Abstract
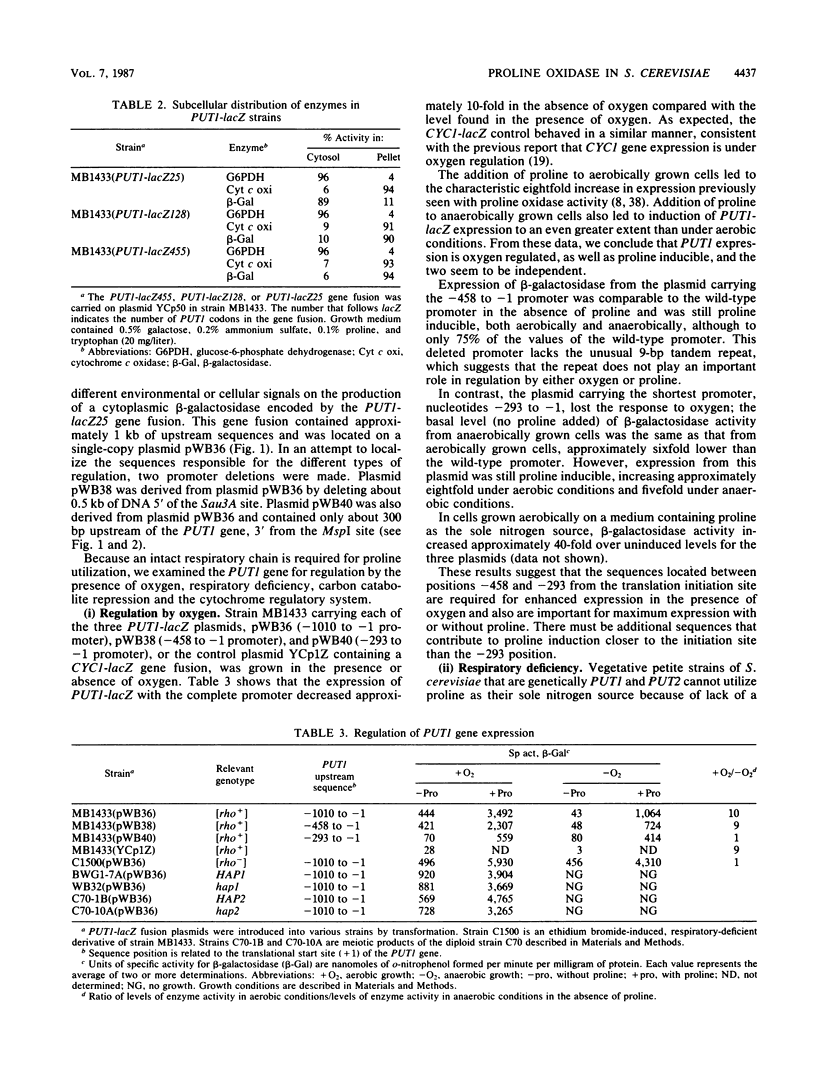
The PUT1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, believed to encode proline oxidase, has been completely sequenced and contains an open reading frame capable of encoding a polypeptide of 476 amino acids in length. The amino terminus of the protein deduced from the DNA sequence has a characteristic mitochondrial import signal; two PUT1-lacZ gene fusions were constructed that produced mitochondrially localized beta-galactosidase in vivo. The transcription initiation and termination sites of the PUT1 mRNA were determined. By using a PUT1-lacZ gene fusion that makes a cytoplasmic beta-galactosidase, the regulation of the PUT1 gene was studied. PUT1 is inducible by proline, responds only slightly to carbon catabolite repression, and is not regulated by the cytochrome activator proteins HAP1 and HAP2. The PUT1 gene is under oxygen regulation; expression in anaerobically grown cells is 10-fold lower than in aerobically grown cells. Oxygen regulation is abolished when cells are respiratory deficient. PUT1 expression in a [rho-] strain grown either aerobically or anaerobically is as high as that seen in a [rho+] strain grown aerobically. Studies on PUT1 promoter deletions define a region between positions -458 and -293 from the translation initiation site that is important for full expression of the PUT1 gene and required for oxygen regulation.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. Codon selection in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3026–3031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boggess S. F., Koeppe D. E. Oxidation of proline by plant mitochondria. Plant Physiol. 1978 Jul;62(1):22–25. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.1.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandriss M. C. Evidence for positive regulation of the proline utilization pathway in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1987 Nov;117(3):429–435. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.3.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandriss M. C., Krzywicki K. A. Amino-terminal fragments of delta 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase direct beta-galactosidase to the mitochondrial matrix in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3502–3512. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandriss M. C., Magasanik B. Genetics and physiology of proline utilization in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: enzyme induction by proline. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):498–503. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.498-503.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandriss M. C., Magasanik B. Genetics and physiology of proline utilization in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: mutation causing constitutive enzyme expression. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):504–507. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.504-507.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandriss M. C., Magasanik B. Proline: an essential intermediate in arginine degradation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Sep;143(3):1403–1410. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.3.1403-1410.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandriss M. C., Magasanik B. Subcellular compartmentation in control of converging pathways for proline and arginine metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1359–1364. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1359-1364.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandriss M. C. Proline utilization in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: analysis of the cloned PUT2 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1846–1856. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunner G., Neupert W. Localisation of proline oxidase and Delta-pyrroline-5-carboxylic acid dehydrogenase in rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1969 Jun;3(4):283–286. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80159-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clifton D., Weinstock S. B., Fraenkel D. G. Glycolysis mutants in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1978 Jan;88(1):1–11. doi: 10.1093/genetics/88.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daum G., Böhni P. C., Schatz G. Import of proteins into mitochondria. Cytochrome b2 and cytochrome c peroxidase are located in the intermembrane space of yeast mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):13028–13033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas M. G., McCammon M. T., Vassarotti A. Targeting proteins into mitochondria. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Jun;50(2):166–178. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.2.166-178.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald M., Shenk T. The sequence 5'-AAUAAA-3'forms parts of the recognition site for polyadenylation of late SV40 mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90521-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Lalonde B., Gifford P., Alani E. Distinctly regulated tandem upstream activation sites mediate catabolite repression of the CYC1 gene of S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):503–511. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90243-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Kelly J. D., Cohen E. H. Transcription terminates in yeast distal to a control sequence. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):607–614. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90441-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hörtner H., Ammerer G., Hartter E., Hamilton B., Rytka J., Bilinski T., Ruis H. Regulation of synthesis of catalases and iso-1-cytochrome c in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by glucose, oxygen and heme. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Nov;128(1):179–184. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06949.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Correlation between the abundance of yeast transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in protein genes. Differences in synonymous codon choice patterns of yeast and Escherichia coli with reference to the abundance of isoaccepting transfer RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 15;158(4):573–597. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90250-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Possible role of flanking nucleotides in recognition of the AUG initiator codon by eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5233–5252. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krzywicki K. A., Brandriss M. C. Primary structure of the nuclear PUT2 gene involved in the mitochondrial pathway for proline utilization in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2837–2842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. C., Roeder R. G. Transcription of adenovirus type 2 genes in a cell-free system: apparent heterogeneity of initiation at some promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;1(7):635–651. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.7.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menzel R., Roth J. Purification of the putA gene product. A bifunctional membrane-bound protein from Salmonella typhimurium responsible for the two-step oxidation of proline to glutamate. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9755–9761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middelhoven W. J., Broekhuizen B., van Eijk J. Detection, with the dye phloxine B, of yeast mutants unable to utilize nitrogenous substances as the sole nitrogen source. J Bacteriol. 1976 Dec;128(3):851–852. doi: 10.1128/jb.128.3.851-852.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers A. M., Tzagoloff A., Kinney D. M., Lusty C. J. Yeast shuttle and integrative vectors with multiple cloning sites suitable for construction of lacZ fusions. Gene. 1986;45(3):299–310. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov YuA Rhodopsin and bacteriorhodopsin: structure-function relationships. FEBS Lett. 1982 Nov 8;148(2):179–191. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80805-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parikh V. S., Morgan M. M., Scott R., Clements L. S., Butow R. A. The mitochondrial genotype can influence nuclear gene expression in yeast. Science. 1987 Jan 30;235(4788):576–580. doi: 10.1126/science.3027892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkham J. L., Olesen J. T., Guarente L. P. Sequence and nuclear localization of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae HAP2 protein, a transcriptional activator. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):578–585. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RACKER E. Spectrophotometric measurements of the enzymatic formation of fumaric and cis-aconitic acids. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1950 Jan;4(1-3):211–214. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(50)90026-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpulla R. C., Soffer R. L. Membrane-bound proline dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli. Solubilization, purification, and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):5997–6001. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. S., Brandriss M. C. Proline utilization in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: analysis of the cloned PUT1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2638–2645. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Sherman F. DNA sequence required for efficient transcription termination in yeast. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zitomer R. S., Sellers J. W., McCarter D. W., Hastings G. A., Wick P., Lowry C. V. Elements involved in oxygen regulation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae CYC7 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2212–2220. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]