Abstract
Inorganic arsenic is a well-known human skin carcinogen. Chronic arsenic exposure results in various types of human skin lesions, including squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). To investigate whether mutant stem cells participate in arsenic-associated carcinogenesis, we repeatedly exposed the human spontaneously immortalized skin keratinocytes (HaCaT) cell line to an environmentally relevant level of arsenic (0.05 ppm) in vitrofor 18 weeks. Following sodium arsenite administration, cell cycle, colony-forming efficiency (CFE), cell tumorigenicity, and expression of CD44v6, NF-κB and p53, were analyzed at different time points (0, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25 and 30 passages). We found that a chronic exposure of HaCaT cells to a low level of arsenic induced a cancer stem-like phenotype. Furthermore, arsenictreated HaCaT cells also became tumorigenic in nude mice, their growth cycle was predominantly in G2/M and S phases. Relative to nontreated cells, they exhibited a higher growth rate and a significant increase in CFE. Western blot analysis found that arsenic was capable of increasing cell proliferation and sprouting of cancer stem-like phenotype. Additionally, immunohistochemical analysis demonstrated that CD44v6 expression was upregulated in HaCaT cells exposed to a low level of arsenic during early stages of induction. The expression of CD44v6 in arsenic-treated cells was positively correlated with their cloning efficiency in soft agar (r=0.949, P=0.01). Likewise, the expressions of activating transcription factor NF-κB and p53 genes in the arsenic-treated HaCaT cells were significantly higher than that in non-treated cells. Higher expressions of CD44v6, NF-κB and p53 were also observed in tumor tissues isolated from Balb/c nude mice. The present results suggest that CD44v6 may be a biomarker of arsenicinduced neoplastic transformation in human skin cells, and that arsenic promotes malignant transformation in human skin lesions through a NF-κB signaling pathway-stimulated expression of CD44v6.
Key words: arsenic, human skin keratinocytes, malignant transformation, cell surface markers, CD44v6.
Introduction
Arsenic has been recognized as a Class 1 carcinogen by the International Agency for Research on Cancer in 2004.1 Epidemiological researches indicate that individuals exposed to arsenic are at a higher risk for developing skin, liver, and bladder cancers.2–7 The skin is a major target of arsenic exposure and one of the most sensitive tissues to chronic arsenic exposure. Chronic exposure to arsenic results in various epidermal alterations, including hyperpigmentation, hyperkeratosis, squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) and basal cell carcinoma. Although inorganic arsenic alone does not seem to independently induce skin cancer in animals, it definitely acts together with UV irradiation to stimulate skin cancer in mouse.8,9 Nevertheless, there is still a lack of specific molecular biomarkers to detect arsenic-induced early malignant lesions. Increasing recent evidence indicates that cancers may develop from a small subpopulation of cancer stem cells (CSCs) present in both solid tumors and hematological malignancies.10–14 Analysis of biomarker expression during tumor formation may help to gain a better insight into the process of tumorigenesis and to identify new markers for early diagnosis of squamous cell malignant transformation.14–17 The CSCs biomarkers can be identified by the expression of a variety of cell surface markers, including CD133 and CD44, some of which have phenotypic significance18 and show higher expression of a variety of stem cell maintenance-related genes, including Oct-4, p63 and Notch.10,14,19
CD44 is the receptor for hyaluronic acid (HA). It mediates cell to cell and cell matrix interactions through its affinity for HA. CD44 plays an important role in cell migration, tumor growth and progression, lymphocyte activation recirculation and homing, and hematopoiesis.20–23 CD44 receptor (CD44R) represents a heterogeneous group of CD44 variant isoforms expressed constitutively in epithelial cells and monocyte lineage cells and can be up-regulated in activated leukocytes. CD44R and, in particular, CD44v6 isoforms may be involved in leukocyte attachment to and rolling on endothelial cells, homing to peripheral lymphoid organs and to sites of inflammation. The role of CD44v6 in tumor metastasis has been attributed to an ability to confer metastatic potential to nonmetastatic cell lines,21,24,25 leading to tumor progression and metastasis in human cancers.26,27 Expression of CD44v6 has been found to correlate significantly with lymphatic and/or hematogenous metastasis.28
Arsenic is a well-documented carcinogen that also appears to be a valuable therapeutic tool in cancer treatment.29 Arsenic trioxide (As2O3) was shown to inhibit tumor metastasis by reducing the expression of metastasis-related genes, including CD44v6;30–33 but arsenic cytotoxicity is dependent on the degree of exposure, and presentation of pleiotropic cellular effects.34–37 Long-term arsenic exposure has been reported to cause a malignant transformation of human keratinocytes in vitro.38 Some growth factors that stimulate-melanoma cells can increase the expression of CD44v6 and promote motility in primary human melanocytes through CD44v6 via a NF-κB/Egr-1/C/EBP-beta complex.39 However, there are no reports on growth properties and on CSCs biomarker expression profile in human skin epithelial cell lines exposed to arsenic. In order to investigate the mechanisms of arsenic-induced carcinogenesis, we exposed human spontaneously immortalized skin keratinocytes (HaCaT) to an environmentally relevant level of arsenic in vitro, determined the acquired cancer phenotype and performed immunocytochemical and Western blot (WB) analysis.
Materials and Methods
Chemicals and antibodies
Sodium arsenite (NaAsO2; 99.99% pure) was obtained from Sigma Chemical Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA). The CycleTEST™ PLUS DNA Reagent Kit, mouse monoclonal anti CD44v6, anti CD133, anti p53 and anti NF-κB were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz, CA, USA.
Cell culture
The HaCaT cell line was originally derived from normal human adult skin, and is nontumorigenic. 40 The cells were cultured in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), and antibiotics (100 U/mL penicillin and 100 µg/mL streptomycin). Cultures were maintained at 37°C and in a humidified 5% CO2 atmosphere. For chronic exposure, cells were maintained continuously in a medium containing 0.05 ppm of NaAsO2 for 30 passages (about 18 weeks). Arsenic-treated and nontreated (control) cells for the experiments were selected every 5 passages (about 3 weeks).
Cell cycle analysis
After the cells grew to 90–95% confluence, they were harvested by gentle trypsinization, washed with cold PBS (calcium and magnesium free), and collected by centrifugation. For cell cycle analysis, ~106 cells were resuspended in 1 mL phosphate buffered saline (PBS) pH 7.4 and fixed in 75% ice-cold ethanol with 24 h incubation at −20°C. After a brief centrifugation, cells were washed once with PBS and incubated for 30 min at 37°C in PBS containing 40 µg/mL propidium iodide and 100 U RNase. For each tube, 20,000 cells were immediately measured on a FACSCalibur™ flow cytometer using CellQuest Pro Software (BD Company, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA).
Soft agar colony assay
We assessed colony forming efficiency (CFE) in soft agar every 5 passages (3 weeks to ascertain) acquired malignant phenotype. Cells were subcultured and passed through a 40 mm cell strainer (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA) to get a single cell suspension. Plates were prepared by adding 2 mL of agar medium (0.8 mL of 1.25% agar and 1.2 mL of DMEM with 10% FBS and 10% DPBS) to each plate. HaCaT cells (12,500 cells/35 mm plate) were suspended in 1 mL DMEM with 10% FBS and 0.33% agar and layered on top of the hardened agar medium. Plates were maintained at 37°C for 19 days. Colonies were then counted using an automated colony counter. Only colonies over 0.5 mm in diameter were counted as positive.
Xenograft tumor formation
Once the soft agar colony assay suggested that arsenic-induced carcinogenic conversion had occurred, arsenic-treated and control cells were injected into male Balb/c nude mice (Nu/Nu, 5–6 weeks old, 10 per group). The cells in exponential growth stage were trypsinized, washed twice with serum-free DMEM medium and resuspended in PBS. The cells (2×106/0.2 mL) were injected subcutaneously on the left axillary fossa of the mice. The formation of subcutaneous tumors was monitored and measured with a digital calliper.
The tumor volume (V) was calculated based on the formula
| (1) |
where L is the length and W is the shortest width of the tumor.
Animals were observed for tumor formation over a 6-month period. All procedures carried out in animals were conducted in compliance with the policies and regulations of Guangxi Medical University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (Nanning, China). During the 6-month observation period, no tumors occurred in mice inoculated with untreated HaCaT ells, whereas tumor incidence was over 75% after inoculation with arsenic-treated cells.
Western blotting analysis
After washing three times with ice-cold PBS, whole cell extracts were obtained using Cell Lysis Buffer (Cell Signaling Technology, Inc., Beverly, MA, USA) with 0.5% Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (Sigma) and 1% PMDF. Protein fractions were stored at -70°C until use. Protein concentrations were determined by Bio-Rad protein assay (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA) with bovine serum albumin (BSA) as a standard. Proteins were separated by Novex 12% Nupage Gel (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and transferred onto nitrocellulose membranes. The blots were probed with the primary antibodies (1:400), followed by incubation with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies. Antibody incubations were carried out in Blocker™ BLOTTO in TBS (Pierce, Rockford, IL, USA). Immunoreactive proteins were detected by chemiluminescence using ECL reagent (Amersham Pharmacia, Piscataway, NJ, USA) and subsequent autoradiography. Quantitation of the results was carried out by Bio-Rad Gel Doc 2000 Systems with Bio-Rad TDS Quantity One software. After the blots were stripped using Restore Western Blot Stripping Buffer (Pierce), they were probed for ß-actin (Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.), which was used as the loading control.
Pathological sample preparation and immunohistochemical study
Antibody immunoreactivity in the cells and tumor were assessed by immunofluorescence labeling study as described previously.41 HaCaT cells that had been incubated with arsenic on culture slides (BD Falcon, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA) were fixed with 4% formaldehyde in PBS for 10 min at room temperature and washed with PBS three times. The cells were treated with 0.5% Triton X-100 for 3 min and then incubated with 1% skim milk for 30 min at room temperature. To detect CD44v6, the cells were incubated with mouse monoclonal anti-CD44v6 antibody (0.5 µg/mL, abcam, Tokyo, Japan) overnight at room temperature. To detect CD133, NF-κB and p53, CD133 rabbit polyclonal antibody (1:600, Abcam, Tokyo, Japan), NF-κB monoclonal antibody (1:400, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz, CA, USA) and p53 monoclonal antibody (1:400, Calbiochem, Darmstadt, Germany) were used instead. Then the cells were incubated with fluoresenct secondary antibody Alexa 594-labeled goat antibody against rabbit IgG or Alexa 488-labeled goat antibody against mouse IgG (1:400, Molecular Probes, Eugene, OR, USA) for 3 h. The nuclei were stained with DAPI (Dapi Fluoro-mountG™, Birmingham, AL, USA). The stained cells were examined under a florescent (BX53, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). The staining intensity per cell of CD44v6, NF-κB and p53 were evaluated by analyzing three separate fields containing approximately 800 cells in average for each sample with Image J software. To confirm the immunoreactive specificity of primary antibody, the cells were incubated with omission of primary antibodies. Then, the cells were incubated with Alexa 594-labeled or Alexa 488-labeled secondary antibody and examined as described above.
Statistical analysis
Data are expressed as mean ± SEM of 3–6 determinations. Analysis of variance (ANO-VA) followed by Dunnett's multiple comparison tests were performed for comparisons between treatment groups and corresponding controls. The level of significance was set at P≤0.05 in all cases.
Results
Chronic arsenic exposure of HaCaT cells induced cancer stem-like phenotype
After 25 passages of exposure to 0.05 ppm of arsenic, morphological differences were observed between the arsenic-treated HaCaT cells and passage-matched control cells. Whereas control cells maintained an epithelial-like morphology, arsenic-treated cells developed into giant multinuclear cells, and exhibited a more vigorous growth capacity (Figure 1). The changes in the cell cycle showed that the majority of cells were in G2 and S phase (Figure 2). These data clearly demonstrate that arsenic can induce genomic instability and cell cycles changes. The soft agar colony assay is a useful method to identify malignantly transformed cells in vitro. The incidence of colony formation was increased during arsenic exposure period, which after 30 passages of arsenic exposure was 4.2-fold higher in the arsenic-treated cells than in passage-matched control cells (Figure 3). Together, these characteristics show that arsenic-treated HaCaT cells rapidly acquired a cancer phenotype upon an exposure to arsenite. To establish malignant transformation, arsenic-treated 25 passages cells (2×106/0.2 mL) were injected subcutaneously on the left axillary fossa of Balb/c nude mice. Arsenite-treated cells rapidly developed into highly pleomorphic tumors, with regional invasion. The skin tumors were highly undifferentiated, highly malignant, and composed of immature epithelial- and mesenchymal-like cells, and were identified as SCC (Figure 4). Thus, the cells present after 25 passages of arsenic exposure represent a malignant transformation.
Figure 1.
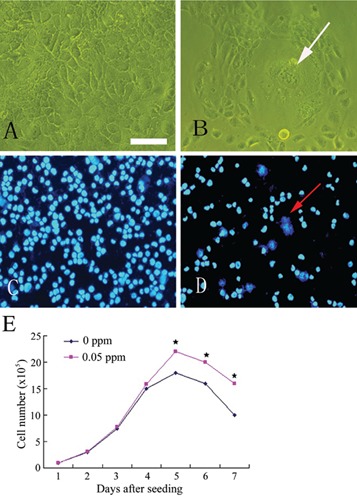
Low-level, chronic arsenic exposure induced malignant transformation in HaCaT cells. A) Control cells maintained an epithelial-like morphology at 25 passages stage. B) Arsenic-treated cells exhibited morphological alterations with the frequent occurrence of giant multinuclear cells at 25 passages stage. C) Control HaCaT cells and D) arsenic-treated cells at 25 passages stage stained with DAPI. Arrows indicate giant multinuclear cells. E) Growth curves in control and arsenite-treated HaCaT cells (means ±SD, n=3). Cells treated by sodium arsenite 25 generations, grown in 100 mm dish and calculated the number of cells in different days by cell counter. Five days later, arsenitetreated HaCaT cells have more vigorous growth capacity compare to passage control cells. *P<0.05 difference from passage control cells. Scale bar: 40 µm.
Figure 2.
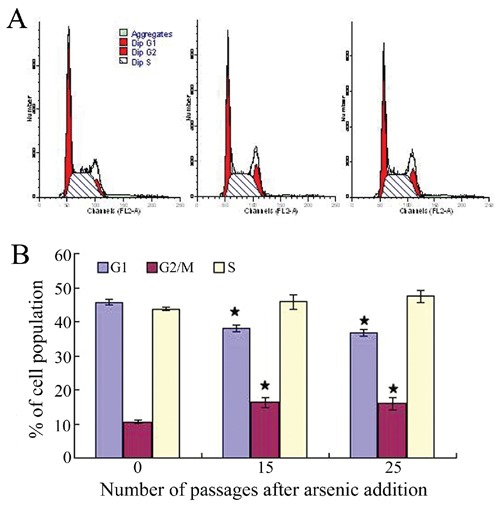
A) Flow cytometric analysis of the cell cycle distribution of cultured HaCaT cells with PI staining. B) Bar chart presentations of the HaCaT cells cycle distribution under the influence of arsenic. The values shown the mean ±SEM, with n=3. *P<0.05 when compared with the passage control.
Figure 3.
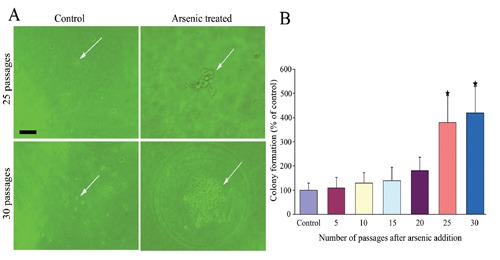
Colony formation was measured by soft agar colony assay in arsenic-treated cells and passage-matched control cells. A) None colony formation in passage-matched control cells (25 passages, 30 passages) (left), but there were colony formations produced by arsenic-treated cells in 25 passage and in 30 passage (right). Arrows indicate colony formations. B) The incidence of colony formation was increased during arsenic exposure period, 30 passages (18 weeks) of arsenic exposure was 4.2-fold higher in the arsenictreated cells than in passage-matched control cells; numerical data represent mean and 95% CI (n=3).*P<0.05 compared with control. Scale bar: 40 µm.
Figure 4.
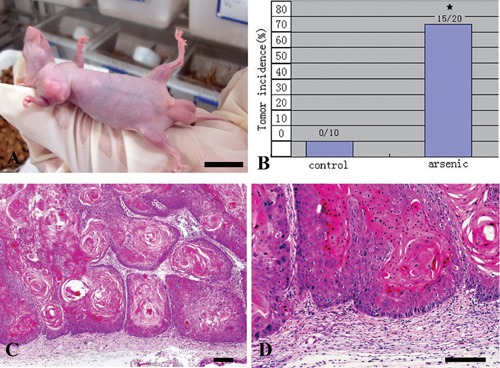
Arsenic-treated 25 passages cells (2×106/0.2 mL) were injected subcutaneously on the left axillary fossa of Balb/c nude mice. A) Arsenic-treated HaCaT cells became apparently tumorigenic in nude mice. Scale bar: 10 mm. B) Tumor incidence after inoculation under the subcutaneous of axillary fossa with control (n=10) and arsenite-treated cells (25 passages) (n=20). C,D) Pathological studies of Xenograft tumor sections showed a highly undifferentiated, pleomorphic nature of tumors from arsenic-treated HaCaT cells, and the tumor testified as squamous cell carcinomas (SCC), a type of cancer that induced by arsenic in skin. Scale bars: 100 µm.
CD44v6 expression in arsenic-treated HaCaT cells
The levels of CD44v6 and CD133 proteins of HaCaT cells exposed to 0.05 ppm of arsenic were analyzed at different post-exposure times by WB and immunofluorescence histochemistry. Figure 5A,B show that CD44v6 protein was increased to a significant extent in the arsenic-treated group from 25 passages relative to HaCaT cells in the 0 ppm arsenic group. Immunohistochemistry showed that CD44v6 strongly stained in the cell membrane, of arsenic-treated HaCaT cells after 20 and 25 passages, with control cells and arsenic-treated HaCaT before 20 passages showing either no or weak immunoreactivity (Figure 5C). In arsenic-treated group, quantitative analysis of CD44v6 immunoreactive HaCaT cells showed that, in the average, the immunoreactivity increased proportionally to the number of passages from 15 to 25 passages. A long term exposure of HaCaT cells to arsenic caused the activity of CD44v6 to increase with an increase in the duration of the exposure (Figure 5D), that the extent of CD44v6 immunoreactivity in arsenic-treated cells was found to positively correlate with the cloning efficiency in soft agar (r=0.949, P=0.01). On the other hand, little or no immunoreactivity was for CD133 was observed in arsenic-treated cells, and no immunoreactivity was observed in passagematched control cells (data not shown).
Figure 5.
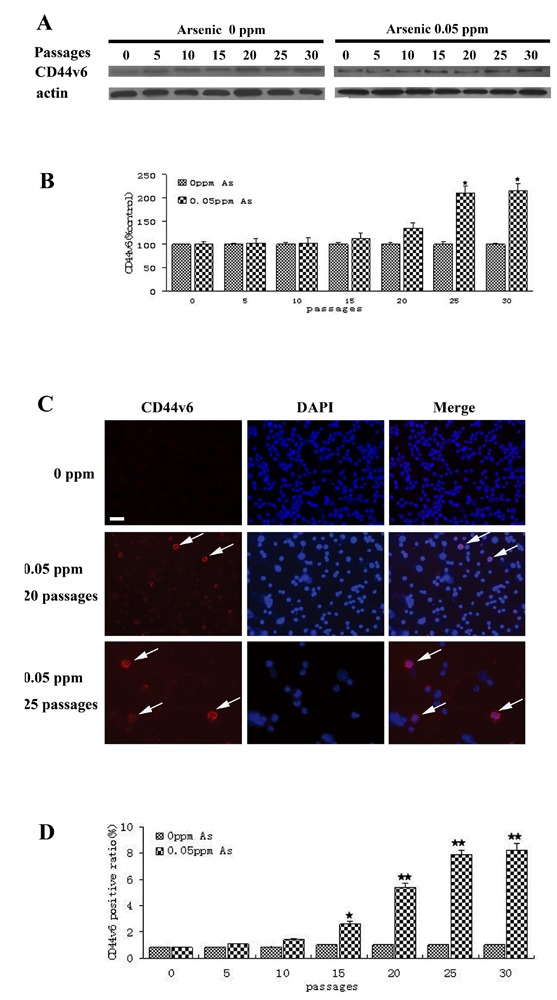
CD44v6 immunoreactivity is localized in arsenic-treated cells. HaCaT cells were exposed to 0.0 ppm or 0.05 ppm sodium arsenite for 30 passages (about 18 weeks). A) Western blot analyses of CD44v6 levels; HaCaT cells were exposed to 0.0 ppm or 0.05 ppm of arsenite for 5, 10, 15, 20, 25 or 30 passages; densities of bands were quantified by Quantity One software; ß-actin level measured in parallel, served as controls. B) Protein levels of CD44v6 (mean ± SD, n=3). *P<0.01 difference from passage-matched control cells. C) CD44v6 expression in arsenic-treated cells and passage-matched control cells (20, 25 passages), CD44v6 immunoreactivity positive cells localized primarily in the membrane of some HaCaT cells. D) CD44v6 positive ratio of CD44v6 immunoreactivity positive cells in arsenic-treated cells and passage-matched control cells is 7.9% at 25 passages of arsenic-treated cells. **P<0.01 difference from passage-matched control cells. Scale bar: 40 µm.
High expression of CD44v6 in xenograft tumors from arsenictransformed HaCaT cells
The expression of CD44v6 in HaCaT cells transplanted from nude mouse tumor tissue was examined by immunohistochemistry. While the expression of CD44v6 in the area surrounding the tumor tissue was nil, a strong membranous staining was found in more than 50% of tumor cells (Figure 6).
Figure 6.

CD44v6 expression in tumor cells of Xenograft tumor. CD44v6 expression was estimated by the percentage of tumor cell membrane staining, exceed 50% tumor cells were CD44v6 immunoreactivity positive. Scale bar: 100 µm.
Alterations of P53 and NF-κB gene expression with arsenic treatment
We examined the expression of transcription factor NF-κB and tumor suppressor gene p53 during arsenic-induced HaCaT cells malignant transformation. As shown in Figure 7, growth of HaCaT cells in 0.05 ppm arsenic for 15 passages or more resulted in a significant increase of NF-κB protein; and in a variable expression of p53 gene, which was first lost and then reactivated by the arsenicinduced malignant transformation. The NF-κB and p53 protein, which was mainly stained in the nucleus, were observed in cancer cells, but not in normal cells (Figure 8). While the detection rate of NF-κB protein in 0 passage HaCaT cells was 22.65%, it was 42.27% in 0.05 ppm arsenic-treated HaCaT cells for 15 passages or more (P<0.05).
Figure 7.
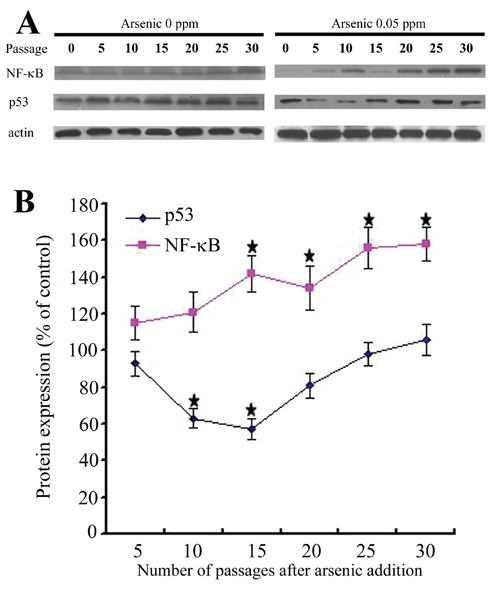
A) Western blot analyses of NF-κB, p53 levels in the arsenic-treated HaCaT cell. Densities of bands were quantified by Quantity One software. ß-actin levels, measured in parallel, served as controls. B) Protein levels of p53 and NF-κB (means ± SD, n=3). *P<0.05 difference from passage-marched control cells.
Figure 8.
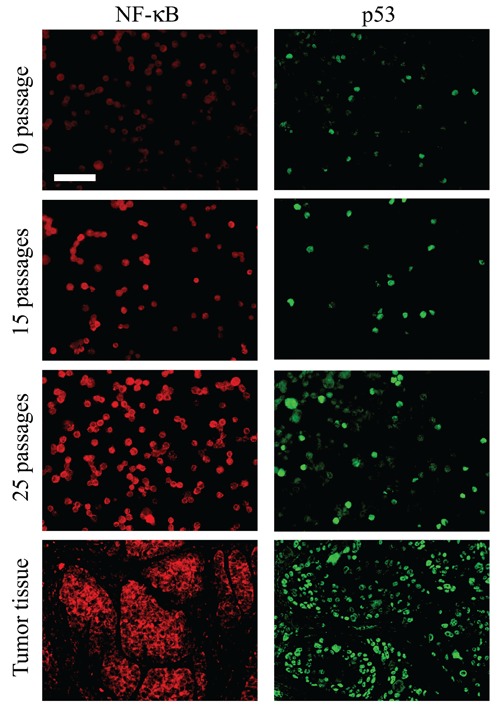
NF-kB and p53 expression in arsenic-treated cells and Xenograft tumor tissues. NF-κB and p53 immunoreactivity were observed primarily in the nucleus of some of HaCaT cell and tumor cells in the Xenograft tumor. Scale bar: 100 µm.
Discussion
Arsenic is one the most toxic metals present in the natural environment.42 The extent of arsenic poisoning depends on various factors such as its dose, an individual's susceptibility to it and the age of the affected individual. Its cytotoxicity is dependent on the extent of exposure, and presentation of pleiotropic cellular effects.34–37 Consistent with the biphasic dose response of environmental agents, a low level of arsenic usually leads to stimulation of cell proliferation and a high one is often cytotoxic.35 A previous research has shown that chronic exposure to low concentrations of arsenite (<5 µM) leads to neoplastic transformation.38 In our study, HaCaT cells exposed to 0.05 ppm arsenite for 30 passages (about 18 weeks) were identified as malignant by their anchorage-independent growth and became tumorigenic in the nude mouse. In addition, arsenic was found to induce morphological changes, exemplified by the occurrence of giant multinuclear cells, and cell cycle changes.
Arsenic has been shown to increase mRNA transcripts of growth factors including granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor, transforming growth factor-α and the inflammatory cytokine-like tumor necrosis factor- α.43,44 Continuously exposure of the human prostate epithelial stem/progenitor cell line WPE-stem to an environmentally relevant level of arsenic (5 µM) in vitro led to the acquisition of cancer phenotype, suppression of self-renewal gene (p63, BMI-1, ABCG2, SHH, OCT-4, and NOTCH-1), and reactivation during acquired cancer stem cells like phenotype. 38 High concentration of As2O3 has been shown to inhibit tumor metastasis by reducing the expression of metastasis-related genes, including CD44v6.33–36 However, there are no reports describing the expression of CD44v6 in cells and tumor as a result of a long-term treatment with a low (0.05 ppm) level of arsenic. In agreement with this finding, we have verified that CD44v6 was expressed in HaCaT cells subjected to a longterm treatment with a low level of arsenic. Moreover, the expression of CD44v6 in arsenic-treated cells was in good agreement with the cloning efficiency in soft agar (r=0.949, P=0.01). The expression of a cell adhesion molecule such as CD44v6 has been shown to be associated with metastasis and poor prognosis in human malignancies such as breast cancer and colorectal cancer;45,46 and increased levels of CD44 and/or different patterns of splice variants have been found in tumors but not in their normal counterparts. 47,48 More significantly, in our study we found that CD44v6 was an independent prognostic biological marker for colony formation of arsenic-treated cells in soft agar, that the strong expression of CD44v6 in arsenicinduced tumor cells will make this metastasis gene a valuable molecular marker for various human skin lesions, including squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), resulting from a chronic exposure to arsenic.
In target cells, carcinogenesis is a multiplestep process, involving serial genetic modifications that lead to alterations in growth control and, consequently, in the formation of malignancies.49,50 In the present study, alteration of the expression of p53 preceded the activation of CD44v6 which, in turn, was followed by the activation of NF-κB, significant cell cycle changes, and uncontrolled cell growth. Hence, it is evident that arsenic can induce genomic instability and initiate cell signal transduction by a number of ways, to cause transcription factor activation, and to induce a series of regulating cell differentiation and tumor-related gene expression events.
People carrying one altered p53 gene in their germline have a high probability of developing a tumor.51,52 Most human cancers result from either mutation in the p53 gene, to generate a dysfunctional or nonexpressed protein, or the altered expression of other gene products that disrupt p53 functions.53,54 Since our study showed that a low (0.05 ppm) level of sodium arsenite was able to induce the proliferation of HaCaT cells but not apoptosis, it is conceivable that arsenite may be inactivating p53 function. Our results show that in HaCaT cells exposed to arsenite there was an initial decline in the protein level of p53 which was subsequently recovered when the cells underwent malignant transformation.
The p53 gene is involved in the maintenance of genome stability. In response to diverse cellular stresses, the p53 protein transactivates downstream target genes required for DNA repair, cell cycle arrest, and apoptosis to raise a barrier to tumor progression. 55,56 There are many mechanisms for break of this barrier, general presume, most notably by p53 mutations that impair the DNA damage response pathway, allows cancers to develop.54 However, arsenic does not induce carcinogenesis via a classic mutagenic mechanism. 42 So, molecular factors may be involved in the inactivation of p53 function induced by low concentrations of arsenite. It is known that NF-κB activation can initiate and accelerate tumorigenesis, and that NF-κB inhibition blocks tumor promoter-induced cell transformation.57 In HaCaT cells exposed to a low level of arsenite, NF-κB was shown to inhibit p53 function by mot-2, an effect that facilitates p53mediated DNA repair and prevents arsenic-induced malignant transformation. 55 In the present study, the activations of CD44v6 expression by arsenic occurred after the activation of the transcription factor NF-κB and changes in p53 gene expression. In addition to changes in gene expression, arsenic caused major cell cycle changes and uncontrolled cell growth; and experiments with HaCaT cells transplanted from tumor tissue taken from nude mice showed a high expression of CD44v6, NF-κB and p53. Our research also determined that CD44v6 can serve as a biomaker of arsenic-induced neoplastic transformation in human skin cells, and that activation of CD44v6 through a NF-κB-dependent signaling pathway may underlie arsenic-induced malignant transformation in human skin lesions.
Acknowledgments:
this work was partly supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan.
References
- 1.International Agency for Research on Cancer. IARC Mono-graphs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. 2004. Some drinking-water disinfectants and contaminants, including arsenci, Monographs on chloramine, chloral and chloral hydrate, dichloroacetic acid and 3-chloro-4-(dichloromethly)-5-hydoroxy-2(5H)-furanone; pp. 269–477. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Alonso FT, Garmendia ML, Bogado ME. Increased skin cancer mortality in Chile beyond the effect of ageing: Temporal analysis 1990 to 2005. Acta Derm Venereol. 2010;90:141–6. doi: 10.2340/00015555-0787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Celik I, Gallicchio L, Boyd K, Lam TK, Matanoski G, Tao X, et al. Arsenic in drinking water and lung cancer: a systematic review. Environ Res. 2008;108:48–55. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2008.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chen CL, Chiou HY, Hsu LI, Hsueh YM, Wu MM, Wang YH, et al. Arsenic in drinking water and risk of urinary tract cancer: a follow-up study from northeastern Taiwan. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2010;19:101–10. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-09-0333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Meliker JR, Slotnick MJ, AvRuskin GA, Schottenfeld D, Jacquez GM, Wilson ML, et al. Lifetime exposure to arsenic in drinking water and bladder cancer: a population-based case-control study in Michigan, USA. Cancer Causes Control. 2010;21:745–57. doi: 10.1007/s10552-010-9503-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Morales KH, Ryan L, Kuo TL, Wu MM, Chen CJ. Risk of internal cancers from arsenic in drinking water. Environ Health Perspect. 2000;108:655–61. doi: 10.1289/ehp.00108655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Smith AH, Hopenhayn-Rich C, Bates MN, Goeden HM, Hertz-Picciotto I, Duggan HM, et al. Cancer risks from arsenic in drinking water. Environ Health Perspect. 1992;97:259–67. doi: 10.1289/ehp.9297259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Rossman TG, Uddin AN, Burns FJ, Bosland MC. Arsenite is a cocarcinogen with solar ultraviolet radiation for mouse skin: an animal model for arsenic carcinogenesis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2001;176:64–71. doi: 10.1006/taap.2001.9277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Rossman TG, Uddin AN, Burns FJ, Bosland MC. Arsenite cocarcinogenesis: an animal model derived from genetic toxicology studies. Environ Health Perspect. 2002;110:749–52. doi: 10.1289/ehp.02110s5749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Lobo NA, Shimono Y, Qian D, Clarke MF. The biology of cancer stem cells. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2007;23:675–99. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.22.010305.104154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.O'Brien CA, Kreso A, Jamieson CH. Cancer stem cells and self-renewal. Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16:3113–20. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-2824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Pardal R, Clarke MF, Morrison SJ. Applying the principles of stem-cell biology to cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:895–902. doi: 10.1038/nrc1232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Polyak K, Hahn WC. Roots and stems: stem cells in cancer. Nat Med. 2006;12:296–300. doi: 10.1038/nm1379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Visvader JE, Lindeman GJ. Cancer stem cells in solid tumours: accumulating evidence and unresolved questions. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:755–68. doi: 10.1038/nrc2499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Pilloni L, Bianco P, Difelice E, Cabras S, Castellanos ME, Atzori L, et al. The usefulness of c-Kit in the immunohistochemical assessment of melanocytic lesions. Eur J Histochem. 2011;55:e20–e20. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2011.e20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bujas T, Marusic Z, Peric Balja M, Mijic A, Kruslin B, Tomas D. MAGE-A3/4 and NYESO- 1 antigens expression in metastatic esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Eur J Histochem. 2011;55:e7–e7. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2011.e7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Nemolato S, Cabras T, Fanari MU, Cau F, Fraschini M, Manconi B, et al. Thymosin beta 4 expression in normal skin, colon mucosa and in tumor infiltrating mast cells. Eur J Histochem. 2012;54:e3–e3. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2010.e3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bomken S, Fiser K, Heidenreich O, Vormoor J. Understanding the cancer stem cell. Br J Cancer. 2010;103:439–45. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF, Weissman IL. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature. 2001;414:105–11. doi: 10.1038/35102167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Omran OM, Ata HS. CD44s and CD44v6 in diagnosis and prognosis of human bladder cancer. Ultrastruct Pathol. 2012;36:145–52. doi: 10.3109/01913123.2011.651522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Gunthert U, Hofmann M, Rudy W, Reber S, Zoller M, Haussmann I, et al. A new variant of glycoprotein CD44 confers metastatic potential to rat carcinoma cells. Cell. 1991;65:13–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90403-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zhou ZJ, Dai Z, Zhou SL, Fu XT, Zhao YM, Shi YH, et al. Overexpression of HnRNP A1 promotes tumor invasion through regulating CD44v6 and indicates poor prognosis for hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2013;132:1080–9. doi: 10.1002/ijc.27742. Epub 2012 Aug 7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Gun BD, Bahadir B, Bektas S, Barut F, Yurdakan G, Kandemir NO, et al. Clinicopathological significance of fascin and CD44v6 expression in endometrioid carcinoma. Diagn Pathol. 2012;7:80–80. doi: 10.1186/1746-1596-7-80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Turley EA, Noble PW, Bourguignon LY. Signaling properties of hyaluronan receptors. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:4589–92. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R100038200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Welsh CF, Zhu D, Bourguignon LY. Interaction of CD44 variant isoforms with hyaluronic acid and the cytoskeleton in human prostate cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 1995;164:605–12. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041640319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hong SC, Song JY, Lee JK, Lee NW, Kim SH, Yeom BW, et al. Significance of CD44v6 expression in gynecologic malignancies. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2006;32:379–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1447-0756.2006.00422.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Mima K, Okabe H, Ishimoto T, Hayashi H, Nakagawa S, Kuroki H, et al. The expression levels of CD44v6 are correlated with the invasiveness of hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro, but do not appear to be clinically significant. Oncol Lett. 2012;3:1047–51. doi: 10.3892/ol.2012.611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Dommann SN, Ziegler T, Dommann-Schener CC, Meyer J, Panizzon R, Burg G. CD44v6 is a marker for systemic spread in cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. A comparative study between nodal and cutaneous lymphomas. J Cutan Pathol. 1995;22:407–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.1995.tb00755.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bode AM, Dong Z. The paradox of arsenic: molecular mechanisms of cell transformation and chemotherapeutic effects. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2002;42:5–24. doi: 10.1016/s1040-8428(01)00215-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Du CW, Wen BG, Li DR, Peng X, Hong CQ, Chen JY, et al. Arsenic trioxide reduces the invasive and metastatic properties of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells in vitro. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2006;39:677–85. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2006000500015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Du Y, Zhang D, Liu H, Lai R. Thermoche-motherapy effect of nanosized As2O3/ Fe3O4 complex on experimental mouse tumors and its influence on the expression of CD44v6, VEGF-C and MMP-9. BMC Biotechnol. 2009;9:84–84. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-9-84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lin TH, Kuo HC, Chou FP, Lu FJ. Berberine enhances inhibition of glioma tumor cell migration and invasiveness mediated by arsenic trioxide. BMC Cancer. 2008;8:58–58. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-8-58. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Yu J, Qian H, Li Y, Wang Y, Zhang X, Liang X, et al. Arsenic trioxide (As2O3) reduces the invasive and metastatic properties of cervical cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Gynecol Oncol. 2007;106:400–6. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2007.04.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Bodwell JE, Kingsley LA, Hamilton JW. Arsenic at very low concentrations alters glucocorticoid receptor (GR)-mediated gene activation but not GR-mediated gene repression: complex dose-response effects are closely correlated with levels of activated GR and require a functional GR DNA binding domain. Chem Res Toxicol. 2004;17:1064–76. doi: 10.1021/tx0499113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.He XQ, Chen R, Yang P, Li AP, Zhou JW, Liu QZ. Biphasic effect of arsenite on cell proliferation and apoptosis is associated with the activation of JNK and ERK1/2 in human embryo lung fibroblast cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2007;220:18–24. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2006.12.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Shen S, Lee J, Weinfeld M, Le XC. Attenuation of DNA damage-induced p53 expression by arsenic: a possible mechanism for arsenic co-carcinogenesis. Mol Carcinog. 2008;47:508–18. doi: 10.1002/mc.20406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Wen G, Calaf GM, Partridge MA, Echiburu-Chau C, Zhao Y, Huang S, et al. Neoplastic transformation of human small airway epithelial cells induced by arsenic. Mol Med. 2008;14:2–10. doi: 10.2119/2007-00090.Wen. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Pi J, Diwan BA, Sun Y, Liu J, Qu W, He Y, et al. Arsenic-induced malignant transformation of human keratinocytes: involvement of Nrf2. Free Radic Biol Med. 2008;45:651–8. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2008.05.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Damm S, Koefinger P, Stefan M, Wels C, Mehes G, Richtig E, et al. HGF-promoted motility in primary human melanocytes depends on CD44v6 regulated via NFkappa B, Egr-1, and C/EBP-beta. J Invest Dermatol. 2010;130:1893–903. doi: 10.1038/jid.2010.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Boukamp P, Petrussevska RT, Breitkreutz D, Hornung J, Markham A, Fusenig NE. Normal keratinization in a spontaneously immortalized aneuploid human keratinocyte cell line. J Cell Biol. 1988;106:761–71. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.761. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Pinlaor S, Ma N, Hiraku Y, Yongvanit P, Semba R, Oikawa S, et al. Repeated infection with Opisthorchis viverrini induces accumulation of 8-nitroguanine and 8-oxo-7,8-dihydro-2'-deoxyguanine in the bile duct of hamsters via inducible nitric oxide synthase. Carcinogenesis. 2004;25:1535–42. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgh157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Huang C, Ke Q, Costa M, Shi X. Molecular mechanisms of arsenic carcinogenesis. Mol Cell Biochem. 2004;255:57–66. doi: 10.1023/b:mcbi.0000007261.04684.78. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Germolec DR, Spalding J, Boorman GA, Wilmer JL, Yoshida T, Simeonova PP, et al. Arsenic can mediate skin neoplasia by chronic stimulation of keratinocytederived growth factors. Mutat Res. 1997;386:209–18. doi: 10.1016/s1383-5742(97)00006-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Kitchin KT. Recent advances in arsenic carcinogenesis: modes of action, animal model systems, and methylated arsenic metabolites. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2001;172:249–61. doi: 10.1006/taap.2001.9157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Tokar EJ, Diwan BA, Waalkes MP. Arsenic exposure transforms human epithelial stem/progenitor cells into a cancer stemlike phenotype. Environ Health Perspect. 2010;118:108–15. doi: 10.1289/ehp.0901059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Liu YJ, Yan PS, Li J, Jia JF. Expression and significance of CD44s, CD44v6, and nm23 mRNA in human cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11:6601–6. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i42.6601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Herrlich P, Pals S, Ponta H. CD44 in colon cancer. Eur J Cancer. 1995;31A:1110–2. doi: 10.1016/0959-8049(95)00252-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Stauder R, Eisterer W, Thaler J, Gunthert U. CD44 variant isoforms in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: a new independent prognostic factor. Blood. 1995;85:2885–99. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Halazonetis TD, Gorgoulis VG, Bartek J. An oncogene-induced DNA damage model for cancer development. Science. 2008;319:1352–5. doi: 10.1126/science.1140735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Protrka Z, Arsenijevic S, Dimitrijevic A, Mitrovic S, Stankovic V, Milosavljevic M, et al. Co-overexpression of bcl-2 and cmyc in uterine cervix carcinomas and premalignant lesions. Eur J Histochem. 2011;55:e8–e8. doi: 10.4081/ejh.2011.e8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Konstantakou EG, Voutsinas GE, Karkoulis PK, Aravantinos G, Margaritis LH, Stravopodis DJ. Human bladder cancer cells undergo cisplatin-induced apoptosis that is associated with p53-dependent and p53-independent responses. Int J Oncol. 2009;35:401–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Lim do Y, Park JH. Induction of p53 contributes to apoptosis of HCT-116 human colon cancer cells induced by the dietary compound fisetin. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2009;296:G1060–8. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.90490.2008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Aylon Y, Oren M. Living with p53, dying of p53. Cell. 2007;130:597–600. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kastan MB. Wild-type p53: tumors can't stand it. Cell. 2007;128:837–40. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.02.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Bukholm IK, Nesland JM. Protein expression of p53, p21 (WAF1/CIP1), bcl-2, Bax, cyclin D1 and pRb in human colon carcinomas. Virchows Arch. 2000;436:224–8. doi: 10.1007/s004280050034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Pietsch EC, Sykes SM, McMahon SB, Murphy ME. The p53 family and programmed cell death. Oncogene. 2008;27:6507–21. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Li JJ, Oberley LW. Overexpression of manganese-containing superoxide dismutase confers resistance to the cytotoxicity of tumor necrosis factor alpha and/or hyperthermia. Cancer Res. 1997;57:1991–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


