Significance
Endocannabinoids act retrogradely at presynaptic sites to activate cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1) receptors, thereby inhibiting neurotransmitter release and fine-tuning synaptic transmission. In murine models of obesity with leptin deficiency, we report that orexin-A neurons undergo a shift from predominant control by CB1-expressing excitatory to CB1-expressing inhibitory inputs. In addition, endocannabinoid biosynthesis is increased in these neurons. CB1 activation by endocannabinoids reduces the inhibition of orexinergic neurons in obese mice, thereby enhancing orexin-A release in target brain areas and contributing to hyperphagia and increased body weight, as well as to alterations of hormone levels typical of obesity.
Keywords: food intake, orexin-A/hypocretin 1, high-fat diet, retrograde signaling
Abstract
Acute or chronic alterations in energy status alter the balance between excitatory and inhibitory synaptic transmission and associated synaptic plasticity to allow for the adaptation of energy metabolism to new homeostatic requirements. The impact of such changes on endocannabinoid and cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1)-mediated modulation of synaptic transmission and strength is not known, despite the fact that this signaling system is an important target for the development of new drugs against obesity. We investigated whether CB1-expressing excitatory vs. inhibitory inputs to orexin-A–containing neurons in the lateral hypothalamus are altered in obesity and how this modifies endocannabinoid control of these neurons. In lean mice, these inputs are mostly excitatory. By confocal and ultrastructural microscopic analyses, we observed that in leptin-knockout (ob/ob) obese mice, and in mice with diet-induced obesity, orexinergic neurons receive predominantly inhibitory CB1-expressing inputs and overexpress the biosynthetic enzyme for the endocannabinoid 2-arachidonoylglycerol, which retrogradely inhibits synaptic transmission at CB1-expressing axon terminals. Patch-clamp recordings also showed increased CB1-sensitive inhibitory innervation of orexinergic neurons in ob/ob mice. These alterations are reversed by leptin administration, partly through activation of the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway in neuropeptide-Y-ergic neurons of the arcuate nucleus, and are accompanied by CB1-mediated enhancement of orexinergic innervation of target brain areas. We propose that enhanced inhibitory control of orexin-A neurons, and their CB1-mediated disinhibition, are a consequence of leptin signaling impairment in the arcuate nucleus. We also provide initial evidence of the participation of this phenomenon in hyperphagia and hormonal dysregulation in obesity.
Modulation of the activity of hypothalamic neurons is involved in the regulation of energy balance exerted by the adipose tissue-derived hormone leptin. In the arcuate nucleus (ARC), these neurons express either pro-opiomelanocortin (POMC) and cocaine and amphetamine-responsive transcript, or neuropeptide Y (NPY) and agouti-related peptide (AgRP). Orexigenic neurons containing the peptide hypocretin-1/orexin-A (hereafter referred to as OX) reside in the lateral hypothalamus (LH) and send projections throughout the brain (1). They have been implicated in a variety of functions, including wakefulness and energy homeostasis (2), behavioral responses to food reward (3, 4) and addictive drugs (5), and neuroendocrine and autonomic outflow (6–8).
Short-term food deprivation results in decreased activity of POMC neurons and increased activity of NPY/AgRP neurons, thus facilitating food consumption (9). Such deprivation also causes enhancement of excitatory inputs to OX neurons. Reduction in leptin levels is responsible for these alterations, as they are reversed by administration of the hormone (9). Although leptin levels are also altered during obesity, there is little information on the potential readjustment of excitatory vs. inhibitory inputs of hypothalamic circuits in animal models of this condition, such as mice with spontaneous nonsense mutation of the leptin gene (ob/ob mice) (10, 11). The hypothalamic endocannabinoid system plays a prominent role in modulating both inhibitory and excitatory neurotransmission, is sensitive to leptin, and its “tone” is altered in obesity (12). The endocannabinoids 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) and anandamide influence food intake by regulating the release of several hypothalamic anorexic and orexigenic neuropeptides (13) through activation of cannabinoid CB1 receptors (CB1Rs), which have been shown to exert a bimodal control of food intake (14). In the LH of lean rodents, CB1Rs inhibit both inhibitory inputs to anorexic neurons that express melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH), and excitatory inputs to OX neurons (15, 16). The presynaptic localization of CB1R in hypothalamic nuclei (17) supports a prominent role of endocannabinoids as retrograde neuromodulators, especially for 2-AG (18), which is usually biosynthesized and released “on demand” by postsynaptic neurons (19, 20). However, it is not known whether in the LH, as in other brain regions (21), the main 2-AG–synthesizing enzyme, diacylglycerol lipase-α (DAGLα), and the degrading enzymes, monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) and serine hydrolase α-β-hydrolase domain 6 (ABHD6), are positioned to facilitate CB1R-mediated retrograde actions, nor whether obesity alters the expression and distribution of these enzymes and CB1Rs. Because OX is implicated in many aspects of mammalian physiology and pathology (3–8), putative obesity-induced changes in endocannabinoid control of OX neuron activity may profoundly affect multiple functions. Thus, the present study was aimed at assessing whether, in obesity, synaptic organization is altered in the LH and affects 2-AG and CB1R modulation of OX neuron activity. Using confocal, ultrastructural, electrophysiological, and biochemical approaches, we investigated the potential alterations of GABAergic and glutamatergic inputs to CB1R-modulated OX neurons, and the activity of these neurons. The study was conducted in male obese ob/ob mice at different postnatal ages and in adult male mice made obese by a prolonged high-fat diet (HFD).
Results
Pre- and Postsynaptic Components of the Endocannabinoid System Are Expressed in OX Neurons.
WT and ob/ob mice were examined at preweaned [3-wk-old: postnatal day (P) 19 to P23], weaned (5-wk-old: P28–P36), and adult (9-wk-old: P56–P64) ages (n = 3 mice per group). Adult (16-wk-old) mice made obese with HFD were compared with lean mice fed with standard fat diet (SFD) (n = 6 per group). In all groups, we observed punctate CB1R immunoreactivity around the soma and primary dendrites of OX neurons, in agreement with previous findings in the mouse LH (17).
Confocal microscopy was used to evaluate whether CB1R puncta were synaptic sites by examining their colocalization with the synaptic marker synaptophysin. The relative abundance of synapses was examined in 10-µm-thick coronal sections through the LH. Only OX neurons with visible nuclei were sampled for synaptic quantification (n = 200). All CB1R-containing axon terminals surrounding OX neurons also contained synaptophysin, whereas 30 ± 4% of synaptophysin-labeled puncta did not colocalize with CB1R.
To determine the production site of 2-AG in the LH, we examined the localization of the 2-AG synthetic enzyme DAGLα. Immunofluorescence visualized DAGLα mainly in punctate labeling in somata and dendrites of OX neurons (Fig. 1A). The specificity of the DAGLα antiserum was verified by the lack of immunolabeling in DAGL-knockout (KO) mice (Fig. S1 A and A1). Moreover, in the LH perifornical area we found only very weak ABHD6 immunoreactivity colocalizing with DAGLα in the somata of OX neurons. Instead, colocalization of CB1R and MAGL was observed throughout the neuropil of the perifornical area, especially around OX neurons (Fig. 1B). The specificity of the MAGL antiserum was also verified by the lack of immunolabeling in MAGL-KO mice (22) (Fig. S1 B and B1). Electron microscopy showed that axon terminals expressing CB1Rs formed more frequently asymmetrical (putative excitatory) (Fig. 1C and Fig. S1C) than symmetrical (putative inhibitory) (Fig. 1D and Fig. S1D) synapses with somata and proximal dendrites of DAGLα-expressing neurons in the LH of lean mice, whereas the opposite was found in ob/ob mice (see also below). This finding was verified using secondary antibodies conjugated with ultrasmall gold particles, visualized by two sequential steps of silver enhancement (23) (Fig. 1 C–G), and further characterized by preembedding double-immunogold labeling with gold particles of 6 nm and 10 nm (SI Materials and Methods and Fig. S1 C–E). In OX neurons, DAGLα was concentrated just beneath the membrane of somata and proximal dendrites, in agreement with previous findings in other brain regions (24, 25). In these neurons, most gold particles of OX immunolabeling were found in dense cytoplasmic vesicles (Fig. 1 E and F, and Fig. S1E), with a few particles being dispersed in low-density vesicles and around the endoplasmic reticulum or Golgi apparatus. Accumulation of OX particles was found in neuronal perikarya contacted by symmetrical or asymmetrical CB1R-immunolabeled boutons (Fig. 1G). A similar subcellular localization of DAGLα and OX was observed in ob/ob mice and WT littermates of different ages, and in adult HFD and SFD mice.
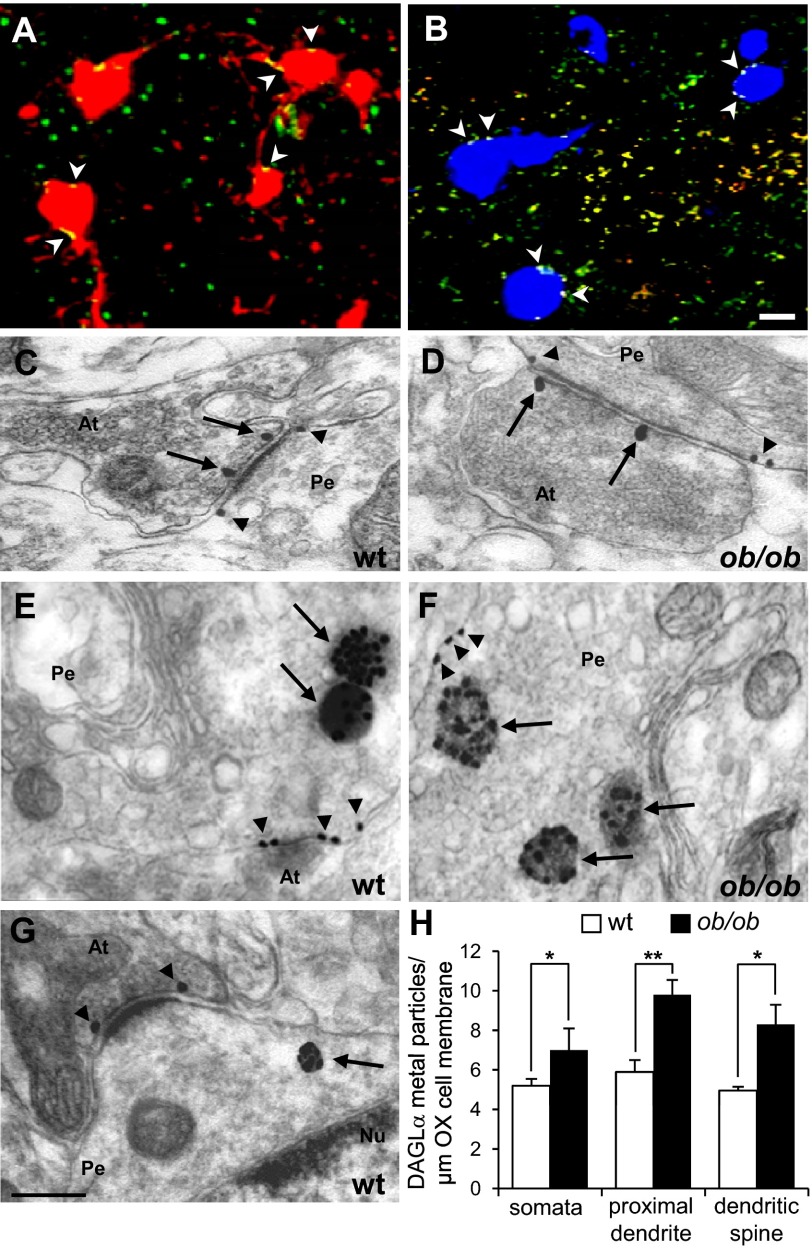
Fig. 1.
Components of the endocannabinoid system are expressed in OX neurons. (A) Images of clustering of DAGLα (green) puncta on the membrane of OX (red) cell bodies and proximal dendrites (yellow: DAGLα and OX merged signals; arrowheads) and throughout the neuropil. (B) CB1R/MAGL colocalization (yellow: merge) in the neuropil of LH and onto OX (blue) neurons (white dots: merge). (Scale bar, 25 µm.) (C–G) Representative electron micrographs showing double OX/DAGLα or CB1R/DAGLα or OX/CB1R immunogold detection by sequential silver enhancing in adult obese ob/ob mice and lean WT littermates. (C) Asymmetrical, putative excitatory, axosomatic synapse and (D) symmetrical, putative inhibitory, axosomatic synapse between an axon terminal (At), which exhibits marked CB1R immunogold labeling (arrows) in the presynaptic membrane opposite to DAGLα accumulation (arrowheads) at the edges of the postsynaptic density. (E and F) Accumulation of OX gold particles in clusters (with size up to ∼threefold larger than a single OX gold particle) inside vesicles (arrows) within the perikaryon (Pe) of a cell expressing DAGLα concentrated on the somatic membrane (arrowheads) and forming an asymmetrical synapse with a putative excitatory axon terminal (At). (G) Accumulation of OX immunogold in highly dense vesicles (arrow) in the perikarya of a neuron that receives an asymmetrical putative excitatory CB1R-immunolabeled synapse (arrowheads). CB1R labeling is evident at the edges of presynaptic membrane specializations. No difference in the ultrastructural localization of DAGLα and OX was found between WT (C, E, and G) and ob/ob (D and F) mice. (Scale bar, 0.6 µm.) (H) Bar graph showing the mean number of metal particles for DAGLα per 1 μm of membrane on each domain of OX neuron (n = 5 neurons per animal followed through 24 consecutive serial ultrathin sections; n = 3 mice per group). The similar density in somata, proximal dendrites, and dendritic spines indicates that DAGLα is equally distributed in these compartments (see Fig. S1 C and D for details of DAGLα localization in dendritic spines). Nu, nucleus. Data are mean ± SEM *P < 0.01, **P < 0.001.
The density of DAGLα metal particles on each domain of OX neurons was measured at the electron microscopic level per 1 μm of OX cell membrane. In both ob/ob and WT littermates, DAGLα particles were equally distributed in somata, proximal dendrites, and dendritic spines (Fig. 1H and Fig. S1 C, D, and E2). However, in all somatodendritic compartments of OX neurons the number of DAGLα particles was significantly higher in ob/ob than WT mice (Fig. 1H).
Biosynthesis of 2-AG Is Up-Regulated in the LH of Obese Mice.
Body weight was significantly higher in HFD mice than in control SFD mice (Fig. S2A). This rise was accompanied by leptin resistance, as evidenced by increased plasma leptin levels (Fig. S2B) and decreased phosphorylation of STAT3, a main intracellular signal transducer and activator of transcription of the long form of the leptin receptor (LepRb) (26). Importantly, at variance with weaned ob/ob mice (Fig. S2C), STAT3 phosphorylation in HFD mice was impaired in the ARC but not in the LH, and did not increase after acute leptin administration (5 mg/kg, i.p.) (Fig. S2 D and E). The levels of 2-AG in the LH were higher in 9-wk-old ob/ob mice compared with both 3- and 5-wk-old ob/ob mice and to 9-wk-old WT mice; no difference was observed between 16-wk-old HFD mice and 9-wk-old ob/ob mice (Fig. S3A). Instead, 2-AG levels in the LH were significantly lower in 16-wk-old lean SFD mice than in age-matched obese HFD mice, and ∼15-fold higher in 16-wk-old MAGL-KO mice (1,735 ± 226 pmol/mg lipid extract, mean ± SD, n = 3), which exhibit a lean phenotype (22), than WT mice (115 ± 28 pmol/mg lipid extract, mean ± SD, n = 3). The percent increase of 2-AG levels vs. corresponding lean controls was comparable in 16-wk-old HFD and 9-wk-old ob/ob mice. No statistically significant difference in anandamide levels was found between adult ob/ob or HFD mice and their lean counterparts. In 9-wk-old ob/ob mice and adult HFD mice, DAGLα immunoreactivity was significantly enhanced in OX neurons compared with younger ob/ob mice and matched lean controls (Fig. S3B). The increase in DAGLα immunoreactivity was comparable in OX neurons of 9-wk-old ob/ob and adult HFD mice, whereas ABHD6 immunoreactivity was very faint in the same OX neurons, with no difference in the intensity of immunosignal and localization between lean (SFD: 0.19 ± 0.04 optical density; WT: 0.16 ± 0.5 optical density, mean ± SD, n = 3) and obese (HFD: 0.21 ± 0.04 optical density; ob/ob: 0.18 ± 0.03 optical density, mean ± SD, n = 3) mice. MAGL immunoreactivity was similar, both in terms of intensity and localization, in OX neurons of 9-wk-old ob/ob mice and adult HFD mice compared with lean controls (WT: 0.79 ± 0.18 optical density; ob/ob: 0.81 ± 0.18 optical density; SFD: 0.72 ± 0.15 optical density; HFD: 0.74 ± 0.15 optical density, mean ± SD n = 3), and in OX neurons of younger ob/ob mice matched to lean controls mice (WT 3 wk: 0.32 ± 0.05 optical density; WT 5 wk: 0.39 ± 0.08 optical density; ob/ob 3 wk: 0.35 ± 0.03 optical density; ob/ob 5 wk: 0.41 ± 0.09 optical density, mean ± SD n = 3). Thus, both the obese phenotypes and developmental ages did not affect the expression of the degrading enzymes ABHD6 and MAGL in the LH. Therefore, the higher levels of 2-AG in adult obese mice are likely a result of increased expression of the biosynthetic enzyme DAGLα. Finally, in MCH neurons, another site of endocannabinoid release in the LH (16), no difference in DAGLα immunopositivity was found between ob/ob and WT mice of different ages or HFD mice and their lean counterparts.
CB1R-Expressing Axon Terminals Apposed to OX Neurons Are Rearranged in Obesity from Glutamatergic to GABAergic Predominance.
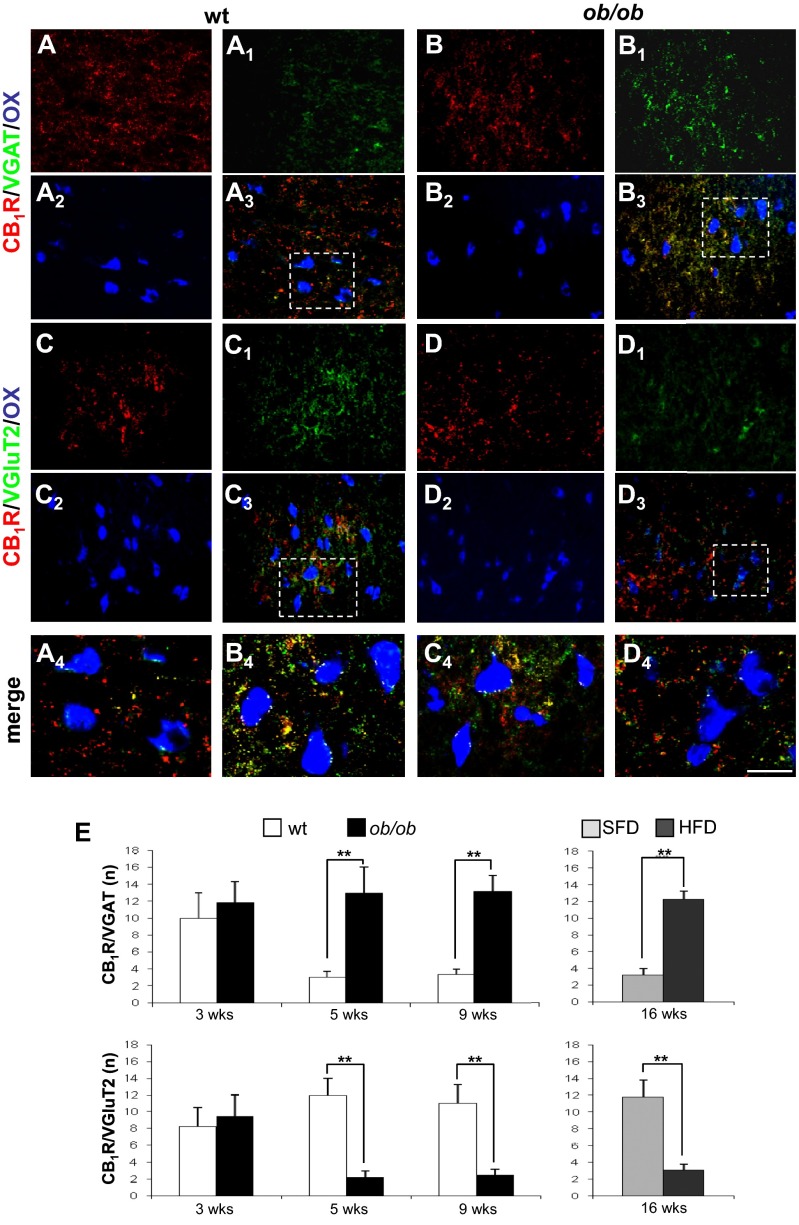
The afferents to OX neurons were characterized as inhibitory or excitatory (that is, GABAergic or glutamatergic) synaptic endings, using as markers the synaptic protein synaptophysin combined with the vesicular GABA transporter (VGAT) or vesicular glutamate transporter 2 (VGluT2), respectively. A high density of VGluT2/CB1 puncta was observed in the LH of lean mice, almost all presynaptic because of their colocalization with synaptophysin. We also characterized the pattern of expression of the glutamate vesicular transporter type 1 (VGluT1). However, VGluT1/CB1 puncta were only sparsely distributed, and rarely colocalized with synaptophysin, and were not, therefore, studied further. The relative abundance of excitatory and inhibitory synapses apposed to OX neurons of obese and lean mice was assessed by confocal microscopy and quantification of synaptophysin/VGAT and synaptophysin/VGluT2 colocalization (n = 120 ± 10 OX neurons per mouse; n = 3 mice per group). Adjacent 10-µm-thick sections were examined and alternatively processed for synaptophysin/VGluT2/OX and synaptophysin/VGAT/OX immunofluorescence. Only OX neurons identified in adjacent sections and with visible nuclei were sampled to assess synaptic distribution. Interestingly, in ob/ob mice the percentage of VGAT+ axon terminals contacting OX neurons was markedly and significantly higher than in WT littermates (64 ± 6% in ob/ob vs. 26 ± 4% in WT; P < 0.001) (see, for example, Fig. 3C), whereas that of VGluT2+ terminals was markedly and significantly lower (32 ± 5% in ob/ob vs. 70 ± 8% in WT; P < 0.001) (see, for example, Fig. 3C). This switch from predominantly glutamatergic to GABAergic afferents was detected only in weaned and adult ob/ob mice and 16-wk-old HFD mice. No difference was found instead between preweaned (3-wk-old) ob/ob mice and matched WT mice. Because presynaptic CB1Rs were found in both inhibitory and excitatory axon terminals apposed to OX neurons, quantitative analyses of CB1R/VGAT vs. CB1R/VGluT2 immunolabeled terminals apposed to OX perikarya and proximal dendrites were performed to assess whether the synaptic rearrangement on these neurons was paralleled by rearrangement of CB1Rs. The analyses were performed in ob/ob mice before and after weaning, and in HFD mice using confocal microscopy and quantification of CB1R/VGAT and CB1R/VGluT2 colocalization at OX neurons with the same criterion as above (n = 150 ± 20 OX neurons per mouse; n = 3 mice per group). Interestingly, in obese ob/ob and HFD mice the number of CB1R/VGAT+ axon terminals apposed to OX neurons was significantly higher than in WT littermates and SFD mice and that of CB1R/VGluT2+ axon terminals was significantly lower (Fig. 2 A–D). No difference was found instead between the number of CB1R/VGAT vs. CB1R/VGluT2 axon terminals in 3-wk-old ob/ob mice and WT mice (Fig. 2E). Moreover, the total number of CB1R+ axon terminals was similar in obese ob/ob or HFD mice and their lean counterparts, and no difference in the intensity of CB1R immunosignal was observed between these groups (Fig. S3C). The percentage of CB1R-immunopositive afferents to OX neurons with respect to the total number of axon terminals (labeled by synaptophysin) was similar in all groups of obese and lean mice (Fig. S3D). Furthermore, no significant difference in the number of CB1R/VGAT and CB1R/VGluT2 terminals apposed to MCH neurons of adult ob/ob and WT mice was found (CB1R/VGAT: 60 ± 16% in ob/ob vs. 48 ± 13% in WT; CB1R/VGluT2: 40 ± 10% in ob/ob vs. 52 ± 14% in WT).
Fig. 3.
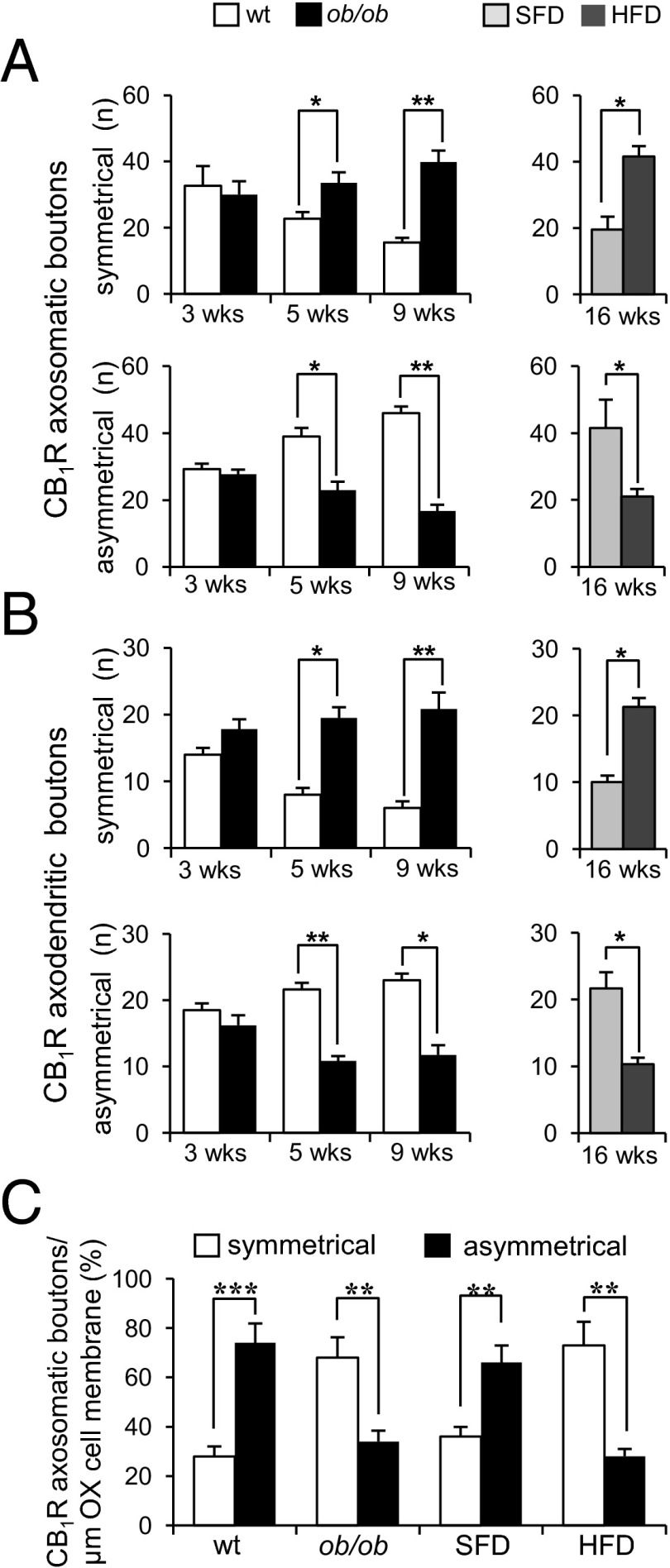
Quantitative analysis of axosomatic and axodendritic CB1R-expressing boutons apposed to OX neurons as determined by immunoelectron microscopy. (A and B) CB1R symmetrical synapses outnumber CB1R asymmetrical synapses in weaned (5 or 9 wk) ob/ob and HFD (16 wk) mice. No difference was found between 3-wk-old WT and ob/ob mice. (C) Percentage of CB1R-expressing boutons over the total of inhibitory or excitatory boutons per 1 μm of OX membrane in 9-wk-old mice. Data are mean ± SEM, n = 5 OX neurons per mouse; n = 3 mice per group of age, genotype or diet. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
Fig. 2.
CB1R–expressing axon terminals apposed to OX neurons are rearranged during obesity from glutamatergic to GABAergic. (A–D) Confocal microscopy images showing inhibitory CB1R/VGAT- (A and B) and excitatory CB1R/VGluT2- (C and D) immunolabeled puncta apposed to OX neurons of adult ob/ob and WT mice. (A4–D4) Higher magnification of fields depicted in boxed areas. [Scale bar: 100 µm (A–D), 20 µm (A4 and D4), and 30 µm (B4 and C4).] (E) Bar graph showing the mean number of double CB1R/VGAT- and CB1R/VGluT2–expressing puncta per OX neuron (n = 3 mice and n = 200 ± 20 OX neurons per genotype and diet group). Note that CB1R/VGAT inputs significantly outnumber CB1R/VGluT2 inputs in obese (ob/ob and HFD) mice, except for preweaned WT vs. ob/ob mice. Data are mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01.
Using VGluT2/MAGL or VGAT/MAGL immunofluorescence, we observed that, like CB1Rs, MAGL was also preferentially expressed in GABAergic axon terminals apposed to OX neurons in 9-wk-old ob/ob mice and in glutamatergic axon terminals apposed to OX neurons of WT mice (Fig. S4 A–D). Importantly, the distribution of VGluT2/CB1R and VGAT/CB1R was similar in 16-wk-old MAGL-KO mice and WT, as well as in WT littermates of ob/ob mice (Fig. S4 E–H) or 16-wk-old SFD mice.
The relative abundance of CB1R inhibitory or excitatory inputs to OX neurons was further investigated with unbiased electron microscopic analysis. This investigation was based on CB1R/OX double-immunogold labeling of ultrathin sections through the LH from obese mice (ob/ob mice of all age groups and HFD mice), compared with matched lean mice (WT littermates and SFD mice, respectively) (n = 3 per group). In these blinded experiments, excitatory synapses were identified by their asymmetrical morphology (Figs. 1 C and G, and Fig. S1C) and inhibitory synapses by their symmetrical morphology (27) (Fig. 1D and Fig. S1D). Selected boutons on OX neurons (n = 5 per mouse) were followed through 24 consecutive serial ultrathin (60 nm) sections, according to the synaptological method used by Horvath and Gao (9). In 5- and 9-wk-old ob/ob mice and in HFD mice, CB1R inhibitory synapses markedly outnumbered CB1R excitatory axosomatic (Fig. 3A) and axodendritic (Fig. 3B) synapses. In preweaned ob/ob mice and WT littermates, an equivalent number of CB1R inhibitory and CB1R excitatory synapses was found in the evaluation of axosomatic (Fig. 3A) and axodendritic (Fig. 3B) boutons. Finally, we analyzed the proportion of the inhibitory or excitatory boutons over the total number of CB1R-expressing boutons apposed to OX neurons in adult ob/ob and HFD mice. CB1R-expressing axosomatic boutons were found to be predominantly inhibitory, at variance with lean mice in which they were predominantly excitatory (Fig. 3C).
Functional Evidence of Enhanced Inhibitory Innervation of OX Neurons in ob/ob Mice.
To estimate the number of functional inhibitory inputs, whole-cell voltage-clamp recording of miniature inhibitory postsynaptic currents (mIPSCs) was performed in LH neurons from brain slices of preweaning (n = 10), weaned (n = 6), and adult (n = 6) mice. OX neurons were identified by their characteristic electrophysiological responses to injected currents (28, 29), further validated here by means of neurobiotin filling through the recording electrode and OX immunolabeling (SI Materials and Methods and Fig. S5 A–C).
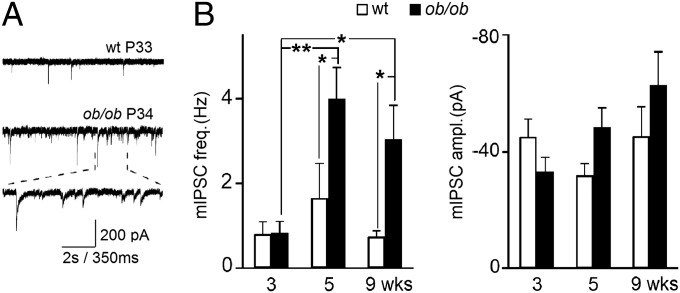
ANOVA across ages and phenotypes revealed a difference in the mIPSC frequency [F(5,43) = 3.9; P = 0.006] but not in their amplitude [F(5,43) = 1.9; P = 0.12]. When performing individual comparisons of frequency, before weaning no difference was observed between ob/ob and WT neurons (0.8 ± 0.28 Hz, n = 8 and 0.8 ± 0.29 Hz, n = 5, ob/ob and WT, respectively) (Fig. 4B, Left). In addition, mIPSC frequency was similar in age-matched C57BL/6 mouse OX neurons (1.1 ± 0.53 Hz, n = 8, P > 0.5 relative to ob/ob), and corresponded to that previously observed (30). After weaning the mean mIPSC frequency was significantly higher in ob/ob than in WT OX neurons (5 wk: ob/ob: 4.0 ± 0.74 Hz, n = 10 and WT: 1.6 ± 0.83 Hz, n = 10; 9 wk: ob/ob: 3.0 ± 0.81 Hz, n = 10 and WT: 0.7 ± 0.15 Hz, n = 6, P < 0.05 for both comparisons) (Fig. 4B, Left), a finding consistent with our data on synaptic organization. Across ages, mIPSC frequency did not vary in WT but significantly increased after weaning in ob/ob neurons. When performing individual comparisons of amplitude, before and after weaning no difference was observed between ob/ob and WT neurons (pA for WT and ob/ob: −45.0 ± 6.25 and −33.1 ± 4.92, P = 0.19; −31.8 ± 4.11 and −48.5 ± 6.58, P = 0.09; −45.2 ± 10.17 and −62.9 ± 11.32, P = 0.28; 3, 5, and 9 wk, respectively; same neurons as in frequency) (Fig. 4B, Right). We then calculated the inactivation kinetics of all mIPSCs measuring their decaying τ, and found no difference between ob/ob and WT at any age (8.7 ± 0.23 ms, n = 635 and 9.1 ± 0.11 ms, n = 2,345, P = 0.16, WT and ob/ob, respectively, values at different ages pooled), but a general trend toward slower τ was evident in older animals, irrespective of the phenotype: 7.1 ± 0.53 ms, n = 510; 8.3 ± 0.53 ms, n = 1,455 and 10.2 ± 0.79 ms, n = 1,015) [F(2, 2,977) = 131.7; P < 0.00001, ANOVA], 3, 5, and 9 wk, respectively, WT and ob/ob pooled (Fig. S5D). It is noteworthy that, at all ages, the inactivation kinetics was independent from mIPSC amplitude (Fig. S5D). In fact, no difference was found when comparing the average τ values of small amplitude mIPSCs vs. large amplitude mIPSCs recorded in animals of the same age (milliseconds of small and large mIPSC: 7.1 ± 0.35, n = 255 and 7.3 ± 0.27, n = 255, P = 0.76; 8.3 ± 0.21, n = 727 and 8.0 ± 0.16, n = 728, P = 0.23; 10.9 ± 0.25, n = 507 and 11.2 ± 0.26, n = 508, P = 0.36; 3, 5, and 9 wk, respectively, WT and ob/ob pooled). This observation confirmed that all of the measured electric events shared the same biological nature (mIPSC). Further confirmation was provided by the absence of mIPSCs when adding bicuculline at the end of each experiment.
Fig. 4.
Inhibitory activity onto OX neurons from ob/ob mice, but not WT mice, increases after weaning. (A) Representative recordings of mIPSCs from neurons voltage-clamped at −70 mV. (B) Mean ± SEM frequency (Left) and amplitude (Right) of mIPSCs in ob/ob and WT OX neurons before (n = 5 and 8, ob/ob and WT, respectively) and after weaning (5 wk: n = 10 in both groups; 9 wk: n = 10 and 6, ob/ob and WT, respectively). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005.
CB1R Modulates Inhibitory Synaptic Activity in OX Neurons of ob/ob Mice.
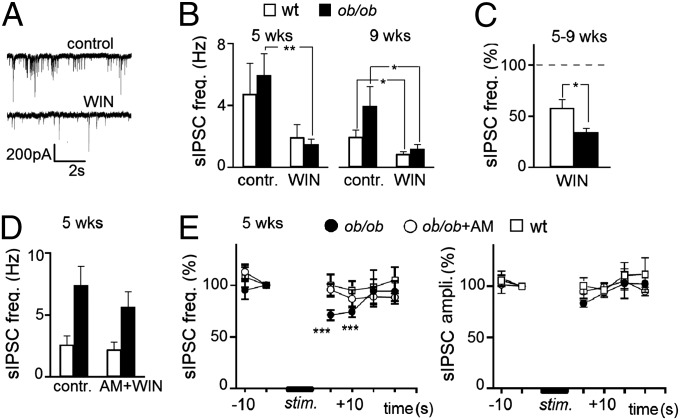
A depressant effect of endocannabinoids on neurotransmitter release, especially of inhibitory inputs, has been repeatedly reported (18, 19). Thus, we expected that CB1 agonist, WIN55,212-2 (WIN), depress inhibitory synapses more effectively in ob/ob than in WT OX neurons after weaning. To test this hypothesis, we recorded the inhibitory synaptic activity in the absence of TTX. Under these conditions, spontaneous action potential activity is present in the slice, and thus two populations of IPSCs are simultaneously recorded, collectively named as “spontaneous inhibitory postsynaptic currents” (sIPSCs). One population corresponds to mIPSCs and is caused by spontaneous synaptic vesicle fusion, and the second population is evoked in response to spontaneous presynaptic action potentials. Because the activation of CB1Rs is known to depress the action potential-evoked Ca++ influx (20, 31), underlying synaptic vesicle release, sIPSCs provide a more comprehensive measure of the effect of CB1R activation on synaptic transmission than just measuring mIPSCs.
Similarly to mIPSCs, sIPSC frequency was higher in postweaning ob/ob OX neurons than in WT neurons (Fig. S5E). Bath application of WIN (5 µM) reduced the frequency of sIPSCs in both ob/ob and WT neurons, although in the latter the effect did not reach statistical significance in the 5-wk-old group of neurons (pre- and post-WIN, respectively: ob/ob 6.0 ± 1.40 and 1.5 ± 0.32 Hz, n = 9, P < 0.01; WT 4.7 ± 1.99 and 1.9 ± 0.84 Hz, n = 9, P > 0.1). The effect of WIN was evident also at 9 wk of age (pre- and post-WIN: ob/ob 4.0 ± 1.26 and 1.2 ± 0.28 Hz, n = 7, P < 0.05; WT 2.0 ± 0.45 and 0.9 ± 0.17 Hz, n = 8, P < 0.05) (Fig. 5 B and C). The reduction of sIPSC frequency appeared specific for the drug, because the application of vehicle alone (DMSO, same percent as with WIN) did not cause any significant effect in WT neurons (pre- and post-DMSO: 2.9 ± 0.73 and 2.3 ± 0.57 Hz, n = 7 at 5 wk and 2 at 9 wk, pooled, P > 0.5). To better estimate a stronger effect of WIN on ob/ob sIPSC frequency predicted by our morphological data, we calculated the frequencies after WIN relative to the frequencies before WIN. In agreement with our hypothesis, the average effect of WIN resulted significantly higher in ob/ob than in WT neurons (relative ob/ob sIPSCs frequency with WIN: 34.1 ± 3.99%; WT: 57.9 ± 8.42%, P = 0.018) (Fig. 5C). In a previous study, WIN did not modulate sIPSC frequency in OX neurons expressing green fluorescent protein (16). One likely explanation for this discrepancy is the difference in the animals age, which in our case was consistently 2 or 6 wk after weaning (mice of 5 and 9 wk of age, respectively), whereas in Huang et al.’s study it ranged from 2 to 6 wk after birth (16), thus spanning a much broader age before and after weaning, during which mIPSC frequency (and possibly also sIPSC modulation) changes substantially (Fig. 4).
Fig. 5.
Inhibitory synapses to OX neurons are depressed by the CB1 agonist WIN and by retrograde endocannabinoid signaling in ob/ob. (A) Representative sIPSC recordings from a P33 ob/ob neuron voltage-clamped at −70 mV, before (control) and 5 min after (WIN) the addition of 5 μM WIN. (B) WIN-mediated sIPSC absolute frequency reduction in ob/ob and WT OX neurons at two different postweaning ages (5 wk: n = 9 for both groups; 9 wk: n = 7 ob/ob and 8 WT). (C) Same data as in B but relative to sIPSC frequency before WIN. Data from 5- and 9-wk-old animals were pooled. (D) Block of CB1R with AM abolishes the WIN-mediated sIPSC frequency reduction (ob/ob n = 6, WT n = 4; no significant differences). (E) Study of DSI. (Left) sIPSC frequency as a function of time (5-s bins) before and after a 5-s step-depolarization to 0 mV (marked as “stim.” and a corresponding thicker portion along the abscissa). Values are relative to the frequency 5 s before the depolarization. DSI is absent in WT (n = 14) but present in ob/ob neurons (n = 11). Block of CB1R with AM251 (AM) in ob/ob neurons abolishes DSI (n = 11). (Right) No effect on sIPSC amplitude. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
Two pieces of evidence favor a CB1R-mediated mechanism of action for WIN. First, the reduction of sIPSC frequency was not accompanied by significant amplitude reduction (Fig. S5F). This finding suggests that the primary site of action of WIN was presynaptic, in agreement with the characteristic presynaptic location and function of CB1Rs. Second, in the presence of the selective CB1R blocker AM251 (AM, 4 μM), WIN failed to significantly reduce sIPSC frequency of 5-wk-old neurons (pre- and post-AM+WIN: ob/ob 7.4 ± 1.5 and 5.6 ± 1.2 Hz, n = 6, P > 0.08; WT 2.6 ± 0.72 and 2.2 ± 0.6 Hz, n = 4, P > 0.5) (Fig. 5D). The application of AM+WIN did not affect sIPSC amplitude in either ob/ob or WT neurons (Fig. S5G). Finally, AM alone did not affect sIPSC frequency or amplitude.
Retrograde Modulation of Inhibitory Inputs to OX Neurons of ob/ob Mice.
So far we have shown that the strong inhibitory innervations of ob/ob OX neurons can be depressed by an exogenous CB1R agonist (WIN) acting through presynaptic CB1Rs (Fig. 5 B–D). We have also shown that the same type of neurons express increased levels of DAGLα, which plays a key role in the production of the endocannabinoid 2-AG, and that 2-AG concentration in the LH of ob/ob mice is higher than in WT (Fig. S3A). Thus, it is likely that ob/ob OX neurons release 2-AG, which in turn acts retrogradely on CB1R-expressing inhibitory inputs to reduce their activity. This result may represent a positive feedback loop to increase the firing of ob/ob OX neurons. Evoking a depolarization-induced suppression of inhibition (DSI) is a well-known method to investigate this phenomenon (19). DSI was not observed in a previous study examining OX neurons of WT lean mice (16). Interestingly, in the same study, a clear inhibitory effect was described on excitatory inputs (i.e., a negative-feedback mechanism on the firing of OX neurons). These previous results can be reconciled by the present observation of a predominance of CB1R-expressing excitatory inputs to OX neurons of WT and SFD lean mice.
To test the hypothesis that DSI is present in OX neurons of ob/ob mice (5 wk of age), we step-depolarized these neurons from −70 to 0 mV for 5 s and measured the frequency and amplitude of sIPSCs before and after depolarization. We found a significant 25–30% frequency reduction in ob/ob OX neurons after depolarization (absolute frequencies at −5, +5, and +10 s relative to the time of depolarization: 11.4 ± 3.33, 8.5 ± 2.58, and 7.8 ± 2.07 Hz, n = 11, P < 0.05 for values at +5 and +10 s vs. −5 s) (Fig. 5E, Left). No difference was observed in sIPSC amplitude (Fig. 5E, Right), a result which is consistent with the null effect of WIN on sIPSC amplitude (Fig. S5F). DSI was short-lived, because it lasted about 15 s, by which time sIPSCs frequency had recovered to control values. Furthermore, DSI was possibly mediated by the release of endocannabinoids acting at CB1Rs, because DSI was not observed when the experiment was repeated in the presence of AM (frequencies at −5, +5, and +10 s: 3.6 ± 1.12, 3.4 ± 0.99 and 2.8 ± 0.68 Hz, n = 11, P > 0.1 for both comparisons) (Fig. 5E). Finally, DSI was specific for ob/ob OX neurons because it was not observed in WT OX neurons, in agreement with a previous report (16) (absolute values at −5, +5, and +10 s: 5.1 ± 1.66, 4.8 ± 1.72 and 5.0 ± 1.88 Hz, not significant, n = 14) (Fig. 5E).
Predominant CB1-Inhibitory vs. Excitatory Innervation of OX Neurons Is Reversed by Mammalian Target of Rapamycin-Dependent Leptin Action on NPY Neurons of the ARC.
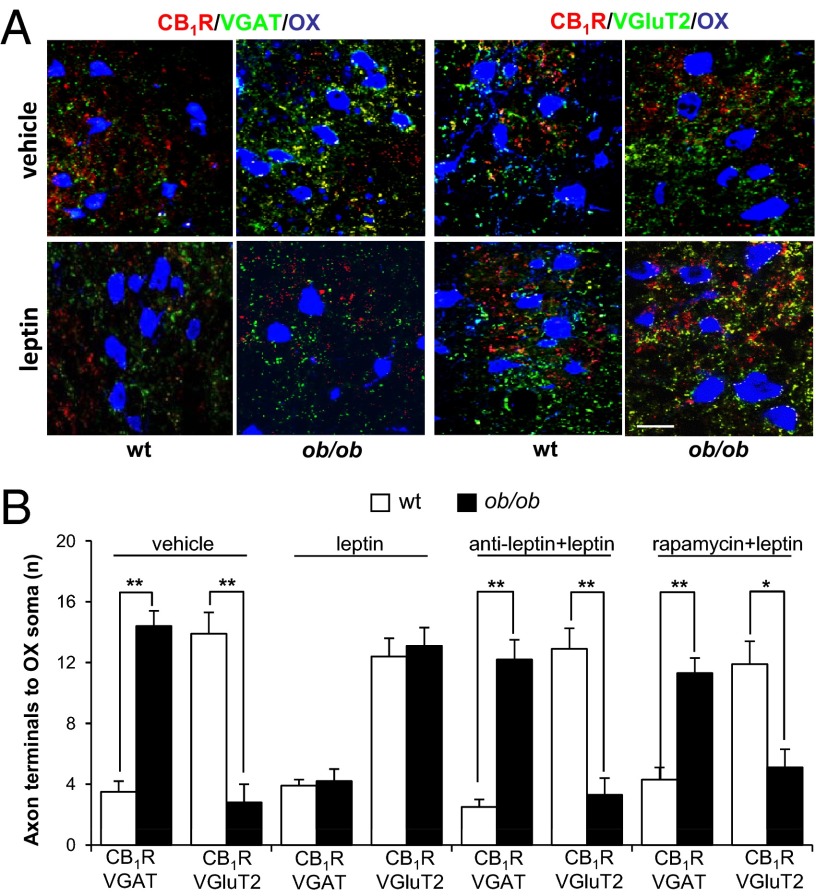
To test whether the altered synaptology of OX neurons was because of leptin deficiency, glutamatergic vs. GABAergic inputs to OX neurons were analyzed in 9-wk-old ob/ob and WT mice after injection of recombinant leptin (5 mg/kg, i.p.) after 24-h food deprivation (n = 3 mice per group). Increased VGluT2 immunoreactivity and decreased VGAT immunoreactivity was observed in the LH of ob/ob mice after leptin administration, resembling the pattern observed in vehicle-injected WT mice (Fig. 6A). This finding was assessed by analysis of the number of CB1R/VGAT- vs. CB1R/VGluT2-immunoreactive axon terminals apposed to OX perikarya (Fig. 6B). Importantly, the effects of leptin were completely abolished by previous injection of a LepRb antagonist, and partly reversed by previous injection of rapamycin, the inhibitor of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) (Fig. 6B). These findings indicate that the hormone acts through leptin receptors and, at least in part, via the mTOR branch of the LepRb signaling cascade (32). These leptin-induced synaptic changes were paralleled by functional changes in inhibitory signaling on OX neurons. In fact, we found no difference in mIPSC frequency when recording from ob/ob and WT OX neurons 24 h after recombinant leptin injection (performed as above, n = 4 mice per group). Specifically, after leptin administration, mIPSC frequency was comparable in ob/ob and WT neurons (ob/ob: 1.35 ± 0.52 Hz, n= 9; WT: 1.71 ± 0.76 Hz, n = 12, P > 0.5) and similar to the low levels observed in untreated WT neurons (see data in Fig. 4).
Fig. 6.
Leptin administration reverses the remodeling of OX neurons in ob/ob mice via an mTOR-dependent mechanism. (A) Representative CB1R/VGAT/OX and CB1R/VGluT2/OX immunofluorescence showing the paucity and abundance of CB1R-expressing inhibitory terminals to OX neurons in WT and ob/ob mice, respectively. Leptin administration to ob/ob mice restores the CB1R/VGAT/OX and CB1R/VGluT2/OX pattern to that seen in WT mice. (Scale bar, 50 µm.) (B) Quantitative analysis of CB1R/VGAT- and CB1R/VGluT2-immunoreative puncta apposed to OX somata, performed after leptin injection, without or with previous injection of a leptin antagonist (see Materials and Methods; denoted here as “anti-leptin”) or rapamycin in adult ob/ob mice fasted for 24 h (n = 3 mice and n = 100–120 OX neurons per genotype). Data are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001.
HFD mice show a shift from excitatory to inhibitory CB1R-expressing inputs to OX neurons very similar to that observed in ob/ob mice, and yet they exhibit leptin insensitivity in the ARC but not in the LH (Fig. S2E), in agreement with previous observations (33). Because HFD and ob/ob mice are otherwise quite different, we hypothesized that the leptin-dependent rearrangement of inputs to OX neurons could originate at least in part from the ARC and not from the LH. Accordingly, we showed above that the mTOR pathway (Fig. 6B), which is triggered by leptin in the ARC (32), is involved in the reversal by exogenously administered leptin of the phenotypic alterations observed here. mTOR activity is increased through its phosphorylation, which in turn triggers phosphorylation first of ribosomal S6-kinase-1 (S6K1) to phospho-S6K1 (pS6K1) and then of the targets of the latter kinase, such as ribosomal protein S6 (S6RP). In a previous study, activation of this pathway was found in ∼90% of NPY/AgRP neurons and ∼45% of POMC neurons of the mouse ARC (32). On the other hand, NPY-expressing axon terminals are known to be GABAergic, whereas α-melanocyte-stimulating hormones (MSH)-expressing terminals can be either GABAergic or glutamatergic (34). Considering also the role of the mTOR pathway in regulating neuronal plasticity (35), we hypothesized that: (i) the CB1R/GABAergic afferents to OX neurons, which increase in obese mice and decrease in ob/ob mice after leptin treatment, are represented, at least in part, by NPY fibers originating in the ARC; and (ii) mTOR mediates the down-regulation by leptin of these afferents.
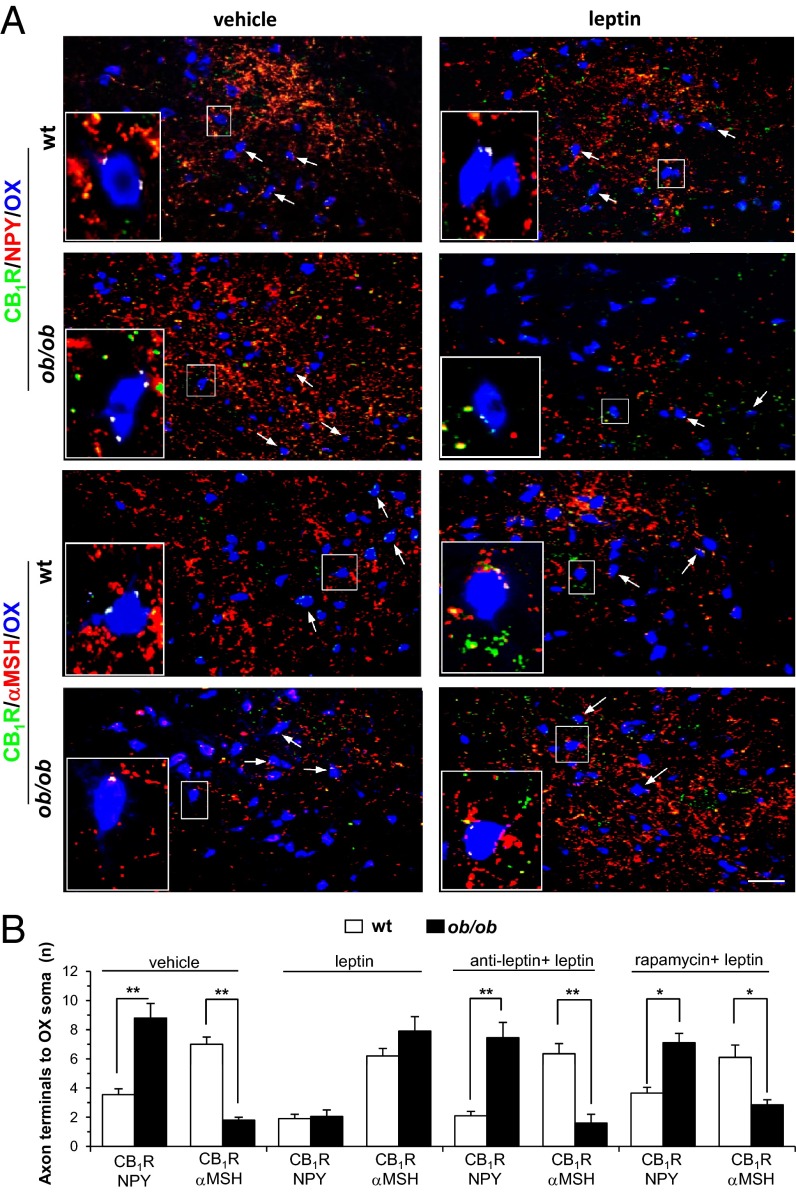
Three sets of data strongly supported these hypotheses. First, we could confirm that in 9-wk-old ob/ob mice 24-h leptin administration enhanced the levels of pS6K1 and phospho-S6RP in the ARC (Fig. S6 A and B), and of pS6K1 in the majority of ARC NPY neurons (85 ± 8%, n = 100 NPY neurons; n = 3 mice) with a much lower effect on POMC neurons (40 ± 6%, n = 100 POMC neurons; n = 3 mice) (Fig. S6C). Second, in both adult HFD mice and 9-wk-old ob/ob mice, CB1R/NPY afferents to OX neurons largely outnumbered CB1R/αMSH afferents (Fig. 7). By confocal microscopy analysis we determined that 8.7 ± 1.3 CB1R/NPY axon terminals per neuron were apposed to OX neurons. Considering that NPY axon terminals are GABAergic, and that the overall number of CB1R/VGAT axon terminals per OX neuron was 13 ± 2 in adult obese ob/ob and HFD mice (see above and Fig. 2), the CB1R/NPY afferents accounted for ∼70% of the GABAergic afferents to OX neurons (Fig. 7B). An opposite scenario was observed in OX neurons of the corresponding lean controls and of leptin-treated ob/ob mice. Third, in ob/ob mice injection of a LepRb antagonist or rapamycin 1 h before leptin restored both the innervation pattern (Fig. 7B) and the levels of phospho-S6RP to control values observed in untreated ob/ob mice (Fig. S6A).
Fig. 7.
Role of ARC mTOR signaling in the remodeling of OX neurons induced by lack of leptin in ob/ob mice. (A) Representative CB1R/NPY/OX and CB1R/αMSH/OX immunofluorescence in WT and ob/ob mice showing significantly higher colocalization of CB1R with NPY than with αMSH in axon terminals apposed to OX in the latter mice. This phenomenon is reversed by leptin administration. Arrows point to OX somata receiving CB1R/αMSH or CB1R/NPY puncta. (Scale bar, 50 µm.) The insets depict the corresponding boxed areas at higher magnification. (Scale bar, 15 µm.) (B) Quantification of CB1R/NPY- vs. CB1R/αMSH-immunolabeled axon terminals apposed to OX perikarya, after vehicle or leptin injection, the latter with or without previous injection of leptin receptor antagonist (“anti-leptin”) or rapamycin, in adult ob/ob mice fasted for 24 h. Note the drastic leptin-induced decrease and increase of CB1R coexpression with NPY and αMSH, respectively, in terminals apposed to OX neurons in ob/ob mice. This effect was reversed when anti-leptin or rapamycin were coinjected with leptin. Data are mean ± SEM; n = 200 OX neurons, *P < 0.01, **P < 0.001.
Synaptic Alterations of OX Neurons Are Accompanied by Increased OX Expression in LH Terminal Fields, Which Is Reversed by CB1R Blockade.
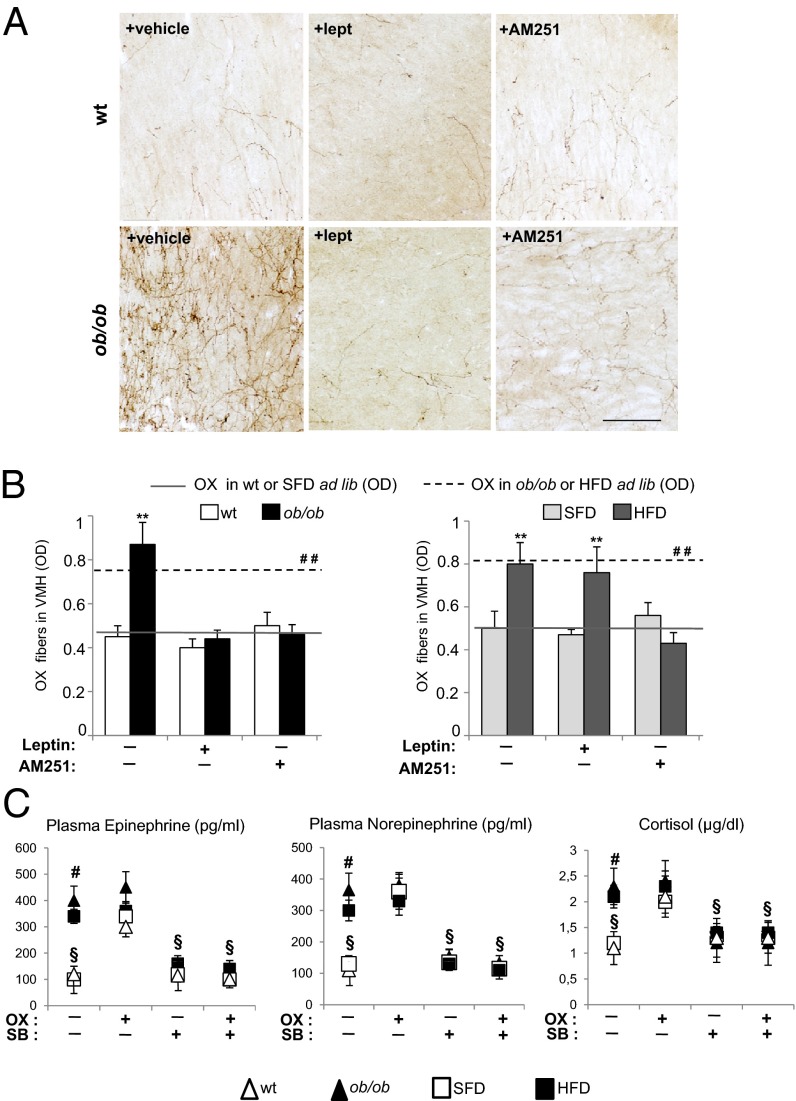
To examine the consequences of altered endocannabinoid control over OX signaling, we first measured the expression of preproorexin mRNA in the LH of preweaned, postweaned, and adult ob/ob mice and matched WT mice, and found an increase of this transcript only in adult obese mice (Fig. S7A). In contrast, OX immunosignal in cell bodies assessed by densitometric analysis did not significantly differ between ob/ob and HFD mice vs. matched controls (Fig. S7C). However, in obese (ob/ob and HFD) mice the OX immunosignal was higher in fibers innervating target areas, such as the ARC, nucleus accumbens, ventral tegmental area (Fig. S7 D–F), and ventral medial hypothalamus (VMH) (Fig. 8 A and B). Importantly, these alterations were also reversed by administration of exogenous leptin injection. The mice used for these measurements were food-deprived for 24 h before leptin administration and then given free access to food. However, when the OX immunosignal density was measured in the same areas of vehicle-treated, ad libitum-fed lean (Fig. 8B and Fig. S7 C–F) and obese (Fig. 8B and Fig. S7 C–F) mice, a similar phenotypic difference was observed. Interestingly, in OX-innervated regions, the OX immunosignal did not differ between MAGL-WT and MAGL-KO mice (Fig. S7B). This finding suggests that 2-AG level elevation is not sufficient to cause changes in OX signaling in the absence of alterations of excitatory vs. inhibitory innervation of OX neurons. However, CB1R are involved in mediating the elevation of orexinergic signaling in target areas of obese (ob/ob and HFD) mice. In fact, when these animals were treated for 2 h with the CB1R inverse agonist AM251 (AM; 10 mg/kg, i.p.), the increased OX immunoreactivity returned to control levels (Fig. 8B and Fig. S7 C–F). It is noteworthy that leptin was ineffective at reducing OX signal in output areas of HFD mice, most likely because of their leptin-insensitivity in the ARC (Fig. S7 D–F).
Fig. 8.
Orexin is increased in fibers innervating the VMH of obese mice with possible involvement in up-regulation of epinephrine, norepinephrine and cortisol in obesity. (A) OX immunoreactivity in fibers projecting to the VMH of WT and ob/ob mice. OX expression is markedly increased in ob/ob mice vs. WT and reduced by leptin or CB1R antagonist AM251 treatment. (Scale bar, 50 µm.) (B) Densitometric evaluation (OD, optical density units) of immunosignal intensity in OX fibers innervating the VMH of 24 h fasted, obese (ob/ob and HFD) mice or lean (wt and SFD) littermates. Optical density measument for OX immunostaining is also shown for ad libitum-fed lean mice (solid lines) and obese mice (dotted lines). n = 3 mice per group. (C) Effect of intraperitoneal administration of vehicle (saline) or OX and OX receptor antagonist SB-334867 (SB) on the plasma concentrations of Epi (epinephrine), NE (norepinephrine), and cortisol of obese and lean mice. Data are mean ± SEM. **P < 0.001 vs. corresponding fasted lean mouse controls; ##P < 0.05 vs. solid lines; #P < 0.05 vs. corresponding lean mouse controls fed ad lib; §P < 0.001 vs. OX-injected mice.
Enhanced OX Signaling Undelies Hyperphagia and Alterations in Sympathetic Nerve Outflow Typical of Obesity.
To investigate whether the synaptic switch to OX neurons in obesity underlies some of the comorbidities typical of this condition, we performed two different sets of experiments. The levels of epinephrine (Epi), norepinephrine (NE), and cortisol, which are normally elevated in obesity, were measured in the blood obtained from the abdominal aorta of adult anesthetized (pentobarbital sodium, 50 mg/kg i.p.) male weight- and age-matched lean (WT and SFD, n = 3 per group) and obese (ob/ob and HFD, n = 3 per group) mice, 2 h after injection of vehicle or the orexin-A receptor antagonist SB-334867 (60 mg/kg, i.p.), followed by 1-h treatment with vehicle or OX (40 mg/kg, i.p.). In vehicle-treated obese mice, in agreement with previous studies (36), Epi, NE, and cortisol levels were significantly higher than in the corresponding vehicle-treated lean mice. OX injection elevated Epi, NE, and cortisol levels in lean but not in obese mice, this effect being reversed by SB-334867, which also reduced the levels of these hormones in obese mice to control levels. These data suggest that increased OX signaling underlies at least in part the dysregulation of autonomic sympathetic nervous outflow typical of obesity, possibly through overactivation of OX receptors in the VMH (8). Indeed, in this target area we observed the strongest leptin deficiency-induced and CB1R-mediated elevation of OX immunoreactivity (Fig. 8 A and B).
Next, SB-334867 (60 mg/kg, i.p.) or vehicle were injected twice daily for 1 wk, 4 h before dark and light phase onset, in adult obese (ob/ob and HFD, n = 5 per group) mice, and body weight and food intake measured daily. A strong reduction of food intake (Fig. S8A) and body weight (Fig. S8B) was observed in the SB-334867–injected mice vs. vehicle-injected obese mice. Interestingly, food-intake was more affected by SB-334867 in ob/ob than HFD mice (28 ± 2% vs. 20 ± 3%, in ob/ob vs. HFD), whereas the effect on weight reduction was stronger in HFD than in ob/ob mice (13 ± 0.9% vs. 9 ± 0.7%, in ob/ob vs. HFD), suggesting that body weight reduction was not merely a consequence of food-intake inhibition.
Discussion
Anatomy and Neuromodulatory Role of the Endocannabinoid System in the LH.
We showed here that in the LH of lean mice, as in other brain areas (20, 21), endocannabinoid metabolic enzymes are well positioned to facilitate the retrograde action of postsynaptically produced 2-AG onto presynaptic CB1Rs. Specifically, OX neurons: (i) express the 2-AG-biosynthetic enzyme DAGLα in the membrane of their somata and proximal dendrites; and (ii) are contacted by axon terminals that express both CB1Rs and the 2-AG–hydrolyzing enzyme MAGL and are mostly glutamatergic. Such synaptic chemical signature: (i) is in agreement with findings in other brain areas, showing that DAGLα is mostly distributed in somata and dendritic spines contacted by excitatory axon terminals (20); and (ii) provides anatomical bases for the previously observed CB1R-mediated inhibition of excitatory postsynaptic currents and for endocannabinoid involvement in depolarization-induced suppression of excitation (DSE) in OX neurons (16).
Obesity Is Accompanied by Remodeling of Inhibitory vs. Excitatory Fibers in the LH.
The data obtained here with a variety of experimental approaches indicate that the axon terminals innervating OX neurons, particularly those that coexpress CB1Rs and MAGL, become predominantly inhibitory in both ob/ob mice after weaning and in adult HFD mice. Such alteration is not present, instead, in axon terminals apposed to another population of LH neurons, those producing MCH, and results in: (i) increased mIPSC and sIPSC frequency; (ii) increased presynaptic inhibition of sIPSC by CB1R agonists; and (iii) endocannabinoid-mediated DSI as opposed to DSE in control mice (16), in OX neurons. Furthermore, the biosynthesis of 2-AG is elevated in the LH of adult ob/ob and HFD mice, thus allowing for stronger endocannabinoid-mediated disinhibition of OX neurons in obese mice. Taken together these findings provide an unprecedented example of a substantial obesity-related functional switch of endocannabinoid-mediated “retrograde” modulation of neuronal activity from inhibition of excitation to inhibition of inhibition.
Remodeling of CB1R-Expressing Inhibitory vs. Excitatory Fibers in the LH Is Because of Leptin Signaling Impairment.
We found that CB1R distribution in glutamatergic and GABAergic axon terminals in the LH is similar in MAGL-KO mice and WT littermates despite the very high levels of 2-AG in the former. Therefore, it is unlikely that the increased LH levels of 2-AG in obese mice contribute to the shift from excitatory to inhibitory transmission onto OX neurons. Instead, we observed that, in ob/ob mice, this shift occurs after weaning. Leptin, which plays a key role in food deprivation-induced changes in the synaptic innervation of the hypothalamus, and the LH in particular (9), is transferred from heterozygote dams to suckling pups during lactation, as early maternal milk contains this hormone (37). Thus, weaned ob/ob pups that do not receive milk from their dams become progressively leptin-depleted, as shown also here by the presence of phospho-STAT3 in the hypothalamus of preweaned ob/ob mice and its disappearance after weaning. On this basis, we hypothesized that the enhanced CB1R/GABAergic innervation of OX neurons observed after weaning might be because of lack of leptin. Accordingly, we found that 24-h leptin administration to adult ob/ob mice was sufficient to fully reverse this phenomenon, as assessed by both immunohistochemical analyses and functional patch-clamp measurements.
Impaired Leptin Signaling via the mTOR Pathway in NPY Neurons of the ARC Is Partly Responsible for the Remodeling of OX Neuron Synapses.
Experiments in mice made obese and leptin-resistant by HFD extend our findings to an animal model relevant to human obesity, and support the involvement of leptin in the observed synaptic rearrangement of CB1R-expressing fibers. Moreover, in agreement with previous observations (33), our HFD mice exhibited leptin resistance in the ARC but not in the LH. Longer administration of HFD to mice also causes irreversible leptin resistance in the ARC as assessed by electrophysiological techniques (38). Therefore, we hypothesized that the observed synaptic remodeling of inputs to OX neurons could originate from the ARC. Indeed, of the two major cell populations in the ARC, that is, NPY/AgRP and POMC neurons, the former account for many GABAergic terminals in the LH. Conversely, POMC neurons also send glutamatergic αMSH-expressing efferents to the LH, and thus account for fewer inhibitory terminals in this area. Accordingly, we found that the increase of CB1R-expressing GABAergic afferents to OX neurons of obese mice was mostly because of NPY-expressing fibers.
Leptin anorectic actions and signaling via LepRb in NPY/AgRP neurons of the ARC occur through phosphorylation of mTOR and its downstream targets, S6K1 and S6RP (32). On this basis, we hypothesized that impairment of this signaling cascade, and of its well-known effects on synaptic plasticity (35), could underlie, at least in part, the increase of CB1R-GABAergic inputs to OX neurons in obese mice. Accordingly, we found that administration of the mTOR inhibitor rapamycin to ob/ob mice attenuated (similarly to a LepRb antagonist) the leptin-induced reduction of both CB1R/VGAT and CB1R/NPY inputs to OX neurons, while concomitantly inhibiting S6RP phosphorylation in the ARC.
Additional Mechanisms for the Remodeling of OX Neuron Synapses.
Rapamycin also attenuated the leptin-induced enhancement of CB1R/VGluT2 and CB1R/αMSH afferents to OX neurons. This finding confirms the previous observation that the mTOR pathway is also stimulated in POMC neurons of the ARC, although to a lesser extent than in NPY/AgRP neurons (32). Therefore, the reduction of glutamatergic inputs to OX neurons in ob/ob mice, or at least those inputs that also express αMSH and derive from the ARC, may also be a direct consequence of impaired leptin-mTOR signaling in this area. However, because αMSH afferents can also be GABAergic, additional mechanisms could account for the observed alterations of CB1R glutamatergic afferents to the LH. For example, the reduction of these afferents may represent an indirect maladaptive mechanism resulting from destabilization of the hypothalamic network, as recently described in the striatum of an animal model of Huntington’s chorea (39). Indeed, only part of the excitatory and inhibitory afferents to OX neurons originate from the ARC, although these account for a large part of CB1R-expressing innervation. Furthermore, not all species fed a HFD develop a true leptin insensitivity in the ARC, as changes in the connectivity of this area in rats may respond to high doses of leptin, possibly because of astrocyte-mediated actions (40). Thus, although we identified herein a mechanism through which obesity and impaired leptin signaling in the ARC determine a reorganization of a contingent of these afferents, additional mechanisms could contribute to this phenomenon. For example, local LepRb-expressing GABAergic neurons, which inhibit the activity of OX, but not MCH, neurons (41) could also participate in the observed alterations.
Consequences of the Remodeling of OX Neuron Synapses on OX Signaling and Its Potential Role in Obesity Comorbidities.
The leptin deficiency-driven remodeling of CB1R control of OX neurons, and the resulting shift from CB1R-mediated inhibition of excitation to disinhibition, was accompanied by a marked increase of OX immunoreactivity in target areas, an effect that was reversed not only by leptin (only in ob/ob mice) but also by CB1R blockade. One interpretation of these findings is that OX release is increased in these areas, because increased release of a neuropeptide up-regulates its trafficking to terminals. Accordingly, expression of preproorexin mRNA was increased in the LH, whereas OX immunoreactivity did not change, as it would be expected if increased production and trafficking to terminals were substantially balanced. Increased OX signaling in the ARC, nucleus accumbens, and ventral tegmental area might underlie higher preference for palatable food and hyperphagia (42), whereas in the VMH it may cause hyperactivation of sympathetic outflow and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis (8, 36), which are all conditions typical of obesity. Accordingly, we have shown here that an OX-A receptor antagonist reduces food intake and body weight, and fully reverses Epi, NE, and cortisol elevation in both ob/ob and HFD mice.
In conclusion, we provided an unprecedented example of how endocannabinoid neuromodulatory control of excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission can be profoundly altered in obesity because of leptin-dependent reorganization of glutamatergic and GABAergic synapses. In the LH, this reorganization may result in disinhibition of OX neurons via enhanced retrograde inhibition of inhibitory inputs. The full functional implications of this phenomenon, and of the consequently enhanced OX release in target brain areas and in the bloodstream, together with the possible occurrence of leptin-dependent synaptic reorganization in other brain regions, need now to be investigated.
Materials and Methods
Preembedding Immunogold Silver-Enhanced Electron Microscopy and Analysis.
Preembedding double-immunogold sequential silver-enhanced labeling was performed according to the procedure of Yi et al. (23) (for details see, SI Materials and Methods and Fig. S1 F, G, and I). Synapse characterization was performed at 30,000 magnification. Excitatory synapses were identified by their asymmetrical morphology (Fig. 1 C and G and Fig. S1C) and inhibitory synapses by their symmetrical morphology (27) (Fig. 1D and Fig. S1D). Synapses were counted only if the pre- and postsynaptic symmetrical and asymmetrical membrane specializations were clearly seen and synaptic vesicles were present in the presynaptic bouton. Orexinergic neurons (n = 5 per animal; n = 3 mice per group of age, genotype, or diet) were followed through 24 consecutive ultrathin 60-nm sections, according to the synaptological method used by Horvath and Gao (9). We randomly sampled every element of the analysis as bouton at high-power magnification, OX perikarya, and the plane of each transected cell. CB1R-expressing boutons contacting the somata of OX neurons (n = 20 per animal) were analyzed (an average of four CB1R-expressing boutons per OX neuron). The percentage of CB1R-expressing boutons relative to the total number of inhibitory or excitatory boutons of adult ob/ob and HFD mice was calculated on the same samples. Because boutons contacting proximal dendrites provide an additional measure of the overall excitation/inhibition balance, we also analyzed CB1R-expressing axo-dendritic boutons (n = 10 per mouse) from additional 20 consecutive ultrathin sections different from those used for the quantitative analysis of axosomatic CB1R-expressing boutons. The total length of examined OX cell membrane was 21 µm in the soma and 18 µm in proximal dendrites per group of age, genotype, and diet.
Electrophysiology.
Mice were anesthetized by inhalation of ether and depth of anesthesia was judged by lack of a righting reflex. Animals were then perfused transcardially with ice-cold dissection media (DM), and the cerebral hemispheres quickly removed and reduced to blocks in ice-cold DM. DM consisted of: 220 mM sucrose, 26 mM NaHCO3, 1.23 mM NaH2PO4, 2.5 mM KCl, 6 mM MgCl2, 1 mM CaCl2, and 10 mM glucose, equilibrated with 95% O2/5% CO2 (vol/vol). Hypothalamic coronal slices (200-μm thick) were cut in ice-cold DM and then incubated at 32 °C for 45 min in artificial cerebrospinal fluid (ACSF) consisting of: 122 mM NaCl, 26 mM NaHCO3, 1.23 mM NaH2PO4, 2.5 mM KCl, 2 mM MgCl2, 2 mM CaCl2, 1 mM Na-ascorbate, 3 mM Na-pyruvate, and 10 mM glucose, equilibrated as above. Slices were subsequently transferred in a recording chamber perfused at 2–3 mL/min with ACSF at room temperature. Excitatory inputs were blocked with 10 μM NBQX and CPP (Sigma). The addition of 30 μM bicuculline (Sigma) invariably confirmed the inhibitory nature of the recorded synaptic activity. When appropriate, CB1Rs were activated by adding 5 μM WIN mesylate (Tocris), or blocked with 4 μM AM251 ( Tocris). Whole-cell recordings were performed with an Axopatch 200B amplifier (Axon Instruments), under a custom-made microscope equipped with an infrared video camera (Hamamatsu) and differential interference contrast optics. Neurons were functionally identified as OX by determination, in current clamp mode, of their typical responses to injected current pulses (details in SI Materials and Methods and in Fig. S5 A and B). Neurons were then voltage-clamped at −70 mV and the spontaneous activity of inhibitory inputs recorded in the presence (for mIPSC) or absence (for sIPSC) of 1 μM TTX (Sigma). DSI was induced in voltage clamp with a 5-s step-depolarization to 0 mV and measured as sIPSC frequency modulation (details in SI Materials and Methods). Recording electrodes (2–5 MΩ) were made with borosilicate glass (Warner Instruments) and filled with: 145 mM KCl, 10 mM Hepes, 0.2 mM EGTA, 2 mM Mg-ATP, 0.5 mM Na-GTP, pH 7.4 with KOH. Signals were filtered at 10 kHz by pClamp 9.2 and digitized at 20 kHz (Digidata 1322A; Axon Instruments). Series resistance (<20 MΩ) and whole-cell capacitance were not compensated. The recording was terminated if series resistance changed more than 20%. All experiments were performed at least 4 min after establishing the whole cell configuration, to allow the spontaneous synaptic activity to reach a stable frequency (details in SI Materials and Methods). The frequencies of mIPSCs and sIPSCs were measured over a period of 1 min. The effect of AM and WIN was measured 4–5 min after the addition of the drugs. Data were analyzed with Clampfit 9.2 (Axon Instruments). A subset of 17 neurons were loaded with 2% FITC-Neurobiotin (Vector Lab) through the recording electrode. At the end of the recordings, the slices were fixed in 4% (wt/vol) paraformaldheyde in phosphate buffer for 1 h and kept in phosphate buffer until incubation in a mixture of goat anti-OX/rabbit and anti-MCH primary antibodies (Santa Cruz Biotechnology), labeled with anti-rabbit Alexa546/anti-goat Alexa350 secondary antibodies (Fig. S5C). See SI Materials and Methods for further details.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank V. Guglielmotti for assistance in the preparation of samples for electron microscopy; Stazione Zoologica “Anton Dohrn” for technical assistance at Transmission Electron Microscopy and Confocal Microscopy Facilities; CISME of Federico II for TEM image acquisition; R. Zechner and R. Zimmermann for the gift of monoacyclycerol lipase-knockout mice. This work was supported by Compagnia San Paolo Foundation “Program in Neuroscience” Grant CSP-1268 (to L.C.) and National Institutes of Health Grants DA-011322 and DA-021696 (to K.M.) and DA-009789 (to V.D.M.).
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
*This Direct Submission article had a prearranged editor.
See Commentary on page 9625.
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1219485110/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Peyron C, et al. Neurons containing hypocretin (orexin) project to multiple neuronal systems. J Neurosci. 1998;18(23):9996–10015. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-23-09996.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sakurai T, Mieda M. Connectomics of orexin-producing neurons: Interface of systems of emotion, energy homeostasis and arousal. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2011;32(8):451–462. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2011.03.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Leinninger GM, et al. Leptin action via neurotensin neurons controls orexin, the mesolimbic dopamine system and energy balance. Cell Metab. 2011;14(3):313–323. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.06.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Leinninger GM, et al. Leptin acts via leptin receptor-expressing lateral hypothalamic neurons to modulate the mesolimbic dopamine system and suppress feeding. Cell Metab. 2009;10(2):89–98. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2009.06.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Borgland SL, Taha SA, Sarti F, Fields HL, Bonci A. Orexin A in the VTA is critical for the induction of synaptic plasticity and behavioral sensitization to cocaine. Neuron. 2006;49(4):589–601. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2006.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.van den Pol AN. Neuropeptide transmission in brain circuits. Neuron. 2012;76(1):98–115. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.09.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Horvath TL, et al. Hypocretin (orexin) activation and synaptic innervation of the locus coeruleus noradrenergic system. J Comp Neurol. 1999;415(2):145–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Shiuchi T, et al. Hypothalamic orexin stimulates feeding-associated glucose utilization in skeletal muscle via sympathetic nervous system. Cell Metab. 2009;10(6):466–480. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2009.09.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Horvath TL, Gao XB. Input organization and plasticity of hypocretin neurons: Possible clues to obesity’s association with insomnia. Cell Metab. 2005;1(4):279–286. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2005.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bouret SG, Draper SJ, Simerly RB. Trophic action of leptin on hypothalamic neurons that regulate feeding. Science. 2004;304(5667):108–110. doi: 10.1126/science.1095004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Pinto S, et al. Rapid rewiring of arcuate nucleus feeding circuits by leptin. Science. 2004;304(5667):110–115. doi: 10.1126/science.1089459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Di Marzo V, et al. Leptin-regulated endocannabinoids are involved in maintaining food intake. Nature. 2001;410(6830):822–825. doi: 10.1038/35071088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Di Marzo V, Matias I. Endocannabinoid control of food intake and energy balance. Nat Neurosci. 2005;8(5):585–589. doi: 10.1038/nn1457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bellocchio L, et al. Bimodal control of stimulated food intake by the endocannabinoid system. Nat Neurosci. 2010;13(3):281–283. doi: 10.1038/nn.2494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jo YH, Chen YJ, Chua SC, Jr, Talmage DA, Role LW. Integration of endocannabinoid and leptin signaling in an appetite-related neural circuit. Neuron. 2005;48(6):1055–1066. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.10.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Huang H, et al. Cannabinoids excite hypothalamic melanin-concentrating hormone but inhibit hypocretin/orexin neurons: Implications for cannabinoid actions on food intake and cognitive arousal. J Neurosci. 2007;27(18):4870–4881. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0732-07.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wittmann G, et al. Distribution of type 1 cannabinoid receptor (CB1)-immunoreactive axons in the mouse hypothalamus. J Comp Neurol. 2007;503(2):270–279. doi: 10.1002/cne.21383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Safo PK, Cravatt BF, Regehr WG. Retrograde endocannabinoid signaling in the cerebellar cortex. Cerebellum. 2006;5(2):134–145. doi: 10.1080/14734220600791477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wilson RI, Nicoll RA. Endocannabinoid signaling in the brain. Science. 2002;296(5568):678–682. doi: 10.1126/science.1063545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Alger BE, Kim J. Supply and demand for endocannabinoids. Trends Neurosci. 2011;34(6):304–315. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2011.03.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Di Marzo V. Endocannabinoid signaling in the brain: Biosynthetic mechanisms in the limelight. Nat Neurosci. 2011;14(1):9–15. doi: 10.1038/nn.2720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Taschler U, et al. Monoglyceride lipase deficiency in mice impairs lipolysis and attenuates diet-induced insulin resistance. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(20):17467–17477. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.215434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yi H, Leunissen J, Shi G, Gutekunst C, Hersch S. A novel procedure for pre-embedding double immunogold-silver labeling at the ultrastructural level. J Histochem Cytochem. 2001;49(3):279–284. doi: 10.1177/002215540104900301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Uchigashima M, et al. Subcellular arrangement of molecules for 2-arachidonoyl-glycerol-mediated retrograde signaling and its physiological contribution to synaptic modulation in the striatum. J Neurosci. 2007;27(14):3663–3676. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0448-07.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Yoshida T, et al. Unique inhibitory synapse with particularly rich endocannabinoid signaling machinery on pyramidal neurons in basal amygdaloid nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108(7):3059–3064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1012875108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Coppari R, Bjørbæk C. Leptin revisited: Its mechanism of action and potential for treating diabetes. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2012;11(9):692–708. doi: 10.1038/nrd3757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.van den Pol AN, Wuarin JP, Dudek FE. Glutamate, the dominant excitatory transmitter in neuroendocrine regulation. Science. 1990;250(4985):1276–1278. doi: 10.1126/science.1978759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Eggermann E, et al. The wake-promoting hypocretin-orexin neurons are in an intrinsic state of membrane depolarization. J Neurosci. 2003;23(5):1557–1562. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-05-01557.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Li Y, Gao XB, Sakurai T, van den Pol AN. Hypocretin/Orexin excites hypocretin neurons via a local glutamate neuron-A potential mechanism for orchestrating the hypothalamic arousal system. Neuron. 2002;36(6):1169–1181. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(02)01132-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Rao Y, et al. Regulation of synaptic efficacy in hypocretin/orexin-containing neurons by melanin concentrating hormone in the lateral hypothalamus. J Neurosci. 2008;28(37):9101–9110. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1766-08.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Mackie K, Hille B. Cannabinoids inhibit N-type calcium channels in neuroblastoma-glioma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1992;89(9):3825–3829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Cota D, et al. Hypothalamic mTOR signaling regulates food intake. Science. 2006;312(5775):927–930. doi: 10.1126/science.1124147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Matheny M, Shapiro A, Tümer N, Scarpace PJ. Region-specific diet-induced and leptin-induced cellular leptin resistance includes the ventral tegmental area in rats. Neuropharmacology. 2011;60(2-3):480–487. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2010.11.002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Dicken MS, Tooker RE, Hentges ST. Regulation of GABA and glutamate release from proopiomelanocortin neuron terminals in intact hypothalamic networks. J Neurosci. 2012;32(12):4042–4048. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6032-11.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hoeffer CA, Klann E. mTOR signaling: At the crossroads of plasticity, memory and disease. Trends Neurosci. 2010;33(2):67–75. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2009.11.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Shirasaka T, Nakazato M, Matsukura S, Takasaki M, Kannan H. Sympathetic and cardiovascular actions of orexins in conscious rats. Am J Physiol. 1999;277(6 Pt 2):R1780–R1785. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1999.277.6.R1780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Casabiell X, et al. Presence of leptin in colostrum and/or breast milk from lactating mothers: A potential role in the regulation of neonatal food intake. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997;82(12):4270–4273. doi: 10.1210/jcem.82.12.4590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Diano S, et al. Peroxisome proliferation-associated control of reactive oxygen species sets melanocortin tone and feeding in diet-induced obesity. Nat Med. 2011;17(9):1121–1127. doi: 10.1038/nm.2421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Chiodi V, et al. Unbalance of CB1 receptors expressed in GABAergic and glutamatergic neurons in a transgenic mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Neurobiol Dis. 2012;45(3):983–991. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2011.12.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Horvath TL, et al. Synaptic input organization of the melanocortin system predicts diet-induced hypothalamic reactive gliosis and obesity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107(33):14875–14880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1004282107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Louis GW, Leinninger GM, Rhodes CJ, Myers MG., Jr Direct innervation and modulation of orexin neurons by lateral hypothalamic LepRb neurons. J Neurosci. 2010;30(34):11278–11287. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1340-10.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hirasawa M, Parsons MP, Alberto CO. Interaction between orexins and the mesolimbic system for overriding satiety. Rev Neurosci. 2007;18(5):383–393. doi: 10.1515/revneuro.2007.18.5.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.