Abstract
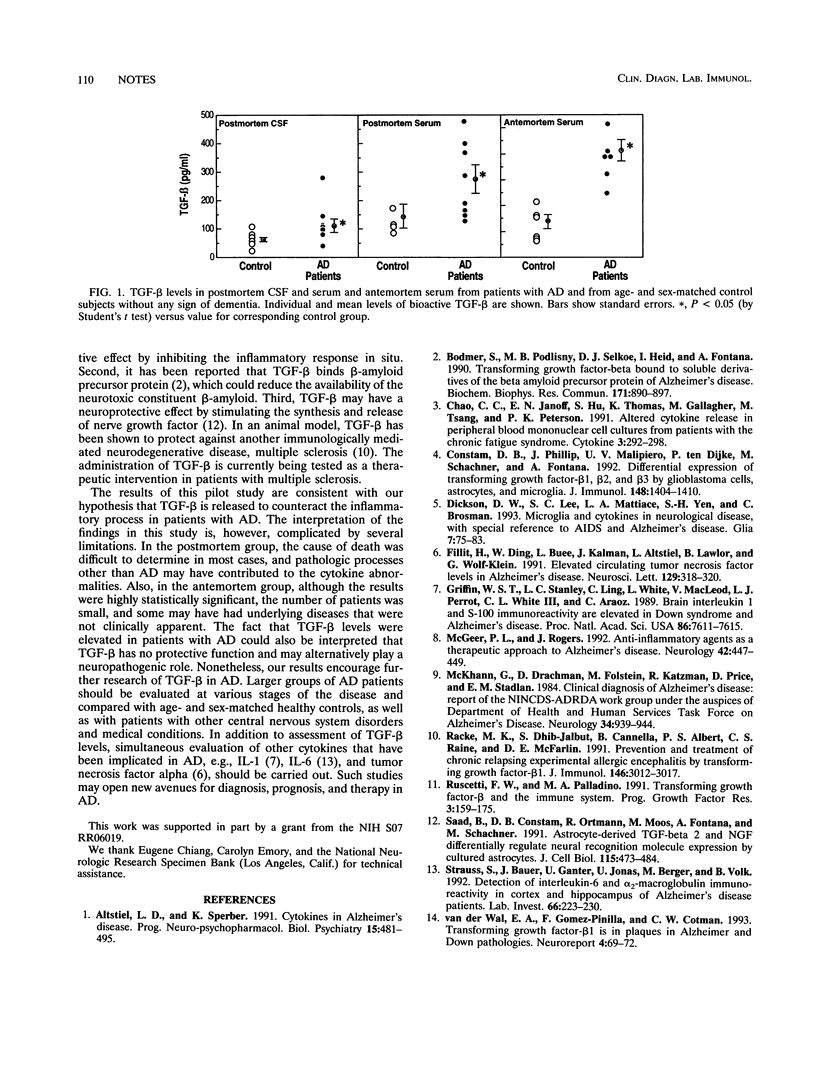
Alzheimer's disease (AD) has been hypothesized to be an inflammatory condition. We hypothesized that anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta), counteract the inflammatory process. In the present study, we found that TGF-beta levels were elevated in both cerebrospinal fluid and serum samples obtained from AD patients < 6 h after death. Serum TGF-beta levels were also markedly elevated before death. These results suggest that elevated TGF-beta levels in AD may represent a protective host response to immunologically mediated neuronal injury.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altstiel L. D., Sperber K. Cytokines in Alzheimer's disease. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 1991;15(4):481–495. doi: 10.1016/0278-5846(91)90023-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer S., Podlisny M. B., Selkoe D. J., Heid I., Fontana A. Transforming growth factor-beta bound to soluble derivatives of the beta amyloid precursor protein of Alzheimer's disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 14;171(2):890–897. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91229-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao C. C., Janoff E. N., Hu S. X., Thomas K., Gallagher M., Tsang M., Peterson P. K. Altered cytokine release in peripheral blood mononuclear cell cultures from patients with the chronic fatigue syndrome. Cytokine. 1991 Jul;3(4):292–298. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(91)90497-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Constam D. B., Philipp J., Malipiero U. V., ten Dijke P., Schachner M., Fontana A. Differential expression of transforming growth factor-beta 1, -beta 2, and -beta 3 by glioblastoma cells, astrocytes, and microglia. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 1;148(5):1404–1410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson D. W., Lee S. C., Mattiace L. A., Yen S. H., Brosnan C. Microglia and cytokines in neurological disease, with special reference to AIDS and Alzheimer's disease. Glia. 1993 Jan;7(1):75–83. doi: 10.1002/glia.440070113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fillit H., Ding W. H., Buee L., Kalman J., Altstiel L., Lawlor B., Wolf-Klein G. Elevated circulating tumor necrosis factor levels in Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett. 1991 Aug 19;129(2):318–320. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(91)90490-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin W. S., Stanley L. C., Ling C., White L., MacLeod V., Perrot L. J., White C. L., 3rd, Araoz C. Brain interleukin 1 and S-100 immunoreactivity are elevated in Down syndrome and Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7611–7615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeer P. L., Rogers J. Anti-inflammatory agents as a therapeutic approach to Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1992 Feb;42(2):447–449. doi: 10.1212/wnl.42.2.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKhann G., Drachman D., Folstein M., Katzman R., Price D., Stadlan E. M. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's Disease. Neurology. 1984 Jul;34(7):939–944. doi: 10.1212/wnl.34.7.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Racke M. K., Dhib-Jalbut S., Cannella B., Albert P. S., Raine C. S., McFarlin D. E. Prevention and treatment of chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis by transforming growth factor-beta 1. J Immunol. 1991 May 1;146(9):3012–3017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscetti F. W., Palladino M. A. Transforming growth factor-beta and the immune system. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1991;3(2):159–175. doi: 10.1016/s0955-2235(05)80006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saad B., Constam D. B., Ortmann R., Moos M., Fontana A., Schachner M. Astrocyte-derived TGF-beta 2 and NGF differentially regulate neural recognition molecule expression by cultured astrocytes. J Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;115(2):473–484. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.2.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss S., Bauer J., Ganter U., Jonas U., Berger M., Volk B. Detection of interleukin-6 and alpha 2-macroglobulin immunoreactivity in cortex and hippocampus of Alzheimer's disease patients. Lab Invest. 1992 Feb;66(2):223–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Wal E. A., Gómez-Pinilla F., Cotman C. W. Transforming growth factor-beta 1 is in plaques in Alzheimer and Down pathologies. Neuroreport. 1993 Jan;4(1):69–72. doi: 10.1097/00001756-199301000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



