Abstract
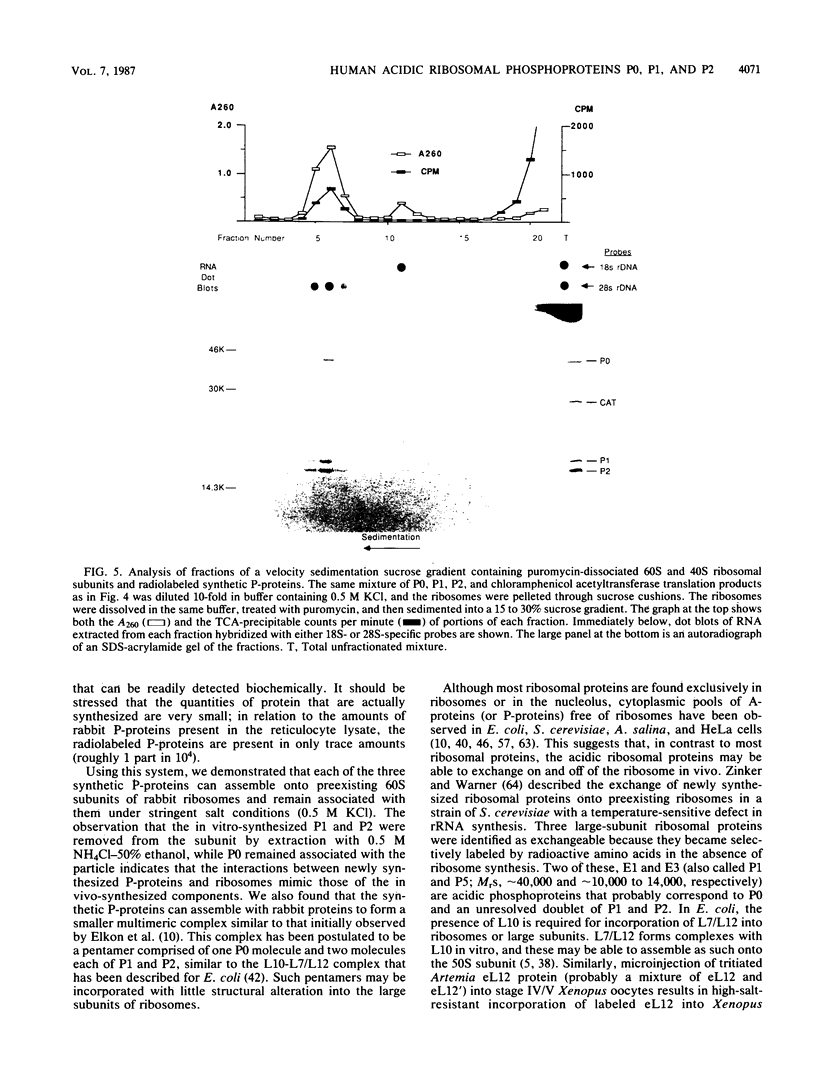
cDNA clones encoding three antigenically related human ribosomal phosphoproteins (P-proteins) P0, P1, and P2 were isolated and sequenced. P1 and P2 are analogous to Escherichia coli ribosomal protein L7/L12, and P0 is likely to be an analog of L10. The three proteins have a nearly identical carboxy-terminal 17-amino-acid sequence (KEESEESD(D/E)DMGFGLFD-COOH) that is the basis of their immunological cross-reactivity. The identities of the P1 and P2 cDNAs were confirmed by the strong similarities of their encoded amino acid sequences to published primary structures of the homologous rat, brine shrimp, and Saccharomyces cerevisiae proteins. The P0 cDNA was initially identified by translation of hybrid-selected mRNA and immunoprecipitation of the products. To demonstrate that the coding sequences are full length, the P0, P1, and P2 cDNAs were transcribed in vitro by bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase and the resulting mRNAs were translated in vitro. The synthetic P0, P1, and P2 proteins were serologically and electrophoretically identical to P-proteins extracted from HeLa cells. These synthetic P-proteins were incorporated into 60S but not 40S ribosomes and also assembled into a complex similar to that described for E. coli L7/L12 and L10.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amons R., Pluijms W., Möller W. The primary structure of ribosomal protein eL12/eL12-P from Artemia salina 80 S ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1979 Aug 1;104(1):85–89. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)81089-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonfa E., Elkon K. B. Clinical and serologic associations of the antiribosomal P protein antibody. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Aug;29(8):981–985. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonfa E., Golombek S. J., Kaufman L. D., Skelly S., Weissbach H., Brot N., Elkon K. B. Association between lupus psychosis and anti-ribosomal P protein antibodies. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 30;317(5):265–271. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707303170503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brot N., Weissbach H. Chemistry and biology of E. coli ribosomal protein L12. Mol Cell Biochem. 1981 Apr 13;36(1):47–63. doi: 10.1007/BF02354831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. M., McClure B. A., Houchins J. P. A rapid single-stranded cloning strategy for producing a sequential series of overlapping clones for use in DNA sequencing: application to sequencing the corn mitochondrial 18 S rDNA. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P. L. Random subcloning of sonicated DNA: application to shotgun DNA sequence analysis. Anal Biochem. 1983 Feb 15;129(1):216–223. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90072-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkon K. B., Parnassa A. P., Foster C. L. Lupus autoantibodies target ribosomal P proteins. J Exp Med. 1985 Aug 1;162(2):459–471. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elkon K., Skelly S., Parnassa A., Moller W., Danho W., Weissbach H., Brot N. Identification and chemical synthesis of a ribosomal protein antigenic determinant in systemic lupus erythematosus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7419–7423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francoeur A. M., Peebles C. L., Heckman K. J., Lee J. C., Tan E. M. Identification of ribosomal protein autoantigens. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2378–2384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J., Towbin H., Rosenthal M. Antibodies directed against ribosomal protein determinants in the sera of patients with connective tissue diseases. J Rheumatol. 1982 Mar-Apr;9(2):247–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gudkov A. T., Venyaminov SYu, Amons R., Möller W., Itoh T. A physical study of acidic ribosomal proteins from Artemia salina, Bacillus subtilis and Micrococcus lysodeikticus. FEBS Lett. 1981 Dec 28;136(2):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80625-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamel E., Koka M., Nakamoto T. Requirement of an Escherichia coli 50 S ribosomal protein component for effective interaction of the ribosome with T and G factors and with guanosine triphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 10;247(3):805–814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R., Weintraub H. Translation of mRNA injected into Xenopus oocytes is specifically inhibited by antisense RNA. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):1094–1099. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.1094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway G. M., Traugh J. A. Casein kinases--multipotential protein kinases. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1982;21:101–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horak I., Schiffmann D. Acidic phosphoproteins of the 60-S ribosomal subunits from HeLa cells. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Oct 3;79(2):375–380. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11818.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard G. A., Smith R. L., Gordon J. Chicken liver ribosomes: characterization of cross-reaction and inhibition of some functions by antibodies prepared against Escherichia coli ribosomal proteins L7 and L12. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 25;106(3):623–637. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90255-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issinger O. G. Phosphorylation of acidic ribosomal proteins from rabbit reticulocytes by a ribosome-associated casein kinase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jul 15;477(2):185–189. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(77)90234-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh T. Primary structure of an acidic ribosomal protein YPA1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Isolation and characterization of peptides and the complete amino acid sequence. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 30;671(1):16–24. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(81)90088-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalthoff H., Richter D. In vivo studies on the incorporation of microinjected acidic proteins of the large ribosomal subunit from Escherichia coli and artermia salina into oocyte ribosomes from Xenopus laevis. Biochemistry. 1979 Sep 18;18(19):4144–4147. doi: 10.1021/bi00586a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kudlicki W., Szyszka R., Paleń E., Gasior E. Evidence for a highly specific protein kinase phosphorylating two strongly acidic proteins of yeast 60 S ribosomal subunit. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec 15;633(3):376–385. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(80)90196-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leader D. P., Coia A. A. The phosphorylation of an acidic protein of the large ribosomal subunit of Krebs II ascites cells. Biochem J. 1977 Jan 15;162(1):199–200. doi: 10.1042/bj1620199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leijonmarck M., Liljas A. Structure of the C-terminal domain of the ribosomal protein L7/L12 from Escherichia coli at 1.7 A. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jun 5;195(3):555–579. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90183-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A., Wittmann-Liebold B., McNally J., Wool I. G. The primary structure of the acidic phosphoprotein P2 from rat liver 60 S ribosomal subunits. Comparison with ribosomal 'A' proteins from other species. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):9189–9197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maassen J. A., Schop E. N., Brands J. H., van Hemert F. J., Lenstra J. A., Möller W. Molecular cloning and analysis of cDNA sequences for two ribosomal proteins from Artemia. The coordinate expression of genes for ribosomal proteins and elongation factor 1 during embryogenesis of Artemia. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Jun 18;149(3):609–616. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08968.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacConnell W. P., Kaplan N. O. The activity of the acidic phosphoproteins from the 80 S rat liver ribosome. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5359–5366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacConnell W. P., Kaplan N. O. The role of ethanol extractable proteins from the 80S rat liver ribosome. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 15;92(1):46–52. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91517-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meggio F., Brunati A. M., Donella-Deana A., Pinna L. A. Detection of type-2 casein kinase and its endogenous substrates in the components of the microsomal fraction of rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jan 16;138(2):379–385. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb07926.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimori T., Hinterberger M., Pettersson I., Steitz J. A. Autoantibodies to the U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein in a patient with scleroderma-polymyositis overlap syndrome. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):560–565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. J., Weissbach H., Brot N. The identification and characterization of proteins similar to L7, L12 in ribosome-free extracts of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 8;65(1):293–302. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller W., Slobin L. I., Amons R., Richter D. Isolation and characterization of two acidic proteins of 60s ribosomes from Artemia salina cysts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4744–4748. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettersson I., Hardy S. J., Liljas A. The ribosomal protein L8 is a complex L7/L12 and L10. FEBS Lett. 1976 Apr 15;64(1):135–138. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80267-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Automation of the computer handling of gel reading data produced by the shotgun method of DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Aug 11;10(15):4731–4751. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.15.4731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Madrid F., Reyes R., Conde P., Ballesta J. P. Acidic ribosomal proteins from eukaryotic cells. Effect on ribosomal functions. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 1;98(2):409–416. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Madrid F., Vidales F. J., Ballesta J. P. Effect of phosphorylation on the affinity of acidic proteins from Saccharomyces cerevisiae for the ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Mar;114(3):609–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05187.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Madrid F., Vidales F. J., Ballesta J. P. Functional role of acidic ribosomal proteins. Interchangeability of proteins from bacterial and eukaryotic cells. Biochemistry. 1981 May 26;20(11):3263–3266. doi: 10.1021/bi00514a043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Ramjoué H. P., Kuster H., Liverani D., Gordon J. Monoclonal antibodies against eucaryotic ribosomes. Use to characterize a ribosomal protein not previously identified and antigenically related to the acidic phosphoproteins P1/P2. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12709–12715. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurugi K., Collatz E., Todokoro K., Ulbrich N., Lightfoot H. N., Wool I. G. Isolation of eukaryotic ribosomal proteins. Purification and characterization of the 60 S ribosomal subunit proteins La, Lb, Lf, P1, P2, L13', L14, L18', L20, and L38. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 10;253(3):946–955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurugi K., Ogata K. Evidence for the exchangeability of acidic ribosomal proteins on cytoplasmic ribosomes in regenerating rat liver. J Biochem. 1985 Dec;98(6):1427–1431. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiumi T., Kikuchi M., Ogata K. Cross-linking study on protein neighborhoods at the subunit interface of rat liver ribosomes with 2-iminothiolane. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9663–9667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiumi T., Kikuchi M., Terao K., Iwasaki K., Ogata K. Cross-linking of elongation factor 2 to rat-liver ribosomal proteins by 2-iminothiolane. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Apr 1;156(1):37–48. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09545.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiumi T., Kikuchi M., Terao K., Ogata K. Cross-linking study on protein topography of rat liver 60 S ribosomal subunits with 2-iminothiolane. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5675–5682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchiumi T., Wahba A. J., Traut R. R. Topography and stoichiometry of acidic proteins in large ribosomal subunits from Artemia salina as determined by crosslinking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5580–5584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidales F. J., Sanchez-Madrid F., Ballesta J. P. The acidic proteins of eukaryotic ribosomes. A comparative study. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Nov 27;656(1):28–35. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90022-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods D. E., Markham A. F., Ricker A. T., Goldberger G., Colten H. R. Isolation of cDNA clones for the human complement protein factor B, a class III major histocompatibility complex gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(18):5661–5665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.18.5661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinker S. P5/P5' the acidic ribosomal phosphoproteins from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980;606(1):76–82. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90099-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinker S., Warner J. R. The ribosomal proteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Phosphorylated and exchangeable proteins. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 25;251(6):1799–1807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Agthoven A., Kriek J., Amons R., Möller W. Isolation and characterization of the acidic phosphoproteins of 60-S ribosomes from Artemia salina and rat liver. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Nov 15;91(2):553–565. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12709.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]