Abstract
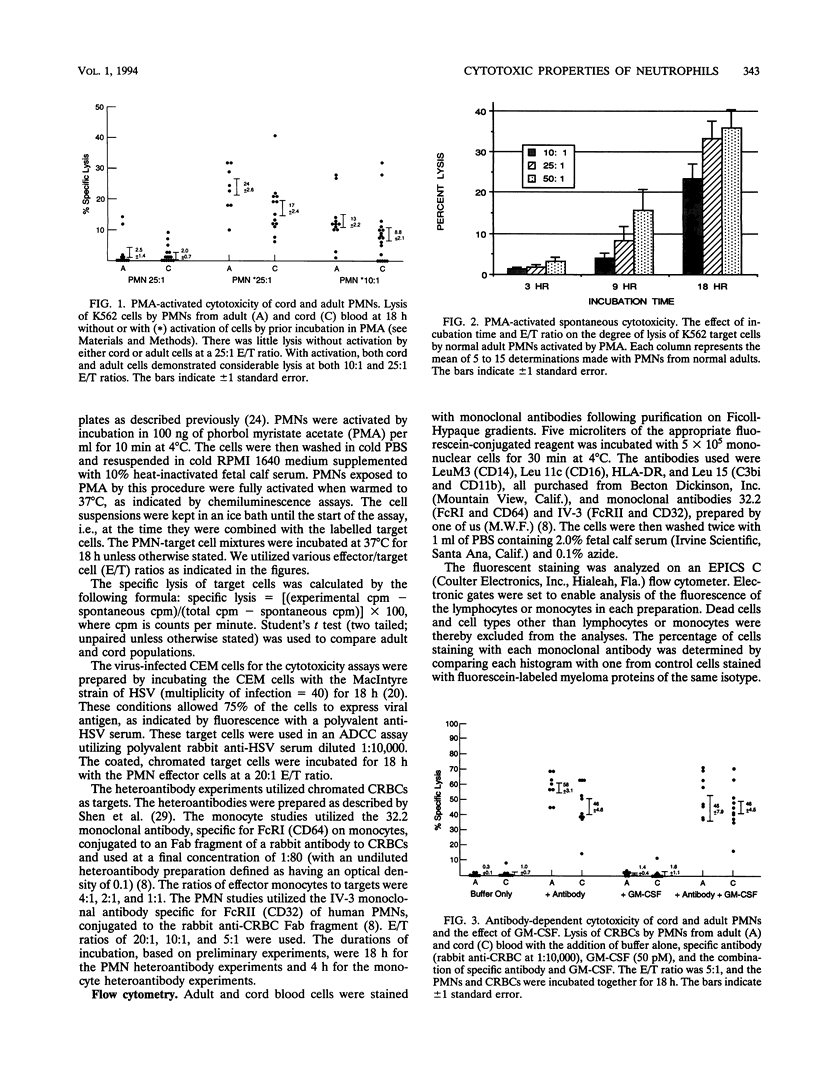
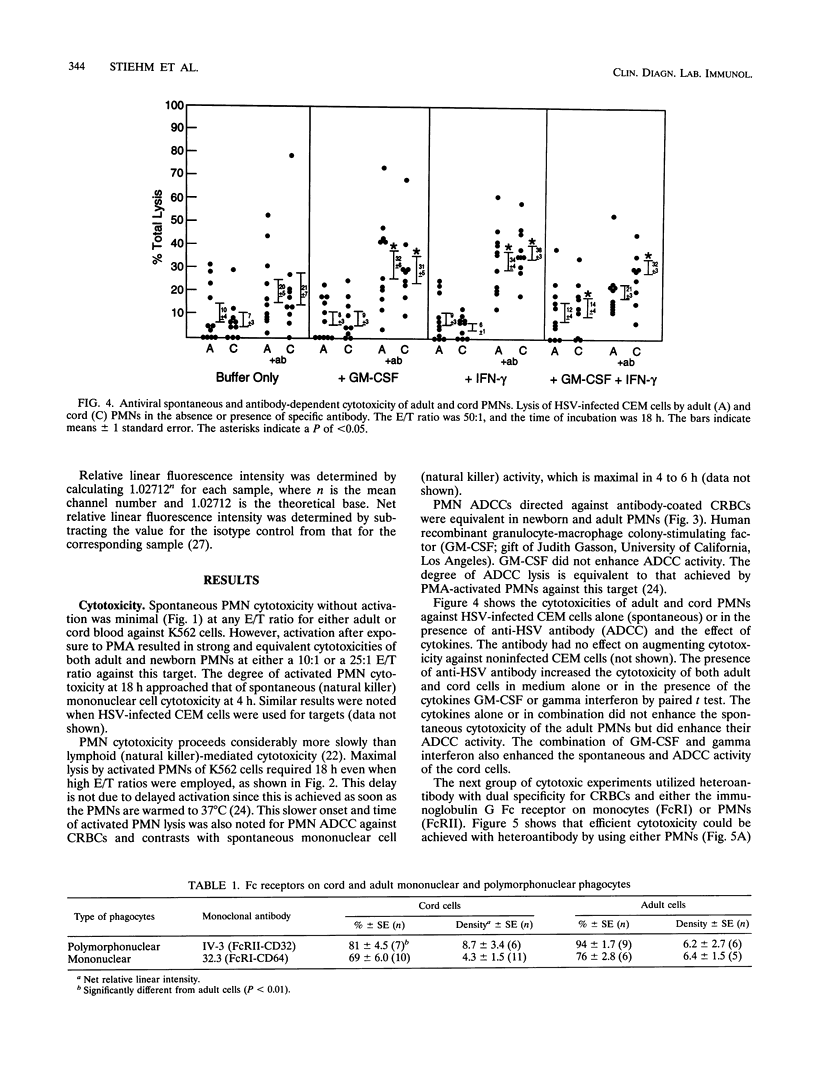
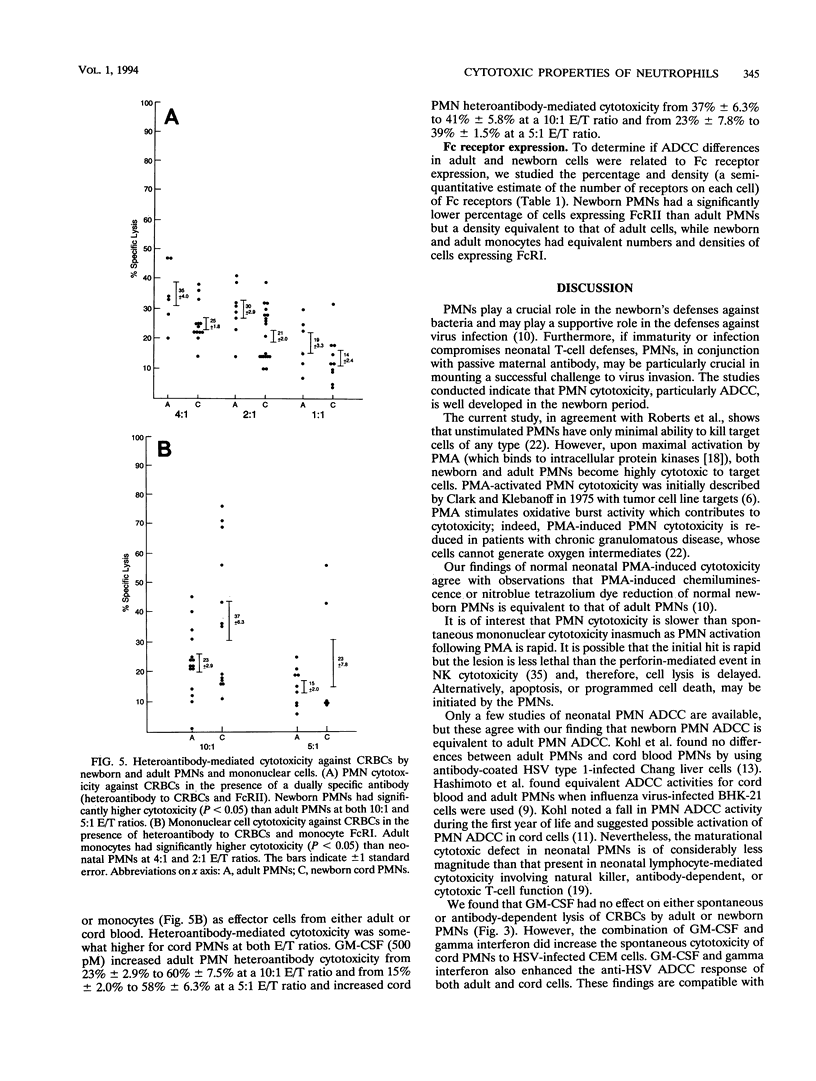
We studied cytotoxic capabilities of newborn polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNs) and monocytes and their enhancement by cytokines and antibodies. Umbilical cord PMNs were assessed for their ability to kill various target cells spontaneously, after activation with phorbol myristate acetate, in the presence of antiserum (antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity), and in the presence of dually specific antibody (heteroantibody-mediated cytotoxicity). Target cells included the K562 cell line (natural killer cell target), chicken erythrocytes (CRBCs), and herpes simplex virus-infected CEM cell lines. Newborn PMNs were equivalent to adult PMNs in their cytotoxic capacity in several cytotoxicity assays. Neither adult nor newborn PMNs lyse tumor cell targets (i.e., K562 cells) spontaneously, but both lyse K562 cells following activation with phorbol myristate acetate. Both adult and newborn PMNs lyse CRBCs and herpes simplex virus-infected CEM cells in antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity assays, and this lysis could be enhanced by the cytokines granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and gamma interferon. PMN heteroantibody-mediated cytotoxicity, resulting from the use of an antibody with dual specificity to CRBCs and immunoglobulin G FcRII, was greater in newborn PMNs than in adult PMNs; however, monocyte heteroantibody-mediated cytotoxicity, resulting from the use of an antibody to CRBCs and monocyte immunoglobulin G FcRI, was lower in newborn monocytes than in adult monocytes. The percentage, but not the density, of PMNs expressing FcRII was significantly reduced in newborn PMNs compared with that in adult PMNs, while the percentages and densities of FcRI expression were equivalent in newborn and adult monocytes. We conclude that the cytotoxic capability in term newborn PMNs is equivalent to that in adult PMNs, that the activity of newborn PMNs can be enhanced by antibody and/or cytokines, and that PMNs can contribute to the newborn's ability to kill virus-infected cells.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldwin G. C., Gasson J. C., Quan S. G., Fleischmann J., Weisbart R., Oette D., Mitsuyasu R. T., Golde D. W. Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor enhances neutrophil function in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2763–2766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryson Y. J., Winter H. S., Gard S. E., Fischer T. J., Stiehm E. R. Deficiency of immune interferon production by leukocytes of normal newborns. Cell Immunol. 1980 Sep 15;55(1):191–200. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(80)90150-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cairo M. S., van de Ven C., Toy C., Mauss D., Sender L. Recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor primes neonatal granulocytes for enhanced oxidative metabolism and chemotaxis. Pediatr Res. 1989 Nov;26(5):395–399. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198911000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr R., Davies J. M. Abnormal FcRIII expression by neutrophils from very preterm neonates. Blood. 1990 Aug 1;76(3):607–611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr R., Huizinga T. W., Kleijer M., Davies J. M. Changes in plasma FcRIII demonstrate increasing receptor production during late pregnancy and after preterm birth. Pediatr Res. 1992 Nov;32(5):505–508. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199211000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. A., Klebanoff S. J. Neutrophil-mediated tumor cell cytotoxicity: role of the peroxidase system. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1442–1447. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faden H., Ogra P. Neutrophils and antiviral defense. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1986 Jan-Feb;5(1):86–92. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198601000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanger M. W., Shen L., Graziano R. F., Guyre P. M. Cytotoxicity mediated by human Fc receptors for IgG. Immunol Today. 1989 Mar;10(3):92–99. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(89)90234-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto G., Wright P. F., Karzon D. T. Ability of human cord blood lymphocytes to mediate antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity against influenza virus-infected cells. Infect Immun. 1983 Oct;42(1):214–218. doi: 10.1128/iai.42.1.214-218.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill H. R. Biochemical, structural, and functional abnormalities of polymorphonuclear leukocytes in the neonate. Pediatr Res. 1987 Oct;22(4):375–382. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198710000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S. Defective infant antiviral cytotoxicity to herpes simplex virus-infected cells. J Pediatr. 1983 Jun;102(6):885–888. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(83)80019-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S., Frazier J. P., Pickering L. K., Loo L. S. Normal function of neonatal polymorphonuclear leukocytes in antibody-dependent cellular-cytotoxicity to herpes simplex virus-infected cells. J Pediatr. 1981 May;98(5):783–785. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(81)80847-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohl S. Role of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in defense against herpes simplex virus infections. Rev Infect Dis. 1991 Jan-Feb;13(1):108–114. doi: 10.1093/clinids/13.1.108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrer R. I., Daher K., Ganz T., Selsted M. E. Direct inactivation of viruses by MCP-1 and MCP-2, natural peptide antibiotics from rabbit leukocytes. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):467–472. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.467-472.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis D. B., Yu C. C., Meyer J., English B. K., Kahn S. J., Wilson C. B. Cellular and molecular mechanisms for reduced interleukin 4 and interferon-gamma production by neonatal T cells. J Clin Invest. 1991 Jan;87(1):194–202. doi: 10.1172/JCI114970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maródi L., Leijh P. C., van Furth R. Characteristics and functional capacities of human cord blood granulocytes and monocytes. Pediatr Res. 1984 Nov;18(11):1127–1131. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198411000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda K., Kinoshita Y., Kobayashi Y. Heterogeneity of Fc receptor expression in chemotaxis and adherence of neonatal neutrophils. Pediatr Res. 1989 Jan;25(1):6–10. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198901000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May W. S., Sahyoun N., Jacobs S., Wolf M., Cuatrecasas P. Mechanism of phorbol diester-induced regulation of surface transferrin receptor involves the action of activated protein kinase C and an intact cytoskeleton. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 5;260(16):9419–9426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaeger-Marshall S., Ank B. J., Altenburger K. M., Pizer L. I., Johnston R. B., Jr, Stiehm E. R. Replication of herpes simplex virus in blood monocytes and placental macrophages from human neonates. Pediatr Res. 1989 Aug;26(2):135–139. doi: 10.1203/00006450-198908000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pross S. H., Hallock J. A., Armstrong R., Fishel C. W. Complement and Fc receptors on cord blood and adult neutrophils. Pediatr Res. 1977 Feb;11(2):135–137. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197702000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. L., Ank B. J., Fanger M. W., Shen L., Stiehm E. R. Role of oxygen intermediates in cytotoxicity: studies in chronic granulomatous disease. Inflammation. 1993 Feb;17(1):77–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00916393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. L., Ank B. J., Salusky I. B., Stiehm E. R. Purification and properties of peritoneal eosinophils from pediatric dialysis patients. J Immunol Methods. 1990 Feb 9;126(2):205–211. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(90)90152-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. L., Ank B. J., Stiehm E. R. Human eosinophils are more toxic than neutrophils in antibody-independent killing. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1991 Jun;87(6):1105–1115. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(91)92156-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts R. L., Hatori N., Drury J. K., Stiehm E. R. Purification and properties of porcine polymorphonuclear cells. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Oct 23;103(1):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouse B. T., Babiuk L. A., Henson P. M. Neutrophils in antiviral immunity: inhibition of virus replication by a mediator produced by bovine neutrophils. J Infect Dis. 1980 Feb;141(2):223–232. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.2.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid I., Schmid P., Giorgi J. V. Conversion of logarithmic channel numbers into relative linear fluorescence intensity. Cytometry. 1988 Nov;9(6):533–538. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990090605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L., Guyre P. M., Anderson C. L., Fanger M. W. Heteroantibody-mediated cytotoxicity: antibody to the high affinity Fc receptor for IgG mediates cytotoxicity by human monocytes that is enhanced by interferon-gamma and is not blocked by human IgG. J Immunol. 1986 Dec 1;137(11):3378–3382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen L., Guyre P. M., Fanger M. W. Polymorphonuclear leukocyte function triggered through the high affinity Fc receptor for monomeric IgG. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 15;139(2):534–538. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. B., Campbell D. E., Ludomirsky A., Polin R. A., Douglas S. D., Garty B. Z., Harris M. C. Expression of the complement receptors CR1 and CR3 and the type III Fc gamma receptor on neutrophils from newborn infants and from fetuses with Rh disease. Pediatr Res. 1990 Aug;28(2):120–126. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199008000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speer C. P., Ambruso D. R., Grimsley J., Johnston R. B., Jr Oxidative metabolism in cord blood monocytes and monocyte-derived macrophages. Infect Immun. 1985 Dec;50(3):919–921. doi: 10.1128/iai.50.3.919-921.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szelc C. M., Mitcheltree C., Roberts R. L., Stiehm E. R. Deficient polymorphonuclear cell and mononuclear cell antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in pediatric and adult human immunodeficiency virus infection. J Infect Dis. 1992 Sep;166(3):486–493. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.3.486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward P. A., Cohen S., Flanagan T. D. Leukotactic factors elaborated by virus-infected tissues. J Exp Med. 1972 May 1;135(5):1095–1103. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.5.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West B. C., Escheté M. L., Cox M. E., King J. W. Neutrophil uptake of vaccinia virus in vitro. J Infect Dis. 1987 Oct;156(4):597–606. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.4.597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteside T. L., Herberman R. B. The role of natural killer cells in human disease. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1989 Oct;53(1):1–23. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(89)90096-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



