Abstract
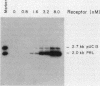
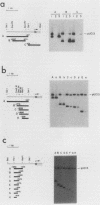
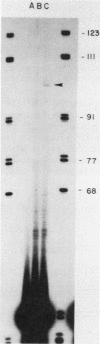
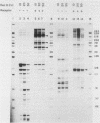
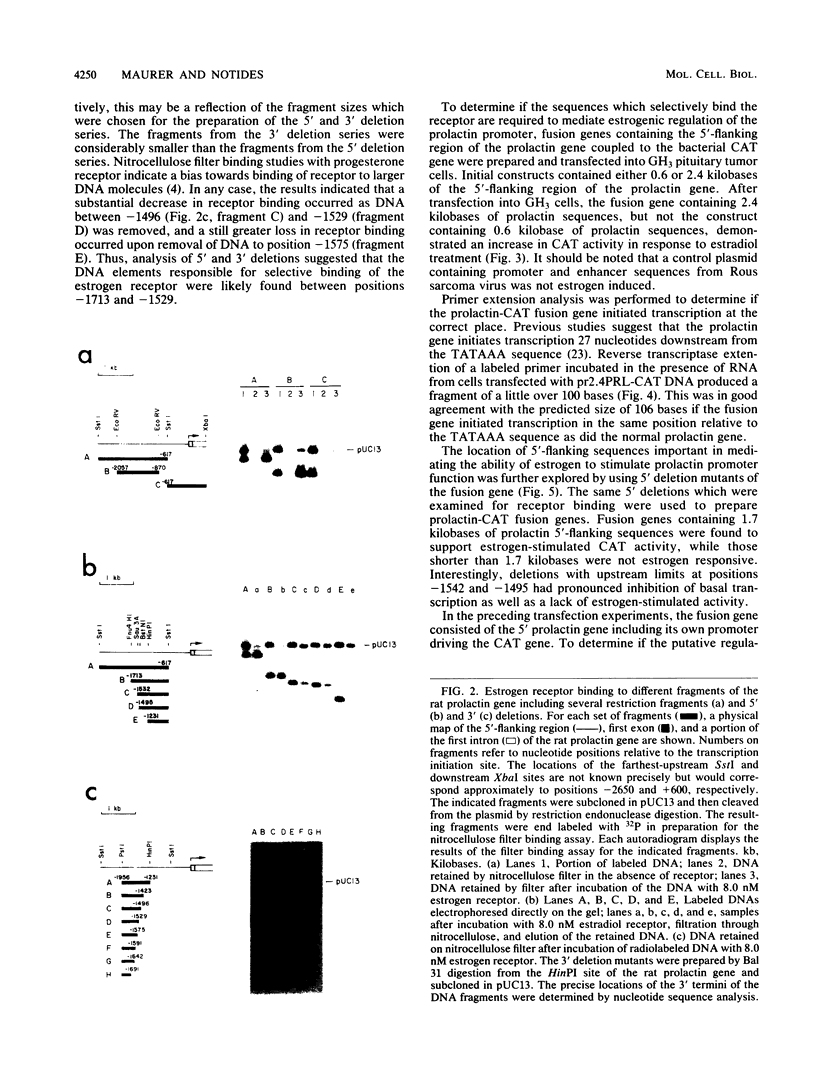
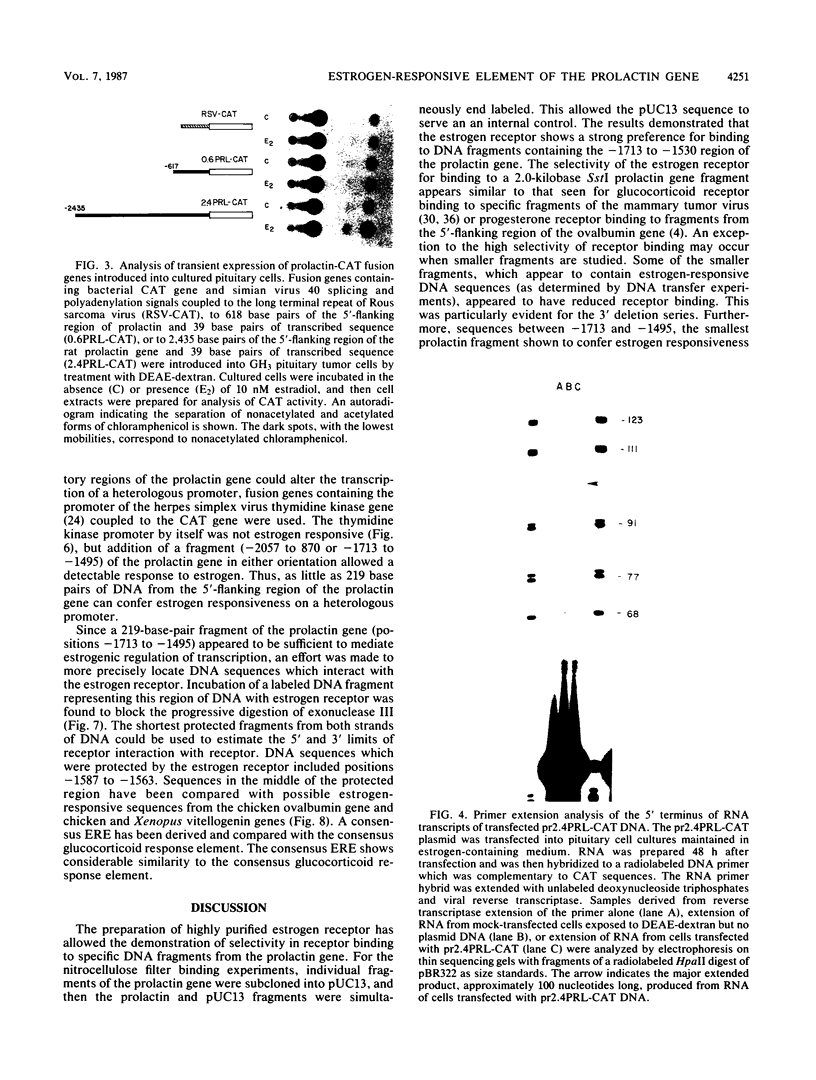
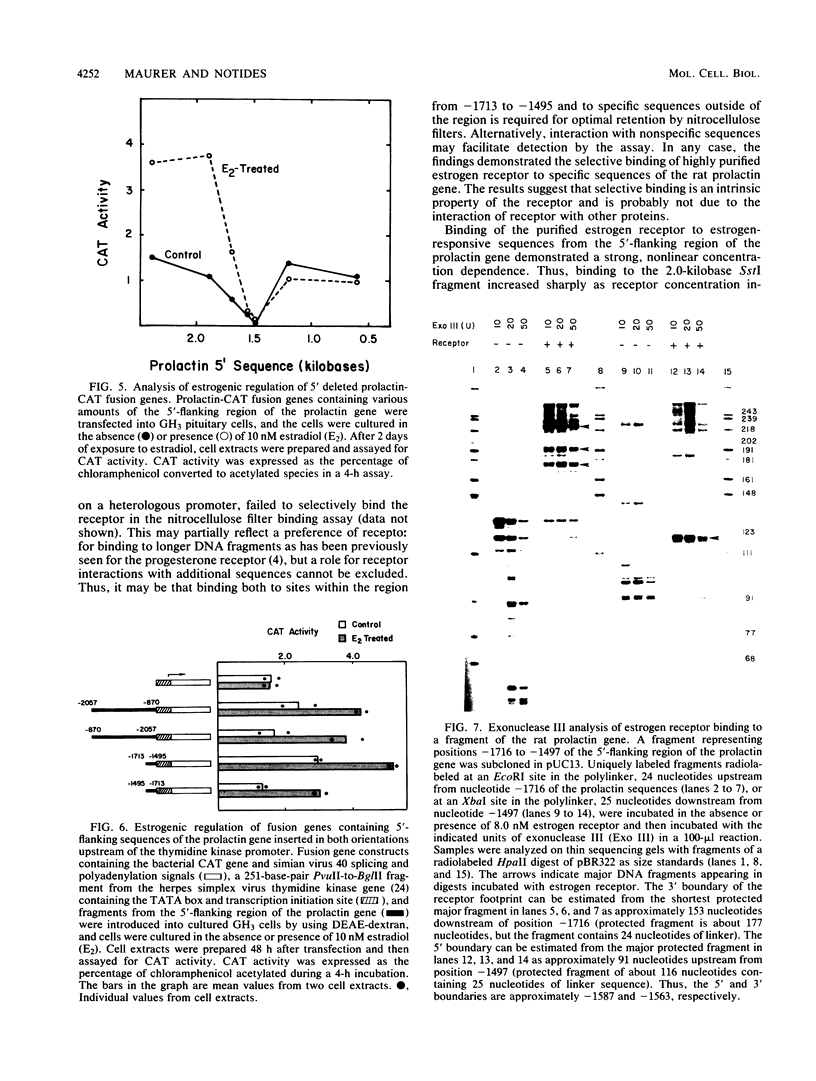
The DNA sequences which interact with the estrogen receptor and which mediate the estrogenic regulation of prolactin gene transcription have been investigated by the use of receptor-DNA-binding experiments and gene transfer studies. Nitrocellulose filter binding assays using highly purified estrogen receptor and cloned fragments of the 5'-flanking region of the rat prolactin gene demonstrate that the receptor selectively binds to DNA sequences located between nucleotides -1713 and -1532 with respect to the transcription initiation site. The binding of the estrogen receptor to this region of the prolactin gene was strongly dependent on receptor concentration, suggesting that receptor dimers may be important in DNA binding. These data demonstrate that the selective binding of purified estrogen receptor to specific sequences of the rat prolactin gene is an intrinsic property of the receptor and is not due to the interaction of receptor with other proteins. The role of specific prolactin gene sequences in mediating the estrogenic regulation of prolactin gene transcription was confirmed by the use of prolactin-chloramphenicol acetyltransferase fusion genes. These studies demonstrated that sequences upstream of position -1532 are required for estrogen responsiveness. Furthermore, the region of the prolactin gene at -1713 to -1495 was able to confer estrogen responsiveness on the thymidine kinase promoter. Exonuclease III protection experiments further localized the receptor-binding sequences to positions -1587 to -1563. Comparison of the nucleotide sequence of the region of the prolactin gene which binds the estrogen receptor with the sequence of other estrogen-responsive genes suggested the presence of the conserved sequence [sequence in text], which shows similarity to sequences thought to mediate glucocorticoid receptor effects on transcription.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Becker P. B., Gloss B., Schmid W., Strähle U., Schütz G. In vivo protein-DNA interactions in a glucocorticoid response element require the presence of the hormone. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):686–688. doi: 10.1038/324686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cato A. C., Geisse S., Wenz M., Westphal H. M., Beato M. The nucleotide sequences recognized by the glucocorticoid receptor in the rabbit uteroglobin gene region are located far upstream from the initiation of transcription. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2771–2778. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02208.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler V. L., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. DNA sequences bound specifically by glucocorticoid receptor in vitro render a heterologous promoter hormone responsive in vivo. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):489–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compton J. G., Schrader W. T., O'Malley B. W. DNA sequence preference of the progesterone receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):16–20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean D. C., Gope R., Knoll B. J., Riser M. E., O'Malley B. W. A similar 5'-flanking region is required for estrogen and progesterone induction of ovalbumin gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):9967–9970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V., Hollenberg S. M., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Functional domains of the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):645–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90339-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene G. L., Nolan C., Engler J. P., Jensen E. V. Monoclonal antibodies to human estrogen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5115–5119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haug E., Gautvik K. M. Effects of sex steroids on prolactin secreting rat pituitary cells in culture. Endocrinology. 1976 Dec;99(6):1482–1489. doi: 10.1210/endo-99-6-1482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwitz K. B., Costlow M. E., McGuire W. L. MCF-7; a human breast cancer cell line with estrogen, androgen, progesterone, and glucocorticoid receptors. Steroids. 1975 Dec;26(6):785–795. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(75)90110-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes N., van Ooyen A. J., Kennedy N., Herrlich P., Ponta H., Groner B. Subfragments of the large terminal repeat cause glucocorticoid-responsive expression of mouse mammary tumor virus and of an adjacent gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3637–3641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeltsch J. M., Roberts M., Schatz C., Garnier J. M., Brown A. M., Chambon P. Structure of the human oestrogen-responsive gene pS2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1401–1414. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jost J. P., Seldran M., Geiser M. Preferential binding of estrogen-receptor complex to a region containing the estrogen-dependent hypomethylation site preceding the chicken vitellogenin II gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):429–433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Haslinger A., Holtgreve H., Richards R. I., Krauter P., Westphal H. M., Beato M. Characterization of DNA sequences through which cadmium and glucocorticoid hormones induce human metallothionein-IIA gene. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):513–519. doi: 10.1038/308513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein-Hitpass L., Schorpp M., Wagner U., Ryffel G. U. An estrogen-responsive element derived from the 5' flanking region of the Xenopus vitellogenin A2 gene functions in transfected human cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1053–1061. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90705-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krust A., Green S., Argos P., Kumar V., Walter P., Bornert J. M., Chambon P. The chicken oestrogen receptor sequence: homology with v-erbA and the human oestrogen and glucocorticoid receptors. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):891–897. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04300.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Green S., Staub A., Chambon P. Localisation of the oestradiol-binding and putative DNA-binding domains of the human oestrogen receptor. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2231–2236. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04489.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E. C., Riser M. E., O'Malley B. W. Regulated expression of the chicken ovalbumin gene in a human estrogen-responsive cell line. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12693–12701. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer R. A., Erwin C. R., Donelson J. E. Analysis of 5' flanking sequences and intron-exon boundaries of the rat prolactin gene. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10524–10528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer R. A. Estradiol regulates the transcription of the prolactin gene. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2133–2136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer R. A. Selective binding of the estradiol receptor to a region at least one kilobase upstream from the rat prolactin gene. DNA. 1985 Feb;4(1):1–9. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer R. A. Transcriptional regulation of the prolactin gene by ergocryptine and cyclic AMP. Nature. 1981 Nov 5;294(5836):94–97. doi: 10.1038/294094a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L. The nucleotide sequence and transcript map of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 20;8(24):5949–5964. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.24.5949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrissey J. H. Silver stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels: a modified procedure with enhanced uniform sensitivity. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 1;117(2):307–310. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90783-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson C., Crenshaw E. B., 3rd, Franco R., Lira S. A., Albert V. R., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Discrete cis-active genomic sequences dictate the pituitary cell type-specific expression of rat prolactin and growth hormone genes. Nature. 1986 Aug 7;322(6079):557–562. doi: 10.1038/322557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols B. P., Donelson J. E. 178-Nucleotide sequence surrounding the cos site of bacteriophage lambda DNA. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):429–434. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.429-434.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notides A. C., Lerner N., Hamilton D. E. Positive cooperativity of the estrogen receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4926–4930. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payvar F., Wrange O., Carlstedt-Duke J., Okret S., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Purified glucocorticoid receptors bind selectively in vitro to a cloned DNA fragment whose transcription is regulated by glucocorticoids in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6628–6632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirrotta V., Chadwick P., Ptashne M. Active form of two coliphage repressors. Nature. 1970 Jul 4;227(5253):41–44. doi: 10.1038/227041a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renkawitz R., Schütz G., von der Ahe D., Beato M. Sequences in the promoter region of the chicken lysozyme gene required for steroid regulation and receptor binding. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):503–510. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90380-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Suzuki H., Bourgeois S. Lac repressor-operator interaction. I. Equilibrium studies. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 28;48(1):67–83. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan R., Shupnik M. A., Gorski J. Effect of estrogen on preprolactin messenger ribonucleic acid sequences. Biochemistry. 1979 May 15;18(10):2044–2048. doi: 10.1021/bi00577a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels H. H., Stanley F., Casanova J. Depletion of L-3,5,3'-triiodothyronine and L-thyroxine in euthyroid calf serum for use in cell culture studies of the action of thyroid hormone. Endocrinology. 1979 Jul;105(1):80–85. doi: 10.1210/endo-105-1-80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Geisse S., Westphal H. M., Beato M. The glucocorticoid receptor binds to defined nucleotide sequences near the promoter of mouse mammary tumour virus. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):749–752. doi: 10.1038/304749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seo H., Refetoff S., Martino E., Vassart G., Brocas H. The differential stimulatory effect of thyroid hormone on growth hormone synthesis and estrogen on prolactin synthesis due to accumulation of specific messenger ribonucleic acids. Endocrinology. 1979 Apr;104(4):1083–1090. doi: 10.1210/endo-104-4-1083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull J. D., Gorski J. Estrogen stimulates prolactin gene transcription by a mechanism independent of pituitary protein synthesis. Endocrinology. 1984 May;114(5):1550–1557. doi: 10.1210/endo-114-5-1550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skafar D. F., Notides A. C. Modulation of the estrogen receptor's affinity for DNA by estradiol. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12208–12213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone R. T., Maurer R. A., Gorski J. Effect of estradiol-17 beta on preprolactin messenger ribonucleic acid activity in the rat pituitary gland. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 1;16(22):4915–4921. doi: 10.1021/bi00641a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashjian A. H., Jr, Yasumura Y., Levine L., Sato G. H., Parker M. L. Establishment of clonal strains of rat pituitary tumor cells that secrete growth hormone. Endocrinology. 1968 Feb;82(2):342–352. doi: 10.1210/endo-82-2-342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. An exonuclease protection assay reveals heat-shock element and TATA box DNA-binding proteins in crude nuclear extracts. Nature. 1985 Sep 5;317(6032):84–87. doi: 10.1038/317084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von der Ahe D., Janich S., Scheidereit C., Renkawitz R., Schütz G., Beato M. Glucocorticoid and progesterone receptors bind to the same sites in two hormonally regulated promoters. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):706–709. doi: 10.1038/313706a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]