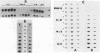Abstract
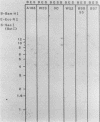
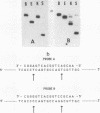
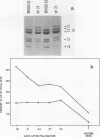
Allelic variation between inbred lines at the 27-kilodalton zein gene locus in maize has been used to study gene expression in developing endosperm. The inbred lines W22 and W23 contain two genes for this protein within two tandem repeats; the individual genes are virtually identical, with 99.9% homology in the 5'-flanking regions. Using gene-specific oligonucleotide probes, we have shown that transcripts of the downstream gene are found at a 2.5-fold-higher level than those of the upstream gene. Another inbred line, BSSS53, has one copy of the gene which is a recombinant of the duplicated genes at the 3'-flanking region. This line has been used in reciprocal crosses to demonstrate dosage effects for the overexpression of the downstream gene and to show that the overexpression of mRNA is reflected in a corresponding increase in the protein level. The accumulation of the protein through development does not, however, always correspond to the difference in mRNA levels.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry J. O., Nikolau B. J., Carr J. P., Klessig D. F. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase gene expression in light- and dark-grown amaranth cotyledons. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2238–2246. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. Determinants of messenger RNA stability. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90346-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr B., Burr F. A. Zein synthesis in maize endosperm by polyribosomes attached to protein bodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):515–519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burr F. A., Burr B. In vitro uptake and processing of prezein and other maize preproteins by maize membranes. J Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;90(2):427–434. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.2.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodchoy N., Levine B. J., Sprecher C., Skoultchi A. I., Marzluff W. F. Expression of mouse histone genes: transcription into 3' intergenic DNA and cryptic processing sites downstream from the 3' end of the H3 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1039–1047. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomet P. S., Wessler S., Dellaporta S. L. Inactivation of the maize transposable element Activator (Ac) is associated with its DNA modification. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):295–302. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04753.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluhr R., Chua N. H. Developmental regulation of two genes encoding ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit in pea and transgenic petunia plants: Phytochrome response and blue-light induction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2358–2362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluhr R., Kuhlemeier C., Nagy F., Chua N. H. Organ-specific and light-induced expression of plant genes. Science. 1986 May 30;232(4754):1106–1112. doi: 10.1126/science.232.4754.1106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregor P. D., Morrison S. L. Myeloma mutant with a novel 3' flanking region: loss of normal sequence and insertion of repetitive elements leads to decreased transcription but normal processing of the alpha heavy-chain gene products. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):1903–1916. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.1903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt I., Kuhn A., Bartsch I., Rosenbauer H. A transcription terminator located upstream of the mouse rDNA initiation site affects rRNA synthesis. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):901–911. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90805-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart R. P., McDevitt M. A., Ali H., Nevins J. R. Definition of essential sequences and functional equivalence of elements downstream of the adenovirus E2A and the early simian virus 40 polyadenylation sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2975–2983. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson A. O., Larkins B. A. Influence of Ionic Strength, pH, and Chelation of Divalent Metals on Isolation of Polyribosomes from Tobacco Leaves. Plant Physiol. 1976 Jan;57(1):5–10. doi: 10.1104/pp.57.1.5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowles R. V., Phillips R. L. DNA amplification patterns in maize endosperm nuclei during kernel development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7010–7014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larkins B. A., Hurkman W. J. Synthesis and deposition of zein in protein bodies of maize endosperm. Plant Physiol. 1978 Aug;62(2):256–263. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.2.256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier U. G., Brown J. W., Tologcyzki C., Feix G. Binding of a nuclear factor to a consensus sequence in the 5' flanking region of zein genes from maize. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):17–22. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04712.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Gaffney D., Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. The consensus sequence YGTGTTYY located downstream from the AATAAA signal is required for efficient formation of mRNA 3' termini. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1347–1368. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McStay B., Reeder R. H. A termination site for Xenopus RNA polymerase I also acts as an element of an adjacent promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):913–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90806-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy F., Kay S. A., Boutry M., Hsu M. Y., Chua N. H. Phytochrome-controlled expression of a wheat Cab gene in transgenic tobacco seedlings. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1119–1124. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04335.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrander J., Kempe T., Messing J. Construction of improved M13 vectors using oligodeoxynucleotide-directed mutagenesis. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okamuro J. K., Jofuku K. D., Goldberg R. B. Soybean seed lectin gene and flanking nonseed protein genes are developmentally regulated in transformed tobacco plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8240–8244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park W. D., Lewis E. D., Rubenstein I. Heterogeneity of zein mRNA and protein in maize. Plant Physiol. 1980 Jan;65(1):98–106. doi: 10.1104/pp.65.1.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen K., Argos P., Naravana S. V., Larkins B. A. Sequence analysis and characterization of a maize gene encoding a high-sulfur zein protein of Mr 15,000. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 15;261(14):6279–6284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prat S., Cortadas J., Puigdomènech P., Palau J. Nucleic acid (cDNA) and amino acid sequences of the maize endosperm protein glutelin-2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1493–1504. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrmann G., Yuen L., Moss B. Transcription of vaccinia virus early genes by enzymes isolated from vaccinia virions terminates downstream of a regulatory sequence. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):1029–1035. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90702-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Serrano J. J., Keil M., O'Connor A., Schell J., Willmitzer L. Wound expression of a potato proteinase inhibitor II gene in transgenic tobacco plants. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):303–306. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04754.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz-Sommer Z., Shepherd N., Tacke E., Gierl A., Rohde W., Leclercq L., Mattes M., Berndtgen R., Peterson P. A., Saedler H. Influence of transposable elements on the structure and function of the A1 gene of Zea mays. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):287–294. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04752.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shure M., Wessler S., Fedoroff N. Molecular identification and isolation of the Waxy locus in maize. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90225-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voelker T. A., Staswick P., Chrispeels M. J. Molecular analysis of two phytohemagglutinin genes and their expression in Phaseolus vulgaris cv. Pinto, a lectin-deficient cultivar of the bean. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3075–3082. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04613.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walling L., Drews G. N., Goldberg R. B. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of soybean seed protein mRNA levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2123–2127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. Z., Esen A. Primary structure of a proline-rich zein and its cDNA. Plant Physiol. 1986 May;81(1):70–74. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.1.70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]