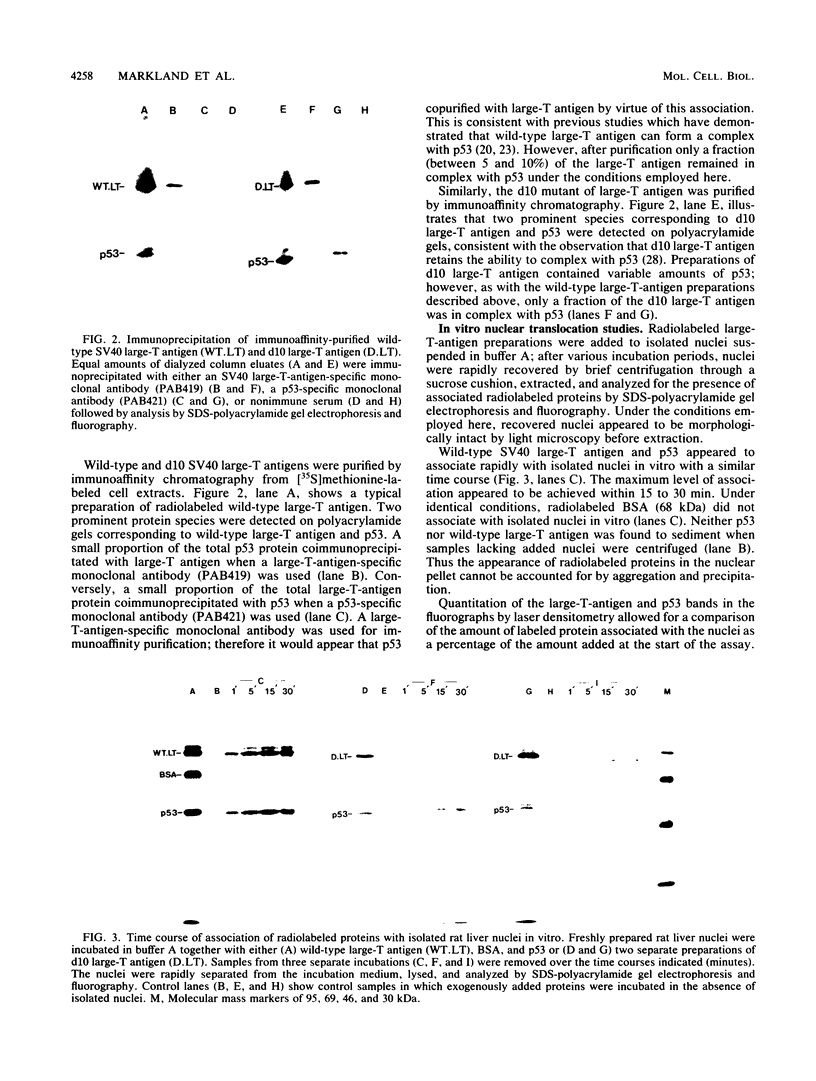
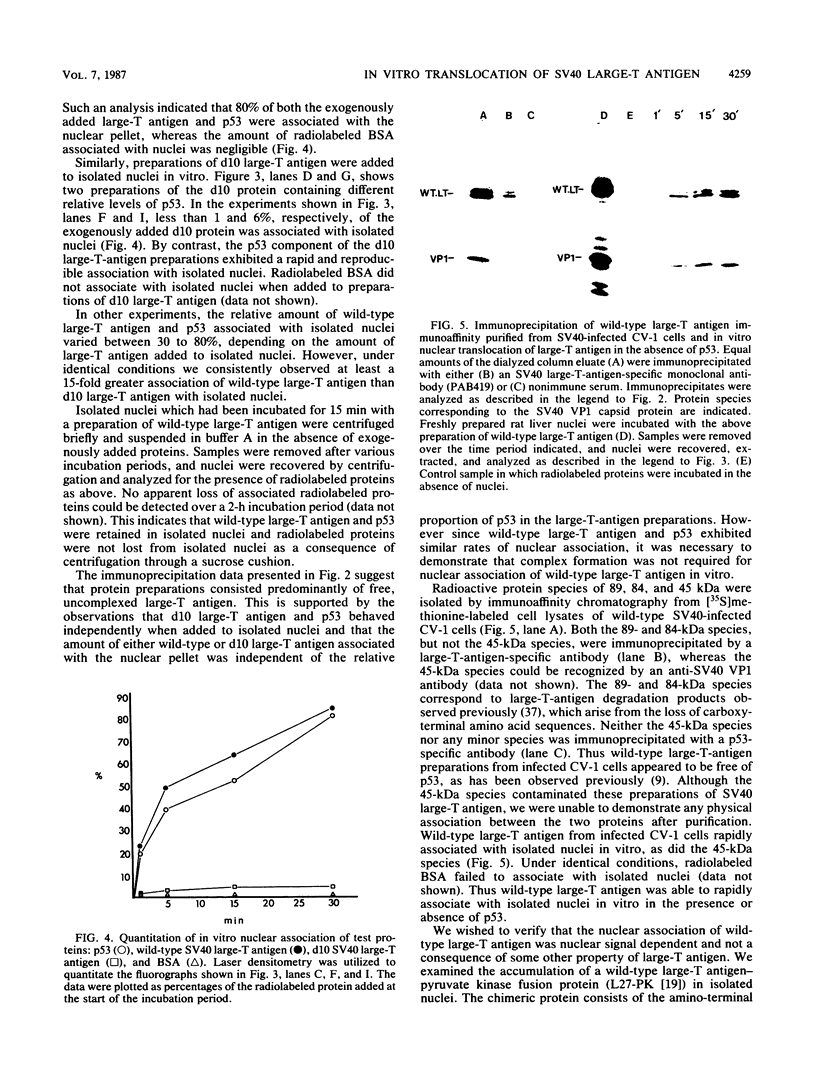
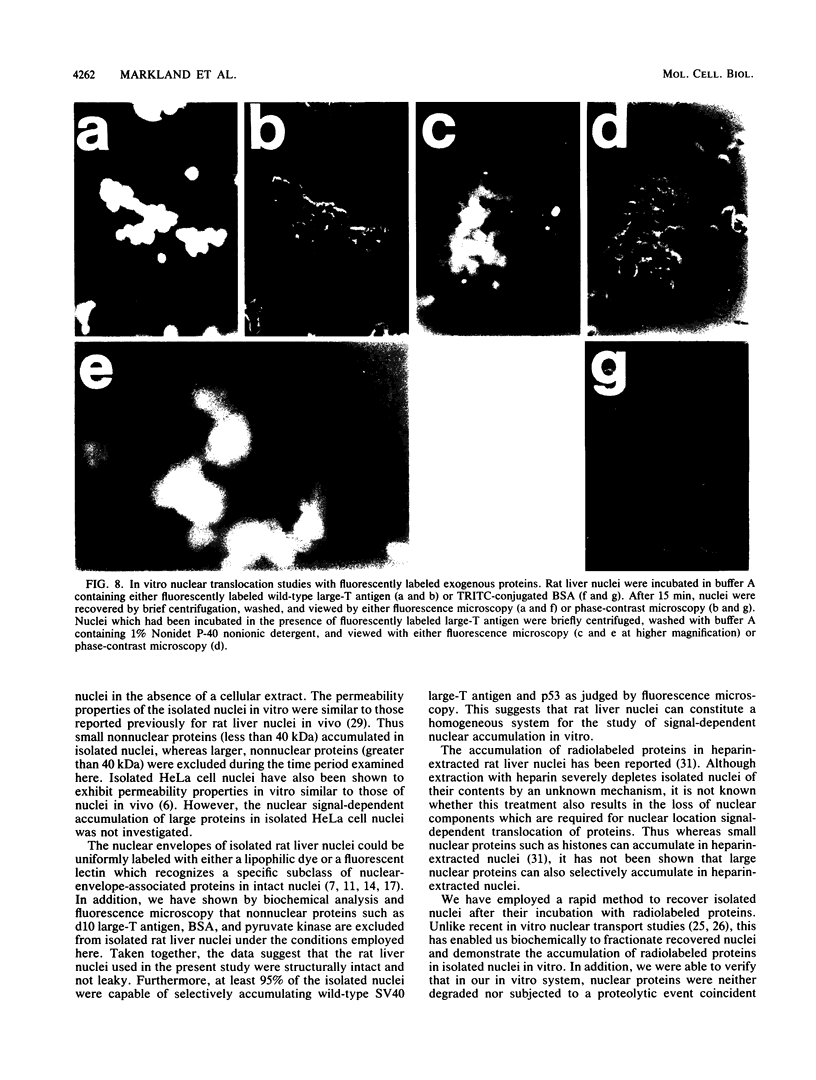
Abstract
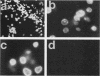
An in vitro nuclear translocation system is described in which isolated rat liver nuclei were incubated in a defined buffered medium containing radiolabeled or fluorescently labeled exogenous proteins. The nuclei were rapidly recovered, extracted, and analyzed for the presence of associated radiolabeled or fluorescently labeled proteins. The isolated nuclei exhibited the same specificity for protein uptake as seen previously in vivo, accumulating simian virus 40 wild-type large-T antigen and p53 while excluding a cytoplasmic variant of large-T antigen (d10) and bovine serum albumin. The rapid nuclear accumulation of wild-type large-T antigen was shown to be selective and dependent upon the recognition of a wild-type nuclear location signal, ATP and temperature dependent, and unidirectional. Taken together, the data suggest that in our in vitro system the nuclear translocation of wild-type large-T antigen exhibits some of the characteristics of an active transport process.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berrios M., Blobel G., Fisher P. A. Characterization of an ATPase/dATPase activity associated with the Drosophila nuclear matrix-pore complex-lamina fraction. Identification of the putative enzyme polypeptide by direct ultraviolet photoaffinity labeling. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4548–4555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berrios M., Fisher P. A. A myosin heavy-chain-like polypeptide is associated with the nuclear envelope in higher eukaryotic cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):711–724. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Potter V. R. Nuclei from rat liver: isolation method that combines purity with high yield. Science. 1966 Dec 30;154(3757):1662–1665. doi: 10.1126/science.154.3757.1662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colledge W. H., Richardson W. D., Edge M. D., Smith A. E. Extensive mutagenesis of the nuclear location signal of simian virus 40 large-T antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):4136–4139. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.4136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox G. S. Discrimination in the uptake of soluble proteins by isolated nuclei. J Cell Sci. 1982 Dec;58:363–384. doi: 10.1242/jcs.58.1.363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. I., Blobel G. Identification and characterization of a nuclear pore complex protein. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):699–709. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90784-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Nathans D. Purification of simian virus 40 large T antigen by immunoaffinity chromatography. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):1001–1004. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.1001-1004.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldherr C. M., Kallenbach E., Schultz N. Movement of a karyophilic protein through the nuclear pores of oocytes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2216–2222. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay D. R., Newmeyer D. D., Price T. M., Forbes D. J. Inhibition of in vitro nuclear transport by a lectin that binds to nuclear pores. J Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;104(2):189–200. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.2.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher P. A., Berrios M., Blobel G. Isolation and characterization of a proteinaceous subnuclear fraction composed of nuclear matrix, peripheral lamina, and nuclear pore complexes from embryos of Drosophila melanogaster. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):674–686. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerace L., Ottaviano Y., Kondor-Koch C. Identification of a major polypeptide of the nuclear pore complex. J Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;95(3):826–837. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.3.826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass W. F., 2nd, Briggs R. C., Hnilica L. S. Use of lectins for detection of electrophoretically separated glycoproteins transferred onto nitrocellulose sheets. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jul 15;115(1):219–224. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90549-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfarb D. S., Gariépy J., Schoolnik G., Kornberg R. D. Synthetic peptides as nuclear localization signals. Nature. 1986 Aug 14;322(6080):641–644. doi: 10.1038/322641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Crawford L. V., Pim D. C., Williamson N. M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for simian virus 40 tumor antigens. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):861–869. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.861-869.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt G. D., Hart G. W. The subcellular distribution of terminal N-acetylglucosamine moieties. Localization of a novel protein-saccharide linkage, O-linked GlcNAc. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):8049–8057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Richardson W. D., Markham A. F., Smith A. E. Sequence requirements for nuclear location of simian virus 40 large-T antigen. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):33–38. doi: 10.1038/311033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. A short amino acid sequence able to specify nuclear location. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):499–509. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90457-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Crawford L. V. T antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):261–263. doi: 10.1038/278261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E., Butel J. S. Construction and characterization of an SV40 mutant defective in nuclear transport of T antigen. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):801–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90415-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanford R. E., Kanda P., Kennedy R. C. Induction of nuclear transport with a synthetic peptide homologous to the SV40 T antigen transport signal. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):575–582. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90883-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Levine A. J. Characterization of a 54K dalton cellular SV40 tumor antigen present in SV40-transformed cells and uninfected embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg N., Gilbert W. Primary structure of chicken muscle pyruvate kinase mRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3661–3665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmeyer D. D., Finlay D. R., Forbes D. J. In vitro transport of a fluorescent nuclear protein and exclusion of non-nuclear proteins. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2091–2102. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmeyer D. D., Lucocq J. M., Bürglin T. R., De Robertis E. M. Assembly in vitro of nuclei active in nuclear protein transport: ATP is required for nucleoplasmin accumulation. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):501–510. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04239.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paucha E., Kalderon D., Harvey R. W., Smith A. E. Simian virus 40 origin DNA-binding domain on large T antigen. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):50–64. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.50-64.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paucha E., Kalderon D., Richardson W. D., Harvey R. W., Smith A. E. The abnormal location of cytoplasmic SV40 large T is not caused by failure to bind to DNA or to p53. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3235–3240. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04071.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters R. Fluorescence microphotolysis to measure nucleocytoplasmic transport and intracellular mobility. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Dec 22;864(3-4):305–359. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(86)90003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson W. D., Roberts B. L., Smith A. E. Nuclear location signals in polyoma virus large-T. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):77–85. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90486-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel N., Fasold H. Nuclear-envelope vesicles as a model system to study nucleocytoplasmic transport. Specific uptake of nuclear proteins. Biochem J. 1987 Jan 1;241(1):213–219. doi: 10.1042/bj2410213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. The effect of protein context on nuclear location signal function. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):465–475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90500-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schickedanz J., Scheidtmann K. H., Walter G. Kinetics of nuclear transport and oligomerization of simian virus 40 large T antigen. Virology. 1986 Jan 15;148(1):47–57. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90402-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler M., Jiang L. W. Nuclear actin and myosin as control elements in nucleocytoplasmic transport. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):859–862. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. E., Kalderon D., Roberts B. L., Colledge W. H., Edge M., Gillett P., Markham A., Paucha E., Richardson W. D. The nuclear location signal. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Oct 22;226(1242):43–58. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. E., Smith R., Paucha E. Extraction and fingerprint analysis of simian virus 40 large and small T-antigens. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):140–153. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.140-153.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R. S., Warner J. R. Cytoplasmic synthesis of nuclear proteins. Kinetics of accumulation of radioactive proteins in various cell fractions after brief pulses. J Cell Biol. 1971 Dec;51(3):643–652. doi: 10.1083/jcb.51.3.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wychowski C., Benichou D., Girard M. A domain of SV40 capsid polypeptide VP1 that specifies migration into the cell nucleus. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2569–2576. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04536.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]