Abstract
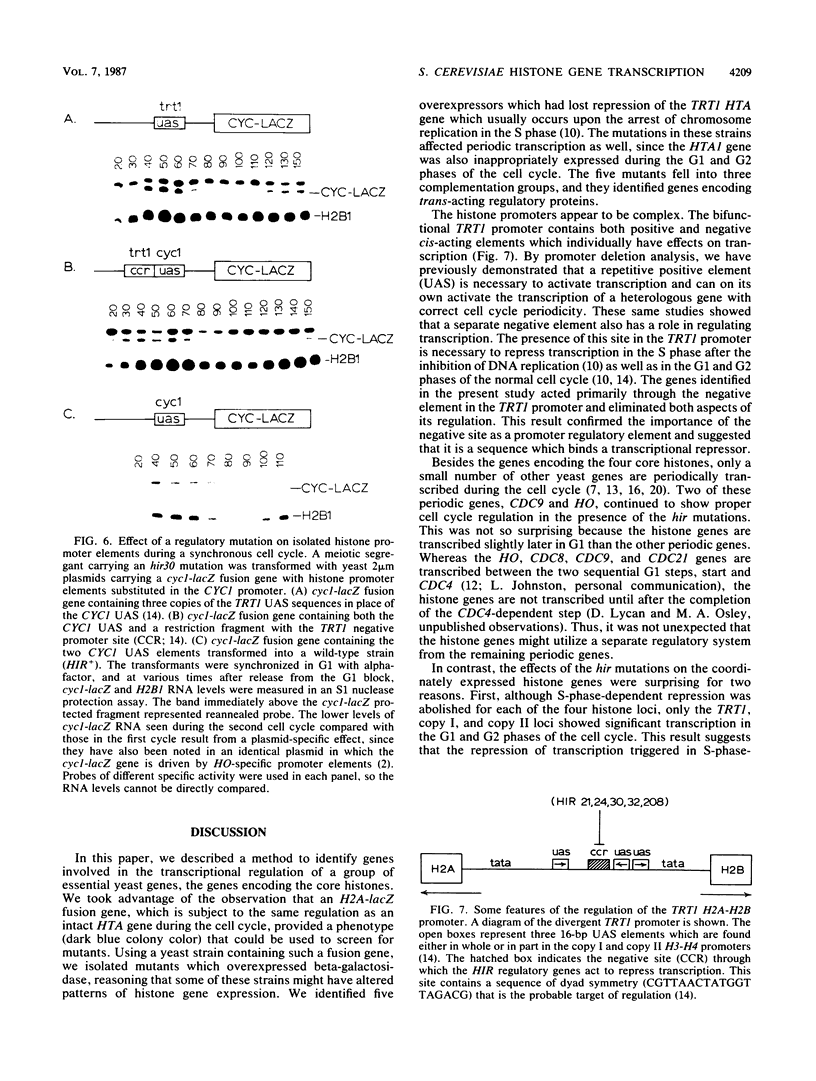
Using a Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain containing an integrated copy of an H2A-lacZ fusion gene, we screened for mutants which overexpressed beta-galactosidase as a way to identify genes which regulate transcription of the histone genes. Five recessive mutants with this phenotype were shown to contain altered regulatory genes because they had lost repression of HTA1 transcription which occurs upon inhibition of chromosome replication (D. E. Lycan, M. A. Osley, and L. Hereford, Mol. Cell. Biol. 7:614-621, 1987). Periodic transcription was affected in the mutants as well, since the HTA1 gene was transcribed during the G1 and G2 phases of the cell cycle, periods in the cell cycle when this gene is normally not expressed. A similar loss of cell cycle-dependent transcription was noted for two of the three remaining histone loci, while the HO and CDC9 genes continued to be expressed periodically. Using isolated promoter elements inserted into a heterologous cycl-lacZ fusion gene, we demonstrated that the mutations fell in genes which acted through a negative site in the TRT1 H2A-H2B promoter.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Artishevsky A., Delegeane A. M., Lee A. S. Use of a cell cycle mutant to delineate the critical period for the control of histone mRNA levels in the mammalian cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2364–2369. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breeden L., Nasmyth K. Cell cycle control of the yeast HO gene: cis- and trans-acting regulators. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):389–397. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90190-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detke S., Lichtler A., Phillips I., Stein J., Stein G. Reassessment of histone gene expression during cell cycle in human cells by using homologous H4 histone cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4995–4999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Macromolecule synthesis in temperature-sensitive mutants of yeast. J Bacteriol. 1967 May;93(5):1662–1670. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.5.1662-1670.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Sive H. L., Roeder R. G. Regulation of human histone gene expression: kinetics of accumulation and changes in the rate of synthesis and in the half-lives of individual histone mRNAs during the HeLa cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):539–550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L. M., Osley M. A., Ludwig T. R., 2nd, McLaughlin C. S. Cell-cycle regulation of yeast histone mRNA. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):367–375. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90326-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L., Bromley S., Osley M. A. Periodic transcription of yeast histone genes. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycan D. E., Osley M. A., Hereford L. M. Role of transcriptional and posttranscriptional regulation in expression of histone genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):614–621. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meeks-Wagner D., Hartwell L. H. Normal stoichiometry of histone dimer sets is necessary for high fidelity of mitotic chromosome transmission. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90483-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. A repetitive DNA sequence that confers cell-cycle START (CDC28)-dependent transcription of the HO gene in yeast. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):225–235. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80118-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. Molecular analysis of a cell lineage. Nature. 1983 Apr 21;302(5910):670–676. doi: 10.1038/302670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osley M. A., Gould J., Kim S., Kane M. Y., Hereford L. Identification of sequences in a yeast histone promoter involved in periodic transcription. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90285-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osley M. A., Hereford L. M. Yeast histone genes show dosage compensation. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):377–384. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90327-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson T. A., Prakash L., Prakash S., Osley M. A., Reed S. I. Regulation of CDC9, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene that encodes DNA ligase. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):226–235. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumb M., Stein J., Stein G. Coordinate regulation of multiple histone mRNAs during the cell cycle in HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2391–2410. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. M., Andrésson O. S. DNA sequences of yeast H3 and H4 histone genes from two non-allelic gene sets encode identical H3 and H4 proteins. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 25;169(3):663–690. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storms R. K., Ord R. W., Greenwood M. T., Mirdamadi B., Chu F. K., Belfort M. Cell cycle-dependent expression of thymidylate synthase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2858–2864. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]