Abstract
Replacement of protons by deuterons in the glassing solvents led to 2–3-fold improvement of the 13C dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) solid-state NMR signal for samples doped with large electron spin resonance (ESR) linewidth free radicals galvinoxyl, DPPH, and 4-oxo-TEMPO. Meanwhile, the reverse effect is observed for 13C DNP using small ESR linewidth free radicals BDPA and trityl OX063.
In vivo and in vitro nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) and imaging (MRI) of nuclei with relatively low gyromagnetic ratio γ such as 13C is challenging due to the inherently low Boltzmann thermal polarization. Dynamic nuclear polarization (DNP) amplifies the NMR signal by transferring the high electron thermal polarization to the nuclear spins via microwave irradiation at low temperature (close to 1 K) and high magnetic field (>1 T).1 The invention of the dissolution method in DNP2 in 2003 extended the application of this technique in chemistry3 and biomedical MRS/MRI4 by producing highly polarized solutions at physiological temperature with several thousand-fold NMR signal enhancement.
Various factors related to the DNP hardware as well as the sample composition can have strong effects on the absolute DNP enhancements. Experimental data show that lowering the operating temperature and increasing the magnetic field of the polarizer would yield higher 13C nuclear polarization.5 Free radicals that have narrow ESR linewidth (D) appear more favorable in the DNP of low-γ nuclei such as 2H, 13C, and 89Y.6,7 The inclusion of trace amounts of Gd3+ in the DNP sample has also been shown to improve the nuclear polarization.8–10 It was reported in a previous study that deuteration of the glassing solvents of 13C samples doped with TEMPO free radical approximately doubled the nuclear polarization.11 Based on this paper, it is becoming customary to use deuterated glassing matrices regardless of the type of free radical polarizing agent. The goal of the present work, therefore, was to study the influence of deuteration of the glassing matrix on 13C DNP samples doped with different free radical polarizing agents (Fig. 1) commonly used for dissolution DNP: BDPA, trityl OX063, galvinoxyl, DPPH, and 4-oxo-TEMPO.12–14
Fig. 1.
Structures of the free radicals used in this work.
13C DNP experiments were perfomed using free radicals with different ESR linewidths in non-deuterated (ND), partially deuterated (PD), and fully deuterated (FD) glassing matrices (Table 1). Since it is difficult to determine the full width at half height for inhomogenously-broadened ESR spectra of free radicals such as galvinoxyl, DPPH, and 4-oxo-TEMPO, we define the ESR linewidth D of the free radicals as the width from 2 % height from the base of ESR spectra in absorptive mode. Based on this criterion, the W-band ESR linewidths of BDPA, trityl OX063, galvinoxyl, DPPH, and 4-oxo-TEMPO measured at 100 K are 63 MHz, 115 MHz, 250 MHz, 290 MHz, and 465 MHz, respectively (ESI).
Table 1.
W-band ESR linewidths D of different free radicals and composition of DNP samples.
| Free Radical | ESR D (MHz)a | c (mM)b | 13C compound | Non-deuterated/ND (v:v)c | GLASSING MATRIX Partially deuterated/PD (v:v)c | Fully deuterated/FD (v:v)c |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BDPA | 63 | 20 | 2 M [13C]urea | 1:1 sulfolane:DMSO | 1:1 sulfolane:d6-DMSO | 1:1 d8-sulfolane:d6-DMSO |
| Trityl OX063 | 115 | 15 | 1.4 M [1-13C]pyruvate | 1:1 glycerol:H2O | 1:1 glycerol:D2O | 1:1 d8-glycerol:D2O |
| Galvinoxyl | 250 | 40 | 10% v [1-13C]EtOAcd | 4:5 EtOAc:DMSO | 4:5 EtOAc:d6-DMSO | 4:5 d8-EtOAc:d6-DMSO |
| DPPH | 290 | 20 | 2 M [13C]urea | 1:1 sulfolane:DMSO | 1:1 sulfolane:d6-DMSO | 1:1 d8-sulfolane:d6-DMSO |
| 4-oxo-TEMPO | 465 | 40 | 1.4 M [1-13C]pyruvate | 1:1 glycerol:H2O | 1:1 glycerol:D2O | 1:1 d8-glycerol:D2O |
ESR linewidth measured at ~2% height from the base. Data collected at 100 K in a W-band ESR spectrometer (ESI).
optimum free radical concentration for DNP.
volume ratio at 25 °C.
10% of total volume of the DNP sample.
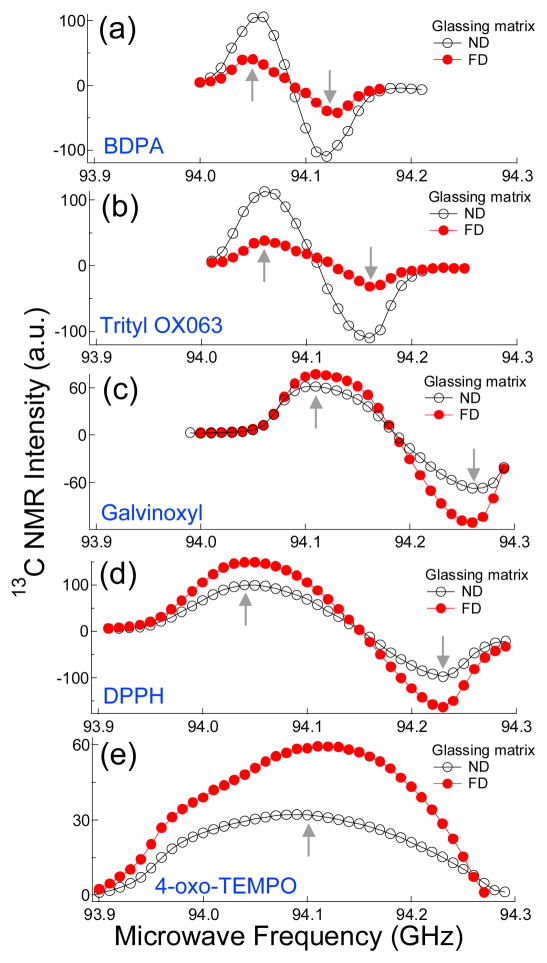
The locations of the optimum microwave irradiation frequencies, namely the positive P(+) and negative P(−) polarization peaks, for 13C DNP samples at 3.35 T and 1.1 K with ND and FD glassing matrices are displayed in the microwave DNP spectra in Fig. 2. In the case of 13C samples doped with 4-oxo-TEMPO, only half of the DNP spectra could be recorded (Fig. 2e) due to the limited sweepable bandwidth of the microwave source (93.9–94.3 GHz). Inspection of a full 13C DNP spectrum of [13C]acetate sample doped with TEMPO from a previous work revealed that the separation between P(+) and P(−) is about 330 MHz.15 As expected based on data published for TEMPO, samples doped with the large D free radicals such as galvinoxyl, DPPH, and 4-oxo-TEMPO displayed improvement in the relative 13C NMR intensity of the DNP spectra with a FD glassing matrix. However, 13C DNP spectra of samples doped with narrow linewidth free radicals BDPA (Fig 2a) and trityl OX063 (Fig. 2b) showed significant decreases in the NMR intensity in deuterated matrices. Except for the NMR intensity, there is no dramatic change in the locations of P(+) and P(−) or the shape of the 13C DNP spectra with ND and FD glassing matrices.
Fig. 2.
13C DNP spectra of frozen samples with non-deuterated (ND) and fully deuterated (FD) glassing matrices doped with a) BDPA, b) trityl OX063, c) galvinoxyl, d) DPPH and e) 4-oxo-TEMPO taken in the HyperSense polarizer at 3.35 T and 1.1 K using a 100 mW microwave source. The up and down arrows indicate the locations of the positive P(+) and negative P(−) polarization peaks, respectively. Note that only half of the 13C DNP spectra of samples doped with 4-oxo-TEMPO are shown due to the limited frequency sweep bandwidth of the microwave source.
To make an accurate quantitative comparison of the effect of deuteration on 13C DNP, the relative maximum nuclear polarizations (Fig. 3) were determined for each radical by normalizing the maximum solid-state hyperpolarized NMR signal (average of N=3 trials) to the DNP-enhanced 13C polarization obtained in ND glassing matrix. The relative 13C polarization buildup curves (ESI) for each sample were obtained in triplicate with microwave irradiation frequency set at P(+). The 13C polarization was reduced to about a half with full deuteration of the glassing solvents when narrow D radicals BDPA and trityl OX063 were used (Figs. 3a and 3b, respectively) while for 13C samples doped with large D free radicals galvinoxyl (D=250 MHz), DPPH (D=290 MHz), and 4-oxo-TEMPO (D=465 MHz), considerable improvements in the 13C polarization were observed in deuterated glassing mixtures. The largest increase was observed for DPPH, where deuteration led to almost a 3.5-fold amplification of the 13C polarization. As expected, partial deuteration resulted in an intermediate effect for all radicals. Similar increases were observed for solid-state MAS-DNP with deuterated solvents and deuterated proteins using nitroxide-based radicals, albeit with a different mechanism mainly involving nuclear relaxation.16,17 In our case at low temperatures close to 1 K, the effect of deuteration on the DNP enhancement can be qualitatively explained using a simplified thermodynamic description of thermal mixing, the dominant mechanism of DNP expected under our current experimental conditions.
Fig. 3.
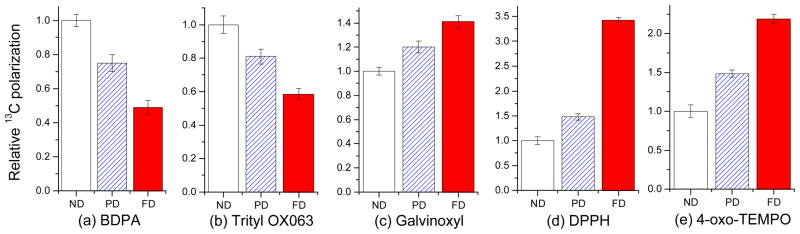
Relative DNP-enhanced 13C polarization of frozen DNP samples with non-deuterated (ND), partially deuterated (PD), and fully deuterated (FD) glassing matrices doped with a) BDPA, b) trityl OX063, c) galvinoxyl, d) DPPH, and e) 4-oxo-TEMPO taken at 3.35 T and 1.1 K. The error bars are standard deviations of N=3 trials for each sample. See Table 1 and ESI for details of the composition of samples.
Thermal mixing occurs when the ESR D is greater than or comparable to the nuclear Larmor frequency, and the electron dipolar system (EDS) and nuclear Zeeman system are in thermal contact because the electron dipolar energy <De> matches with the nuclear Zeeman energy <Zn>.1,18 The ESR linewidth of nitroxyl radicals is generally larger than the 1H Larmor frequency (143 MHz at 3.35 T) and therefore, it is expected that the EDS and the nuclear Zeeman system involving all NMR-active nuclei in the sample (1H, 2H and 13C) are in thermal contact.1,18 The specific heat capacity (CZ) of the nuclear Zeeman system is approximately given by CZ~NΩn2 where N is the number of nuclear spins.18 Since CZ(2H)<CZ(1H), replacement of 1H (γ=42.577 MHz/T) by 2H (γ=6.536 MHz/T) spins leads to lower total specific heat capacity for the nuclear Zeeman system. As a consequence, in thermal mixing, the EDS can “cool down” the 13C Zeeman system to a lower spin temperature. Evidence of thermal mixing as the predominant DNP mechanism for 1H and 13C in TEMPO-doped samples was shown in a previous work11 and the same trend is expected for DNP with galvinoxyl and DPPH. However, for the free radicals BDPA and trityl OX063, the ESR D is not large enough to cover the the proton Larmor frequency and consequently 1H DNP is expected to proceed mainly via solid effect.19 Thus, the 1H nuclear Zeeman system is not thermally coupled to EDS and does not or barely contributes to the total nuclear Zeeman system heat load. On the other hand, it was shown in previous works7,20,21 that low-γ nuclear spins such as 13C, 15N, 2H, and 89Y, could be polarized at the same microwave frequency using trityl OX063, characteristic of thermal mixing. When protons are replaced by deuterons in the glassing matrix, the 2H spins (Ωn=21.9 MHz) will be in thermal contact with the EDS, adding to the total nuclear Zeeman system heat load. Glassing solvent deuteration for samples doped with narrow ESR D free radicals would lead to higher 13C spin temperature.
In conclusion, we have shown that deuteration of the glassing matrix increases the 13C polarization of samples doped with free radicals that have ESR D comparable to or larger than the 1H Larmor frequency such as galvinoxyl, DPPH, and 4-oxo-TEMPO. This is attributed to the lower heat capacity of the deuteron Zeeman system compared to protons. However, glassing solvent deuteration is not recommended for DNP with free radicals that have narrow ESR linewidth such as BDPA and trityl OX063 where the proton Zeeman system has little or no contact with EDS. In this case, deuteration would only add more heat load to the nuclear Zeeman system, resulting in lower 13C polarization. These observations can be generalized to optimize sample preparation for other cases as well. If the target compound for DNP is ionic, the NMR active nuclei of the counterion will have an effect on the maximal polarization depending on the Larmor frequency and the ESR linewidth of the radical used. For example, in the case of BDPA and trityl OX063, the ammonium ion, NH4+, would likely be superior to 23Na, since the protons of the ammonium would not couple to the EDS and the 14N would have a significantly lower heat capacity than 23Na.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant numbers R21EB009147 and NIBIB RR02584 and by CPRIT RP-101243. The authors would like to thank Likai Song and Johan van Tol of NHMFL in Tallahassee, Florida for the ESR measurements.
Footnotes
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) available: [W-band ESR spectra of free radicals at 100 K, sample preparation and methods, 13C polarization buildup curves].
Notes and references
- 1.Abragam A, Goldman M. Rep Prog Phys. 1978;41:395. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ardenkjær-Larsen JH, Fridlund B, Gram A, Hansson G, Hansson L, Lerche MH, Servin R, Thaning M, Golman K. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:10158–10163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1733835100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Gunther U. Dynamic nuclear hyperpolarization in liquids. Top Curr Chem. 2012:1–47. doi: 10.1007/128_2011_229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kurhanewicz J, Vigneron DB, Brindle K, Chekmenev EY, Comment A, Cunningham CH, DeBerardinis RJ, Green GG, Leach MO, Rajan SS, Rizi RR, Ross BD, Warren WS, Malloy CR. Neoplasia. 2011;13:81. doi: 10.1593/neo.101102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Meyer W, Heckmann J, Hess C, Radtke E, Reicherz G, Triebwasser L, Wang L. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res Sect A. 2011;631:1–5. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Heckmann J, Meyer W, Radtke E, Reicherz G, Goertz S. Phys Rev B. 2006;74:134418. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lumata L, Jindal AK, Merritt ME, Malloy C, Sherry AD, Kovacs Z. J Am Chem Soc. 2011;133:8673–8680. doi: 10.1021/ja201880y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lumata L, Merritt ME, Malloy CR, Sherry AD, Kovacs Z. J Phys Chem A. 2012;116:5129–5138. doi: 10.1021/jp302399f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gordon JW, Fain SB, Rowland IJ. Magn Reson Med. 2012;68:1949–1952. doi: 10.1002/mrm.24207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Waldner LF, Chen A, Mander W, Scholl T, McKenzie C. J Magn Reson. 2012;223:85–89. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2012.07.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kurdzesau F, van der Brandt B, Comment A, Hautle P, Jannin S, van der Klink JJ, Konter JA. J Phys D: Appl Phys. 2008;41:155506. doi: 10.1063/1.2951994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lumata L, Ratnakar SJ, Jindal A, Merritt M, Comment A, Malloy C, Sherry AD, Kovacs Z. Chem Eur J. 2011;17:10825–10827. doi: 10.1002/chem.201102037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lumata LL, Merritt ME, Malloy CR, Sherry AD, van Tol J, Song L, Kovacs Z. J Magn Reson. 2013;227:14–19. doi: 10.1016/j.jmr.2012.11.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lumata L, Merritt M, Khemtong C, Ratnakar SJ, van Tol J, Yu L, Song L, Kovacs Z. RSC Adv. 2012;2:12812–12817. doi: 10.1039/C2RA21853D. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jannin S, Comment A, Kurdzesau F, Konter JA, Hautle P, van der Brandt B, van der Klink JJ. J Chem Phys. 2008:128–241102. doi: 10.1063/1.2951994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hu KN, Yu HH, Swager TM, Griffin RG. J Am Chem Soc. 2004;126:10844–10845. doi: 10.1021/ja039749a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Akbey U, Franks WT, Linden A, Lange S, Griffin RG, Van Rossum BJ, Oschkinat H. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2010;49:7803–7806. doi: 10.1002/anie.201002044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Goertz ST. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res, Sect A. 2004;526:28–42. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wolber J, Ellner F, Fridlund B, Gram A, Johannesson H, Hansson G, Hansson LH, Lerche MH, Mansson S, Servin R, Thaning M, Golman K, Ardenkjaer-Larsen JH. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res, Sect A. 2004;526:173–181. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Reynolds S, Patel H. Appl Magn Reson. 2008;34:495–508. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Day IJ, Mitchell JC, Snowden MJ, Davis AL. Magn Reson Chem. 2007;45:1018–1021. doi: 10.1002/mrc.2090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.