Abstract
The antimalaria drug chloroquine has been used as an anti-inflammatory agent for treating systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. We report that chloroquine promoted the transrepression of proinflammatory cytokines by the glucocorticoid receptor (GR). In a mouse collagen-induced arthritis model, chloroquine enhanced the therapeutic effects of glucocorticoid treatment. By inhibiting lysosome function, chloroquine synergistically activated glucocorticoid signaling. Lysosomal inhibition by either bafilomycin A1 (an inhibitor of the vacuolar adenosine triphosphatase) or knockdown of transcription factor EB (TFEB, a master activator of lysosomal biogenesis) mimicked the effects of chloroquine. The abundance of the GR, as well as that of the androgen receptor and estrogen receptor, correlated with changes in lysosomal biogenesis. Thus, we showed that glucocorticoid signaling is regulated by lysosomes, which provides a mechanistic basis for treating inflammation and autoimmune diseases with a combination of glucocorticoids and lysosomal inhibitors.
INTRODUCTION
Glucocorticoids are among the most potent and effective agents for treating inflammation and autoimmune diseases. Synthetic glucocorticoids, including dexamethasone (Dex), fluticasone propionate, and many other steroid analogs, are used clinically for treating asthma, allergy, and rheumatoid arthritis as well as in the treatment of certain cancers, such as leukemia and lymphoma (1). However, at therapeutic dosages, glucocorticoids induce a range of debilitating side effects, including diabetes, osteoporosis, skin atrophy, and growth retardation (2, 3). Therefore, the discovery and development of novel synthetic glucocorticoids that retain their beneficial therapeutic effects but reduce adverse side effects remain major medical challenges.
The action of glucocorticoids is mediated through the glucocorticoid receptor (GR), a steroid hormone–regulated transcriptional factor that belongs to the nuclear receptor superfamily. GR regulates gene expression either by transcriptional activation (transactivation) or by transcriptional repression (transrepression). To mediate transactivation, GR binds to a glucocorticoid response element (GRE) and activates downstream gene transcription. To mediate transrepression, GR functionally interacts with other transcriptional factors [such as nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) or activating protein 1 (AP-1)] and represses transcription of their downstream target genes (4). The transrepression activity of GR, especially at genes targeted by NF-κB or AP-1, is considered to be the major basis for the anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of glucocorticoids.
Lysosomes are ubiquitous organelles that are central to cellular homeostasis. They sequester digestive enzymes, such as acidic hydrolases, which are responsible for the degradation and recycling of cellular substrates transferred from exosomes, endosomes, or autophagosomes (5). Lysosome biogenesis is coordinated by the transcription factor EB (TFEB), which activates a genetic program that stimulates lysosomal biogenesis and function in response to changing cellular conditions (6, 7). Lysosomal activity is essential to autophagy, a cellular pathway that delivers cytoplasmic components to lysosomes for degradation and is involved in many diseases, including cancer, metabolic syndrome, and viral infections (8).
The lumen of lysosomes is acidic (pH ~ 5.0) relative to the slightly alkaline cytosol (pH 7.2). The acidity of lysosomes is maintained by vacuolar adenosine triphosphatase (V-ATPase) proton pumps, which transport protons from the cytosol into the lysosomal lumen, and chloride ion channels, which transport chloride anion from the lumen to the cytosol (9, 10). The acidic pH of lysosomes is critical for the enzymatic digestion of substrates as well as for vesicle fusion with other vacuolar compartments such as autophagosomes, a key step in autophagy. Neutralization of the internal acidic environment by weak alkaline compounds, such as chloroquine (CQ), or by inhibition of the proton pumps with bafilomycin A1 inhibits lysosomal function (8, 11). CQ is a widely used antimalaria drug that inhibits the growth of parasites by disrupting their lysosome-mediated digestion of heme, which is obtained from feeding on the host’s red blood cells (12, 13). CQ and its analog amodiaquine (AQ) have been used as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to treat rheumatoid arthritis and lupus erythematosus (14, 15), but the mechanism by which these drugs work remains unclear.
Here, we show that inhibition of lysosomal function, with either CQ or bafilomycin A1 or by knockdown of TFEB, repressed inflammation through potentiation of glucocorticoid signaling, thus providing a mechanistic basis for therapeutic strategies that combine glucocorticoid and lysosomal inhibitors in the treatment of inflammation and autoimmune diseases.
RESULTS
GR mediated the anti-inflammatory effects of CQ through transrepression of proinflammatory cytokines
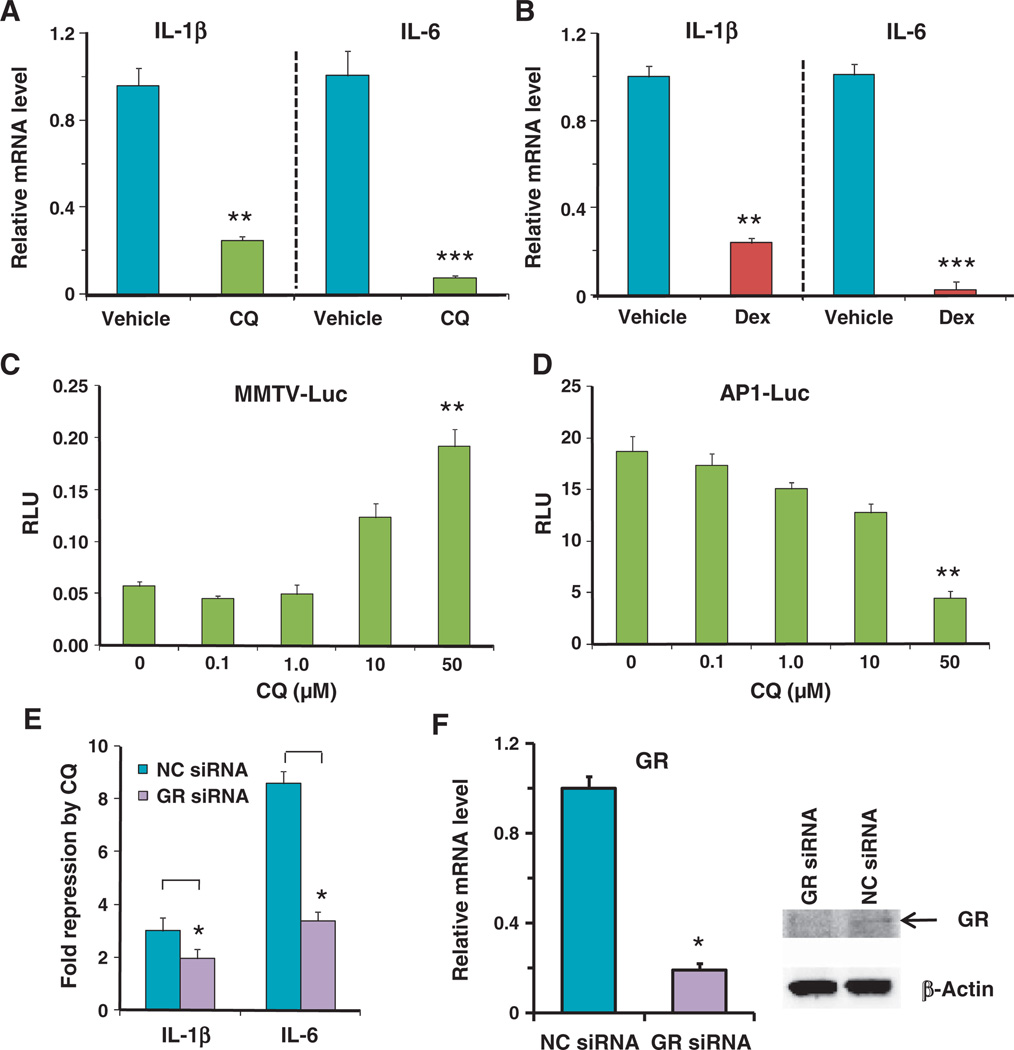
CQ suppresses the activity of proinflammatory factors (16–18), but it is not clear whether CQ represses the inflammatory signals at the mRNA level or at the protein level. Because macrophages are key cellular mediators of inflammatory responses, we used real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to measure the effects of CQ on the mRNA abundance of interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and IL-6, two proinflammatory cytokines produced by the human THP-1 cells in response to stimulation with lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (Fig. 1A). [THP-1 cells are a monocyte cell line that can be induced to differentiate into macrophages by the phorbol ester PMA (phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate).] CQ significantly decreased the abundance of transcripts encoding IL-1β and IL-6. Similar results were obtained from mouse macrophage RAW264.7 cells (fig. S1A), suggesting that CQ may inhibit the transcription of these cytokines.
Fig. 1.
The anti-inflammatory effect of CQ was partially mediated by GR. (A) In THP-1 cells exposed to LPS (1 µg/ml), CQ (50 µM) reduced the mRNA abundance of IL-1β and IL-6 (measured by real-time PCR) compared to PBS (vehicle)–treated cells exposed to LPS (1 µg/ml). Data represent the means and SD (n ≥ 3 samples). (B) Dex (100 nM) repressed IL-1β and IL-6 mRNA transcription in LPS-stimulated THP-1 cells. Data represent the means and SD (n ≥ 3 samples). (C) Dose effect of CQ in activation of the MMTV-luciferase reporter in AD293 cells without added exogenous glucocorticoid. Cells were treated with CQ for 16 hours. RLU, relative luciferase units that were normalized with Renilla luciferase. Data represent the means and SD (n ≥ 3 samples). Statistical significance between the 50 µM and 0 µM CQ samples is indicated. (D) Dose effect of CQ in repression of the AP-1 luciferase reporter in AD293 cells exposed to PMA (6.25 ng/ml) in the absence of exogenous glucocorticoid. Data represent the means and SD (n ≥ 3 samples). Statistical significance between the 50 µM and 0 µM CQ samples is indicated. (E) Knockdown of GR by siRNA decreased the repression by CQ of IL-1β and IL-6 mRNA in LPS-stimulated THP-1 cells. Data represent the means and SD (n ≥ 3 samples). NC siRNA, negative control siRNA. (F) GR knockdown efficiency was measured at the mRNA level by real-time PCR and at the protein level by Western blotting with the PA1-511A antibody that recognizes human GR. β-Actin was used as a loading control. mRNA data represent the means and SD of n ≥ 3 samples and the Western blotting data are representative of three experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
Because the effects of CQ were similar to those of Dex (Fig. 1B), we analyzed the effect of CQ on GR-mediated transactivation and transrepression, using AD293 cells coexpressing the GR with a luciferase reporter gene controlled either by the mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV) promoter, which is transactivated by GR (19), or by an AP-1–controlled promoter, which is transrepressed by GR (20, 21). CQ activated the MMTV reporter and repressed the AP-1 reporter in a dose-dependent manner (Fig. 1, C and D), with a significant effect apparent at 50 µM CQ. Similar results were obtained with the CQ analog AQ (fig. S1B). Knockdown of the endogenous GR in THP-1 cells by small interfering RNA (siRNA) reduced the inhibitory effects of CQ on the expression of the genes encoding IL-1β and IL-6 (Fig. 1, E and F). Together, these data suggest that the anti-inflammatory effects of CQ may be mediated through GR.
CQ potentiates GR signaling in the presence of glucocorticoid
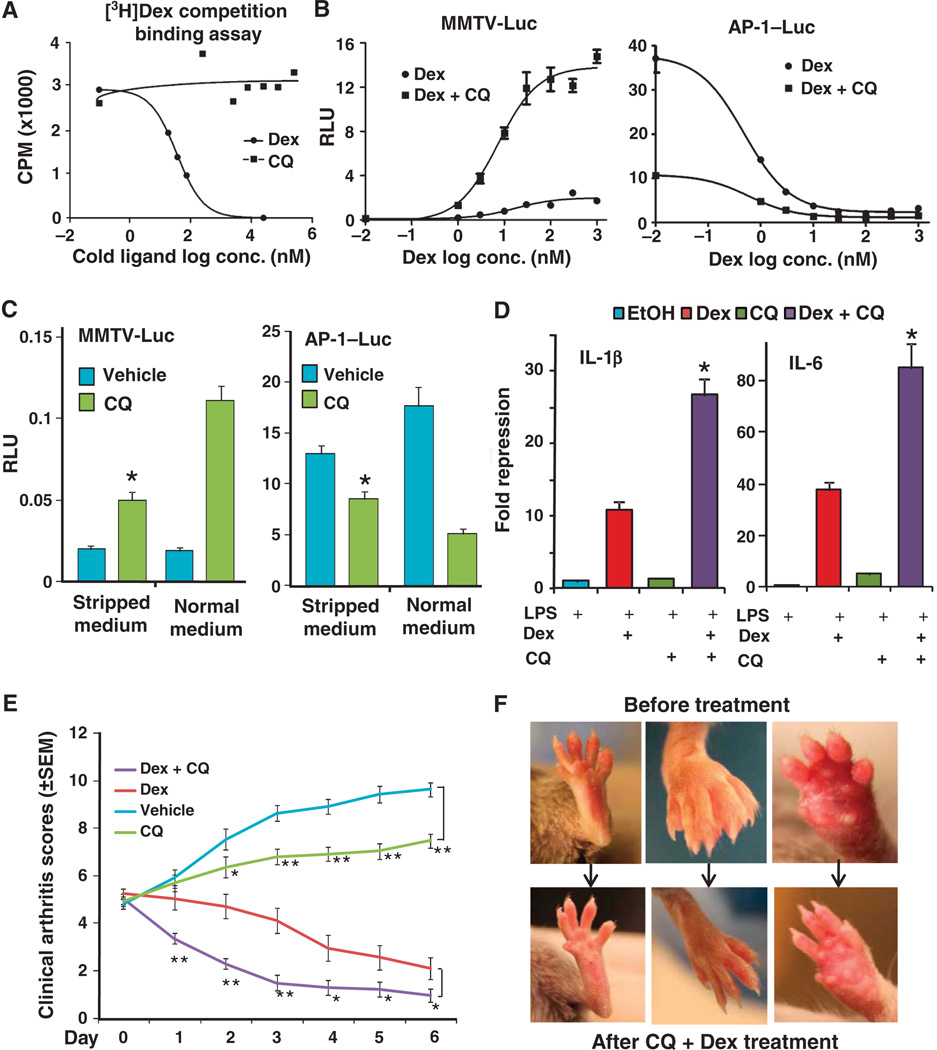
To evaluate the mechanism by which CQ enhanced glucocorticoid signaling, we assayed the effect of CQ on GR distribution, the ability of CQ to compete with GR ligands for binding to the GR, and the ability of CQ to bind heat shock protein 90 (HSP90, a chaperone protein required for GR function). CQ failed to alter the distribution of GR in cells in the presence or absence of the GR ligand Dex (fig. S2). In cell extracts, CQ failed to compete with Dex for binding to GR (Fig. 2A); however, CQ modestly increased the maximal binding (Bmax; Bmax,PBS = 3.8, Bmax,CQ = 4.9) of Dex to GR without having much of an effect on the affinity (Kd; Kd,PBS = 5.2 nM, Kd,CQ = 5.8 nM) (fig. S3A). CQ failed to compete with radio-labeled 17AAG, an inhibitor of HSP90 (22), for binding to HSP90 (fig. S3B), suggesting that CQ does not alter GR activity by affecting the activity of its chaperone. The effect of CQ on increasing GR-Dex binding activity is consistent with a previous observation that CQ increased GR activity in rat liver extract (23). Therefore, we hypothesized that the anti-inflammatory effect of CQ is mediated by promoting glucocorticoid-mediated GR signaling, which may in part be mediated by increasing the GR-Dex binding activity.
Fig. 2.
CQ enhances glucocorticoid-mediated GR signaling. (A) CQ and Dex competition assays show that CQ did not bind to GR. Data are representative of three experiments. (B) CQ (50 µM) enhanced Dex-stimulated transactivation of the MMTV reporter (MMTV-Luc) or transrepression of the AP-1 reporter (AP-1–Luc) in AD293 cells. For the AP-1 reporter assay, the cells were stimulated with PMA (6.25 ng/ml). Data represent the means and SD (n ≥ 3 samples). (C) Removal of endogenous GR ligands from serum with charcoal (stripped medium) decreased the effectiveness of CQ (50 µM) on enhancing GR-mediated changes in gene expression in AD293 cells. *P < 0.05 compared to CQ treatment in the presence of normal medium. Data represent the means and SD (n ≥ 3 samples). (D) CQ (50 µM) enhanced glucocorticoid (Dex, 100 nM)–mediated repression of IL-1β and IL-6 mRNA in THP-1 cells exposed to LPS (1 mg/ml). *P < 0.05 compared to Dex-alone treatment. Data represent the means and SD (n ≥ 3 samples). (E) Mean clinical arthritis scores of mice treated with vehicle (PBS, n = 10), Dex (4 mg per mouse, n = 13), CQ (400 mg per mouse, n = 10), or Dex + CQ [(4 µg + 400 µg) per mouse, n = 15]. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (F) Representative pictures of the feet of arthritic mice before and after CQ + Dex treatment.
We examined the effect of CQ in the presence of Dex on both GR transactivation and transrepression in AD293 cells. CQ increased Dex-stimulated GR activity, as shown by enhanced activation of the MMTV promoter or repression of the AP-1 promoter (Fig. 2B). This enhancement occurred with all concentrations of Dex, even the highest concentration tested (1 µM in Fig. 2B). CQ also enhanced the gene regulatory responses of other synthetic glucocorticoids, including budesonide, fluticasone propionate, deacylcortivazol, and mometasone furoate, as well as the endogenous hormone cortisol (fig. S3C).
Because CQ stimulated the expression of the MMTV reporter and inhibited that of the AP-1 reporter even in the absence of exogenous Dex (Figs. 1, C and D, and 2C), we reasoned that the activity of CQ on the GR reporters could be due to an effect of CQ on the signaling by endogenous GR ligands (for example, cortisol) in the serum. Indeed, cells exposed to CQ in the presence of serum treated with charcoal, which removes most of endogenous hydrophobic steroids from the serum, exhibited less of an effect on GR-regulated gene expression (Fig. 2C) than did cells exposed to CQ in the presence of untreated serum.
In LPS-stimulated THP-1 cells, CQ significantly enhanced Dex-mediated transrepression of the endogenous GR target genes encoding proinflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-6 (Fig. 2D), which was also reflected in reduced secretion of these cytokines (fig. S3D). Similar results were obtained from mouse macrophage RAW264.7 cells exposed to LPS, where we observed a profound enhancement of the reduction in IL-1β mRNA in response to combined treatment with Dex and CQ compared to the response to either CQ or Dex alone (fig. S3E).
The enhancement of Dex-mediated transrepression by CQ in THP-1 cells suggested that this combination might achieve better therapeutic efficacy than either agent alone in treating autoimmune diseases. To test this idea, we measured the therapeutic effects of CQ, Dex, and their combination in a mouse collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) model. We immunized DBA/1 mice with chicken collagen to elicit an inflammatory response. Three weeks later, after the onset of arthritis, mice were given Dex, CQ, or both. Combined treatment with CQ and a low dose of Dex was more effective at ameliorating symptoms than was treatment with either drug alone (Fig. 2, E and F).
CQ enhances glucocorticoid signaling and affects global gene expression in macrophage cells
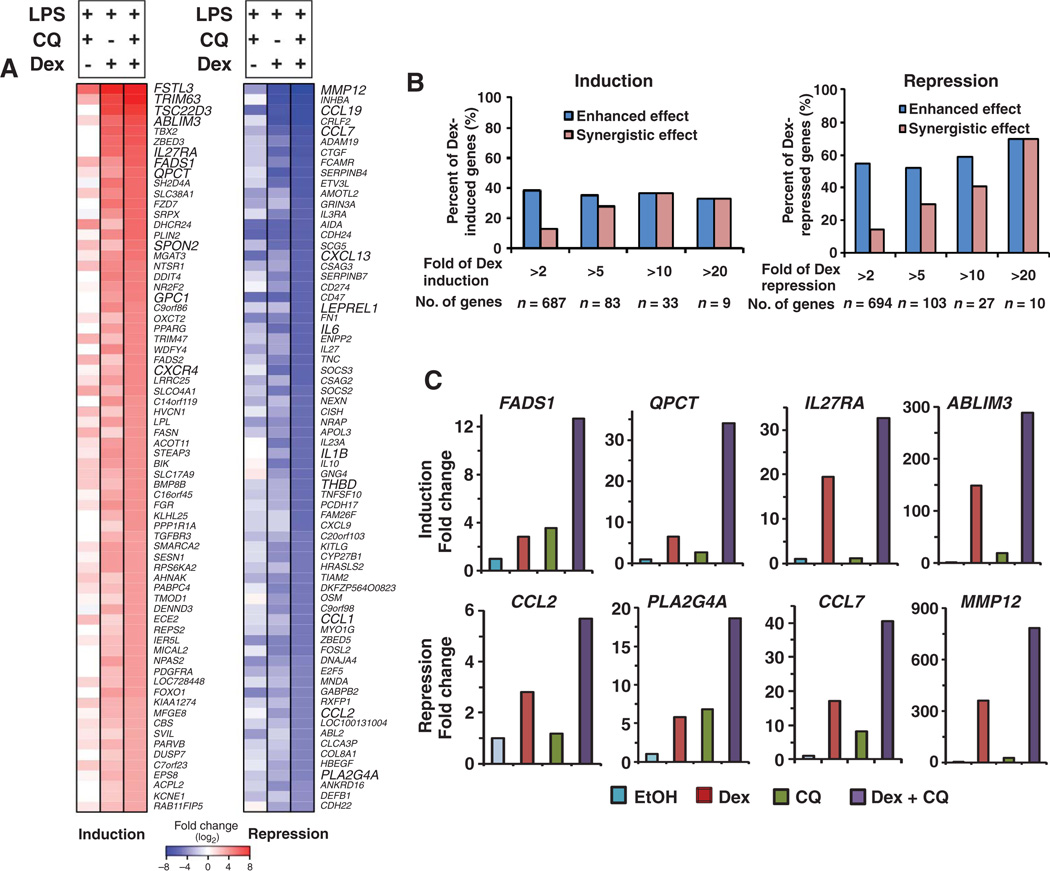
We performed gene expression profiling on LPS-stimulated THP-1 cells after addition of Dex, CQ, or both (Fig. 3A). We characterized the response to combined treatment as either “enhanced” or “synergistic.” Enhanced responses were those that exhibited a greater response in the presence of both Dex and CQ than either drug alone. Synergistic responses were a subset of the enhanced responses and represented those in which in the presence of both Dex and CQ, the response exceeded the sum of the response to either drug individually. The 70 genes with the largest synergistic transactivation effect or transrepression effect upon combined treatment included genes with varying responsiveness to Dex (Fig. 3A). Of the 70 that were synergistically transactivated or transrepressed, these averaged a ~30-fold change in gene expression compared with a ~12-fold change in response to Dex alone or ~3-fold (stimulated) or ~5-fold (reduced) change in response to CQ (fig. S4A), with fold change relative to cells exposed to LPS in the absence of any drug treatment. Tables S1 to S5 list the top 70 genes regulated by Dex, CQ, or Dex + CQ, as well as the top 70 genes showing a synergistic effect upon Dex + CQ treatment. There is a modest correlation between Dex + CQ– and CQ-regulated genes with a coefficiency of 0.672 and P < 2.2 × 10−16 (fig. S4B). Consistent with this correlation, the synergistic effect occurred more frequently with genes that exhibited the greatest responsiveness to GR (either induced or repressed), and a larger percentage of repressed genes exhibited the synergistic response (Fig. 3B). For example, the synergy was observed for 70% of genes that were repressed more than 20-fold by Dex treatment alone, whereas synergy was observed only for 15% of genes repressed more than 2-fold by Dex.
Fig. 3.
Gene expression profiling of THP-1 cells exposed to CQ, Dex, or both. (A) Top 70 GR-regulated genes that showed a synergistic effect upon treatment with CQ (50 µM) plus Dex (100 nM) in THP-1 cells stimulated with LPS (1 µg/ml). Changes in gene expression of the genes listed in bold capital letters were validated with real-time PCR. (B) Percentage of Dex-induced and Dex-repressed genes that have enhanced or synergistic effects with CQ. Enhanced responses were those that in the presence of both Dex and CQ exhibited a greater response than either drug alone (Dex + CQ cotreatment > Dex alone or CQ alone). Synergistic responses represented those in which in the presence of both Dex and CQ, the response more than exceeded the sum of the response to either drug individually (Dex + CQ co-treatment > Dex alone + CQ alone). (C) Validation of the synergistic effect on the indicated repressed or activated genes by real-time PCR. Selected genes represent a spectrum of Dex-regulated genes (from low to high); for other validations, see fig. S4. Genes include those particularly relevant for inflammatory responses and represent a range of GR-responsive genes.
We analyzed 14 genes that were synergistically transrepressed and 11 genes that were synergistically transactivated in the microarray experiment with real-time PCR (Fig. 3C and fig. S4C). We chose this subset of genes because they represent a spectrum of Dex-responsive genes for validation of microarray data. Twelve of the 14 repressed genes and 10 of the 11 activated genes exhibited an enhanced response to combined CQ and Dex treatment (Fig. 3C and fig. S4C). Of those that were enhanced, most (10 of 10 activated genes and 9 of 12 repressed genes) also exhibited a synergistic response.
Notables among those synergistically transrepressed were genes encoding phospholipase A2 (PLA2G4A) and several chemokines (Fig. 3C and fig. S4C). PLA2G4A is a key enzyme of prostaglandin-mediated inflammation pathways (24), and inhibition of phospholipase A2 is an important mechanism of GR-mediated anti-inflammation (25). Many chemokines serve as activators of inflammation and have been linked to many inflammation and autoimmune diseases including rheumatoid arthritis, allergic asthma, and multiple sclerosis (26, 27). All five chemokines transrepressed by Dex more than twofold (CCL1, CCL2, CCL7, CCL8, and CCL19), which are crucial for monocytes and macrophages to induce inflammation (26), exhibited a synergistic repression in response to both Dex and CQ. Together, these results suggest that treatment with CQ plus glucocorticoid inhibits the major inflammatory chemokines produced by macrophage cells.
Interfering with lysosomal function with V-ATPase inhibitors potentiates glucocorticoid signaling
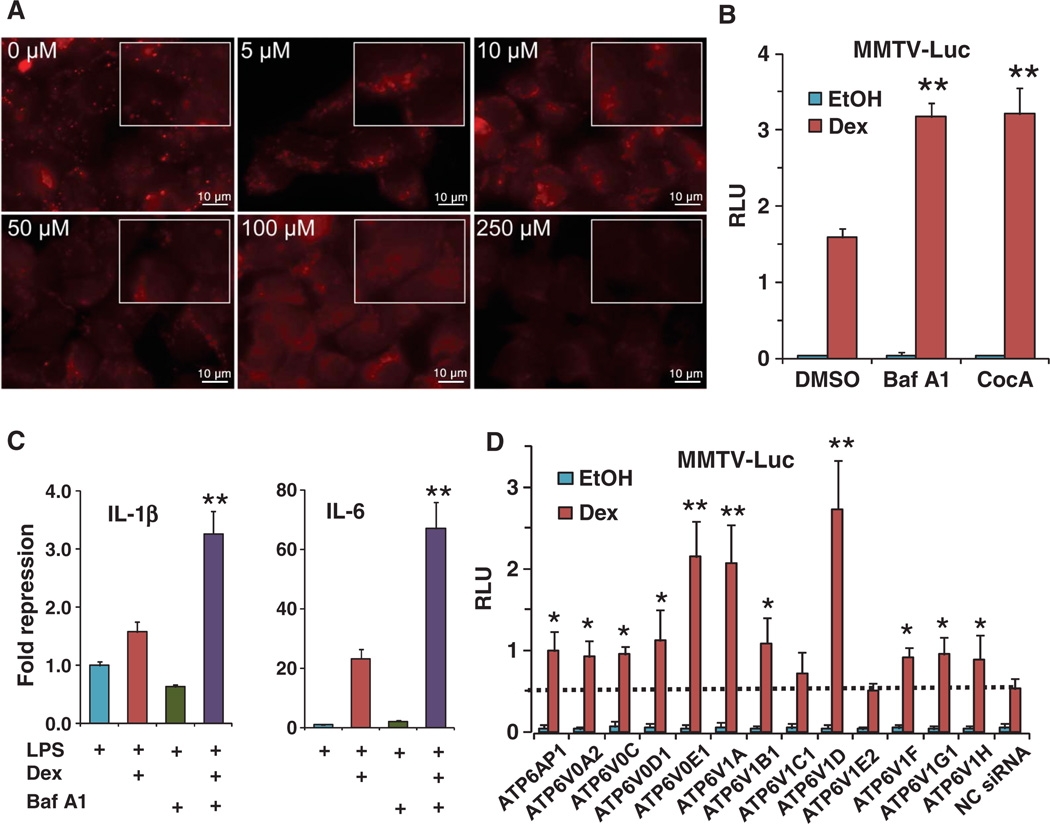
CQ is a lysosomotropic agent that accumulates in lysosomes and raises the lumenal pH, thereby preventing lysosomal fusion with autophagosomes and inhibiting the clearance of the autolysosomes (11, 28). We used LysoTracker as a pH-sensitive indicator to monitor the effect of CQ on lysosomal pH. When we gradually increased CQ concentration (0 to 250 µM), we observed a gradual reduction in the fluorescence intensity (sharpness) of puncta (Fig. 4A), indicating increased lysosomal pH. Using the lysosomal markers LAMP1 (lysosome-associated membrane protein 1) and LAMP2 and the autophagosomal marker LC3, we also detected the accumulation of autolysosomes and autophagosomes after 24-hour CQ treatment in U2OS cells, which are osteosarcoma cells uniquely fit for performing high-quality imaging of lysosomes (29) (fig. S5).
Fig. 4.
The V-ATPase inhibitor bafilomycin A1 potentiated glucocorticoid signaling by inhibiting lyso-somal function. (A) CQ interferes with lysosomal function by increasing lysosomal internal pH. AD293 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of CQ for 4 hours and then stained with LysoTracker Red, which labels all low-pH compartments. The rectangles represent 1.5× magnifications of regions from within the images; images were obtained by 100×/oil objective lens. Scale bars, 10 mm. (B) Bafilomycin A1 (Baf A1, 100 nM) and concanamycin A (CocA, 1 nM) potentiated glucocorticoid (Dex, 10 nM)–stimulated transactivation of the MMTV reporter in AD293 cells. **P < 0.01 compared to Dex induction in the presence of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Data represent the means and SD (n ≥ 3 samples). (C) Baf A1 (100 nM) synergized with glucocorticoid (Dex, 100 nM) in repression of IL-1β and IL-6 mRNA transcription in THP-1 cells in the presence of LPS (1 mg/ml). **P < 0.01 compared to Dex induction treatment. Data represent the means and SD (n ≥ 3 samples). (D) Knockdown of V-ATPase components by siRNA potentiated glucocorticoid (Dex, 10 nM)–mediated transactivation of the MMTV reporter in AD293 cells. Dashed line indicates the transactivation level of negative control siRNA (NC siRNA). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, compared to NC siRNA in cells treated with Dex; average siRNA knockdown efficiency was 70 ± 10% as measured by real-time PCR (fig. S6). Data represent the means and SD (n ≥ 3 samples).
If the effects of CQ on GR signaling are mediated through inhibition of lysosomal functions, other lysosomal inhibitors should have similar effects. Because CQ did not alter GR localization, we verified that inhibition of the V-ATPase proton pump with bafilomycin A1 also did not alter GR localization (fig. S2). Like CQ, bafilomycin A1 and concanamycin A, two inhibitors of the V-ATPase proton pump (30), enhanced Dex-mediated transactivation in the MMTV reporter assays in AD293 cells (Fig. 4B) and had a synergistic effect on Dex-mediated transrepression of the genes encoding IL-1β and IL-6 in THP-1 cells (Fig. 4C). Individual knockdown of 12 of the 13 components of the V-ATPase (9) with siRNAs in AD293 cells increased GR transactivation (Fig. 4D). Efficiency of knockdown as assessed by real-time PCR was variable, with an average knockdown efficiency of ~70% (fig. S6). These results provide further support that inhibition of lysosomal function enhances glucocorticoid signaling.
TFEB regulates GR transcriptional activity by controlling GR protein degradation
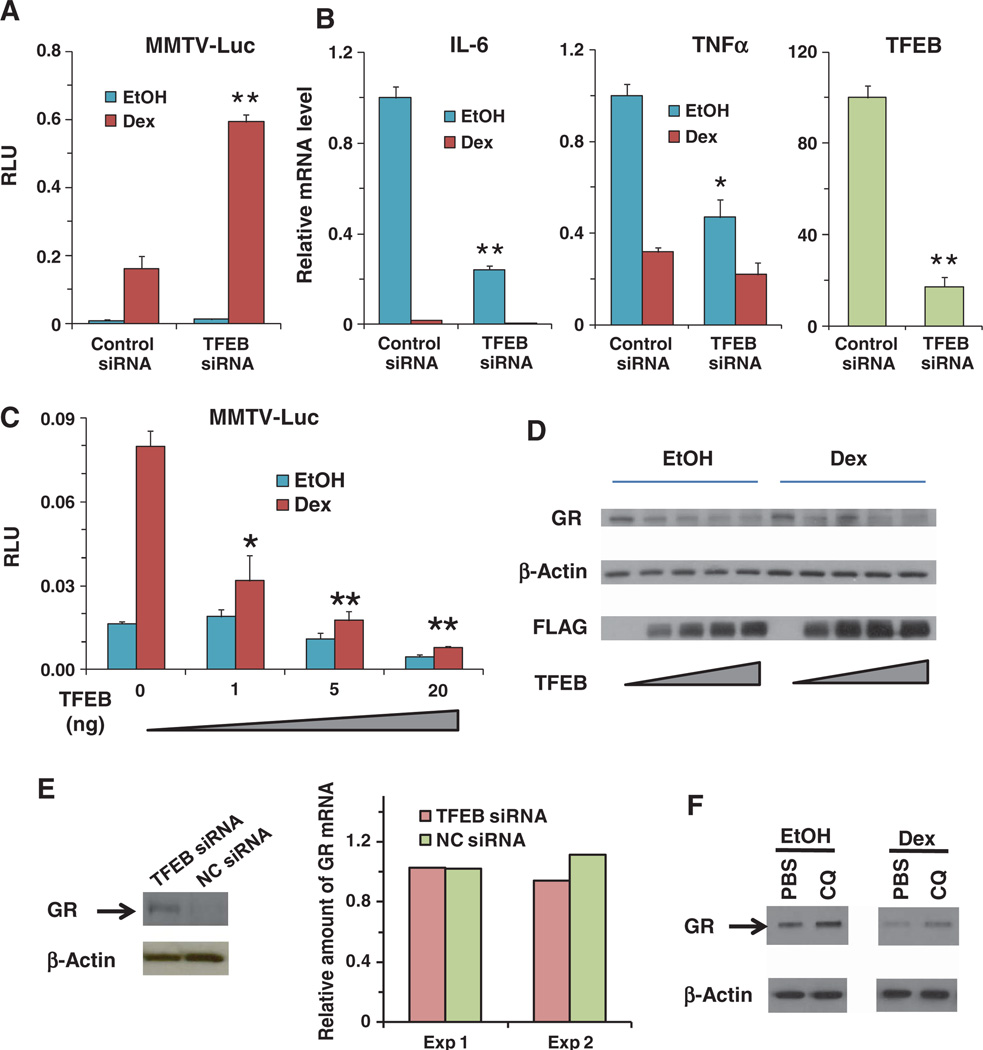
To further establish the relationship between lysosomal function and glucocorticoid signaling, we examined the roles of TFEB, a master transcriptional activator of lysosomal biogenesis (6). The transcriptional activity of TFEB correlates closely with the number of lysosomes in response to stimuli, such as starvation, that result in an increased need for lysosomal function (6, 7). In the MMTV reporter assay, knockdown of TFEB increased Dex-induced gene expression (Fig. 5A). In THP-1 cells, knockdown of TFEB mimicked the effect of CQ in repressing the transcription of proinflammatory cytokines (Fig. 5B). Overexpression of TFEB decreased Dex-induced activation of the reporter gene, as well as the reporter gene activity in the absence of Dex, which is an indicator of basal GR activity (Fig. 5C). These results highlight the inverse relationship between lysosomal function and glucocorticoid signaling.
Fig. 5.
Lysosomal biogenesis master regulator TFEB regulates GR activity. (A) Knockdown of TFEB by siRNA potentiated glucocorticoid (Dex, 10 nM)–mediated transactivation of the MMTV reporter in AD293 cells. **P < 0.01, compared to Dex-treated cells with control siRNA. Data represent the means and SD of n ≥ 3 samples. (B) Knockdown of TFEB by siRNA decreased proinflammatory cytokines IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor–α (TNFα) mRNA abundances, with or without Dex (100 nM), in THP-1 cells exposed to LPS (1 µg/ml). TFEB knockdown efficiency was measured at the mRNA level. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, compared to control siRNA. Data represent the means and SD (n ≥ 3 samples). (C) Overexpression of TFEB in AD293 cells inhibited glucocorticoid (Dex, 10 nM)–mediated induction of the MMTV reporter. The TFEB-expressing plasmid (0 to 20 ng) balanced with an equal amount of vehicle plasmid was used in transfection. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, compared to Dex-treated vehicle control samples (TFEB 0 ng). Data represent the means and SD (n ≥ 3 samples). (D) Cotransfection of TFEB (100 to 1000 ng of 3×FLAG-TFEB per well, six-well plate) with GR (500 ng per well, six-well plate) gradually decreased the amount of GR, with or without GR ligand (Dex, 100 nM) in AD293 cells. GR was detected with the PA1-511A antibody. Data shown are representative of three experiments. (E) Knockdown of TFEB by siRNA increased the abundance of GR in U2OS cells stably expressing GR. Data shown are representative of two experiments. GR mRNA was not affected by TFEB siRNA as measured by real-time PCR. Data from two experiments are shown. (F) CQ (50 µM) increased the amount of GR in U2OS cells stably expressing GR, with or without glucocorticoid (Dex, 100 nM). β-Actin served as the loading control. Data shown are representative of three experiments.
Because one of the key functions of lysosomes is protein degradation, we analyzed whether there was a relationship between lysosomal function and the amount of GR by examining the effect of changing the amount of TFEB on GR abundance and the effect of CQ treatment on GR abundance. In cotransfected AD293 cells, overexpression of TFEB reduced the amount of GR both in the presence and in the absence of Dex (Fig. 5D). Conversely, in U2OS cells stably expressing GR, knockdown of TFEB increased the abundance of GR (Fig. 5E, left) without affecting the amount of GR-encoding mRNA (Fig. 5E, right), indicating that the increased amount of GR was due to decreased lysosomal activity and not to an increase in transcription. Given that CQ is a lysosome inhibitor, CQ may protect GR from degradation by lysosomes. Indeed, CQ increased the amount of GR in U2OS cells stably expressing GR both in the presence and in the absence of Dex (Fig. 5F). A dose-response experiment showed that cells exposed to as little as 10 µM CQ had increased GR (fig. S7), and this was the concentration at which CQ activated the GR-responsive reporter gene (Fig. 1C). Thus, stabilization of GR by CQ through inhibition of lysosomes may contribute to the potentiation of glucocorticoid signaling by CQ.
Degradation of androgen and estrogen receptors is controlled by lysosomal activity
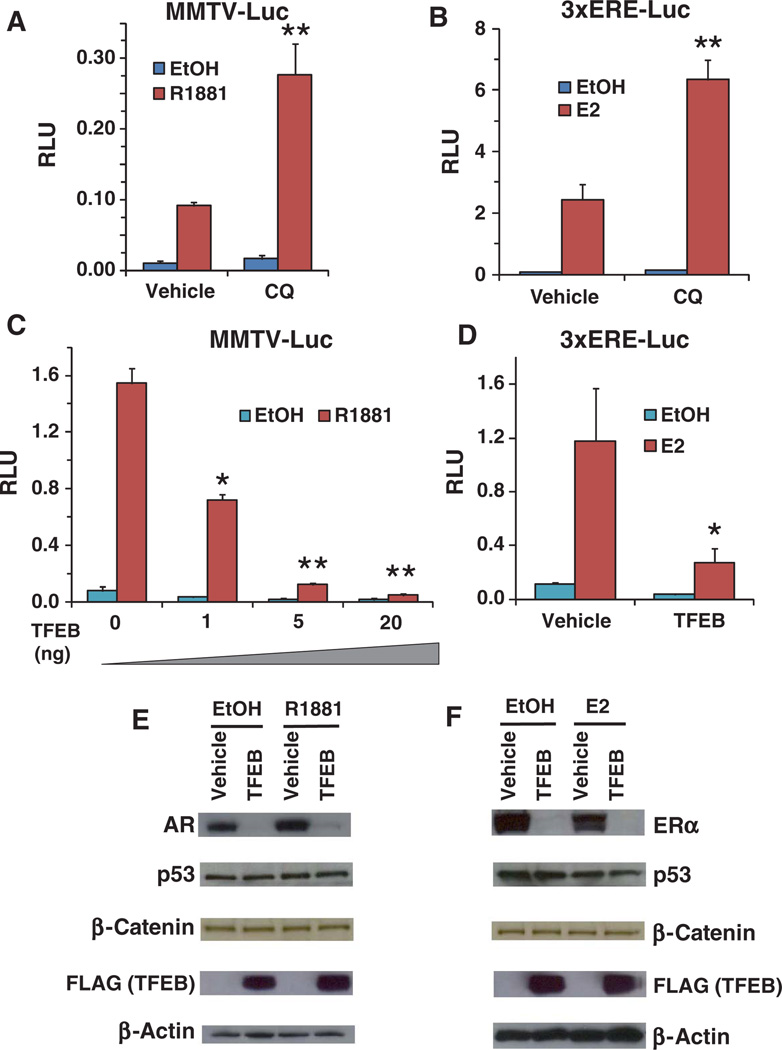
Because androgen receptor (AR) and estrogen receptor (ER) belong to the same nuclear receptor subfamily as GR, we investigated whether AR and ER activities were also regulated by lysosomes. Lysosomal inhibition by CQ enhanced the transcriptional activity of AR and ER in reporter gene assays (Fig. 6, A and B). Increased lysosomal biogenesis resulting from overexpression of TFEB decreased AR and ER activity in reporter gene assays in AD293 cells (Fig. 6, C and D). Correspondingly, overexpression of TFEB reduced the amount of AR and ER (Fig. 6, E and F), without causing any changes in the abundance of p53 or β-catenin, indicating some specificity of lysosome-mediated degradation for steroid hormone receptors. Consistent with this, CQ had no effect on a β-catenin–activated reporter (fig. S8). Thus, lysosomal activity appears to regulate nuclear receptor signaling, which may have implications for developing treatments for diseases associated with aberrant nuclear receptor signaling.
Fig. 6.
Lysosomes regulate AR and ER activity. (A) CQ enhanced the transactivation activity of the AR ligand R1881 (10 nM) on the MMTV reporter in AD293 cells. **P < 0.01 compared to vehicle control R1881–treated cells. Data represent the means and SD (n ≥ 3 samples). (B) CQ enhanced the transactivation activity of the ER ligand E2 (10 nM) on the ERE reporter in AD293 cells. **P < 0.01 compared to vehicle control E2–treated cells. Data represent the means and SD (n ≥ 3 samples). (C) Overexpression of TFEB decreased the AR (R1881, 10 nM)–mediated activation of the MMTV reporter in AD293 cells. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 compared to vehicle control (TFEB 0 ng) R1881–treated cells. Data represent the means and SD (n ≥ 3 samples). (D) Overexpression of TFEB decreased the ER (E2, 10 nM)–mediated activation of the MMTV reporter in AD293 cells. *P < 0.05 compared to vehicle control E2–treated cells. Data represent the means and SD (n ≥ 3 samples). (E) Cotransfection of TFEB (250 ng of 3×FLAG-TFEB per well in 24-well plate) with AR (100 ng/well, 24-well plate) decreased the abundance of AR, with or without the AR ligand R1881 (10 nM), in AD293 cells. AR was detected with the 441 antibody; endogenous p53 and β-catenin were detected with the DO-1 and 610154 antibodies, respectively. (F) Co-transfection of TFEB (250 ng of 3×FLAG-TFEB in 24-well plate) with ER (100 ng/well, 24-well plate) decreased the abundance of ER, with or without the ER ligand E2 (10 nM) in AD293 cells. ER was detected with the F10 antibody.
Lysosomes degrade GR to control the stability of cytoplasmic GR
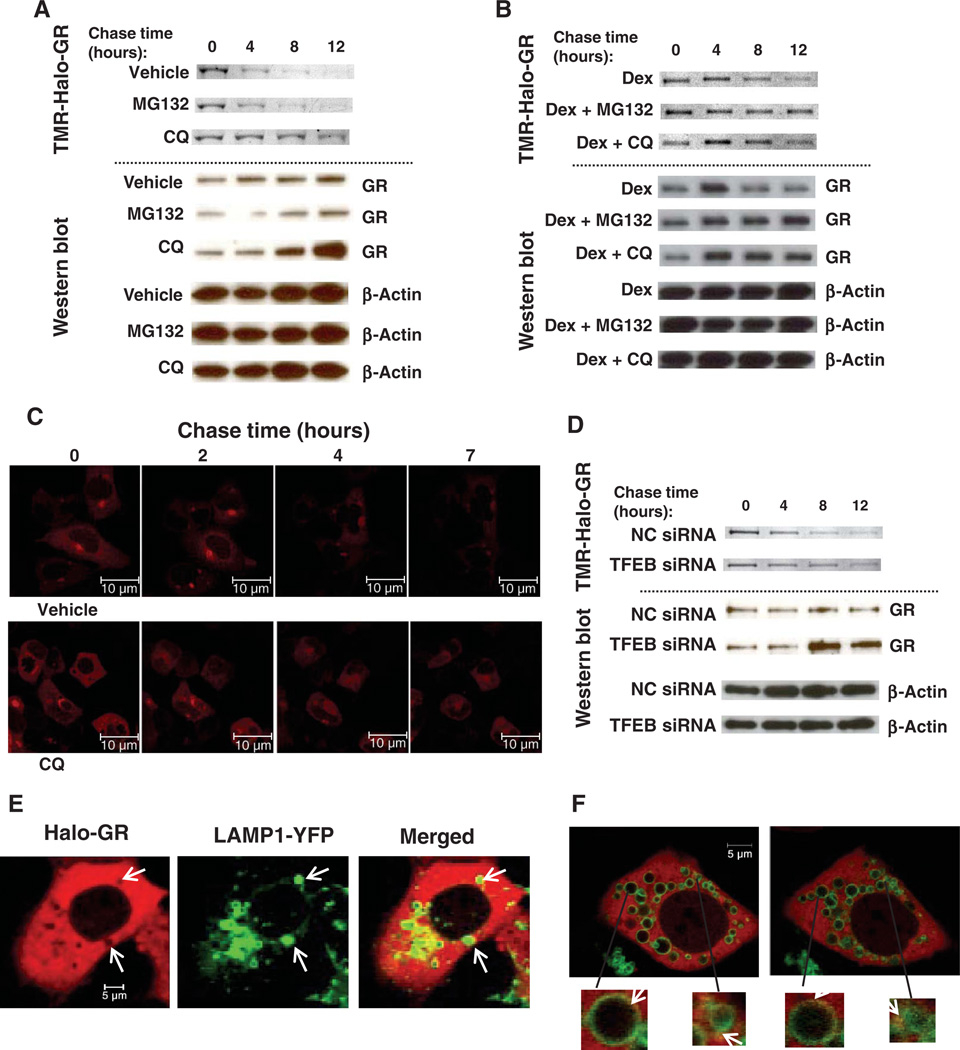
We monitored GR stability in pulse-chase experiments by the HaloTag method (31, 32), which does not require the use of radioactivity. We transiently pulse-labeled Halo-tagged GR (Halo-GR) with the fluorescent TMR (tetramethyl rhodamine) HaloTag ligand, which covalently binds to the HaloTag and then chased with the nonfluorescent succinimidyl ester (O4) HaloTag ligand. In the absence of exogenous GR ligand, the fluorescence signal of TMR-labeled Halo-GR protein [visualized in SDS– polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) gel] decayed, indicating protein degradation (Fig. 7A). Addition of CQ to inhibit lysosomal function, but not the proteasomal inhibitor MG132, delayed the degradation process, indicating that lysosome is a major pathway for the degradation of cytoplasmic GR in AD293 cells. Analysis of the abundance of GR by Western blotting confirmed that GR accumulated in cells exposed to CQ, but not those exposed to MG132 (Fig. 7A). Because there are no lysosomes in nuclei, it is unlikely that lysosomes contribute to the degradation of nuclear ligand-bound GR. Addition of MG132 to AD293 cells protected GR from degradation in the presence of Dex (Fig. 7B), indicating that nuclear GRs are mainly degraded by the proteasome. CQ appeared to partially stabilize or delay GR degradation in the presence of Dex, which may be due to shuttling from the nucleus to the cytoplasm after ligand binding. Consistent with the importance of the lysosomal pathway in AD293 cells, CQ augmented Dex-mediated reporter gene expression, whereas MG132 had little effect on GR activity (fig. S9A).
Fig. 7.
A lysosomal pathway contributes to degradation of cytoplasmic GR. (A) Pulse-chase assay of un-liganded GR in AD293 cells. AD293 cells were transfected with 200 ng of Halo-GR per well in 24 wells. Cells were pulse-labeled with 20 nM TMR ligand and then chased with 10 µM succinimidyl ester (O4) ligand. Upper panels, fluorescent TMR-Halo-GR SDS-PAGE scanning images. Lower panels, Western blots. GR was detected by PA1-511A antibody. CQ (50 µM) and MG132 (10 µM) were added at the same time that chase began. Data shown are representative of three experiments. (B) Pulse-chase assay of liganded GR in AD293 cells. Cells were transfected, labeled, and chased as described for (A). Upper panel, TMR-Halo-GR bands; lower panel, Western blots. Dex (100 nM), CQ (50 µM), and MG132 (10 mM) were added at the same time that chase began. Data shown are representative of three experiments. (C) Live-cell images of Halo-GR in the pulse-chase assay. AD293 cells were passaged into 40-mm glass-bottomed dishes and transfected with 0.5 µg of Halo-GR. Halo-GR was labeled with 2 nM TMR ligand (red fluorescence) and chased with 10 µM O4 ligand. Images were obtained with a 40× confocal microscope. Scale bar, 10 mm. See videos S1 and S2. (D) Pulse-chase assay of GR AD293 cells in which TFEB was knocked down. AD293 cells were transfected with 200 ng of Halo-GR together with 20 nM target siRNA in 24-well plates. Cells were labeled and chased as described in (A). Upper panel, TMR-Halo-GR bands; lower panel, Western blots. Data shown are representative of two experiments. (E) Live-cell images of Halo-GR and LAMP1-YFP in AD293 cells. Cells were transfected with 500 ng of Halo-GR and 500 ng of LAMP1-YFP in 40-mm glass-bottomed dishes. Cells were pulse-labeled by 20 nM TMR ligand; images were obtained with a 40× confocal microscope. Scale bar, 5 µm. Arrows indicate lysosomal location. (F) Dynamic association of Halo-GR and lysosomes in AD293 cells. Cells were transfected and labeled as in (E). Images were obtained with a 60× confocal microscope. Scale bar, 5 µm. Arrows point to the yellow sparks of lysosomes, indicating GR movement. See video S3.
However, MG132 increases GR activity in other cell lines, including COS7 cells (33, 34). To determine whether the relative importance of these two degradation pathways was cell line–specific, we evaluated the effect of CQ and MG132 on Dex-mediated reporter gene expression in COS7 cells. Indeed, in COS7 cells, addition of MG132 resulted in a greater enhancement of Dex-mediated reporter gene activity than did addition of CQ (fig. S9B). Thus, cells have at least two pathways that control the abundance of GR, a lysosomal pathway that operates in the cytoplasm and a proteasomal pathway that operates in the nucleus, and the importance of these pathways varies in different cells.
We then used live-cell imaging to track the degradation process of Halo-GR in real time. An advantage of the HaloTag systems is that the protein fate (synthesis, trafficking, and degradation) can be visualized in living cells. Consistent with the biochemical pulse-chase assays, CQ delayed the degradation of GR in living cells (Fig. 7C and videos S1 and S2). Knockdown of TFEB also delayed Halo-GR degradation in pulse-chase experiments (Fig. 7D, top), such that we detected more GR by Western blot (Fig. 7D, bottom). Thus, in both live-cell experiments and biochemical pulse-chase experiments, we showed that lysosomes contribute to the degradation of GR and that inhibition of lysosomal function can stabilize GR.
Because lysosomes rapidly degrade most proteins, with the exception of lysosomal structural proteins or adaptors such as LAMP1 and LAMP2, we could not detect a stable association of GR with lysosomes or LAMP1 or LAMP2. However, by imaging live cells with Halo-GR, we found that the sites positive for lysosome [LAMP1-YFP (LAMP1 fused to yellow fluorescent protein)] had an empty “hole” of Halo-GR (Fig. 7E). We also noted that the Halo-GR holes moved in the same direction as lysosomes (video S3). We interpret the absence of GR staining in those areas occupied by lysosomes as degradation of GR in the lysosomes. Because the association of GR and lysosomes is transient, we performed continuous recording of GR and lysosomes to visualize the interaction. We captured yellow “sparks” at the border of lysosomes, which may represent GR entering the lysosomes (Fig. 7F and video S3). The yellow sparks appeared and disappeared quickly, which is consistent with the rapid association of GR with lysosomes and fast degradation
DISCUSSION
We present three main discoveries. First, we identify a mechanism by which CQ and its analog AQ function as anti-inflammatory drugs by enhancing the activity of glucocorticoids and thereby repressing the transcription of proinflammation cytokines. Second, we demonstrate an inverse relationship between lysosomal function and glucocorticoid signaling, such that conditions that reduce lysosomal functions (CQ or bafilomycin treatment or TFEB knockdown) lead to increased glucocorticoid signaling. Third, we provide evidence that lysosomes are a site of GR degradation and thus control the stability of cytoplasmic GR. These discoveries provide a mechanistic framework for understanding the role of lysosomes and glucocorticoids in the development and homeostasis of the immune system and also provide a rational basis for developing new therapeutics that can be combined with glucocorticoids for treating inflammation and autoimmune diseases.
As major organelles responsible for the degradation and recycling of cellular substrates, lysosomes play critical roles in host cell defense by digesting intracellular and extracellular pathogens (35, 36). The catabolic functions of lysosomes are required for antigen processing and presentation to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II (37), which is crucial both for the development of self-tolerance and for the development of autoimmune diseases by immune systems. Endogenous glucocorticoids, like cortisol, through their interaction with GR, also have critical roles in the development and homeostasis of immune systems (38). In addition, cortisol and related synthetic glucocorticoids are used to treat inflammation and autoimmune diseases because of their potent inhibitory effects on immune systems. Despite the importance of both the lysosomal and the glucocorticoid pathways in regulating the immune system, the functional relationship between these two pathways had not been identified previously.
The inverse relationship between lysosomal and glucocorticoid pathways provides a new perspective in considering their modulation of the immune system. We reason that lysosomal biogenesis and function would expand in response to attacks of infectious agents on the host cells, which should then repress glucocorticoid signaling so that inflammatory cytokines are produced and attract other components of the immune system. In contrast, the demand for lysosomal functions would be reduced after destruction of the pathogens, and an increased sensitivity to glucocorticoid signaling would repress the expression of genes encoding inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. In this situation of infection and clearance, lysosomes not only serve as clearing houses that help host cells to get rid of pathogens, but also serve as signaling hubs that regulate the activity of the immune system through modulation of glucocorticoid activity.
Having established a relationship between lysosomal function and glucocorticoid signaling, we explored mechanisms by which this occurred and found that lysosomes controlled the stability of cytoplasmic GR without affecting its localization. However, we anticipate that stabilization of the receptor may only be part of the mechanism by which lysosomes regulate cellular responsiveness to glucocorticoids. We speculate that some of the potentiation of glucocorticoid signaling by CQ could result from the cellular consequences of the malfunction of lysosomes. The disruption of lysosomal function affects pathways including protein synthesis, degradation, and trafficking. Homeostasis of lysosomes, as well as of autophagosomes, is critical for many physiological and pathological processes that involve autophagy, including the balance of catabolism and anabolism, antigen presentation, bone remodeling, body development, and tumorigenesis (8). Therefore, it is unlikely that the activation of glucocorticoid signaling due to interference with lysosomal function can be explained by a single signaling event, which may also partially explain the variability in the gene expression response to lysosomal interference. Detailed mechanisms of this dynamic regulation between lysosome function and gluco-corticoid signaling, including how GR is targeted to lysosomes, will be a subject of future investigation.
The identification of a lysosomal pathway for the cytoplasmic degradation of receptors of the nuclear receptor family was unexpected because it is generally established that the ubiquitin-proteasome system is responsible for the rapid clearance of active transcriptional factors (39, 40), and the autophagy-lysosome pathway is responsible for the clearance of aged organelles and aggregated damaged proteins (8). However, we found that nuclear-localized GR (ligand-bound) was mainly degraded by a proteasome-dependent process, and cytoplasmic GR was mainly controlled by lysosomes, although we did note cell-specific differences in the relative contributions of these two pathways. These pathways may also contribute to regulate GR activity differently under different circumstances, such as during differentiation or development.
Similar to GR activity, we found that AR and ER activities were also controlled by lysosomes (Fig. 6). Because AR and ER contribute to the development and progression of prostate cancers and breast cancers (41–43), the reduction in AR and ER abundance in response to overexpressed TFEB suggests that increasing lysosomal function could be used as a strategy to reduce AR and ER signaling, which may lead to therapeutic applications for prostate cancer and breast cancer.
Given the widespread clinical use of glucocorticoids for treating inflammatory diseases and cancers, our discovery of the synergism between CQ and glucocorticoids has immediate therapeutic implications. Clinical studies of rheumatoid arthritis have shown that combined treatment of CQ with a low dose of glucocorticoid (for example, prednisolone at <15 mg/day) achieved a better effect, in terms of reducing joint destruction and increasing the remission rate, than either agent alone (44–46). Our results provide mechanistic insight for this treatment strategy and suggest that combined treatment not only will allow a lower dose of glucocorticoid to be effective but may also achieve therapeutic effects in situations when even a maximal dose of glucocorticoid fails to suppress the inflammation. Our study addresses why the combined treatment has better effects and provides a rational basis for developing new therapeutic applications by leveraging the synergy between glucocorticoids and lysosomal inhibitors.
In summary, we have discovered a mechanism of action for the antiinflammatory effects of CQ and AQ, in which these lysosomal inhibitors synergize with glucocorticoids to mediate transrepression of proinflammatory signals. Although not all of the anti-inflammatory effects of CQ may be mediated by enhancing the immunosuppressive effect of glucocorticoids, our results suggest that this is a major mechanism responsible for the repression of proinflammatory signals at the transcriptional level. Second, we have discovered an inverse relationship between lysosomal biogenesis and function and glucocorticoid signaling, which has both theoretical importance and therapeutic implication. Combined with the established roles of lysosomes in antigen presentation and pathogen clearance, the present work pushes these ubiquitous organelles further to the center of cellular processing of inflammatory responses. Our work opens a new field of opportunity to explore proteins associated with lysosomal pathways as drug targets for treating inflammation, autoimmune diseases, and cancer.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Antibodies and Western blotting
The antibody recognizing GR was purchased from Thermo Scientific (PA1–511A), the antibody recognizing AR (441) was from Santa Cruz (sc7305), the antibody recognizing ERa (F10) was from Santa Cruz (sc8002), the antibody recognizing p53 (DO-1) was from Santa Cruz (sc-126), the antibody recognizing β-catenin was from BD Biosciences (#610154), the antibody recognizing FLAG (M2) was from Sigma (F-1804), the antibody recognizing LAMP1 (LY1C6) was from Abcam (#ab13523), and the antibody recognizing LAMP2 (ABL-93) was from Santa Cruz (sc-20004). For Western blotting, protein lysates separated by 4 to 20% gradient SDS-PAGE were transferred to nitrocellulose membrane. Membranes were blocked with 10% milk and then incubated with appropriate first and second antibodies with extensive washes (three times) between each step. Chemiluminescent signals were detected by SuperSignal West Pico (Pierce).
Cell transfection and reporter gene assays
For testing of GR-mediated transactivation, AD293 cells were transfected with 100 ng of pHHLuc (MMTV-Luc) plasmid, 0.1 ng of pRShGR (encoding human full-length GR) by FuGENE 6 (Roche), and 5 ng of Renilla luciferase control plasmid per well in 24-well plates. For GR-mediated repression, AD293 cells were transfected with 10 ng of AP-1–Luc, 10 to 100 ng of pRShGR, and 5 ng of Renilla luciferase control plasmid per well (24-well plate). At 24 hours after transfection, cells were subjected to various treatments (Dex, CQ, AQ, or different combinations) overnight in the presence of PMA (6.25 ng/ml), which increases AP-1 transcriptional activity to allow detection of repression of its activity by Dex in the AD293 cells. Luciferase activity was assayed with the Dual-Glo Luciferase system (Promega).
For the Wnt TCF (T cell factor) reporter assay, 293STF cells (with an integrated “Super-Top-Flash” TCF luciferase reporter) were transfected with 20 ng of Renilla control plasmid. Cells were induced with the indicated reagents 24 hours after transfection. Cells were harvested 17 hours after induction.
Total RNA extraction and real-time PCR
THP-1 cells were induced with PMA (25 ng/ml) for 48 hours to differentiate into macrophage cells (for RAW264.7 cells, differentiation did not require PMA). The differentiated cells were exposed to the indicated reagents (Dex or other synthetic hormones, CQ, or a combination thereof) in the presence of LPS (1 µg/ml) for 12 hours. Total RNA was extracted with either Trizol (Invitrogen) or a Qiagen RNA extraction kit. Complementary DNA (cDNA) was synthesized from total RNA with an Invitrogen Superscript cDNA synthesis kit. Target genes were quantified with a Power SYBR Green real-time PCR kit (ABI) in a StepOnePlus Real-Time PCR instrument. In every case, GAPDH (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) was used as an internal control and data were analyzed by the ΔΔCt method. The specificity of target primers was tested both in a dissociation curve and against a water control. See table S6 for the sequences of all target gene primers. Fold changes in induction or repression were calculated as compared to the appropriate vehicle control group [for example, DMSO, EtOH, or a mixture thereof, or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)].
siRNA and transfection
THP-1 cells were induced with PMA (100 ng/ml) for 24 hours to differentiate into macrophages, and then they were transfected with 20 to 50 nM siRNA using siLentFect (Bio-Rad). At 24 to 48 hours after transfection, cells were exposed to the indicated reagents in the presence of LPS (1 mg/ml) for 6 to 12 hours, and then RNA was isolated and subjected to realtime PCR analysis. AD293 cells were transfected with 10 nM siRNA by HiPerFect (Qiagen) in 24-well plates; for DNA and siRNA mixture transfection, 100 ng of DNA plasmid and 20 nM siRNA were transfected with Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen) in 24-well plates. See table S7 for all siRNA target sequences.
In vitro GR ligand binding assay and Dex and HSP90 competition assays
We grew U2OS cells stably expressing GR to 100% confluence and then isolated cytosolic fractions as previously described (47). Cytosol (5 to 10%) supplemented with 20 mM sodium molybdate was added to varying concentrations of [3H]Dex (0 to 25 nM) ± 100-fold excess of non-radioactive Dex and incubated at 4°C for 16 hours. To test the effect of CQ on GR-Dex binding, we added 50 µM CQ (or PBS control) to the [3H]Dex cytosol mixtures. Unbound [3H]Dex was removed by dextran-coated charcoal. Standard binding curve was plotted by [bound steroid] versus [free steroid]. The binding capacity and affinity were also determined by Scatchard plot analysis by plotting [bound steroid]/[free steroid] versus [bound steroid]. For the competition binding assay performed with CQ and [3H]Dex, [3H]Dex was fixed at 25 nM, and then varying concentrations of CQ (0.25 to 2.5 mM) were added; the data were plotted as a standard competition curve. For the competition assay with CQ and 17AAG for HSP90 binding, [3H]17AAG was fixed at 25 nM and then varying CQ concentrations (2.5 nM to 500 µM) were added; the data were plotted as a standard competition curve. Experiments were repeated at least three times with duplicate at each point.
Mouse CIA model
DBA/1 male mice (7 to 10 weeks old; Taconic) were intradermally immunized at the base of the tail with 100 ml of chicken collagen/FCA (Freund’s complete adjuvant) emulsion (EK-0210, Hooke Laboratories). Twenty-one days later, they were given a 100-µl booster dose of chicken collagen/FIA (Freund’s incomplete adjuvant) emulsion (EK-0211, Hooke Laboratories). From day 20 after the first immunization, mice were monitored daily for clinical symptoms of arthritis. The clinical score of arthritis per paw was graded according to the Hooke Laboratories manual as follows: 0, normal paw; 1, one toe inflamed and swollen; 2, more than one toe, but not the entire paw, inflamed and swollen, or mild swelling of entire paw; 3, entire paw inflamed and swollen; and 4, very inflamed and swollen paw or ankylosed paw. If the paw was ankylosed, the mouse could not grip the wire top of the cage. Thus, each mouse could be scored from 0 to 16.
Upon arthritis onset (score of 3 to 4), mice were randomized and given the following treatments by intraperitoneal injection: vehicle, Dex (4 µg per mouse), CQ (400 mg), or Dex/CQ (4 mg + 400 mg) in 200 ml of PBS. Blood was withdrawn by intracardiac puncture or from the orbital sinus at the seventh day after treatment, and then the mice were euthanized. All animal procedures were approved by the institutional animal care and ethics committee.
Microarray analysis gene expression of THP-1 cells
THP-1 cells were differentiated into macrophages by treating with PMA (25 ng/ml) for 48 hours, and then the cells were exposed to vehicle (EtOH), Dex (100 nM), CQ (50 µM), or Dex + CQ (100 nM and 50 µM, respectively), in the presence of LPS (1 mg/ml) for 12 hours. Total RNA was isolated with a Qiagen RNeasy kit. Expression measurements were generated with the Agilent Whole Human Genome 44K platform. All subsequent analyses were performed with the Bioconductor software environment (48). Expression data were processed and normalized as described (49) with assistance from the Bioconductor limma package (50). To identify genes associated with CQ treatment, we compared CQ + LPS cells with LPS cells, and CQ + Dex + LPS cells with Dex + LPS cells. Genes in tables S1 to S5 and Fig. 3 were identified using the following criteria: expression after Dex + LPS treatment was at least twofold increased versus LPS alone, and expression in Dex + CQ was greater than expression in either Dex or CQ alone. Similarly, expression after Dex + LPS treatment was at least twofold decreased versus LPS alone, and expression in Dex + CQ was lower than in either Dex or CQ alone.
Pulse-chase experiments with HaloTag
We monitored GR stability in pulse-chase experiments by means of the HaloTag method, a recombinant protein tag method that enables specific labeling of target proteins (31, 32). AD293 cells were passaged and transfected with 200 ng of Halo-GR by Lipofectamine 2000 in 24-well plates. One day after transfection, cells were pulse-labeled with 20 nM TMR ligand for 15 min at 37°C according to the Promega manual, and then cells were washed with fresh phenol-free medium [plus 10% charcoal-stripped fetal bovine serum (FBS)] four times. Cells were chased with 10 µM preblocked succinimidyl ester (O4) ligand in phenol-free (10% charcoal-stripped FBS) medium for various time periods. The succinimidyl ester (O4) ligand was preblocked by incubation in 100 mM tris-Cl (pH 8.0) for 60 min at room temperature to mask the functional group. Cells were lysed by 1× Passive Lysis Buffer (Promega); the lysis solution was mixed with 2× SDS loading buffer, incubated at 95°C for 2 min, and separated by SDS-PAGE. Gels were visualized by the Bio-Rad ChemiDoc XRS Plus system. Experiments were repeated at least three times.
Live-cell imaging
AD293 cells were passaged into 40-mm glass-bottomed culture dishes (MatTek). One day after growth, cells were transfected with Halo-GR with or without LAMP1-YFP (51). Twenty-four hours later, Halo-GR was labeled with 2 nM TMR ligand for 15 min at 37°C. Live-cell images were obtained with a Zeiss LSM 510 Meta confocal system. For pulse-chase experiments to monitor Halo-GR protein stability, cells were chased with 10 µM O4 ligand as described above; pictures were taken every 5 min for up to 7 hours. For colocalization experiments, pictures were taken every 20 s for 1 to 2 hours. Images were analyzed by Zeiss LSM Browser (v4.2). Movies of living cell images were produced with Zeiss 510 Laser Scanning Microscope software V3.2 SP1 (Carl Zeiss Microimaging).
To determine the effect of CQ and bafilomycin A1 on GR localization, we passaged AD293 cells into 24-well plates. One day after growth, cells were transfected with 20 ng of pEYFP-GR by FuGENE 6. Twenty-four hours later, cells were treated with the indicated reagents (CQ and bafilomycin A1) with or without Dex. Fluorescent images were taken 3 hours after treatment with a Nikon Eclipse TE300 system.
Statistical analysis
All mouse data (clinical arthritis scores) were expressed as the means ± SEM (n ≥ 5 samples). Reporter assays and real-time PCR data were expressed as the means ± SD of at least triplicate samples. Data were analyzed by two-tailed, unpaired t tests with GraphPad Prism 5 or Excel software.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the Van Andel Research Institute animal facility (D. Dylewski, L. DeCamp, and E. Boguslawski) for helping in animal study and the microarray facility (M. Vadlapatla) for microarray data collection, Q. Xie for some reagents, S. Stoney Simons Jr. [National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)] for reagents and advice on steroid binding assay, and W. Mothes (Yale School of Medicine) for LAMP1-YFP plasmid.
Funding:
This study was supported by an NIDDK/NIH fund (DK066202 and DK071662), an American Asthma Foundation fund (2010) to H.E.X., Department of Defense Prostate Cancer Research Program of the Office of Congressionally Directed Medical Research Programs PC081089 to J.P.M., and the Jay and Betty Van Andel Foundation.
Footnotes
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/4/180/ra44/DC1
Fig. S1. Activity of CQ and amodiaquine (AQ).
Fig. S2. Effect of CQ and bafilomycin A1 on GR localization in AD293 cells.
Fig. S3. CQ enhances glucocorticoid-mediated GR signaling.
Fig. S4. Microarray analysis of the effect of CQ/Dex on gene expression in THP-1 cells.
Fig. S5. CQ inhibition of lysosomes leads to accumulation of autophagosomes and autolysosomes.
Fig. S6. Knockdown efficiency of the siRNAs targeting components of the V-ATPase.
Fig. S7. CQ stabilizes GR in AD293 cells.
Fig. S8. The effect of CQ on a β-catenin-activated reporter gene.
Fig. S9. Effect of the proteasome inhibitor MG132 and the lysosomal inhibitor CQ on GR activation in AD293 cells and COS7 cells.
Table S1. Top 70 genes regulated by Dex in LPS-stimulated THP-1 cells.
Table S2. Top 70 genes regulated by CQ in LPS-stimulated THP-1 cells.
Table S3. Top 70 genes regulated by Dex + CQ in LPS-stimulated THP-1 cells.
Table S4. Top 70 genes showing a synergistic transactivation effect upon Dex + CQ treatment in LPS-stimulated THP-1 cells.
Table S5. Top 70 genes showing a synergistic transrepression effect upon Dex + CQ treatment in LPS-stimulated THP-1 cells.
Table S6. Real-time PCR primers for target genes.
Table S7. siRNA target sequences.
Descriptions for Videos S1 to S3
Video S1. Pulse chase of Halo-GR in AD293 cells with PBS vehicle.
Video S2. Pulse chase of Halo-GR in AD293 cells exposed to CQ.
Video S3. Dynamic association of GR and lysosomes in AD293 cells.
Author contributions:
Y.H., Y.X., and H.E.X. conceived the project. H.E.X., Y.H., Y.X., J.H.R., A.S.A., J.P.M., and K.A.F. designed the experiments. Y.H. performed the bulk of the experiments with additional contributions from Y.X., C.Z., X.G., K.J.D., K.R.M., E.A.H., A.S.A., and S.K.K. at the different stages of the project. H.E.X. and Y.H. wrote the paper with comments from all authors.
Competing interests:
Compositions of CQ or an analog of CQ in combination with a GR ligand and methods of use (U.S. Patent Application No. 61/236,681).
Accession numbers:
The microarray data have been submitted into the National Center for Biotechnology Information Gene Expression Omnibus database (accession no. GSE24579).
REFERENCES AND NOTES
- 1.Barnes PJ. Anti-inflammatory actions of glucocorticoids: Molecular mechanisms. Clin. Sci. 1998;94:557–572. doi: 10.1042/cs0940557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Schäcke H, Döcke WD, Asadullah K. Mechanisms involved in the side effects of glucocorticoids. Pharmacol. Ther. 2002;96:23–43. doi: 10.1016/s0163-7258(02)00297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Stanbury RM, Graham EM. Systemic corticosteroid therapy—Side effects and their management. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1998;82:704–708. doi: 10.1136/bjo.82.6.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Yamamoto KR. Steroid receptor regulated transcription of specific genes and gene networks. Annu. Rev. Genet. 1985;19:209–252. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Saftig P. Lysosomes. New York: Springer Science+Business Media Inc.; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sardiello M, Palmieri M, di Ronza A, Medina DL, Valenza M, Gennarino VA, Di Malta C, Donaudy F, Embrione V, Polishchuk RS, Banfi S, Parenti G, Cattaneo E, Ballabio A. A gene network regulating lysosomal biogenesis and function. Science. 2009;325:473–477. doi: 10.1126/science.1174447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Settembre C, Di Malta C, Polito VA, Arencibia MG, Vetrini F, Erdin S, Erdin SU, Huynh T, Medina D, Colella P, Sardiello M, Rubinsztein DC, Ballabio A. TFEB links autophagy to lysosomal biogenesis. Science. 2011;332:1429–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.1204592. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Levine B, Kroemer G. Autophagy in the pathogenesis of disease. Cell. 2008;132:27–42. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.12.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Forgac M. Vacuolar ATPases: Rotary proton pumps in physiology and pathophysiology. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007;8:917–929. doi: 10.1038/nrm2272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Jentsch TJ, Friedrich T, Schriever A, Yamada H. The CLC chloride channel family. Pflugers Arch. 1999;437:783–795. doi: 10.1007/s004240050847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Rubinsztein DC, Gestwicki JE, Murphy LO, Klionsky DJ. Potential therapeutic applications of autophagy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007;6:304–312. doi: 10.1038/nrd2272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dorn A, Stoffel R, Matile H, Bubendorf A, Ridley RG. Malarial haemozoin/β-haematin supports haem polymerization in the absence of protein. Nature. 1995;374:269–271. doi: 10.1038/374269a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sullivan DJ, Jr., Gluzman IY, Russell DG, Goldberg DE. On the molecular mechanism of chloroquine’s antimalarial action. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1996;93:11865–11870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.21.11865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Augustijns P, Geusens P, Verbeke N. Chloroquine levels in blood during chronic treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1992;42:429–433. doi: 10.1007/BF00280130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Meinão IM, Sato EI, Andrade LE, Ferraz MB, Atra E. Controlled trial with chloroquine diphosphate in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 1996;5:237–241. doi: 10.1177/096120339600500313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.van den Borne BE, Dijkmans BA, de Rooij HH, le Cessie S, Verweij CL. Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine equally affect tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin 6, and interferon-γ production by peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J. Rheumatol. 1997;24:55–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Karres I, Kremer JP, Dietl I, Steckholzer U, Jochum M, Ertel W. Chloroquine inhibits proinflammatory cytokine release into human whole blood. Am. J. Physiol. 1998;274:R1058–R1064. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1998.274.4.R1058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Jang CH, Choi JH, Byun MS, Jue DM. Chloroquine inhibits production of TNF-α IL-1β and IL-6 from lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human monocytes/macrophages by different modes. Rheumatology. 2006;45:703–710. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kei282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ringold GM, Yamamoto KR, Tomkins GM, Bishop M, Varmus HE. Dexamethasone-mediated induction of mouse mammary tumor virus RNA: A system for studying glucocorticoid action. Cell. 1975;6:299–305. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Jonat C, Rahmsdorf HJ, Park KK, Cato AC, Gebel S, Ponta H, Herrlich P. Antitumor promotion and antiinflammation: Down-modulation of AP-1 (Fos/Jun) activity by glucocorticoid hormone. Cell. 1990;62:1189–1204. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90395-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rogatsky I, Zarember KA, Yamamoto KR. Factor recruitment and TIF2/GRIP1 corepressor activity at a collagenase-3 response element that mediates regulation by phorbol esters and hormones. EMBO J. 2001;20:6071–6083. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.21.6071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Xie Q, Wondergem R, Shen Y, Cavey G, Ke J, Thompson R, Bradley R, Daughtery-Holtrop J, Xu Y, Chen E, Omar H, Rosen N, Wenkert D, Xu HE, Vande Woude GF. Benzoquinone ansamycin 17AAG binds to mitochondrial voltage-dependent anion channel and inhibits cell invasion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2011;108:4105–4110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1015181108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kalimi M. Role of lysosomotrophic reagents in glucocorticoid hormone action. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1986;883:593–597. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(86)90302-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Dennis EA. Diversity of group types regulation and function of phospholipase A2. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:13057–13060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Rhen T, Cidlowski JA. Antiinflammatory action of glucocorticoids—New mechanisms for old drugs. N Engl. J. Med. 2005;353:1711–1723. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra050541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Charo IF, Ransohoff RM. The many roles of chemokines and chemokine receptors in inflammation. N Engl. J. Med. 2006;354:610–621. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra052723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Iwamoto T, Okamoto H, Toyama Y, Momohara S. Molecular aspects of rheumatoid arthritis: Chemokines in the joints of patients. FEBS J. 2008;275:4448–4455. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06580.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mizushima N, Yoshimori T, Levine B. Methods in mammalian autophagy research. Cell. 2010;140:313–326. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.01.028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Martin KR, Xu Y, Looyenga BD, Davis RJ, Wu CL, Tremblay ML, Xu HE, MacKeigan JP. Identification of PTPσ as an autophagic phosphatase. J. Cell Sci. 2011;124:812–819. doi: 10.1242/jcs.080341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Huss M, Wieczorek H. Inhibitors of V-ATPases: Old and new players. J. Exp. Biol. 2009;212:341–346. doi: 10.1242/jeb.024067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yamaguchi K, Inoue S, Ohara O, Nagase T. Pulse-chase experiment for the analysis of protein stability in cultured mammalian cells by covalent fluorescent labeling of fusion proteins. Methods Mol. Biol. 2009;577:121–131. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-232-2_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Los GV, Encell LP, McDougall MG, Hartzell DD, Karassina N, Zimprich C, Wood MG, Learish R, Ohana RF, Urh M, Simpson D, Mendez J, Zimmerman K, Otto P, Vidugiris G, Zhu J, Darzins A, Klaubert DH, Bulleit RF, Wood KV. HaloTag: A novel protein labeling technology for cell imaging and protein analysis. ACS Chem. Biol. 2008;3:373–382. doi: 10.1021/cb800025k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Deroo BJ, Rentsch C, Sampath S, Young J, DeFranco DB, Archer TK. Proteasomal inhibition enhances glucocorticoid receptor transactivation and alters its subnuclear trafficking. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002;22:4113–4123. doi: 10.1128/MCB.22.12.4113-4123.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wallace AD, Cidlowski JA. Proteasome-mediated glucocorticoid receptor degradation restricts transcriptional signaling by glucocorticoids. J. Biol. Chem. 2001;276:42714–42721. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M106033200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Deretic V, Levine B. Autophagy immunity and microbial adaptations. Cell Host Microbe. 2009;5:527–549. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2009.05.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Munz C. Enhancing immunity through autophagy. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2009;27:423–449. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.021908.132537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Levine B, Deretic V. Unveiling the roles of autophagy in innate and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev. Immunol. 2007;7:767–777. doi: 10.1038/nri2161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Winoto A, Littman DR. Nuclear hormone receptors in T lymphocytes. Cell. 2002;109(suppl):S57–S66. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(02)00710-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ciechanover A, Finley D, Varshavsky A. Ubiquitin dependence of selective protein degradation demonstrated in the mammalian cell cycle mutant ts85. Cell. 1984;37:57–66. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90300-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Pickart CM. Back to the future with ubiquitin. Cell. 2004;116:181–190. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(03)01074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Chen CD, Welsbie DS, Tran C, Baek SH, Chen R, Vessella R, Rosenfeld MG, Sawyers CL. Molecular determinants of resistance to antiandrogen therapy. Nat. Med. 2004;10:33–39. doi: 10.1038/nm972. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Bai Z, Gust R. Breast cancer estrogen receptor and ligands. Arch. Pharm. 2009;342:133–149. doi: 10.1002/ardp.200800174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Isaacs JT, Isaacs WB. Androgen receptor outwits prostate cancer drugs. Nat. Med. 2004;10:26–27. doi: 10.1038/nm0104-26. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Möttönen T, Hannonen P, Leirisalo-Repo M, Nissilä M, Kautiainen H, Korpela M, Laasonen L, Julkunen H, Luukkainen R, Vuori K, Paimela L, Blåfield H, Hakala M, Ilva K, Yli-Kerttula U, Puolakka K, Järvinen P, Hakola M, Piirainen H, Ahonen J, Pälvimäki I, Forsberg S, Koota K, Friman C. Comparison of combination therapy with single-drug therapy in early rheumatoid arthritis: A randomised trial. FIN-RACo trial group. Lancet. 1999;353:1568–1573. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(98)08513-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.van Vollenhoven RF. Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: State of the art 2009. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2009;5:531–541. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2009.182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Svensson B, Boonen A, Albertsson K, van der Heijde D, Keller C, Hafström I. Low-dose prednisolone in addition to the initial disease-modifying antirheumatic drug in patients with early active rheumatoid arthritis reduces joint destruction and increases the remission rate: A two-year randomized trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:3360–3370. doi: 10.1002/art.21298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Cho S, Kagan BL, Blackford JA, Jr., Szapary D, Simons SS., Jr. Glucocorticoid receptor ligand binding domain is sufficient for the modulation of glucocorticoid induction properties by homologous receptors coactivator transcription intermediary factor 2, and Ubc9. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005;19:290–311. doi: 10.1210/me.2004-0134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Gentleman RC, Carey VJ, Bates DM, Bolstad B, Dettling M, Dudoit S, Ellis B, Gautier L, Ge Y, Gentry J, Hornik K, Hothorn T, Huber W, Iacus S, Irizarry R, Leisch F, Li C, Maechler M, Rossini AJ, Sawitzki G, Smith C, Smyth G, Tierney L, Yang JY, Zhang J. Bioconductor: Open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol. 2004;5:R80. doi: 10.1186/gb-2004-5-10-r80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Patterson TA, Lobenhofer EK, Fulmer-Smentek SB, Collins PJ, Chu TM, Bao W, Fang H, Kawasaki ES, Hager J, Tikhonova IR, Walker SJ, Zhang L, Hurban P, de Longueville F, Fuscoe JC, Tong W, Shi L, Wolfinger RD. Performance comparison of one-color and two-color platforms within the MicroArray Quality Control (MAQC) project. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006;24:1140–1150. doi: 10.1038/nbt1242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Smyth GK. Linear models and empirical Bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray experiments. Stat. Appl. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2004;3 doi: 10.2202/1544-6115.1027. Article3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Sherer NM, Lehmann MJ, Jimenez-Soto LF, Ingmundson A, Horner SM, Cicchetti G, Allen PG, Pypaert M, Cunningham JM, Mothes W. Visualization of retroviral replication in living cells reveals budding into multivesicular bodies. Traffic. 2003;4:785–801. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0854.2003.00135.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.