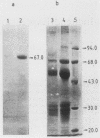
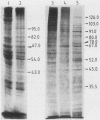
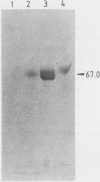
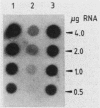
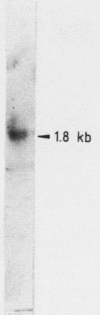
Abstract
An examination of heat-induced expression of proteins in tissues from adult and embryonic liver in rats shows that albumin, which is constitutively expressed in adult liver and is not synthesized in embryos before 16 days of gestation, appears in liver cells at earlier stages of development upon heat shock. On the basis of available evidence for the expression of heat shock proteins at distinct stages of development and on the basis of our findings, it may be argued that there could be common molecular events taking place during development and as a result of heat shock. We suggest also that one of the consequences of heat shock could be an internal change of pH within the cell which, in turn, might trigger alterations in gene expression.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bardwell J. C., Craig E. A. Major heat shock gene of Drosophila and the Escherichia coli heat-inducible dnaK gene are homologous. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):848–852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensaude O., Babinet C., Morange M., Jacob F. Heat shock proteins, first major products of zygotic gene activity in mouse embryo. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):331–333. doi: 10.1038/305331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond U., Schlesinger M. J. Ubiquitin is a heat shock protein in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):949–956. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Knowland J. Classes of proteins synthesized in oocytes, eggs, embryos, and differentiated tissues of Xenopus laevis. Differentiation. 1979;13(2):101–108. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1979.tb01572.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dura J. M. Stage dependent synthesis of heat shock induced proteins in early embryos of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(3):381–385. doi: 10.1007/BF00352509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grainger J. L., Winkler M. M., Shen S. S., Steinhardt R. A. Intracellular pH controls protein synthesis rate in the sea urchine egg and early embryo. Dev Biol. 1979 Feb;68(2):396–406. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(79)90213-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt C., Morimoto R. I. Conserved features of eukaryotic hsp70 genes revealed by comparison with the nucleotide sequence of human hsp70. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6455–6459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson J. D., Epel D. Intracellular pH and activation of sea urchin eggs after fertilisation. Nature. 1976 Aug 19;262(5570):661–664. doi: 10.1038/262661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landry J., Chrétien P. Relationship between hyperthermia-induced heat-shock proteins and thermotolerance in Morris hepatoma cells. Can J Biochem Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;61(6):428–437. doi: 10.1139/o83-058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G. C. Induction of thermotolerance and enhanced heat shock protein synthesis in Chinese hamster fibroblasts by sodium arsenite and by ethanol. J Cell Physiol. 1983 May;115(2):116–122. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041150203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1151–1191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkes P. E. Hyperthermia-induced heat shock response and thermotolerance in postimplantation rat embryos. Dev Biol. 1987 Jan;119(1):115–122. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90212-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ober S. S., Pardee A. B. Intracellular pH is increased after transformation of Chinese hamster embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2766–2770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to the regulatory site of an hsp 70 gene. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):273–283. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90323-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sala-Trepat J. M., Dever J., Sargent T. D., Thomas K., Sell S., Bonner J. Changes in expression of albumin and alpha-fetoprotein genes during rat liver development and neoplasia. Biochemistry. 1979 May 29;18(11):2167–2178. doi: 10.1021/bi00578a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA transferred or dotted nitrocellulose paper. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:255–266. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00060-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman J. L., Petri W., Meselson M. Accumulation of a specific subset of D. melanogaster heat shock mRNAs in normal development without heat shock. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1161–1170. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90299-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]