Abstract
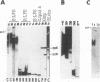
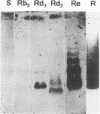
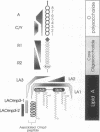
Sera from Brucella abortus-infected and -vaccinated bovines recognized four lipopolysaccharide (LPS) determinants: two in the O-polysaccharide (A and C), one in the core oligosaccharide from rough Brucella LPS (R), and one in lipid A (LA). From 46 different hybridomas secreting monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) against various LPS moieties, 9 different specificities were identified. Two epitopes, A and C/Y, were present in the O-polysaccharide. Two epitopes were found in the core oligosaccharide (R1 and R2) of rough Brucella LPS. MAbs against R1 and R2 epitopes reacted against LPS from different rough Brucella species; however, MAbs directed to the R2 epitope also reacted against enterobacterial LPS from deep rough mutants. Three epitopes (LA1, LA2, and LA3) were located in the lipid A backbone. Different sets of MAbs recognized two epitopes in the lipid A-associated outer membrane protein (LAOmp3-1 and LAOmp3-2). LPS preparations from smooth brucellae had small amounts of rough-type LPS. Although LPS from rough brucellae did not show smooth-type LPS in western blots (immunoblots), two hybridomas generated from mice immunized with rough B. abortus produced antibodies against smooth B. abortus LPS. Results are discussed in relation to the structure and function of B. abortus LPS and to previous findings on the epitopic density of the molecule.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berman D. T., Kurtz R. S. Relationship of biological activities to structures of Brucella abortus endotoxin and LPS. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1987 Jan-Feb;138(1):98–101. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(87)90084-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat U. R., Carlson R. W., Busch M., Mayer H. Distribution and phylogenetic significance of 27-hydroxy-octacosanoic acid in lipopolysaccharides from bacteria belonging to the alpha-2 subgroup of Proteobacteria. Int J Syst Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;41(2):213–217. doi: 10.1099/00207713-41-2-213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowser D. V., Wheat R. W., Foster J. W., Leong D. Occurrence of quinovosamine in lipopolysaccharides of Brucella species. Infect Immun. 1974 Apr;9(4):772–774. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.4.772-774.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bundle D. R., Cherwonogrodzky J. W., Gidney M. A., Meikle P. J., Perry M. B., Peters T. Definition of Brucella A and M epitopes by monoclonal typing reagents and synthetic oligosaccharides. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2829–2836. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2829-2836.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canning P. C., Deyoe B. L., Roth J. A. Opsonin-dependent stimulation of bovine neutrophil oxidative metabolism by Brucella abortus. Am J Vet Res. 1988 Feb;49(2):160–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caroff M., Bundle D. R., Perry M. B., Cherwonogrodzky J. W., Duncan J. R. Antigenic S-type lipopolysaccharide of Brucella abortus 1119-3. Infect Immun. 1984 Nov;46(2):384–388. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.2.384-388.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloeckaert A., Jacques I., de Wergifosse P., Dubray G., Limet J. N. Protection against Brucella melitensis or Brucella abortus in mice with immunoglobulin G (IgG), IgA, and IgM monoclonal antibodies specific for a common epitope shared by the Brucella A and M smooth lipopolysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):312–315. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.312-315.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloeckaert A., Zygmunt M. S., Nicolle J. C., Dubray G., Limet J. N. O-chain expression in the rough Brucella melitensis strain B115: induction of O-polysaccharide-specific monoclonal antibodies and intracellular localization demonstrated by immunoelectron microscopy. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Jun;138(6):1211–1219. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-6-1211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz R., Garatea P., Jones L. M., Moriyon I. Radial immunodiffusion test with a Brucella polysaccharide antigen for differentiating infected from vaccinated cattle. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jul;10(1):37–41. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.1.37-41.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz R., Jones L. M., Leong D., Wilson J. B. Surface antigens of smooth brucellae. J Bacteriol. 1968 Oct;96(4):893–901. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.4.893-901.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diaz R., Oyeledun M. A. Studies of some biological activities of "brucella" endotoxin in normal and infected animals and the role of the hypersensitivity factor. Ann Sclavo. 1977 Jan-Feb;19(1):117–130. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas J. T., Palmer D. A. Use of monoclonal antibodies to identify the distribution of A and M epitopes on smooth Brucella species. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Jul;26(7):1353–1356. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.7.1353-1356.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freudenberg M. A., Fomsgaard A., Mitov I., Galanos C. ELISA for antibodies to lipid A, lipopolysaccharides and other hydrophobic antigens. Infection. 1989 Sep-Oct;17(5):322–328. doi: 10.1007/BF01650719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamazo C., Winter A. J., Moriyón I., Riezu-Boj J. I., Blasco J. M., Díaz R. Comparative analyses of proteins extracted by hot saline or released spontaneously into outer membrane blebs from field strains of Brucella ovis and Brucella melitensis. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1419–1426. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1419-1426.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurvell B., Lindberg A. A. Serological cross-reactions between different Brucella species and Yersinia enterocolitica. Immunochemical studies on phenol-water extracted lipopolysaccharides from Brucella abortus and Yersinia enterocolitica type IX. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand B Microbiol Immunol. 1973 Feb;81(1):113–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones L. M., Diaz R., Taylor A. G. Characterization of allergens prepared from smooth and rough strains of Brucella melitensis. Br J Exp Pathol. 1973 Oct;54(5):492–508. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurtz R. S., Berman D. T. Influence of endotoxin-protein in immunoglobulin G isotype responses of mice to Brucella abortus lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1986 Dec;54(3):728–734. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.3.728-734.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb V. L., Jones L. M., Schurig G. G., Berman D. T. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for bovine immunoglobulin subclass-specific response to Brucella abortus lipopolysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1979 Oct;26(1):240–247. doi: 10.1128/iai.26.1.240-247.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lind S. M., Kenne L., Lindberg A. A. Mapping of the binding specificity for five monoclonal antibodies recognizing 3-deoxy-D-manno-octulosonic acid in bacterial lipopolysaccharides. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 1;146(11):3864–3870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luk J. M., Nnalue N. A., Lindberg A. A. Efficient production of mouse and rat monoclonal antibodies against the O antigens of Salmonella serogroup C1, using LPS-coated bacteria as immunogen. J Immunol Methods. 1990 May 25;129(2):243–250. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90445-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meikle P. J., Perry M. B., Cherwonogrodzky J. W., Bundle D. R. Fine structure of A and M antigens from Brucella biovars. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2820–2828. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2820-2828.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montaraz J. A., Winter A. J., Hunter D. M., Sowa B. A., Wu A. M., Adams L. G. Protection against Brucella abortus in mice with O-polysaccharide-specific monoclonal antibodies. Infect Immun. 1986 Mar;51(3):961–963. doi: 10.1128/iai.51.3.961-963.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Berman D. T., Boettcher L. A. Biological activities of Brucella abortus lipopolysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):362–370. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.362-370.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Borowiak D., Mayer H. Brucella lipopolysaccharides and polysaccharides. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1987 Jan-Feb;138(1):102–105. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(87)90085-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Jones L. M., Berman D. T. Immunochemical characterization of rough Brucella lipopolysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1984 Mar;43(3):779–782. doi: 10.1128/iai.43.3.779-782.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Kurtz R. S., Berman D. T. Induction of immune and adjuvant immunoglobulin G responses in mice by Brucella lipopolysaccharide. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):74–80. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.74-80.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Mayer H., Moriyon I. Characterization of a native polysaccharide hapten from Brucella melitensis. Infect Immun. 1987 Nov;55(11):2850–2853. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.11.2850-2853.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Pitt M. W., Jones L. M., Schurig G. G., Berman D. T. Purification and characterization of smooth and rough lipopolysaccharides from Brucella abortus. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):361–369. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.361-369.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Speth S. L., Jones L. M., Berman D. T. Immunochemical characterization of Brucella lipopolysaccharides and polysaccharides. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):214–222. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.214-222.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno E., Stackebrandt E., Dorsch M., Wolters J., Busch M., Mayer H. Brucella abortus 16S rRNA and lipid A reveal a phylogenetic relationship with members of the alpha-2 subdivision of the class Proteobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3569–3576. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3569-3576.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen K., Cherwonogrodzky J. W., Duncan J. R., Bundle D. R. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for differentiation of the antibody response of cattle naturally infected with Brucella abortus or vaccinated with strain 19. Am J Vet Res. 1989 Jan;50(1):5–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen K., Wright P. F., Cherwonogrodzky J., Duncan J. R., Stemshorn B. Enzyme immunoassay for diagnosis of bovine brucellosis. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1987 Jan-Feb;138(1):75–79. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(87)90078-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer D. A., Douglas J. T. Analysis of Brucella lipopolysaccharide with specific and cross-reacting monoclonal antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Oct;27(10):2331–2337. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.10.2331-2337.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raetz C. R. Biochemistry of endotoxins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:129–170. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurig G. G., Roop R. M., 2nd, Bagchi T., Boyle S., Buhrman D., Sriranganathan N. Biological properties of RB51; a stable rough strain of Brucella abortus. Vet Microbiol. 1991 Jul;28(2):171–188. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(91)90091-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veerman G. M., Kelman R., Colley J., Pike J. G. Rapid confirmatory identification of Mycobacterium bovis using a dot blotting immunodetection technique. Vet Microbiol. 1990 May;22(4):335–340. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(90)90020-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter A. J. Outer membrane proteins of Brucella. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1987 Jan-Feb;138(1):87–89. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(87)90081-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward M. P., Young W. W., Jr, Bloodgood R. A. Detection of monoclonal antibodies specific for carbohydrate epitopes using periodate oxidation. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Apr 8;78(1):143–153. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90337-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de StGroth S. F., Scheidegger D. Production of monoclonal antibodies: strategy and tactics. J Immunol Methods. 1980;35(1-2):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90146-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]