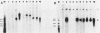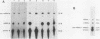Abstract
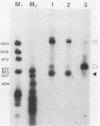
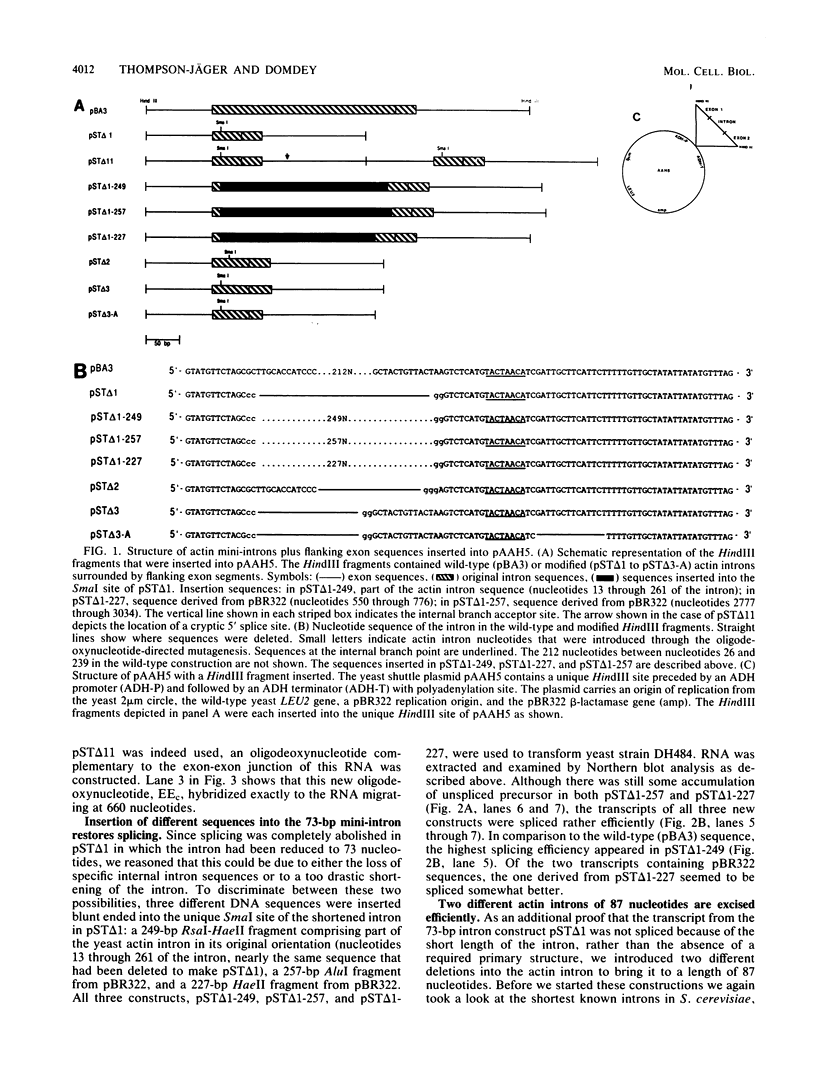
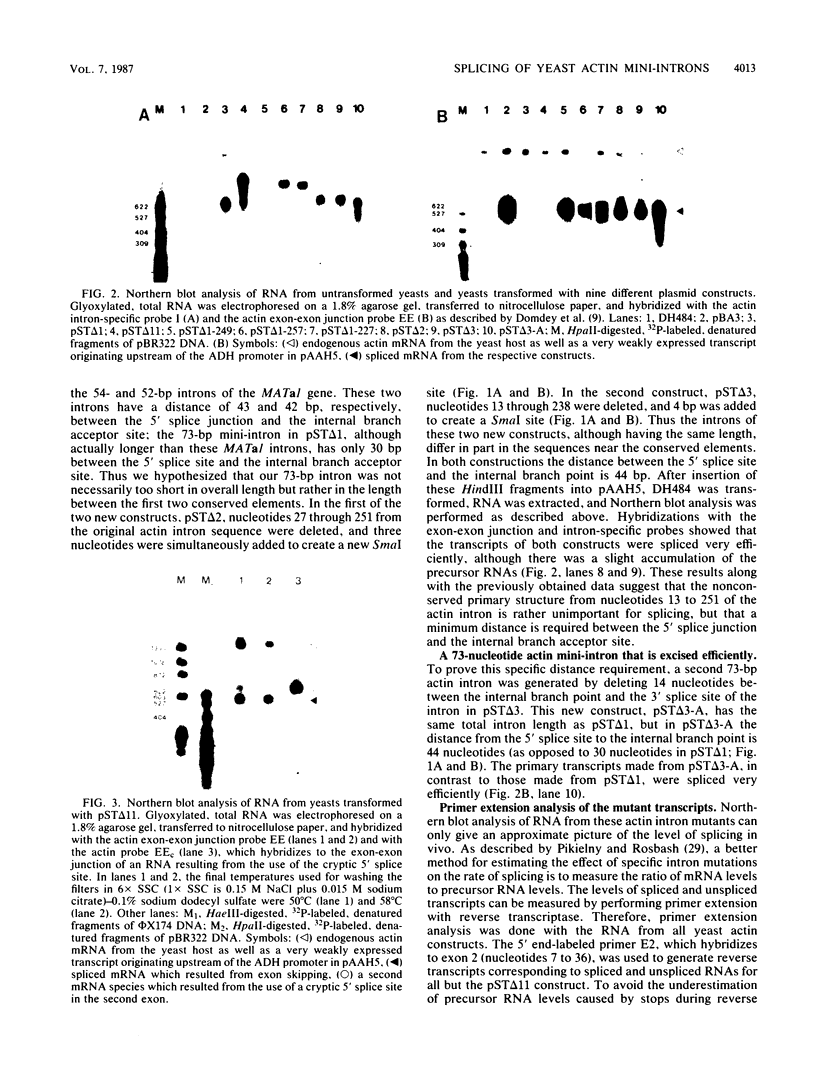
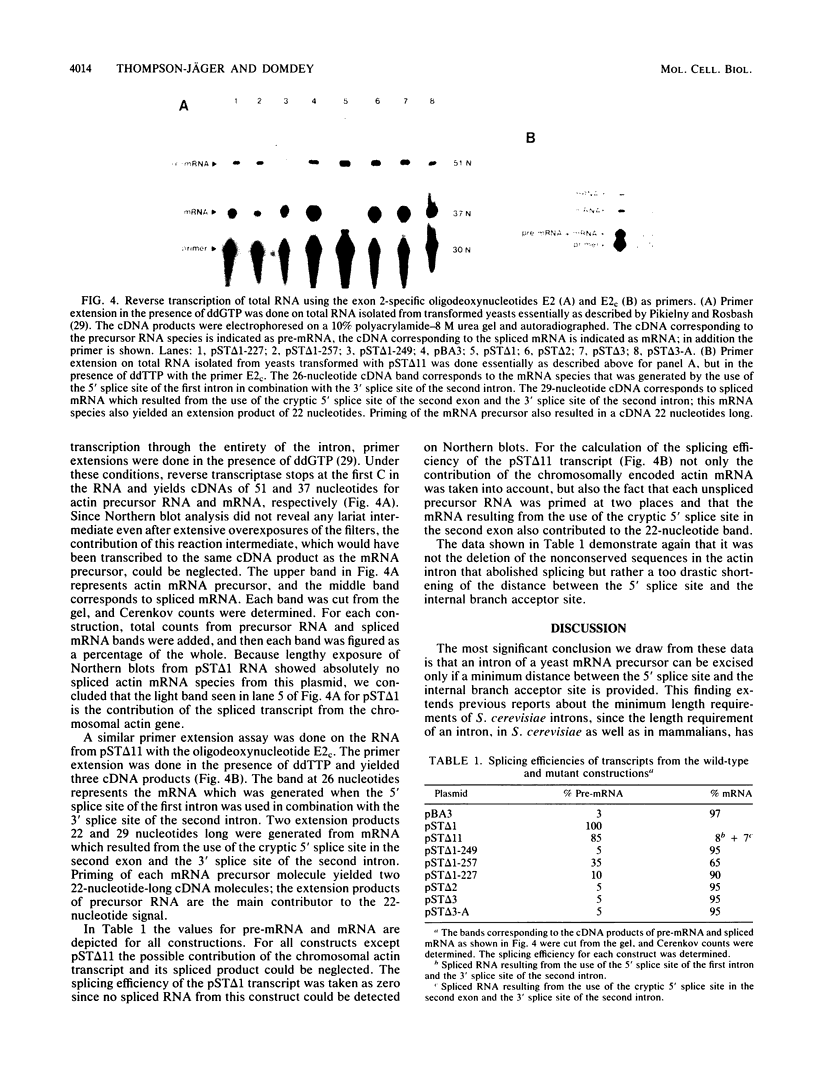
We have generated several deletions within the intron of a yeast actin gene construct which have lead to different splicing efficiencies as measured by Northern blot (RNA blot) and primer extension analyses. Our data especially demonstrate that a minimum distance from the 5' splice site to the internal branch acceptor site is required for accurate and efficient splicing. In a construct in which splicing was completely abolished, splicing could be restored by expanding the distance from the 5' splice site to the internal branch acceptor site with heterologous sequences. Alternative splicing, i.e., exon skipping and the use of a cryptic 5' splice site, was observed when the mRNA precursor was derived from a tandem repeat of a truncated intron with flanking exon sequences.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abelson J. RNA processing and the intervening sequence problem. Annu Rev Biochem. 1979;48:1035–1069. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.48.070179.005131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ammerer G. Expression of genes in yeast using the ADCI promoter. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:192–201. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astell C. R., Ahlstrom-Jonasson L., Smith M., Tatchell K., Nasmyth K. A., Hall B. D. The sequence of the DNAs coding for the mating-type loci of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90356-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brody E., Abelson J. The "spliceosome": yeast pre-messenger RNA associates with a 40S complex in a splicing-dependent reaction. Science. 1985 May 24;228(4702):963–967. doi: 10.1126/science.3890181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cellini A., Felder E., Rossi J. J. Yeast pre-messenger RNA splicing efficiency depends on critical spacing requirements between the branch point and 3' splice site. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):1023–1030. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04317.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cellini A., Parker R., McMahon J., Guthrie C., Rossi J. Activation of a cryptic TACTAAC box in the Saccharomyces cerevisiae actin intron. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1571–1578. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domdey H., Apostol B., Lin R. J., Newman A., Brody E., Abelson J. Lariat structures are in vivo intermediates in yeast pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):611–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90468-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue T. F., Farabaugh P. J., Fink G. R. The nucleotide sequence of the HIS4 region of yeast. Gene. 1982 Apr;18(1):47–59. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90055-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouser L. A., Friesen J. D. Mutations in a yeast intron demonstrate the importance of specific conserved nucleotides for the two stages of nuclear mRNA splicing. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):81–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90540-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D. Construction of a yeast actin gene intron deletion mutant that is defective in splicing and leads to the accumulation of precursor RNA in transformed yeast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3493–3497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Sures I. Structure of a split yeast gene: complete nucleotide sequence of the actin gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2546–2550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiraoka Y., Toda T., Yanagida M. The NDA3 gene of fission yeast encodes beta-tubulin: a cold-sensitive nda3 mutation reversibly blocks spindle formation and chromosome movement in mitosis. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):349–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käufer N. F., Simanis V., Nurse P. Fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe correctly excises a mammalian RNA transcript intervening sequence. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):78–80. doi: 10.1038/318078a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford C. J., Gallwitz D. Evidence for an intron-contained sequence required for the splicing of yeast RNA polymerase II transcripts. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):519–527. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90433-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langford C. J., Klinz F. J., Donath C., Gallwitz D. Point mutations identify the conserved, intron-contained TACTAAC box as an essential splicing signal sequence in yeast. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):645–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90344-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leff S. E., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Complex transcriptional units: diversity in gene expression by alternative RNA processing. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1091–1117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. M. The yeast MATa1 gene contains two introns. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1061–1065. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01927.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A. J., Lin R. J., Cheng S. C., Abelson J. Molecular consequences of specific intron mutations on yeast mRNA splicing in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):335–344. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman A. J., Ogden R. C., Abelson J. tRNA gene transcription in yeast: effects of specified base substitutions in the intragenic promoter. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):117–125. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90214-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng R., Abelson J. Isolation and sequence of the gene for actin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3912–3916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Grabowski P. J., Konarska M. M., Seiler S., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1119–1150. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R., Guthrie C. A point mutation in the conserved hexanucleotide at a yeast 5' splice junction uncouples recognition, cleavage, and ligation. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):107–118. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90065-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikielny C. W., Rosbash M. mRNA splicing efficiency in yeast and the contribution of nonconserved sequences. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):119–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90066-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikielny C. W., Teem J. L., Rosbash M. Evidence for the biochemical role of an internal sequence in yeast nuclear mRNA introns: implications for U1 RNA and metazoan mRNA splicing. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):395–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90373-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez J. R., Pikielny C. W., Rosbash M. In vivo characterization of yeast mRNA processing intermediates. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90467-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli plasmid pBR322. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1979;43(Pt 1):77–90. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1979.043.01.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teem J. L., Abovich N., Kaufer N. F., Schwindinger W. F., Warner J. R., Levy A., Woolford J., Leer R. J., van Raamsdonk-Duin M. M., Mager W. H. A comparison of yeast ribosomal protein gene DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8295–8312. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijayraghavan U., Parker R., Tamm J., Iimura Y., Rossi J., Abelson J., Guthrie C. Mutations in conserved intron sequences affect multiple steps in the yeast splicing pathway, particularly assembly of the spliceosome. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1683–1695. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04412.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieringa B., Hofer E., Weissmann C. A minimal intron length but no specific internal sequence is required for splicing the large rabbit beta-globin intron. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):915–925. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90426-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalkin H., Yanofsky C. Yeast gene TRP5: structure, function, regulation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1491–1500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Santen V. L., Spritz R. A. mRNA precursor splicing in vivo: sequence requirements determined by deletion analysis of an intervening sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2885–2889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]