Abstract
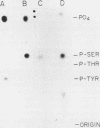
Viral transduction and chromosomal translocations of the c-abl gene result in the synthesis of abl proteins with structurally altered amino termini. These altered forms of the abl protein, but not the c-abl proteins, are detectably phosphorylated on tyrosine in vivo. In contrast, all forms of the abl protein are phosphorylated on serine following in vivo labeling with Pi. Treatment of NIH-3T3 cells with protein kinase C activators resulted in a four- to eightfold increase in the phosphorylation of murine c-abl due to modification of two serines on the c-abl protein. Purified protein kinase C phosphorylated all abl proteins at the same two sites. Both sites are precisely conserved in murine and human abl proteins. The sites on the abl proteins were found near the carboxy terminus. In contrast, for the epidermal growth factor receptor (T. Hunter, N. Ling, and J. A. Cooper, Nature [London] 311:480-483, 1984) and pp60src (K. L. Gould, J. R. Woodgett, J. A. Cooper, J. E. Buss, D. Shalloway, and T. Hunter, Cell 42:849-857, 1985), the sites of protein kinase C phosphorylation are amino-terminal to the kinase domain. The abl carboxy-terminal region is not necessary for the tyrosine kinase activity or transformation potential of the viral abl protein and may represent a regulatory domain. Using an in vitro immune complex kinase assay, we were not able to correlate reproducible changes in c-abl activity with phosphorylation by protein kinase C. However, the high degree of conservation of the phosphorylation sites for protein kinase C between human and mouse abl proteins suggests an important functional role.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abelson H. T., Rabstein L. S. Lymphosarcoma: virus-induced thymic-independent disease in mice. Cancer Res. 1970 Aug;30(8):2213–2222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D., Rosenberg N., Witte O. N. Transformation of immature lymphoid cells by Abelson murine leukemia virus. Immunol Rev. 1979;48:3–22. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartram C. R., de Klein A., Hagemeijer A., van Agthoven T., Geurts van Kessel A., Bootsma D., Grosveld G., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Davies T., Stone M. Translocation of c-ab1 oncogene correlates with the presence of a Philadelphia chromosome in chronic myelocytic leukaemia. Nature. 1983 Nov 17;306(5940):277–280. doi: 10.1038/306277a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Neriah Y., Bernards A., Paskind M., Daley G. Q., Baltimore D. Alternative 5' exons in c-abl mRNA. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):577–586. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90267-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop R., Martinez R., Nakamura K. D., Weber M. J. A tumor promoter stimulates phosphorylation on tyrosine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Sep 15;115(2):536–543. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80178-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollag G. E., Roth R. A., Beaudoin J., Mochly-Rosen D., Koshland D. E., Jr Protein kinase C directly phosphorylates the insulin receptor in vitro and reduces its protein-tyrosine kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5822–5824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Myristic acid, a rare fatty acid, is the lipid attached to the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus and its cellular homolog. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):7–12. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.7-12.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. S., McLaughlin J., Crist W. M., Champlin R., Witte O. N. Unique forms of the abl tyrosine kinase distinguish Ph1-positive CML from Ph1-positive ALL. Science. 1987 Jan 2;235(4784):85–88. doi: 10.1126/science.3541203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet C., Gill G. N., Meisenhelder J., Cooper J. A., Hunter T. C-kinase phosphorylates the epidermal growth factor receptor and reduces its epidermal growth factor-stimulated tyrosine protein kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2553–2558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Gallo R. C., Gallagher R. E. Continuous growth and differentiation of human myeloid leukaemic cells in suspension culture. Nature. 1977 Nov 24;270(5635):347–349. doi: 10.1038/270347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Diverse mitogenic agents induce the phosphorylation of two related 42,000-dalton proteins on tyrosine in quiescent chick cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):30–37. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J., Czech M. P. Tumor-promoting phorbol diesters cause the phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptors in normal human fibroblasts at threonine-654. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1974–1978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Konopka J. B., Witte O. N. Activation of the c-abl oncogene by viral transduction or chromosomal translocation generates altered c-abl proteins with similar in vitro kinase properties. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):204–213. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson B., Pritchard M. L., Feild J., Rieman D., Greig R. G., Poste G., Rosenberg M. Isolation and analysis of an Abelson murine leukemia virus-encoded tyrosine-specific kinase produced in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3652–3657. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari S., Marchiori F., Borin G., Pinna L. A. Distinct structural requirements of Ca2+/phospholipid-dependent protein kinase (protein kinase C) and cAMP-dependent protein kinase as evidenced by synthetic peptide substrates. FEBS Lett. 1985 May 6;184(1):72–77. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80656-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foulkes J. G., Chow M., Gorka C., Frackelton A. R., Jr, Baltimore D. Purification and characterization of a protein-tyrosine kinase encoded by the Abelson murine leukemia virus. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8070–8077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman B., Frackelton A. R., Jr, Ross A. H., Connors J. M., Fujiki H., Sugimura T., Rosner M. R. Tumor promoters block tyrosine-specific phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3034–3038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T., Martin G. S. Phorbol ester and diacylglycerol induce protein phosphorylation at tyrosine. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):487–490. doi: 10.1038/306487a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. P., Gilboa E., Witte O. N., Baltimore D. Structure of the Abelson murine leukemia virus genome and the homologous cellular gene: studies with cloned viral DNA. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90554-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. P., Witte O. N., Gilboa E., Rosenberg N., Baltimore D. Genome structure of Abelson murine leukemia virus variants: proviruses in fibroblasts and lymphoid cells. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):460–468. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.460-468.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould K. L., Woodgett J. R., Cooper J. A., Buss J. E., Shalloway D., Hunter T. Protein kinase C phosphorylates pp60src at a novel site. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):849–857. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90281-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heisterkamp N., Groffen J., Stephenson J. R. The human v-abl cellular homologue. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):57–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann F. M., Fresco L. D., Hoffman-Falk H., Shilo B. Z. Nucleotide sequences of the Drosophila src and abl homologs: conservation and variability in the src family oncogenes. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):393–401. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90172-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Ling N., Cooper J. A. Protein kinase C phosphorylation of the EGF receptor at a threonine residue close to the cytoplasmic face of the plasma membrane. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):480–483. doi: 10.1038/311480a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwashita S., Fox C. F. Epidermal growth factor and potent phorbol tumor promoters induce epidermal growth factor receptor phosphorylation in a similar but distinctively different manner in human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2559–2567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Sahyoun N. E., Saltiel A. R., Cuatrecasas P. Phorbol esters stimulate the phosphorylation of receptors for insulin and somatomedin C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6211–6213. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto A., Nishiyama K., Nakanishi H., Uratsuji Y., Nomura H., Takeyama Y., Nishizuka Y. Studies on the phosphorylation of myelin basic protein by protein kinase C and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12492–12499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloetzer W., Kurzrock R., Smith L., Talpaz M., Spiller M., Gutterman J., Arlinghaus R. The human cellular abl gene product in the chronic myelogenous leukemia cell line K562 has an associated tyrosine protein kinase activity. Virology. 1985 Jan 30;140(2):230–238. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90361-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka J. B., Davis R. L., Watanabe S. M., Ponticelli A. S., Schiff-Maker L., Rosenberg N., Witte O. N. Only site-directed antibodies reactive with the highly conserved src-homologous region of the v-abl protein neutralize kinase activity. J Virol. 1984 Jul;51(1):223–232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.1.223-232.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka J. B., Watanabe S. M., Singer J. W., Collins S. J., Witte O. N. Cell lines and clinical isolates derived from Ph1-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia patients express c-abl proteins with a common structural alteration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1810–1814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka J. B., Watanabe S. M., Witte O. N. An alteration of the human c-abl protein in K562 leukemia cells unmasks associated tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):1035–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90438-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konopka J. B., Witte O. N. Detection of c-abl tyrosine kinase activity in vitro permits direct comparison of normal and altered abl gene products. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3116–3123. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. A., Jensen F., Kennel S. J., Dixon F. J., Des Roches G., Francke U. Karyotypic, virologic, and immunologic analyses of two continuous lymphocyte lines established from New Zealand black mice: possible relationship of chromosomal mosaicism to autoimmunity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Oct;69(10):2965–2969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.10.2965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozzio C. B., Lozzio B. B. Human chronic myelogenous leukemia cell-line with positive Philadelphia chromosome. Blood. 1975 Mar;45(3):321–334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Slamon D. J., Tremblay J. M., Cline M. J., Verma I. M. Differential expression of cellular oncogenes during pre- and postnatal development of the mouse. Nature. 1982 Oct 14;299(5884):640–644. doi: 10.1038/299640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Studies and perspectives of protein kinase C. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):305–312. doi: 10.1126/science.3014651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picton C., Woodgett J., Hemmings B., Cohen P. Multisite phosphorylation of glycogen synthase from rabbit skeletal muscle. Phosphorylation of site 5 by glycogen synthase kinase-5 (casein kinase-II) is a prerequisite for phosphorylation of sites 3 by glycogen synthase kinase-3. FEBS Lett. 1982 Dec 13;150(1):191–196. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)81332-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponticelli A. S., Whitlock C. A., Rosenberg N., Witte O. N. In vivo tyrosine phosphorylations of the Abelson virus transforming protein are absent in its normal cellular homolog. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):953–960. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90458-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds F. H., Jr, Van de Ven W. J., Stephenson J. R. Abelson murine leukemia virus transformation-defective mutants with impaired P120-associated protein kinase activity. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):374–386. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.374-386.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg N. E., Clark D. R., Witte O. N. Abelson murine leukemia virus mutants deficient in kinase activity and lymphoid cell transformation. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):766–774. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.766-774.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg N., Baltimore D., Scher C. D. In vitro transformation of lymphoid cells by Abelson murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1932–1936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg N., Witte O. N. Abelson murine leukemia virus mutants with alterations in the virus-specific P120 molecule. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):340–348. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.340-348.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozengurt E. Early signals in the mitogenic response. Science. 1986 Oct 10;234(4773):161–166. doi: 10.1126/science.3018928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher C. D., Siegler R. Direct transformation of 3T3 cells by Abelson murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1975 Feb 27;253(5494):729–731. doi: 10.1038/253729a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Henderson L. E., Oroszlan S., Garber E. A., Hanafusa H. Amino terminal myristylation of the protein kinase p60src, a retroviral transforming protein. Science. 1985 Jan 25;227(4685):427–429. doi: 10.1126/science.3917576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A., Oroszlan S. Myristylation of gag-onc fusion proteins in mammalian transforming retroviruses. Virology. 1984 Mar;133(2):431–437. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90409-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Raschke W. C. Evidence that the Abelson virus protein functions in vivo as a protein kinase that phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1552–1556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1552. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Trowbridge I. S., Cooper J. A., Scolnick E. M. The transforming proteins of Rous sarcoma virus, Harvey sarcoma virus and Abelson virus contain tightly bound lipid. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):465–474. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shtivelman E., Lifshitz B., Gale R. P., Roe B. A., Canaani E. Alternative splicing of RNAs transcribed from the human abl gene and from the bcr-abl fused gene. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):277–284. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90450-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takayama S., White M. F., Lauris V., Kahn C. R. Phorbol esters modulate insulin receptor phosphorylation and insulin action in cultured hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7797–7801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R. S., Kemp B. E., Su H. D., Kuo J. F. Substrate specificity of phospholipid/Ca2+-dependent protein kinase as probed with synthetic peptide fragments of the bovine myelin basic protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11503–11507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. Y., Baltimore D. Cellular RNA homologous to the Abelson murine leukemia virus transforming gene: expression and relationship to the viral sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):773–779. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. Y., Ledley F., Goff S., Lee R., Groner Y., Baltimore D. The mouse c-abl locus: molecular cloning and characterization. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):349–356. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. Y., Queen C., Baltimore D. Expression of an Abelson murine leukemia virus-encoded protein in Escherichia coli causes extensive phosphorylation of tyrosine residues. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13181–13184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S. M., Witte O. N. Site-directed deletions of Abelson murine leukemia virus define 3' sequences essential for transformation and lethality. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1028–1036. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1028-1036.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte O. N., Dasgupta A., Baltimore D. Abelson murine leukaemia virus protein is phosphorylated in vitro to form phosphotyrosine. Nature. 1980 Feb 28;283(5750):826–831. doi: 10.1038/283826a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte O. N., Goff S., Rosenberg N., Baltimore D. A transformation-defective mutant of Abelson murine leukemia virus lacks protein kinase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4993–4997. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte O. N., Rosenberg N. E., Baltimore D. A normal cell protein cross-reactive to the major Abelson murine leukaemia virus gene product. Nature. 1979 Oct 4;281(5730):396–398. doi: 10.1038/281396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte O. N., Rosenberg N., Paskind M., Shields A., Baltimore D. Identification of an Abelson murine leukemia virus-encoded protein present in transformed fibroblast and lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2488–2492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziegler S. F., Whitlock C. A., Goff S. P., Gifford A., Witte O. N. Lethal effect of the Abelson murine leukemia virus transforming gene product. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):477–486. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90389-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]