Abstract
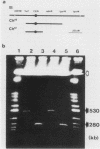
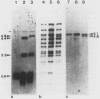
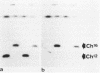
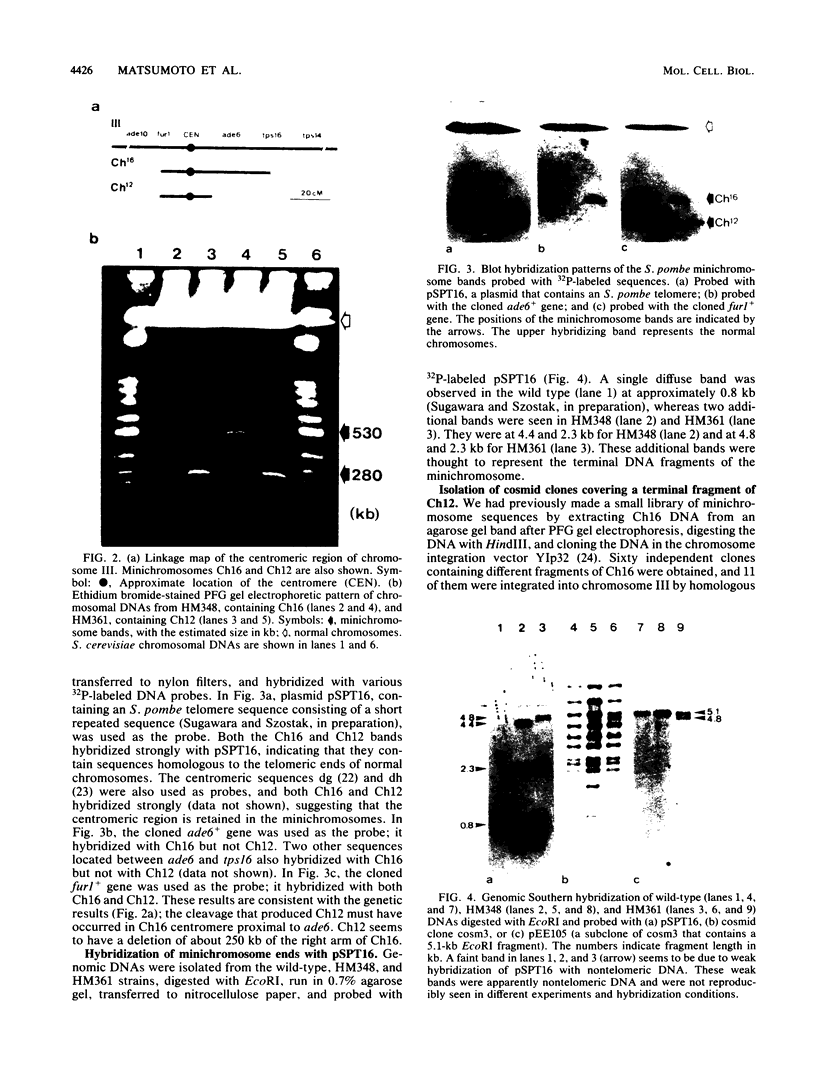
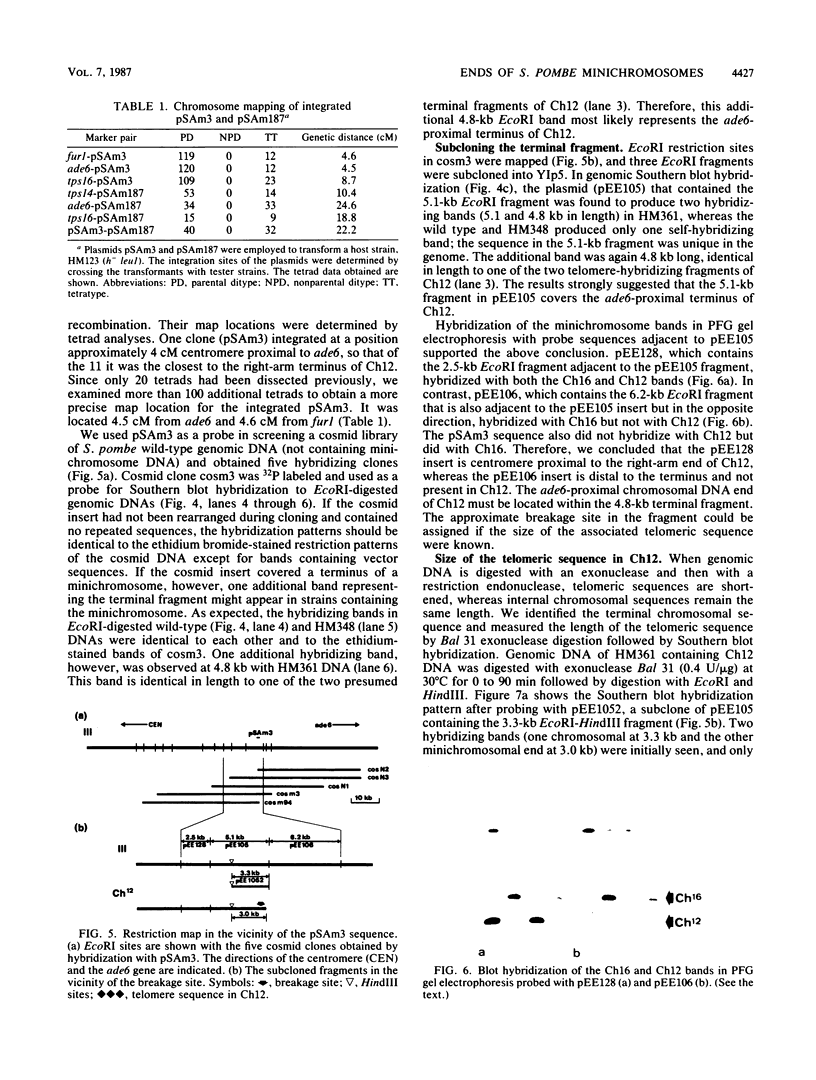
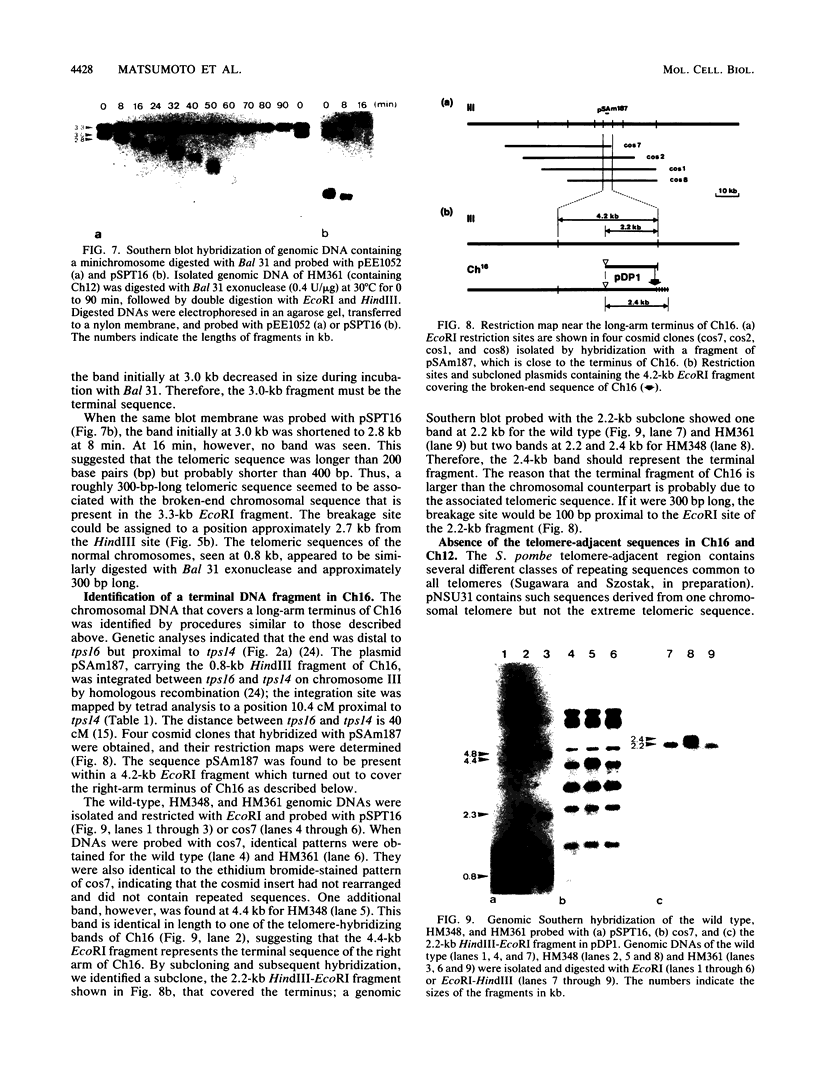
The minichromosome Ch16 of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe is derived from the centromeric region of chromosome III. We show that Ch16 and a shorter derivative, Ch12, made by gamma-ray cleavage, are linear molecules of 530 and 280 kilobases, respectively. Each minichromosome has two novel telomeres, as shown by genomic Southern hybridization with an S. pombe telomere probe. Comparison by hybridization of the minichromosomes and their chromosomal counterparts showed no signs of gross rearrangement. Cosmid clones covering the ends of the long arms of Ch16 and Ch12 were isolated, and subcloned fragments that contained the breakage sites were identified. They are apparently unique in the genome. By hybridization and Bal 31 digestion, the ends appear to consist of the broken-end sequences directly associated with short stretches (about 300 base pairs) of new DNA that hybridizes to a cloned S. pombe telomere. They do not contain the telomere-adjacent repeated sequences that are present in the normal chromosomes. The sizes of the short telomeric stretches are roughly the same as those of the normal chromosomes. Our results show that broken chromosomal ends in S. pombe can be healed by the de novo addition of the short telomeric repeats. The formation of Ch16 must have required two breakage-healing events, whereas a single cleavage-healing event in the long arm of Ch16 yielded Ch12.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blackburn E. H. The molecular structure of centromeres and telomeres. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:163–194. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botstein D., Falco S. C., Stewart S. E., Brennan M., Scherer S., Stinchcomb D. T., Struhl K., Davis R. W. Sterile host yeasts (SHY): a eukaryotic system of biological containment for recombinant DNA experiments. Gene. 1979 Dec;8(1):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. An electrophoretic karyotype for yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3756–3760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Separation of chromosomal DNA molecules from yeast by orthogonal-field-alternation gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5647–5664. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. Isolation of a yeast centromere and construction of functional small circular chromosomes. Nature. 1980 Oct 9;287(5782):504–509. doi: 10.1038/287504a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dani G. M., Zakian V. A. Mitotic and meiotic stability of linear plasmids in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3406–3410. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald-Hayes M., Clarke L., Carbon J. Nucleotide sequence comparisons and functional analysis of yeast centromere DNAs. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):235–244. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90108-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greider C. W., Blackburn E. H. Identification of a specific telomere terminal transferase activity in Tetrahymena extracts. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hieter P., Mann C., Snyder M., Davis R. W. Mitotic stability of yeast chromosomes: a colony color assay that measures nondisjunction and chromosome loss. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):381–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90152-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B., Collins J. A small cosmid for efficient cloning of large DNA fragments. Gene. 1980 Nov;11(3-4):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90069-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohli J., Hottinger H., Munz P., Strauss A., Thuriaux P. Genetic Mapping in SCHIZOSACCHAROMYCES POMBE by Mitotic and Meiotic Analysis and Induced Haploidization. Genetics. 1977 Nov;87(3):471–489. doi: 10.1093/genetics/87.3.471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D., Kent J. C., Hartwell L. H. Genetic analysis of the mitotic transmission of minichromosomes. Cell. 1985 Feb;40(2):393–403. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90153-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClintock B. The Stability of Broken Ends of Chromosomes in Zea Mays. Genetics. 1941 Mar;26(2):234–282. doi: 10.1093/genetics/26.2.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCusker J. H., Haber J. E. Evidence of Chromosomal Breaks near the Mating-Type Locus of SACCHAROMYCES CEREVISIAE That Accompany MATalpha xMATalpha Matings. Genetics. 1981 Nov;99(3-4):383–403. doi: 10.1093/genetics/99.3-4.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Szostak J. W. Chromosome segregation in mitosis and meiosis. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1985;1:289–315. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.01.110185.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Szostak J. W. Construction of artificial chromosomes in yeast. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):189–193. doi: 10.1038/305189a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaseko Y., Adachi Y., Funahashi S., Niwa O., Yanagida M. Chromosome walking shows a highly homologous repetitive sequence present in all the centromere regions of fission yeast. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):1011–1021. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04316.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaseko Y., Kinoshita N., Yanagida M. A novel sequence common to the centromere regions of Schizosaccharomyces pombe chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 25;15(12):4705–4715. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.12.4705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Matsumoto T., Niwa O., Klco S., Fan J. B., Yanagida M., Cantor C. R. An electrophoretic karyotype for Schizosaccharomyces pombe by pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4481–4489. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinchcomb D. T., Mann C., Davis R. W. Centromeric DNA from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 25;158(2):157–190. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90427-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]