Abstract
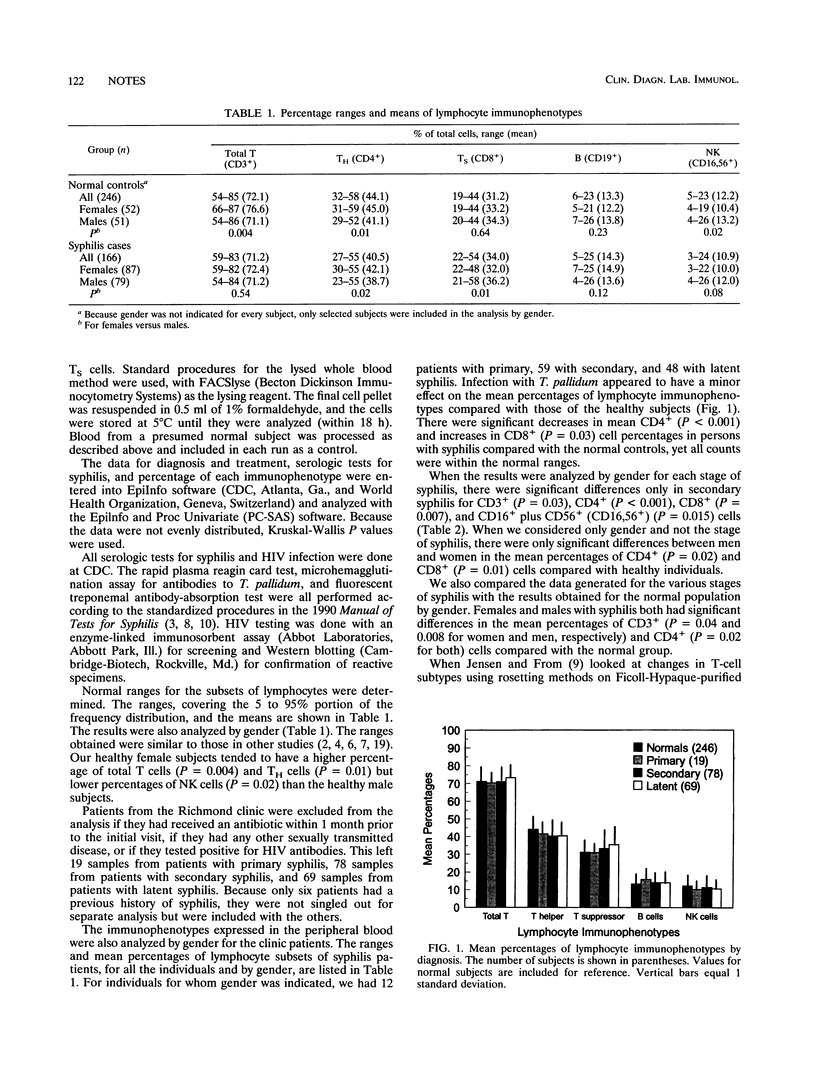
To characterize the human immune response to syphilis, we determined the effect of infection with Treponema pallidum on the percentage of the various lymphocyte subpopulations in the peripheral blood of infected and uninfected persons. Monoclonal antibodies labeled with either fluorescein isothiocyanate or phycoerythrin were used to perform dual color analysis on a FACScan with the following markers: CD3 for total T cells, CD4 for T helper cells, CD8 for T suppressor cells, CD19 for B cells, and CD16 plus CD56 for natural killer cells. Lymphocyte immunophenotype results were analyzed by the stage of untreated syphilis and by gender. Although they were within the ranges of the normal distribution of immunophenotypes, the percentages of CD4+ cells were significantly lower (P < 0.001) and those of CD8+ cells were higher (P = 0.03) in patients with syphilis than in the uninfected population. For infected versus uninfected subjects, both women and men, the differences in the mean percentages of CD3+ and CD4+ cells were significant (P < or = 0.05). Significant differences were noted between the sexes in secondary syphilis only in the mean percentages of cells positive for CD3, CD4, CD8, and CD16 plus CD56. Gender had no effect on lymphocyte subpopulations in subjects with primary or latent syphilis. In the control population, significant differences due to gender were observed in the percentages of cells positive for CD3, CD4, and CD16 plus CD56.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker-Zander S. A., Fohn M. J., Lukehart S. A. Development of cellular immunity to individual soluble antigens of Treponema pallidum during experimental syphilis. J Immunol. 1988 Dec 15;141(12):4363–4369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworsky R., Paganini-Hill A., Ducey B., Hechinger M., Parker J. W. Lymphocyte immunophenotyping in an elderly population: age, sex and medication effects--a flow cytometry study. Mech Ageing Dev. 1989 Jun;48(3):255–266. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(89)90087-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelkens H. J., ten Kate F. J., Judanarso J., Vuzevski V. D., van Lier J. B., Godschalk J. C., van der Sluis J. J., Stolz E. The localisation of treponemes and characterisation of the inflammatory infiltrate in skin biopsies from patients with primary or secondary syphilis, or early infectious yaws. Genitourin Med. 1993 Apr;69(2):102–107. doi: 10.1136/sti.69.2.102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto M., Nishioka K. Age- and sex-related changes of the lymphocyte subsets in healthy individuals: an analysis by two-dimensional flow cytometry. J Gerontol. 1989 Mar;44(2):M51–M56. doi: 10.1093/geronj/44.2.m51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen J. R., From E. Alterations in T lymphocytes and T-lymphocyte subpopulations in patients with syphilis. Br J Vener Dis. 1982 Feb;58(1):18–22. doi: 10.1136/sti.58.1.18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marti G. E., Fleisher T. A. Application of lymphocyte immunophenotyping in selected diseases. Pathol Immunopathol Res. 1988;7(5):319–337. doi: 10.1159/000157126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy M. M., Goetz R. R., Gorman J. M., Grieco M. H., Chess L., Lederman S. Human immunodeficiency virus type-1 infection of homosexual men is accompanied by a decrease in circulating B cells. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1991;4(4):428–434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renzi P., Ginns L. C. Analysis of T cell subsets in normal adults. Comparison of whole blood lysis technique to Ficoll-Hypaque separation by flow cytometry. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Apr 2;98(1):53–56. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schell R. F., Chan J. K., Le Frock J. L. Endemic syphilis: passive transfer of resistance with serum and cells in hamsters. J Infect Dis. 1979 Sep;140(3):378–383. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.3.378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell S., Gamboa D., Baker-Zander S. A., Lukehart S. A., Miller J. N. Host response to Treponema pallidum in intradermally-infected rabbits: evidence for persistence of infection at local and distant sites. J Invest Dermatol. 1980 Dec;75(6):470–475. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12524230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosca A., Lehou J., Hatjivasiliou M., Varelzidis A., Stratigos J. D. Infiltrate of syphilitic lesions before and after treatment. Genitourin Med. 1988 Oct;64(5):289–293. doi: 10.1136/sti.64.5.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vuillier F., Bianco N. E., Montagnier L., Dighiero G. Selective depletion of low-density CD8+, CD16+ lymphocytes during HIV infection. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1988 Apr;4(2):121–129. doi: 10.1089/aid.1988.4.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware J. L., Folds J. D., Baseman J. B. Modulation of normal lymphocyte stimulation by serum from Treponema pallidum-infected rabbits. Cell Immunol. 1980 Jul 15;53(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90423-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westermann J., Pabst R. Lymphocyte subsets in the blood: a diagnostic window on the lymphoid system? Immunol Today. 1990 Nov;11(11):406–410. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90160-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicher V., Wicher K., Jakubowski A., Nakeeb S. M. Adoptive transfer of immunity to Treponema pallidum Nichols infection in inbred strain 2 and C4D guinea pigs. Infect Immun. 1987 Oct;55(10):2502–2508. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.10.2502-2508.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



