Abstract
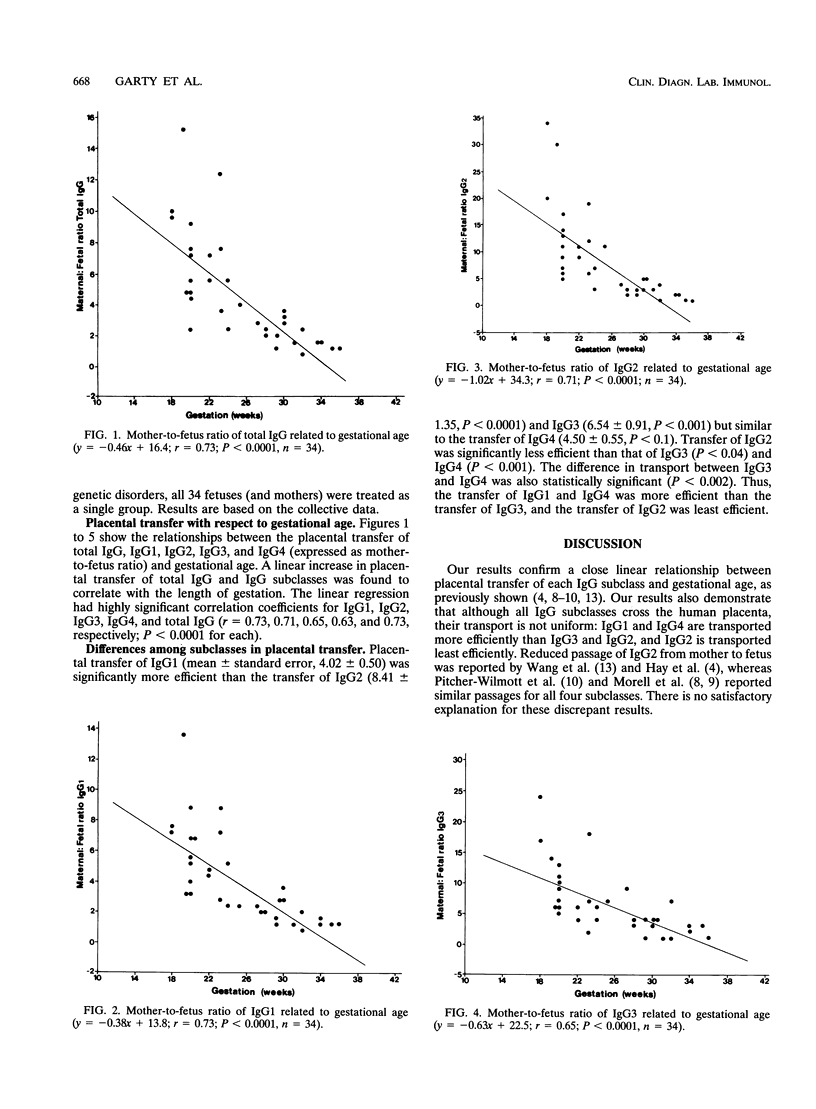
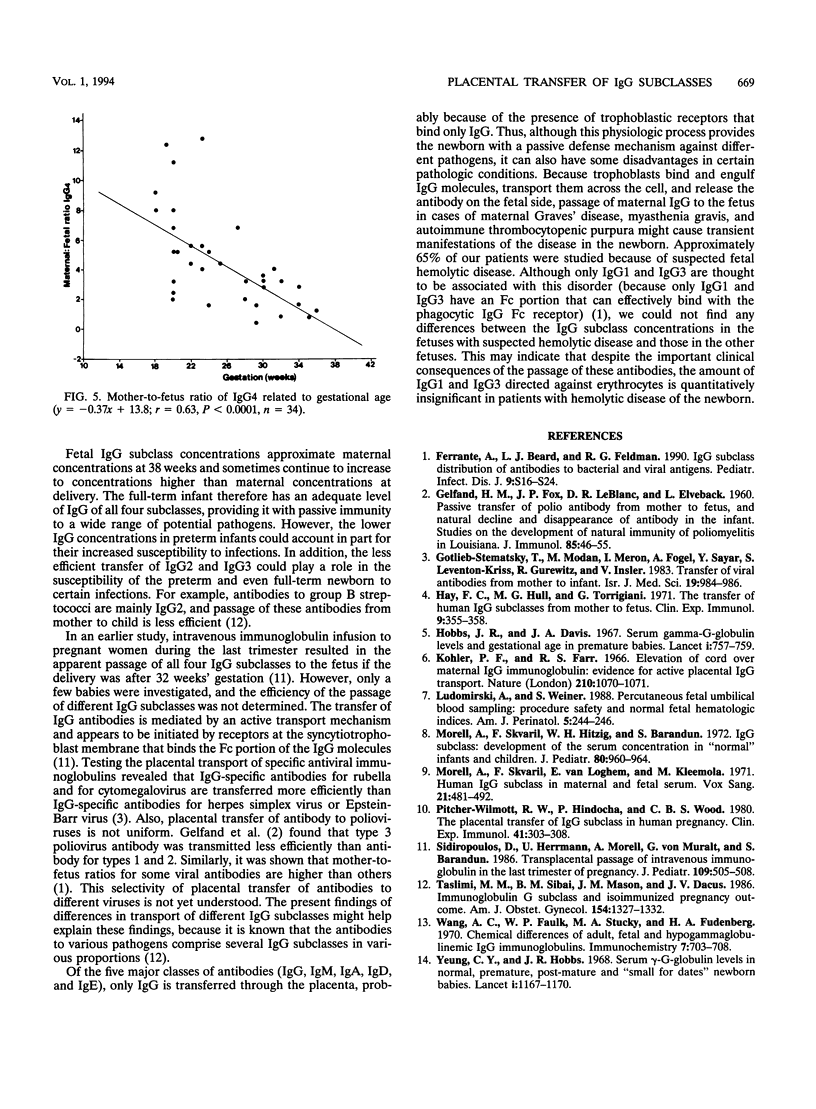
The concentrations in cord blood of total immunoglobulin G (IgG) and the four subclasses of IgG were measured in 34 fetuses at a mean gestational age of 25 weeks (range, 18 to 35 weeks). The blood samples were obtained by percutaneous umbilical blood sampling, and results were compared with the respective IgG subclass concentrations of the mothers. The efficiency of transplacental transfer of the different IgG subclasses was determined. Transfer of IgG1 and IgG4 was found to be significantly more efficient than that of IgG3 and IgG2. IgG2 was the subclass least efficiently transferred from mother to fetus. These differences may partly explain the susceptibility of newborns to various pathogens, such as streptococcus group B.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ferrante A., Beard L. J., Feldman R. G. IgG subclass distribution of antibodies to bacterial and viral antigens. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1990 Aug;9(8 Suppl):S16–S24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GELFAND H. M., FOX J. P., LEBLANC D. R., ELVEBACK L. Studies on the development of natural immunity to poliomyelitis in Louisiana. V. Passive transfer of polioantibody from mother to fetus, and natural decline and disappearance of antibody in the infant. J Immunol. 1960 Jul;85:46–55. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotlieb-Stematsky T., Modan M., Meron I., Fogel A., Sayar Y., Leventon-Kriss S., Gurewitz R., Insler V. Transfer of viral antibodies from mother to infant. Isr J Med Sci. 1983 Nov;19(11):984–986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay F. C., Hull M. G., Torrigiani G. The transfer of human IgG subclasses from mother to foetus. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Sep;9(3):355–358. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs J. R., Davis J. A. Serum gamma-G-globulin levels and gestational age in premature babies. Lancet. 1967 Apr 8;1(7493):757–759. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91369-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler P. F., Farr R. S. Elevation of cord over maternal IgG immunoglobulin: evidence for an active placental IgG transport. Nature. 1966 Jun 4;210(5040):1070–1071. doi: 10.1038/2101070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A., Skvaril F., Hitzig W. H., Barandun S. IgG subclasses: development of the serum concentrations in "normal" infants and children. J Pediatr. 1972 Jun;80(6):960–964. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(72)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morell A., Skvaril F., van Loghem E., Kleemola M. Human IgG subclasses in maternal and fetal serum. Vox Sang. 1971 Dec;21(6):481–492. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1971.tb04808.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitcher-Wilmott R. W., Hindocha P., Wood C. B. The placental transfer of IgG subclasses in human pregnancy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1980 Aug;41(2):303–308. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidiropoulos D., Herrmann U., Jr, Morell A., von Muralt G., Barandun S. Transplacental passage of intravenous immunoglobulin in the last trimester of pregnancy. J Pediatr. 1986 Sep;109(3):505–508. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80132-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taslimi M. M., Sibai B. M., Mason J. M., Dacus J. V. Immunoglobulin G subclasses and isoimmunized pregnancy outcome. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1986 Jun;154(6):1327–1332. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(86)90720-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A. C., Faulk W. P., Stuckey M. A., Fudenberg H. H. Chemical differences of adult, fetal and hypogammaglobulinemic IgG immunoglobulins. Immunochemistry. 1970 Aug;7(8):703–708. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90176-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung C. Y., Hobbs J. R. Serum-gamma-G-globulin levels in normal premature, post-mature, and "small-for-dates" newborn babies. Lancet. 1968 Jun 1;1(7553):1167–1170. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)91865-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



