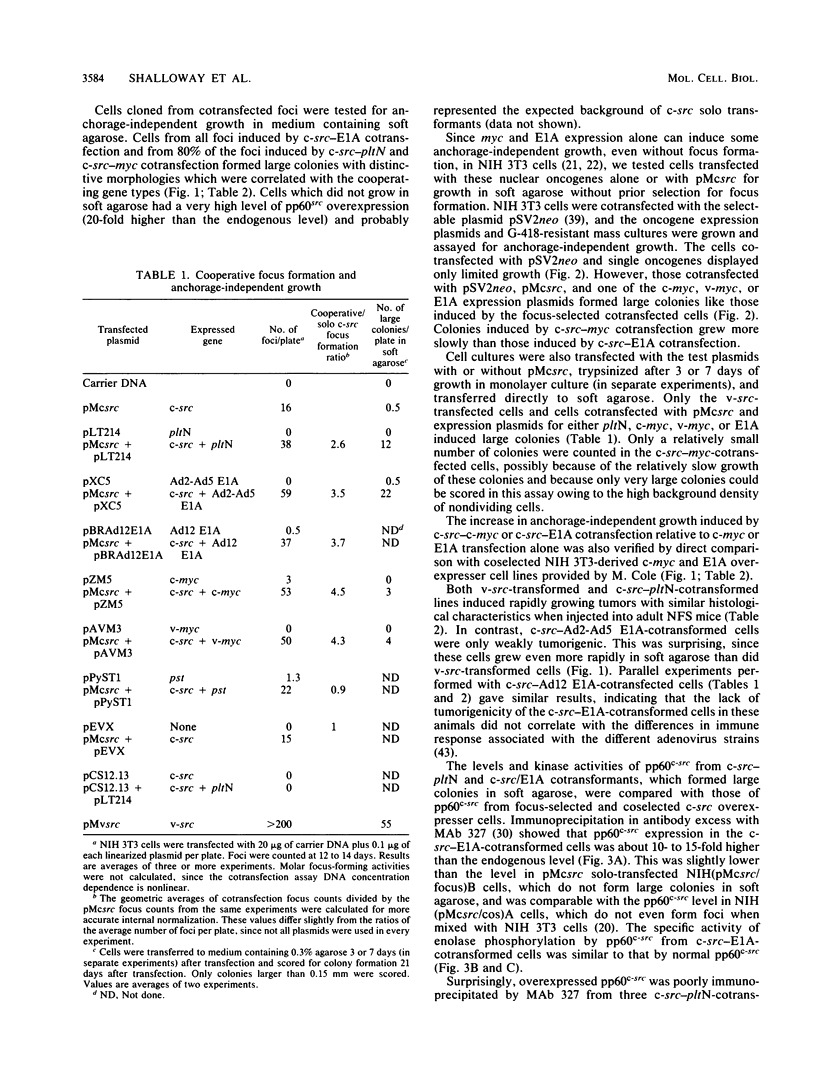
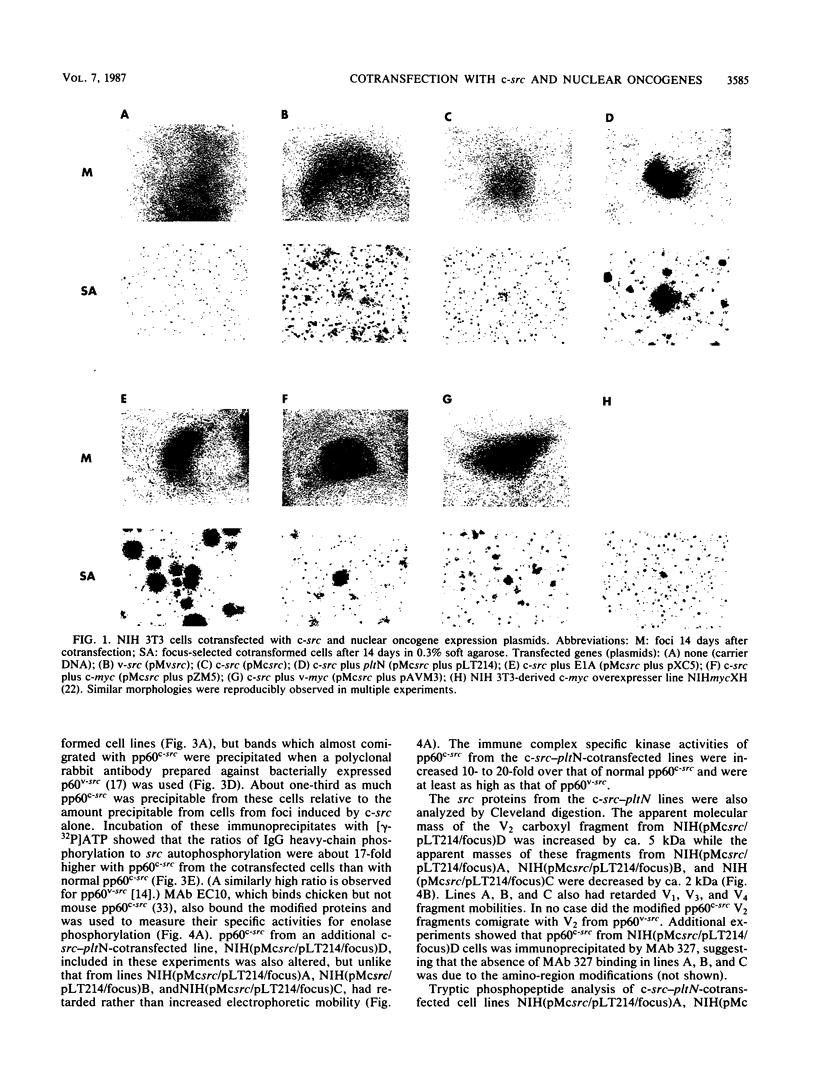
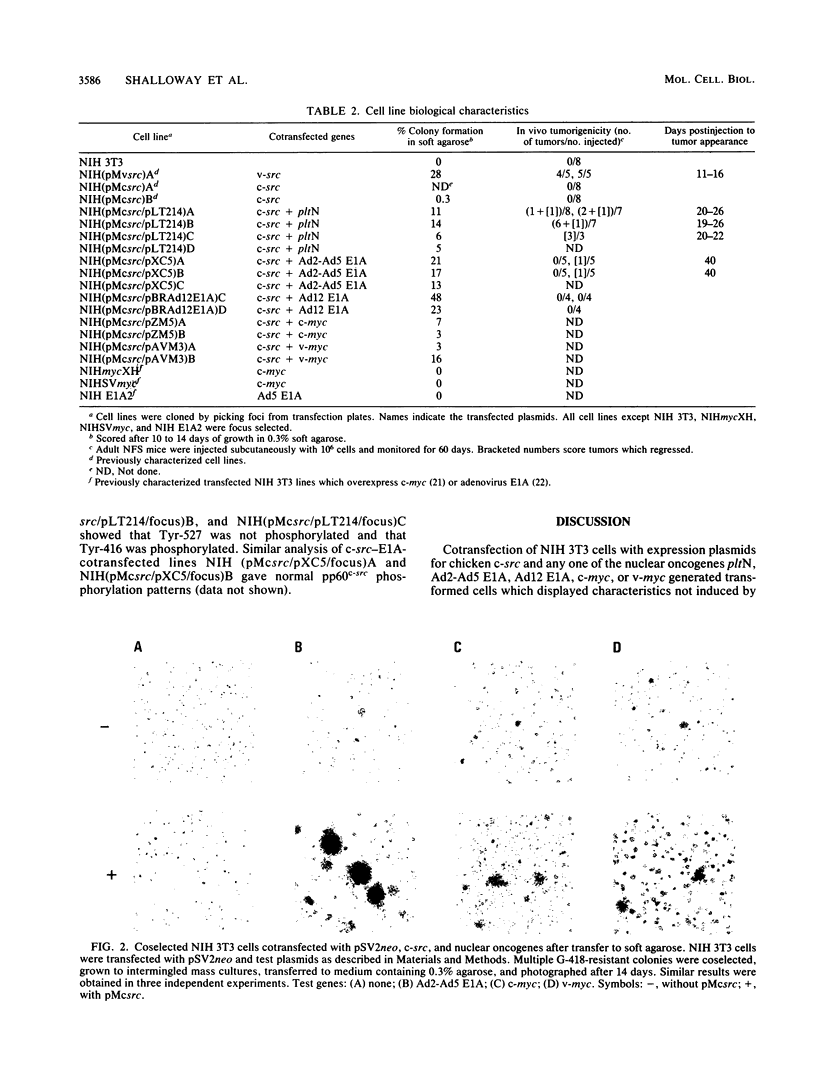
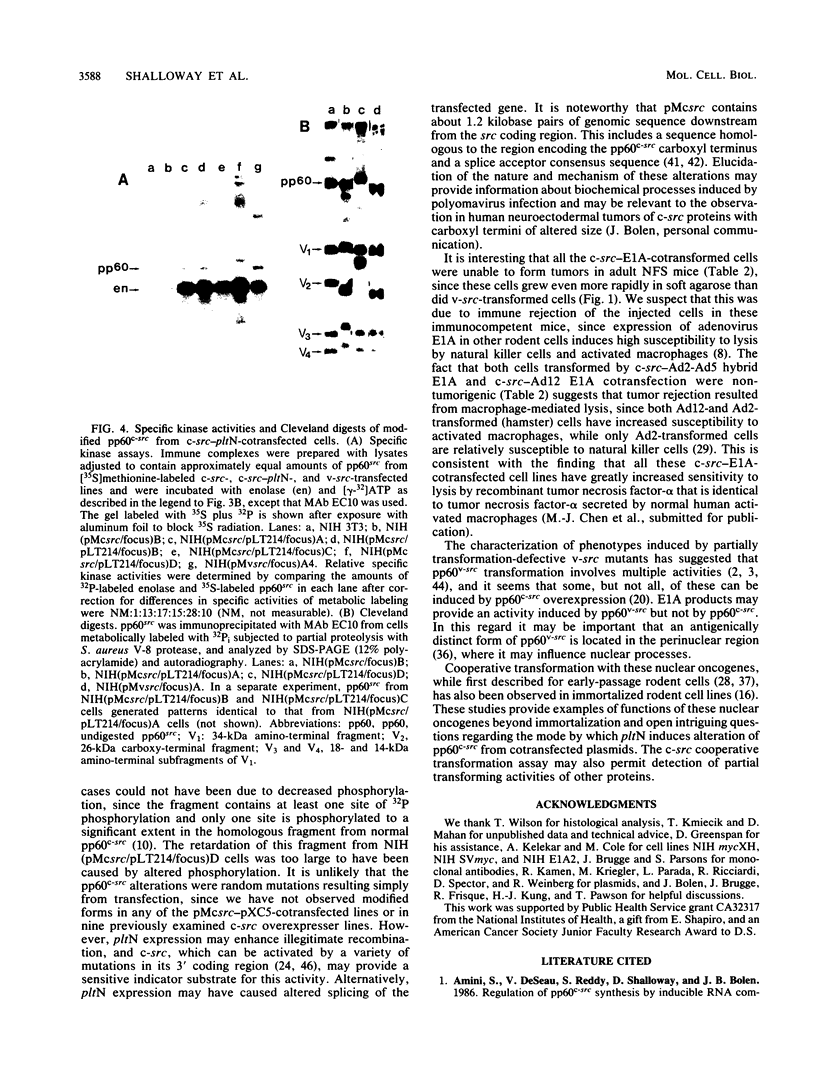
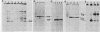Abstract
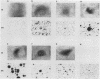
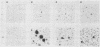
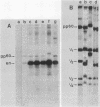
pp60c-src, the cellular homolog of the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein, does not completely transform cells even when present at high levels, but has been shown to be involved in polyomavirus-induced transformation when activated by polyomavirus middle T (pmt)-antigen binding. Here we show that cotransfection, but not solo transfection, of expression plasmids for c-src and either adenovirus E1A, v-myc, c-myc, or the 5' half of polyomavirus large T (pltN) antigen into NIH 3T3 cells induces anchorage-independent growth, enhanced focus formation, and, for pltN cotransfection, tumorigenicity in adult NFS mice. Enhancement of transformation was not observed with polyomavirus small t (pst) antigen. Cotransfection of c-src with pltN induced modification of pp60c-src that altered its electrophoretic mobility and in vivo phosphorylation state and stimulated its in vitro kinase activity. Similar alterations were not seen after c-src-E1A cotransfection, suggesting that at least two different mechanisms of enhancement are involved.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amini S., DeSeau V., Reddy S., Shalloway D., Bolen J. B. Regulation of pp60c-src synthesis by inducible RNA complementary to c-src mRNA in polyomavirus-transformed rat cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2305–2316. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker D., Kurth R., Critchley D., Friis R., Bauer H. Distinguishable transformation-defective phenotypes among temperature-sensitive mutants of Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1042–1055. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1042-1055.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., Claviez M., Jockusch B. M., Graf T. Differential expression of Rous Sarcoma virus-specific transformation parameters in enucleated cells. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):843–856. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90340-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Thiele C. J., Israel M. A., Yonemoto W., Lipsich L. A., Brugge J. S. Enhancement of cellular src gene product associated tyrosyl kinase activity following polyoma virus infection and transformation. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):767–777. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90272-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Eckhart W., Simon S., Kaplan P. L. Cell transformation by pp60c-src mutated in the carboxy-terminal regulatory domain. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90758-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Kaplan P. L., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Eckhart W. Altered sites of tyrosine phosphorylation in pp60c-src associated with polyomavirus middle tumor antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1562–1570. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Belzer S. K. Forms of pp60v-src isolated from Rous sarcoma virus-transformed cells. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1593–1601. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1593-1601.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. L., Walker T. A., Lewis A. M., Jr, Ruley H. E., Graham F. L., Pilder S. H. Expression of the adenovirus E1A oncogene during cell transformation is sufficient to induce susceptibility to lysis by host inflammatory cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6965–6969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Esch F. S., Taylor S. S., Hunter T. Phosphorylation sites in enolase and lactate dehydrogenase utilized by tyrosine protein kinases in vivo and in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7835–7841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Gould K. L., Cartwright C. A., Hunter T. Tyr527 is phosphorylated in pp60c-src: implications for regulation. Science. 1986 Mar 21;231(4744):1431–1434. doi: 10.1126/science.2420005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., King C. S. Dephosphorylation or antibody binding to the carboxy terminus stimulates pp60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4467–4477. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A. Activation of the pp60c-src kinase by middle T antigen binding or by dephosphorylation. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1471–1477. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03805.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Smith A. E. The complex of polyoma virus middle-T antigen and pp60c-src. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):585–591. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01852.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coussens P. M., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Shalloway D. Restriction of the in vitro and in vivo tyrosine protein kinase activities of pp60c-src relative to pp60v-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2753–2763. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerman M., Temin H. M. Genes with promoters in retrovirus vectors can be independently suppressed by an epigenetic mechanism. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):449–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franza B. R., Jr, Maruyama K., Garrels J. I., Ruley H. E. In vitro establishment is not a sufficient prerequisite for transformation by activated ras oncogenes. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):409–418. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90462-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmer T. M., Erikson R. L. Development of anti-pp60src serum with antigen produced in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):462–465. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.462-465.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iba H., Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Hanafusa H. Low level of cellular protein phosphorylation by nontransforming overproduced p60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1058–1066. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iba H., Takeya T., Cross F. R., Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H. Rous sarcoma virus variants that carry the cellular src gene instead of the viral src gene cannot transform chicken embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4424–4428. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. J., Coussens P. M., Danko A. V., Shalloway D. Overexpressed pp60c-src can induce focus formation without complete transformation of NIH 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1073–1083. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keath E. J., Caimi P. G., Cole M. D. Fibroblast lines expressing activated c-myc oncogenes are tumorigenic in nude mice and syngeneic animals. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):339–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelekar A., Cole M. D. Tumorigenicity of fibroblast lines expressing the adenovirus E1a, cellular p53, or normal c-myc genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):7–14. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Baldwin A. S., Sharp P. A. Transcription control by oncogenes. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):3–5. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik T. E., Shalloway D. Activation and suppression of pp60c-src transforming ability by mutation of its primary sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90756-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kriegler M., Perez C. F., Hardy C., Botchan M. Transformation mediated by the SV40 T antigens: separation of the overlapping SV40 early genes with a retroviral vector. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):483–491. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90503-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Chen A. C., Morgenstern J. P., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Behavior of myc and ras oncogenes in transformation of rat embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):1917–1925. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.1917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Tumorigenic conversion of primary embryo fibroblasts requires at least two cooperating oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):596–602. doi: 10.1038/304596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. M., Jr, Cook J. L. A new role for DNA virus early proteins in viral carcinogenesis. Science. 1985 Jan 4;227(4682):15–20. doi: 10.1126/science.3843807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsich L. A., Lewis A. J., Brugge J. S. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies that recognize the transforming proteins of avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.352-360.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Expression of a bacterial gene in mammalian cells. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1422–1427. doi: 10.1126/science.6251549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Expression of v-src and chicken c-src in rat cells demonstrates qualitative differences between pp60v-src and pp60c-src. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90308-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons S. J., McCarley D. J., Ely C. M., Benjamin D. C., Parsons J. T. Monoclonal antibodies to Rous sarcoma virus pp60src react with enzymatically active cellular pp60src of avian and mammalian origin. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):272–282. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.272-282.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piwnica-Worms H., Saunders K. B., Roberts T. M., Smith A. E., Cheng S. H. Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the biochemical and biological properties of pp60c-src. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90757-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassoulzadegan M., Cowie A., Carr A., Glaichenhaus N., Kamen R., Cuzin F. The roles of individual polyoma virus early proteins in oncogenic transformation. Nature. 1982 Dec 23;300(5894):713–718. doi: 10.1038/300713a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resh M. D., Erikson R. L. Highly specific antibody to Rous sarcoma virus src gene product recognizes a novel population of pp60v-src and pp60c-src molecules. J Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;100(2):409–417. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruley H. E. Adenovirus early region 1A enables viral and cellular transforming genes to transform primary cells in culture. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):602–606. doi: 10.1038/304602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shalloway D., Coussens P. M., Yaciuk P. Overexpression of the c-src protein does not induce transformation of NIH 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7071–7075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. J., Tevethia M. J. Identification of a human cytomegalovirus virus DNA segment that complements an adenovirus 5 immediate early mutant. Virology. 1986 Jun;151(2):329–338. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90053-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanstrom R., Parker R. C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Transduction of a cellular oncogene: the genesis of Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2519–2523. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya T., Hanafusa H. Structure and sequence of the cellular gene homologous to the RSV src gene and the mechanism for generating the transforming virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):881–890. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber M. J., Friis R. R. Dissociation of transformation parameters using temperature-conditional mutants of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):25–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90184-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Sweet R., Sim G. K., Wold B., Pellicer A., Lacy E., Maniatis T., Silverstein S., Axel R. Transformation of mammalian cells with genes from procaryotes and eucaryotes. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonemoto W., Jarvis-Morar M., Brugge J. S., Bolen J. B., Israel M. A. Tyrosine phosphorylation within the amino-terminal domain of pp60c-src molecules associated with polyoma virus middle-sized tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4568–4572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Eb A. J., Bernards R. Transformation and oncogenicity by adenoviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;110:23–51. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-46494-2_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]