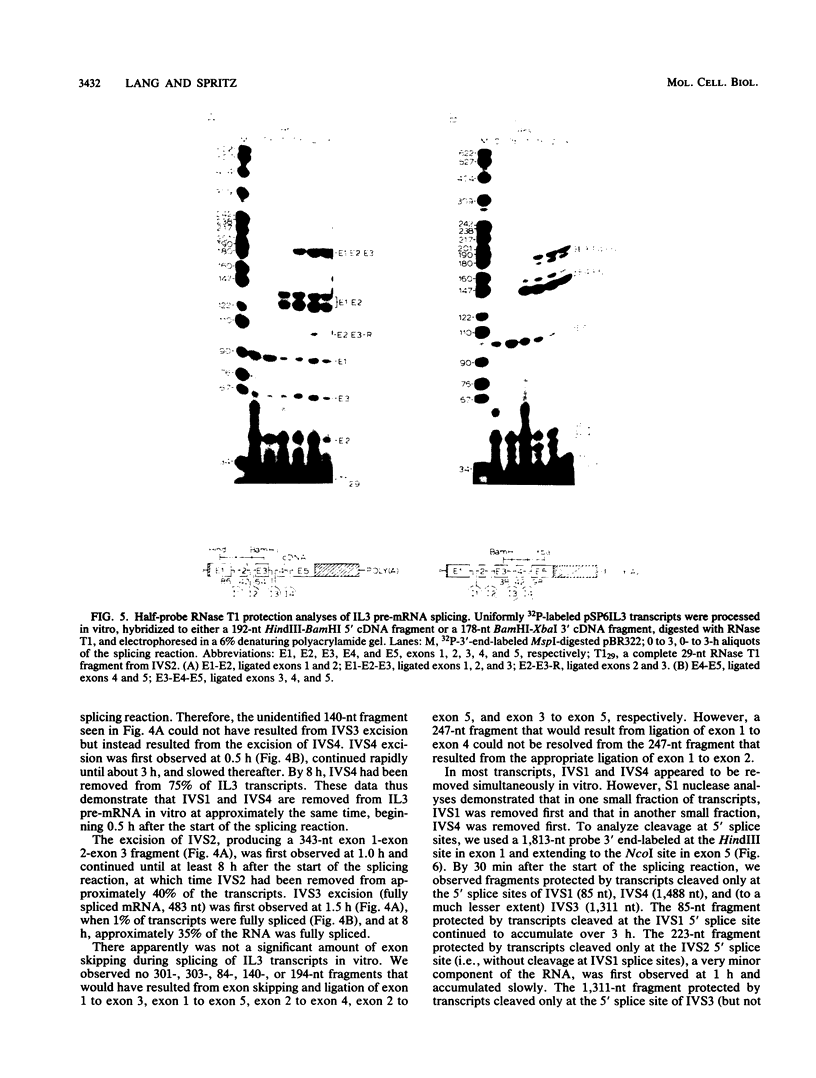
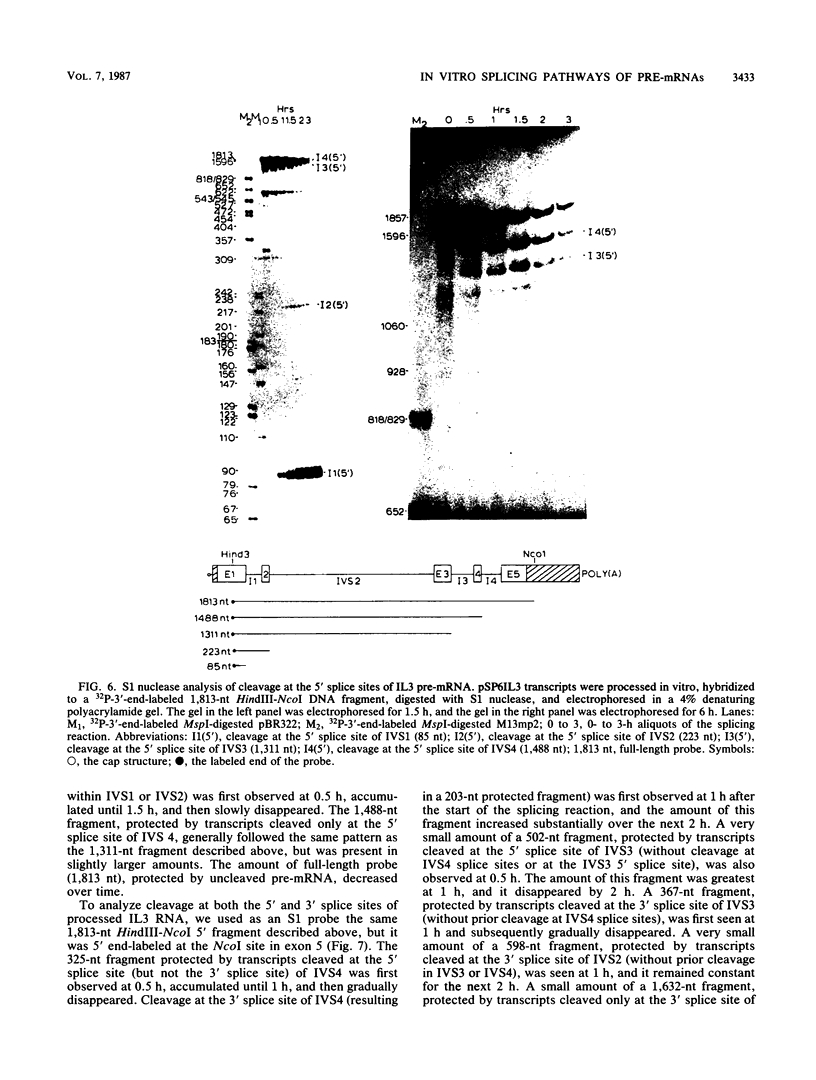

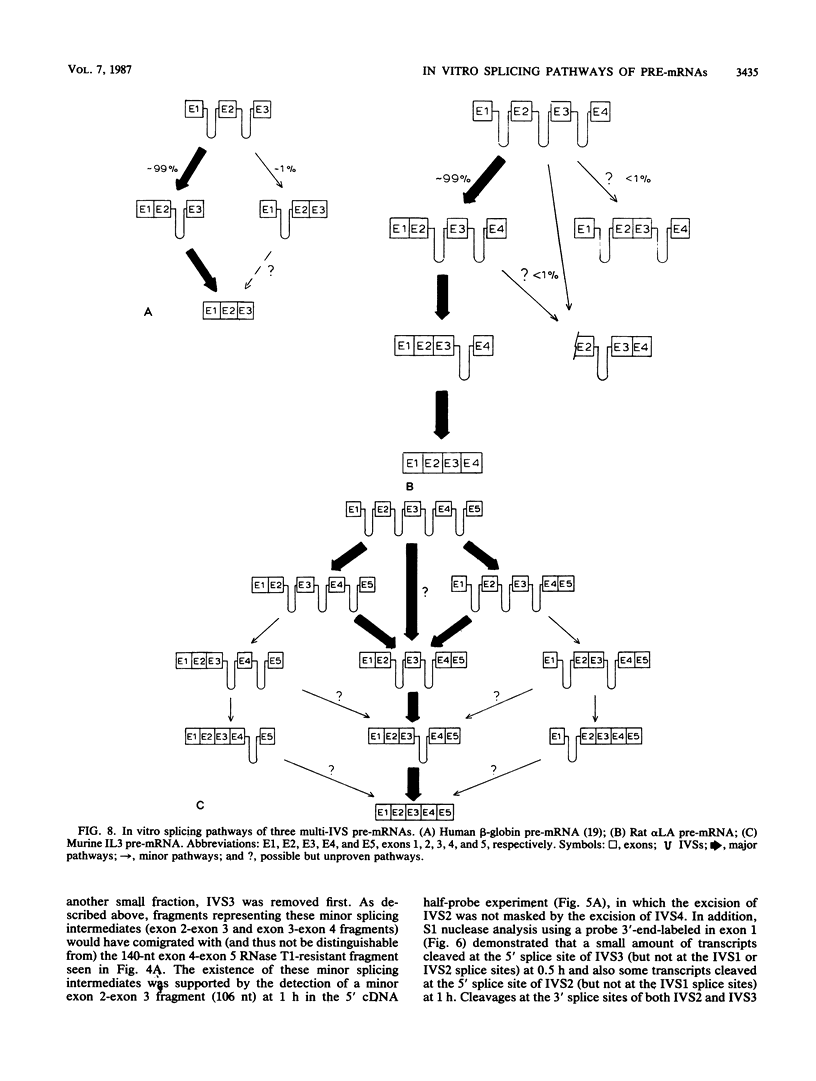


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aebi M., Hornig H., Padgett R. A., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Sequence requirements for splicing of higher eukaryotic nuclear pre-mRNA. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90620-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bovenberg R. A., van de Meerendonk W. P., Baas P. D., Steenbergh P. H., Lips C. J., Jansz H. S. Model for alternative RNA processing in human calcitonin gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 25;14(22):8785–8803. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.22.8785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christofori G., Frendewey D., Keller W. Two spliceosomes can form simultaneously and independently on synthetic double-intron messenger RNA precursors. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1747–1755. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02427.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dandekar A. M., Qasba P. K. Rat alpha-lactalbumin has a 17-residue-long COOH-terminal hydrophobic extension as judged by sequence analysis of the cDNA clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4853–4857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson D. S., McNab A. R., Rovera G., Curtis P. J. Nuclear precursor molecules of the two beta-globin mRNAs in Friend erythroleukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8655–8660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gattoni R., Keohavong P., Stévenin J. Splicing of the E2A premessenger RNA of adenovirus serotype 2. Multiple pathways in spite of excision of the entire large intron. J Mol Biol. 1986 Feb 5;187(3):379–397. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90440-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg C. J., Raskas H. J. Splicing patterns of nuclear precursors to the mRNA for adenovirus 2 DNA binding protein. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90194-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R., Maniatis T., Melton D. A. Human beta-globin pre-mRNA synthesized in vitro is accurately spliced in Xenopus oocyte nuclei. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):681–694. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green M. R. Pre-mRNA splicing. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:671–708. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan D. S., Weissman S. M. Synthesis of predominantly unspliced cytoplasmic RNAs by chimeric herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase-human beta-globin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1894–1900. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatzoglou M., Sekeris C. E., Hanson R. W. Processing of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (GTP) RNA in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4346–4350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keohavong P., Gattoni R., LeMoullec J. M., Jacob M., Stévenin J. The orderly splicing of the first three leaders of the adenovirus-2 major late transcript. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 25;10(4):1215–1229. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.4.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krainer A. R., Maniatis T., Ruskin B., Green M. R. Normal and mutant human beta-globin pre-mRNAs are faithfully and efficiently spliced in vitro. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):993–1005. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90049-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühne T., Wieringa B., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Evidence against a scanning model of RNA splicing. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):727–733. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01492.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang K. M., Spritz R. A. Cloning specific complete polyadenylylated 3'-terminal cDNA segments. Gene. 1985;33(2):191–196. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90093-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang K. M., Spritz R. A. RNA splice site selection: evidence for a 5' leads to 3' scanning model. Science. 1983 Jun 24;220(4604):1351–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.6304877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang K. M., van Santen V. L., Spritz R. A. The two intervening sequences of human beta- and gamma-globin pre-mRNAs are excised in a preferred temporal order in vitro. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):1991–1996. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03882.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Urlaub G., Chasin L. Spontaneous splicing mutations at the dihydrofolate reductase locus in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):1926–1935. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.1926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyatake S., Yokota T., Lee F., Arai K. Structure of the chromosomal gene for murine interleukin 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):316–320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K. J., Haimovich J., Perry R. P. Characterization of productive and sterile transcripts from the immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus: processing of micron and muS mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jul;3(7):1317–1332. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.7.1317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noteborn M., Arnberg A., de Jonge M., Ab G., Gruber M. Splicing pathways of the chicken apo very low density lipoprotein II (pre)messenger RNA. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 1;194(1):151–156. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80067-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osheim Y. N., Miller O. L., Jr, Beyer A. L. RNP particles at splice junction sequences on Drosophila chorion transcripts. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):143–151. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90019-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Hardy S. F., Sharp P. A. Splicing of adenovirus RNA in a cell-free transcription system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5230–5234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qasba P. K., Safaya S. K. Similarity of the nucleotide sequences of rat alpha-lactalbumin and chicken lysozyme genes. Nature. 1984 Mar 22;308(5957):377–380. doi: 10.1038/308377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryffel G. U., Wyler T., Muellener D. B., Weber R. Identification, organization and processing intermediates of the putative precursors of Xenopus vitellogenin messenger RNA. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):53–61. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90387-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Speculations on RNA splicing. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):643–646. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90425-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Orkin S. H., Maniatis T. Specific transcription and RNA splicing defects in five cloned beta-thalassaemia genes. Nature. 1983 Apr 14;302(5909):591–596. doi: 10.1038/302591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai M. J., Ting A. C., Nordstrom J. L., Zimmer W., O'Malley B. W. Processing of high molecular weight ovalbumin and ovomucoid precursor RNAs to messenger RNA. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):219–230. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90170-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota T., Lee F., Rennick D., Hall C., Arai N., Mosmann T., Nabel G., Cantor H., Arai K. Isolation and characterization of a mouse cDNA clone that expresses mast-cell growth-factor activity in monkey cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1070–1074. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeitlin S., Efstratiadis A. In vivo splicing products of the rabbit beta-globin pre-mRNA. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):589–602. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90466-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]