Abstract
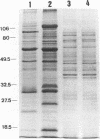
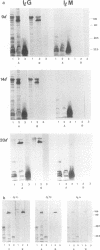
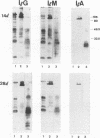
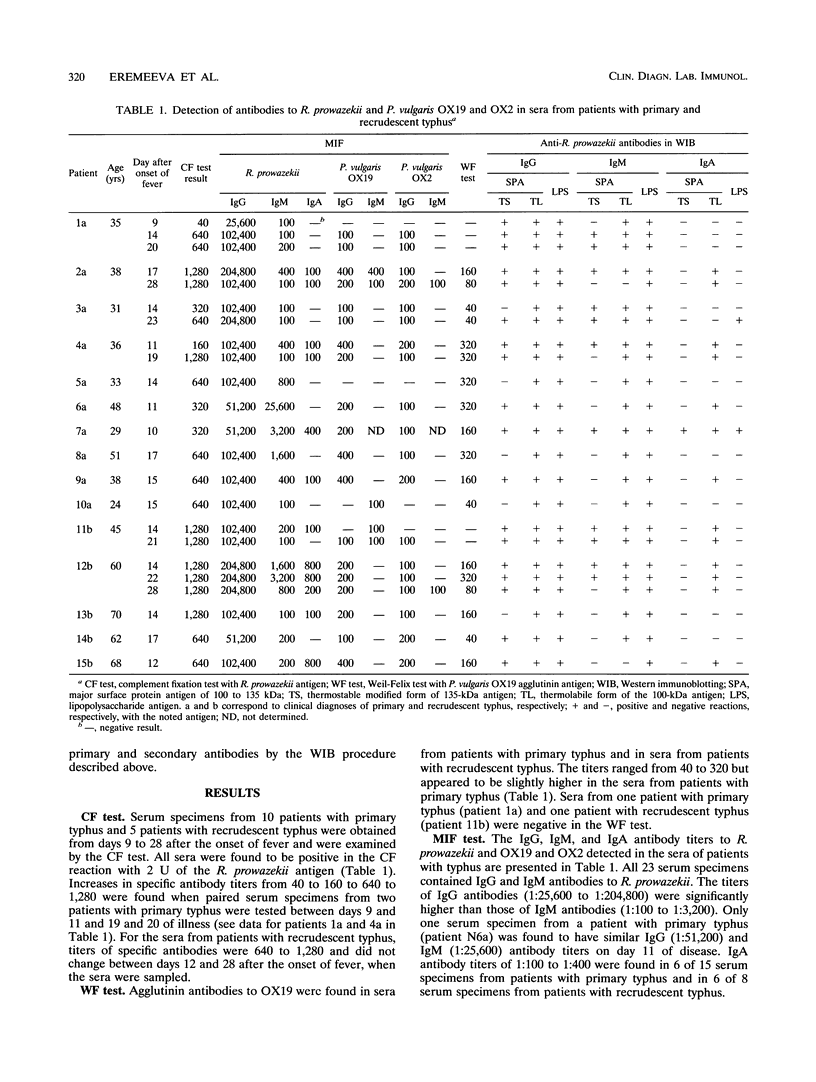
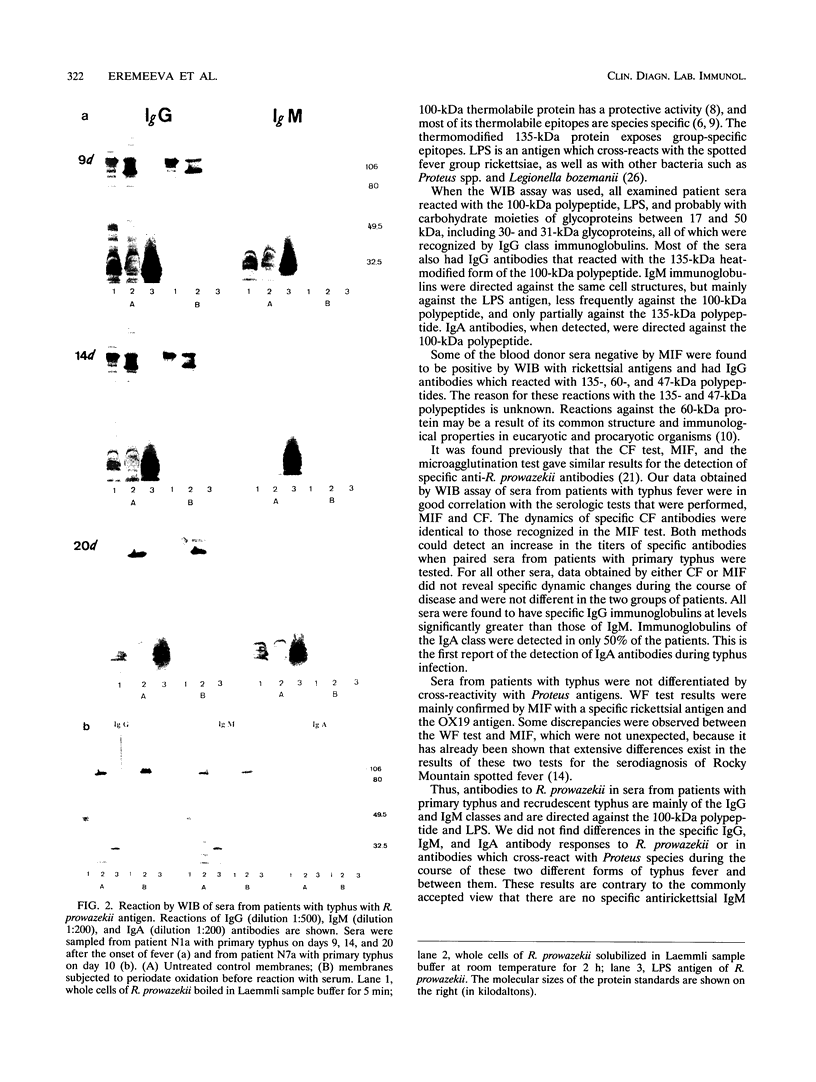
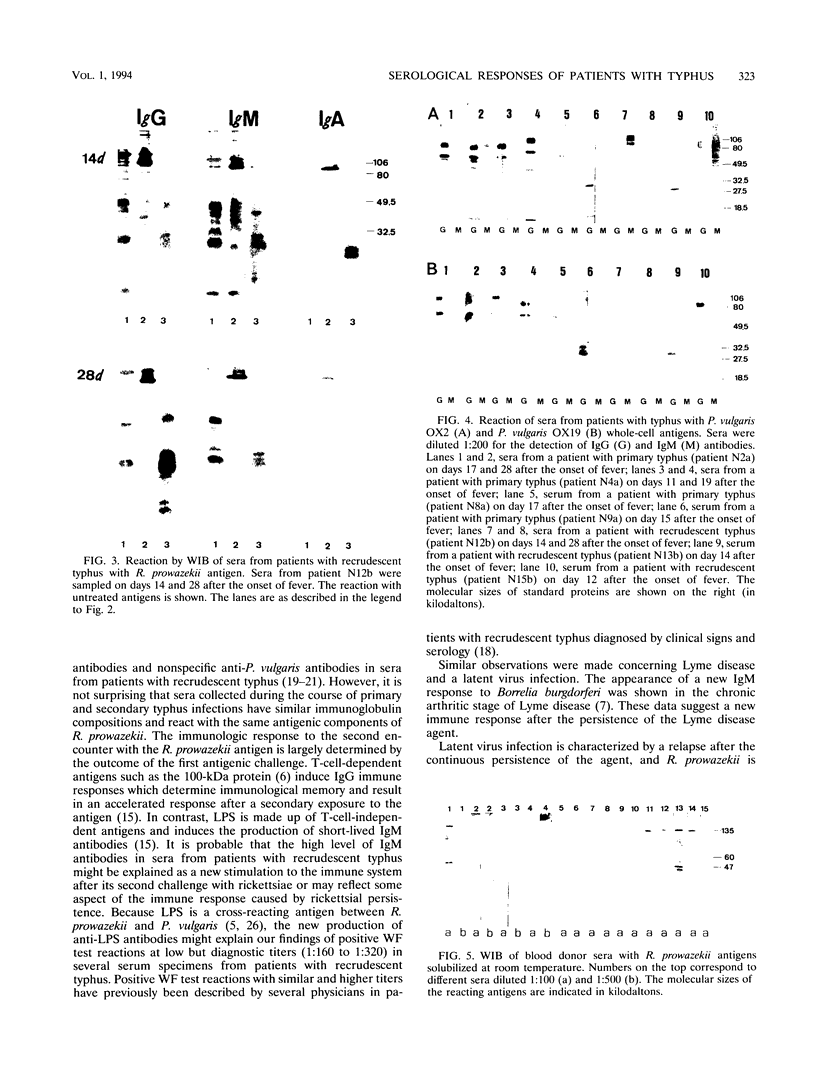
Microimmunofluorescence and Western immunoblotting were compared with the classical complement fixation reaction and the Weil-Felix test to study the serological responses of patients to Rickettsia prowazekii and both Proteus vulgaris OX19 and OX2 during primary and recrudescent typhus infections. The serological response to R. prowazekii was found to be similar during primary and recrudescent typhus, and all sera examined contained antibodies to the same R. prowazekii cell structures. Immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgM were found to be the dominant anti-R. prowazekii immunoglobulins in all sera tested and were found to be directed against the 100-kDa protein and the lipopolysaccharide. IgA antibodies, when present, were mainly against the 100-kDa protein. For P. vulgaris, IgG antibodies recognized the proteins and lipopolysaccharides of both OX19 and OX2 serotypes; IgM antibodies were directed against the P. vulgaris OX2 lipopolysaccharide. In addition, donor blood sera, which were negative by microimmunofluorescence, were found to contain IgG immunoglobulins reacting with R. prowazekii protein antigens of 135, 60, and 47 kDa by western immunoblotting.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aniskovich L. P., Eremeeva M. E., Balaeva N. M., Ignatovich V. F., Artemiev M. I., Emelyanov V. V., Smirnova N. S. Methods for purification of Rickettsia prowazekii separated from the host tissue: a step-by-step comparison. Acta Virol. 1989 Aug;33(4):361–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashley R. L., Militoni J., Lee F., Nahmias A., Corey L. Comparison of Western blot (immunoblot) and glycoprotein G-specific immunodot enzyme assay for detecting antibodies to herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 in human sera. J Clin Microbiol. 1988 Apr;26(4):662–667. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.4.662-667.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balayeva N. M., Eremeeva M. E., Ignatovich V. F., Dmitriev B. A., Lapina E. B., Belousova L. S. Protein antigens of genetically related Rickettsia prowazekii strains with different virulence. Acta Virol. 1992 Jan;36(1):52–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ching W. M., Dasch G. A., Carl M., Dobson M. E. Structural analyses of the 120-kDa serotype protein antigens of typhus group rickettsiae. Comparison with other S-layer proteins. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;590:334–351. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42241.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craft J. E., Fischer D. K., Shimamoto G. T., Steere A. C. Antigens of Borrelia burgdorferi recognized during Lyme disease. Appearance of a new immunoglobulin M response and expansion of the immunoglobulin G response late in the illness. J Clin Invest. 1986 Oct;78(4):934–939. doi: 10.1172/JCI112683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasch G. A., Ching W. M., Kim P. Y., Pham H., Stover C. K., Oaks E. V., Dobson M. E., Weiss E. A structural and immunological comparison of rickettsial HSP60 antigens with those of other species. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;590:352–369. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42242.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberle R., Mou S. W. Relative titers of antibodies to individual polypeptide antigens of herpes simplex virus type 1 in human sera. J Infect Dis. 1983 Sep;148(3):436–444. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.3.436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eremeeva M. E., Lapina E. B., Balaeva N. M., Ignatovich V. F., Belousova L. S. Elektroforeticheskaia i immunokhimicheskaia kharakteristika belkov shtamma Rickettsia prowazekii razlichnoi virulentnosti. Mol Gen Mikrobiol Virusol. 1989 May;(5):20–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hechemy K. E., Stevens R. W., Sasowski S., Michaelson E. E., Casper E. A., Philip R. N. Discrepancies in Weil-Felix and microimmunofluorescence test results for Rocky Mountain spotted fever. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Feb;9(2):292–293. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.2.292-293.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY E. S., GAON J. A., O'CONNOR J. M., MULAHASANOVIC M. SEROLOGIC STUDIES OF PRIMARY EPIDEMIC TYPHUS AND RECRUDESCENT TYPHUS (BRILL-ZINSSER DISEASE). I. DIFFERENCES IN COMPLEMENT-FIXING ANTIBODIES: HIGH ANTIGEN REQUIREMENT AND HEAT LABILITY. J Immunol. 1965 May;94:723–733. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURRAY E. S., O'CONNOR J. M., GAON J. A. SEROLOGIC STUDIES OF PRIMARY EPIDEMIC TYPHUS AND RECRUDESCENT TYPHUS (BRILL-ZINSSER DISEASE). II. DIFFERENCES IN IMMUNOELECTROPHORETIC PATTERNS, RESPONSE TO 2-MERCAPTOETHANOL AND RELATIONSHIPS TO 19 S AND 7 S ANTIBODIES. J Immunol. 1965 May;94:734–740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormsbee R., Peacock M., Philip R., Casper E., Plorde J., Gabre-Kidan T., Wright L. Serologic diagnosis of epidemic typhus fever. Am J Epidemiol. 1977 Mar;105(3):261–271. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. Determination of total protein. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:95–119. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raoult D., Hechemy K. E., Chaudet H. Sérologie de la fièvre boutonneuse méditerranéenne. Cinétique des anticorps détectés par trois méthodes: l'immunofluorescence indirecte, l'hémagglutination indirecte, et l'agglutination latex. Pathol Biol (Paris) 1985 Oct;33(8):839–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner J. J., Smith K. O. Serum antibodies to herpes simplex virus type 1 during active oral herpes infection. Infect Immun. 1980 Jan;27(1):113–117. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.1.113-117.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompolinsky D., Boldur I., Goldwasser R. A., Kahana H., Kazak R., Keysary A., Pik A. Serological cross-reactions between Rickettsia typhi, Proteus vulgaris OX19, and Legionella bozemanii in a series of febrile patients. Isr J Med Sci. 1986 Oct;22(10):745–752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. M., Frasch C. E. A sensitive silver stain for detecting lipopolysaccharides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodward M. P., Young W. W., Jr, Bloodgood R. A. Detection of monoclonal antibodies specific for carbohydrate epitopes using periodate oxidation. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Apr 8;78(1):143–153. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90337-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]