Abstract
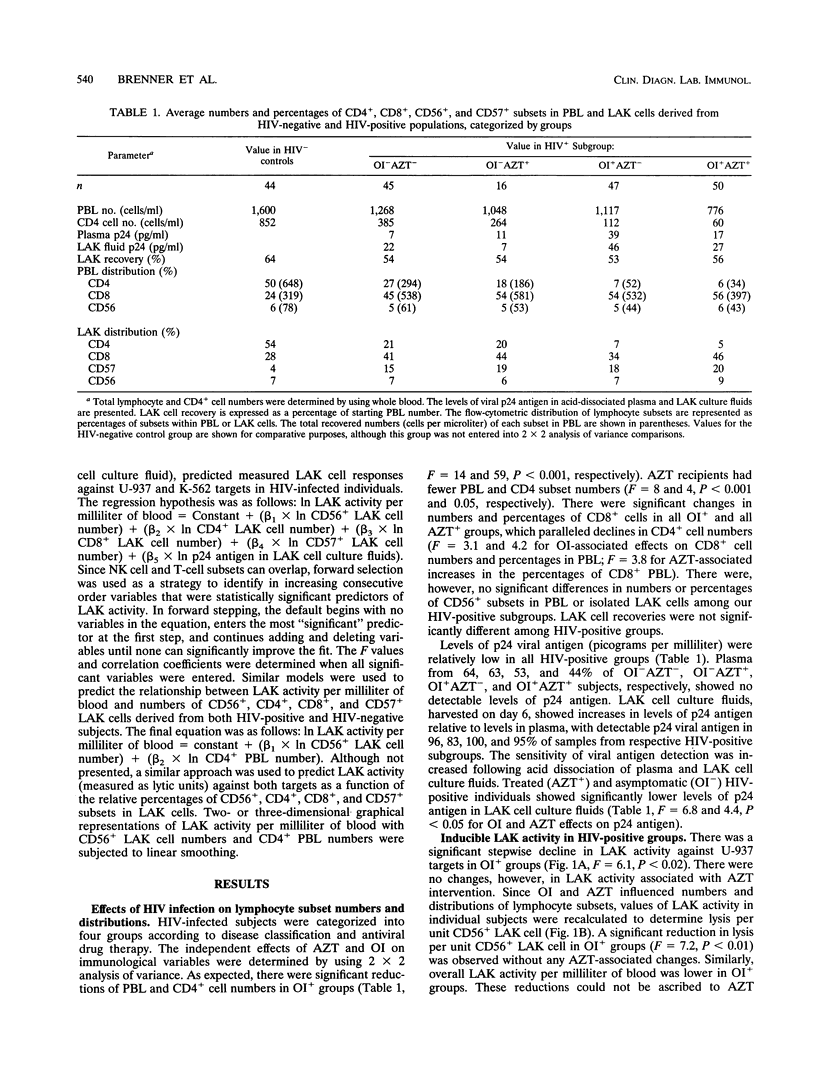
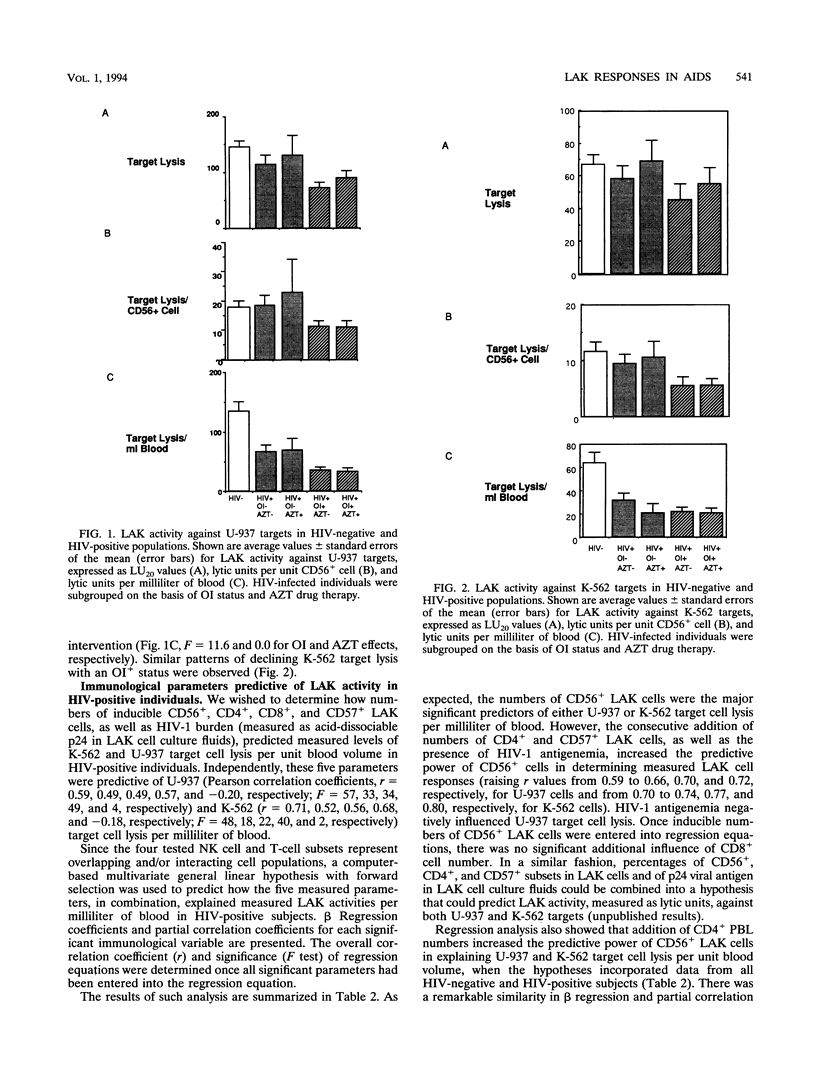
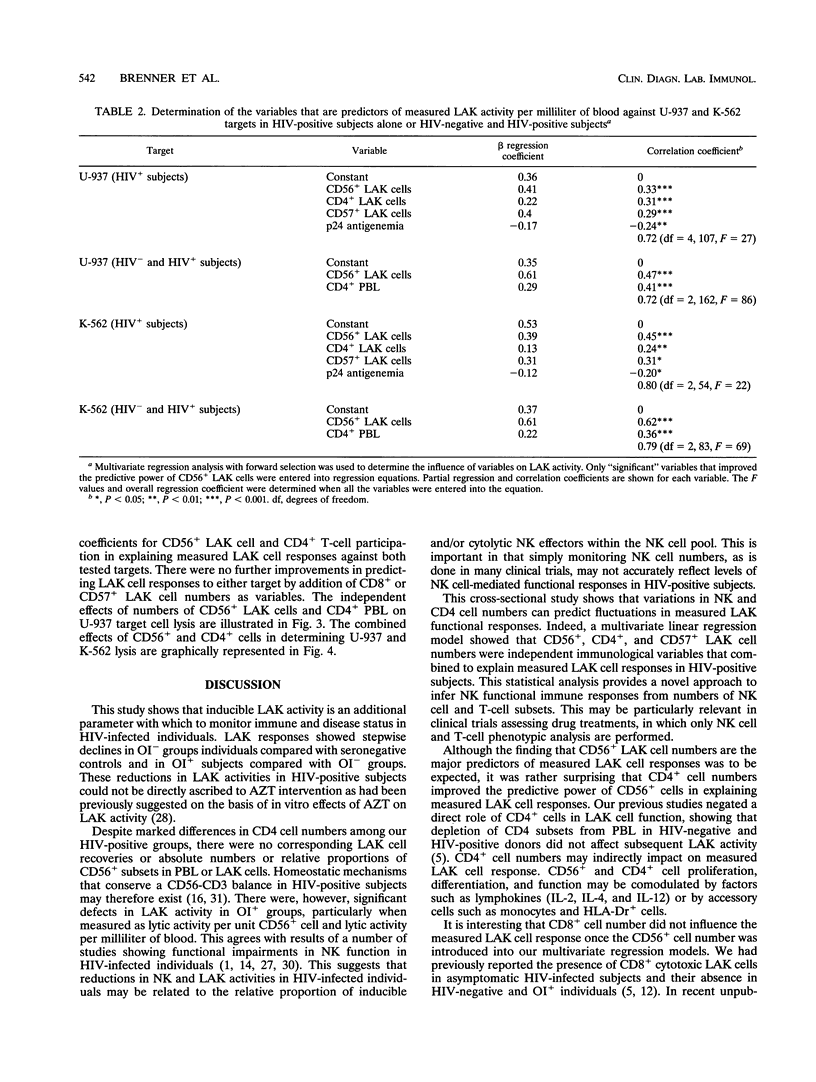
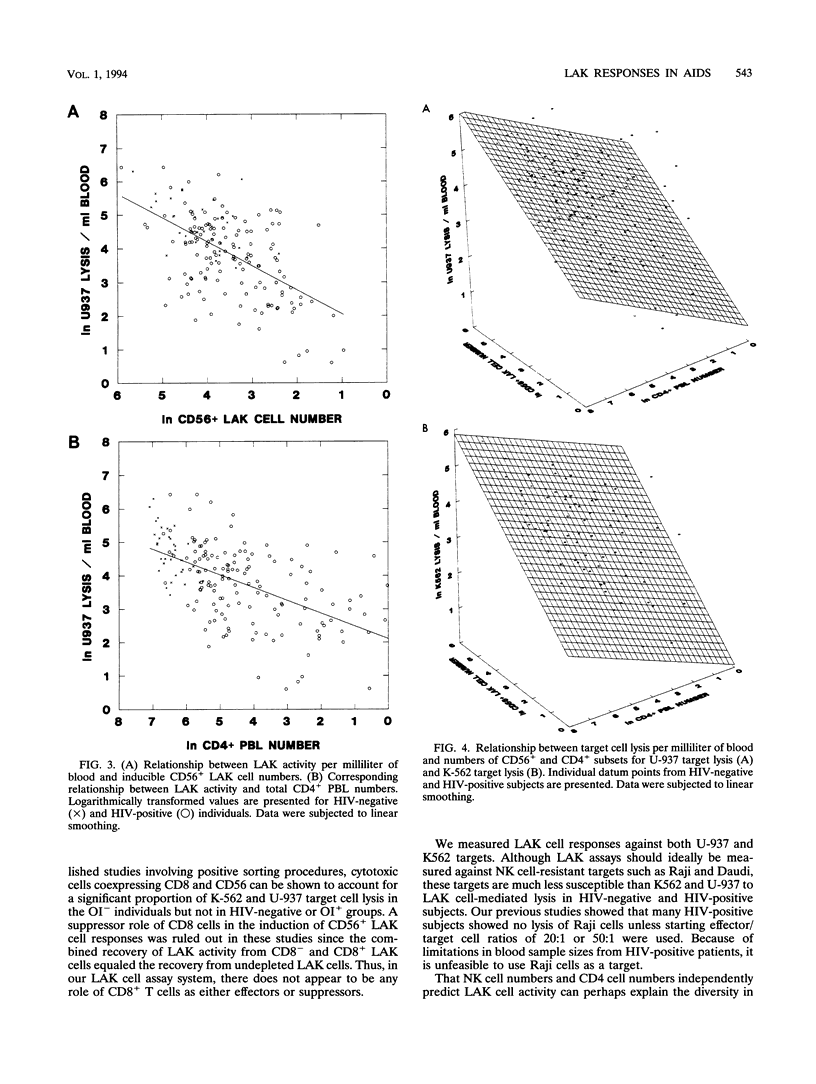
The functions of natural killer (NK) cells and their interleukin-2-deducible counterparts, lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) cells, are often impaired in human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected individuals. A statistical approach was used to establish if changes in LAK activity were associated with antiviral drug therapy, HIV-1 burden, or lymphocyte subset alterations. Our study group included 61 HIV-positive subjects without any opportunistic infections (OI-), 16 of whom received zidovudine (AZT), and 97 HIV-positive individuals with AIDS-related infection (OI+), 50 of whom received AZT. As expected, there was a stepwise decrease in total lymphocyte numbers in OI+ groups as a result of the selective loss of CD4+ cells. The groups receiving AZT therapy had fewer CD4+ cells but lower circulating p24 antigen levels than corresponding untreated groups did. No significant changes in the relative proportions or absolute numbers of CD56+ subsets in HIV-positive groups could be ascribed to OI status or AZT intervention. LAK cell cytotoxic responses, measured as LU20 values (which give a measure of 20% cytolysis of target cells), lysis per unit CD56+ NK cell, or lysis per unit blood volume, declined in OI+ groups. No main or interactive effects of AZT therapy on LAK activities were observed. Multivariate general linear models were used to determine the interactive effects of NK- and T-cell subsets on measured LAK cell numbers were added negative and positive predictors of LAK activity, respectively. These findings indicate that declines in NK-mediated LAK cell responses serve as functional correlates of progression in HIV-infected individuals.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bonavida B., Katz J., Gottlieb M. Mechanism of defective NK cell activity in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and AIDS-related complex. I. Defective trigger on NK cells for NKCF production by target cells, and partial restoration by IL 2. J Immunol. 1986 Aug 15;137(4):1157–1163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. G., Benarrosh S., Margolese R. G. Peripheral blood natural killer cell activity in human breast cancer patients and its modulation by T-cell growth factor and autologous plasma. Cancer. 1986 Aug 15;58(4):895–902. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19860815)58:4<895::aid-cncr2820580416>3.0.co;2-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. G., Dascal A., Margolese R. G., Wainberg M. A. Natural killer cell function in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and related diseases. J Leukoc Biol. 1989 Jul;46(1):75–83. doi: 10.1002/jlb.46.1.75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. G., Gryllis C., Gornitsky M., Cupples W., Wainberg M. Differential effects of chemotherapy-induced and HIV-1-induced immunocompromise on NK and LAK activities using breast cancer and HIV-1 seropositive patient populations. Anticancer Res. 1991 Mar-Apr;11(2):969–974. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. G., Gryllis C., Gornitsky M., Wainberg M. A. Changes in natural immunity during the course of HIV-1 infection. Clin Exp Immunol. 1993 Aug;93(2):142–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1993.tb07956.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner B. G., Gryllis C., Wainberg M. A. Role of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and lymphokine-activated killer cells in AIDS and related diseases. J Leukoc Biol. 1991 Dec;50(6):628–640. doi: 10.1002/jlb.50.6.628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cauda R., Tumbarello M., Ortona L., Kanda P., Kennedy R. C., Chanh T. C. Inhibition of normal human natural killer cell activity by human immunodeficiency virus synthetic transmembrane peptides. Cell Immunol. 1988 Aug;115(1):57–65. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(88)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chehimi J., Bandyopadhyay S., Prakash K., Perussia B., Hassan N. F., Kawashima H., Campbell D., Kornbluth J., Starr S. E. In vitro infection of natural killer cells with different human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1812–1822. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1812-1822.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dadaglio G., Michel F., Langlade-Demoyen P., Sansonetti P., Chevrier D., Vuillier F., Plata F., Hoffenbach A. Enhancement of HIV-specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses by zidovudine (AZT) treatment. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Jan;87(1):7–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06405.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischl M. A., Richman D. D., Causey D. M., Grieco M. H., Bryson Y., Mildvan D., Laskin O. L., Groopman J. E., Volberding P. A., Schooley R. T. Prolonged zidovudine therapy in patients with AIDS and advanced AIDS-related complex. AZT Collaborative Working Group. JAMA. 1989 Nov 3;262(17):2405–2410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryllis C., Wainberg M. A., Bentwich Z., Gornitsky M., Brenner B. G. Increased LAK activity against HIV-infected cell lines in HIV-1+ individuals. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Sep;89(3):356–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06962.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gryllis C., Wainberg M. A., Gornitsky M., Brenner B. Diminution of inducible lymphokine-activated killer cell activity in individuals with AIDS-related disorders. AIDS. 1990 Dec;4(12):1205–1212. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199012000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J. D., Mitsuyasu R., Gottlieb M. S., Lebow L. T., Bonavida B. Mechanism of defective NK cell activity in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) and AIDS-related complex. II. Normal antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) mediated by effector cells defective in natural killer (NK) cytotoxicity. J Immunol. 1987 Jul 1;139(1):55–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landay A., Ohlsson-Wilhelm B., Giorgi J. V. Application of flow cytometry to the study of HIV infection. AIDS. 1990 Jun;4(6):479–497. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199006000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levacher M., Hulstaert F., Tallet S., Ullery S., Pocidalo J. J., Bach B. A. The significance of activation markers on CD8 lymphocytes in human immunodeficiency syndrome: staging and prognostic value. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Dec;90(3):376–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb05854.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazza P., Bocchia M., Tumietto F., Costigliola P., Coronado O., Bandini G., Conte R., Ricchi E., Vianelli N., Raise E. Recombinant interleukin-2 (rIL-2) in acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS): preliminary report in patients with lymphoma associated with HIV infection. Eur J Haematol. 1992 Jul;49(1):1–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0609.1992.tb00905.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon D. K., Winkelstein A., Armstrong J. A., Pazin G. J., Hawk H., Ho M. Zidovudine therapy is associated with an increased capacity of phytohemagglutinin-stimulated cells to express interleukin-2 receptors. Pittsburgh AIDS Clinical Trial Unit. AIDS. 1991 May;5(5):491–496. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199105000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinching A. J. HIV/AIDS pathogenesis and treatment: new twists and turns. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991 Aug;3(4):537–542. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(91)90017-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pross H. F., Baines M. G., Rubin P., Shragge P., Patterson M. S. Spontaneous human lymphocyte-mediated cytotoxicity against tumor target cells. IX. The quantitation of natural killer cell activity. J Clin Immunol. 1981 Jan;1(1):51–63. doi: 10.1007/BF00915477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappocciolo G., Toso J. F., Torpey D. J., 3rd, Gupta P., Rinaldo C. R., Jr Association of alpha interferon production with natural killer cell lysis of U937 cells infected with human immunodeficiency virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1989 Jan;27(1):41–48. doi: 10.1128/jcm.27.1.41-48.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richman D. D., Fischl M. A., Grieco M. H., Gottlieb M. S., Volberding P. A., Laskin O. L., Leedom J. M., Groopman J. E., Mildvan D., Hirsch M. S. The toxicity of azidothymidine (AZT) in the treatment of patients with AIDS and AIDS-related complex. A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 23;317(4):192–197. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707233170402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson M. J., Ritz J. Biology and clinical relevance of human natural killer cells. Blood. 1990 Dec 15;76(12):2421–2438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. H., Skowron G., Merigan T. C. Safety and effects of interleukin-2 plus zidovudine in asymptomatic individuals infected with human immunodeficiency virus. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 1991;4(1):11–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott-Algara D., Vuillier F., Cayota A., Dighiero G. Natural killer (NK) cell activity during HIV infection: a decrease in NK activity is observed at the clonal level and is not restored after in vitro long-term culture of NK cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Nov;90(2):181–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb07925.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sirianni M. C., Soddu S., Malorni W., Arancia G., Aiuti F., Soddus S. Mechanism of defective natural killer cell activity in patients with AIDS is associated with defective distribution of tubulin. J Immunol. 1988 Apr 15;140(8):2565–2568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stine K. C., Tyler D. S., Stanley S. D., Bartlett J. A., Bolognesi D. P., Weinhold K. J. The effect of AZT on in vitro lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) activity in human immunodeficiency virus type-1 (HIV-1) infected individuals. Cell Immunol. 1991 Aug;136(1):165–172. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(91)90391-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G. Biology of natural killer cells. Adv Immunol. 1989;47:187–376. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(08)60664-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler D. S., Stanley S. D., Nastala C. A., Austin A. A., Bartlett J. A., Stine K. C., Lyerly H. K., Bolognesi D. P., Weinhold K. J. Alterations in antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity during the course of HIV-1 infection. Humoral and cellular defects. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3375–3384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



