Abstract
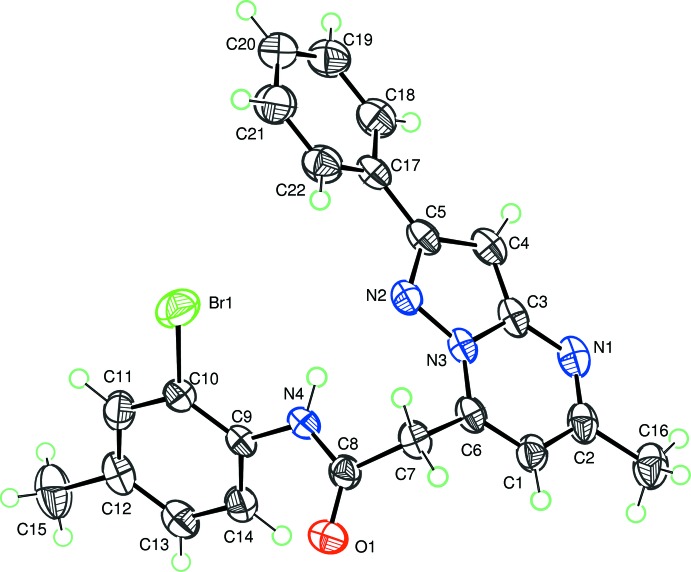
The fused pyrazole and pyrimidine rings in the title compound, C22H19BrN4O, are almost coplanar, their planes being inclined to one another by 2.08 (13)°. The dihedral angles formed by the mean plane of the fused ring system and the phenyl and benzene rings are 16.21 (4) and 82.84 (4)°, respectively. An intramolecular N—H⋯N hydrogen bond is observed. In the crystal, molecules form inversion dimers via pairs of C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. π–π interactions, with centroid–centroid distances of 3.4916 (9) Å, connect the dimers into a three-dimensional network.
Related literature
For pharmacological and biochemical properties of pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives, see: Selleri et al. (2005 ▶); Almansa et al. (2001 ▶); Suzuki et al. (2001 ▶); Chen et al. (2004 ▶). For related structures, see: Bassoude et al. (2013a
▶,b
▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C22H19BrN4O
M r = 435.32
Monoclinic,
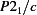
a = 9.8102 (6) Å
b = 7.2915 (4) Å
c = 27.0162 (14) Å
β = 92.942 (3)°
V = 1929.95 (19) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 2.15 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.42 × 0.33 × 0.25 mm
Data collection
Bruker X8 APEXII area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009 ▶) T min = 0.739, T max = 0.867
29996 measured reflections
6371 independent reflections
3830 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.044
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.041
wR(F 2) = 0.107
S = 1.02
6371 reflections
253 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.41 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.62 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2009 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2009 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 2012 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶) and publCIF (Westrip, 2010 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813011811/rz5060sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813011811/rz5060Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813011811/rz5060Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N4—H4A⋯N2 | 0.86 | 2.17 | 2.927 (2) | 147 |
| C14—H14⋯O1i | 0.93 | 2.43 | 3.189 (2) | 139 |
Symmetry code: (i) 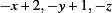 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Unit of Support for Technical and Scientific Research (UATRS, CNRST) for the X-ray diffraction measurements.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
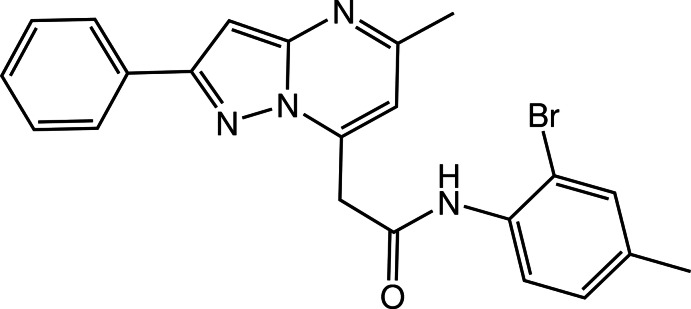
Pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidines have attracted considerable interest because of their biological activity. For instance, they are known for their potent utility as selective peripheral benzodiazepine receptor ligands (Selleri et al., 2005), COX-2 selective inhibitors (Almansa et al., 2001), HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (Suzuki et al., 2001) and CRF1 antagonists (Chen et al., 2004). Our research group targeted at the development of heterocycles with a bridgehead nitrogen atom such the title compound and related compounds recently published (Bassoude et al. 2013a, 2013b).
The crystal structure of the title compound is built up from two fused five (N2/N3/C3–C5) and six-membered (N1/N3/C1–C3/C6) rings linked to one phenyl ring (C17–C22) and to a 2-bromo-4-methylphenyl ring (Br1/C9–C14) through an acetamide group as shown in Fig. 1. The pyrazole and pyrimidine rings are essentially planar with the maximum deviation of 0.0039 (15) and 0.0076 (15) Å for atom C3. The plane through the fused ring system makes a dihedral angles of 16.21 (4)° and 82.84 (4)° with the phenyl ring and with the 2-bromo-4-methylphenyl ring, respectively.
In the crystal (Fig. 2) molecules form inversion dimers via pairs of C14—H14···O1 hydrogen bonds. In addition, π–π interactions connect the dimers into a three-dimensional network, with centroid–centroid distances of 3.4916 (9) Å. An intramolecular N4—H4A···N2 hydrogen bond my help to define the conformation of the molecule.
Experimental
To a solution of 2-bromo-4-methylaniline (0.1 ml, 0.78 mmol) in 4 ml dichloromethane, under argon and at 273 K, were added 0.8 ml of trimethylaluminium in toluene (2M, 1.6 mmol), then the mixture was stirred for 15 min followed by addition of 0.2 g (0.68 mmol) of 7-ethoxycarbonyl-methyl-5-methylpyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine. The reaction mixture was stirred to room temperature for 30 min then heated to reflux for 5 h. After evaporation of solvent under reduced pressure, the residue was extracted with CH2Cl2 and washed with a saturated NaCl solution. The combined organic layers were dried with MgSO4 and concentrated under vacuum. The residue was purified on silica gel by column chromatography using mixture of petroleum ether and ethyl acetate (9:1 v/v) as eluent. The compound was recrystallized from a mixture of cyclohexane/ diethyl ether (1:1 v/v) to give colourless crystals.
Refinement
All H atoms could be located in a difference Fourier map and were treated as riding, with C—H = 0.93–0.97 Å, N–H = 0.86 Å, and with Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(C, N) or 1.5 Ueq(C) for methyl H atoms. Two outliers (1 0 0; 0 0 2) were omitted from the last refinement cycles
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level. H atoms are represented as small circles of arbitrary radii.
Fig. 2.
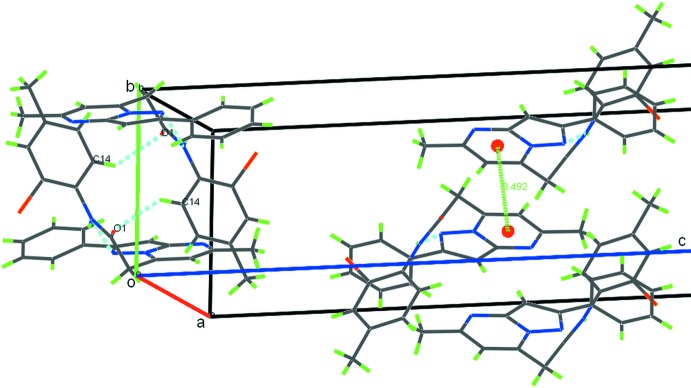
Partial crystal packing of the title compound showing C14–H14A···O1 and N4–H4···N2 hydrogen bonds as blue dashed lines and a π···π contact as green line. The red spheres represent the centroids of the pyrimidine rings.
Crystal data
| C22H19BrN4O | F(000) = 888 |
| Mr = 435.32 | Dx = 1.498 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 6371 reflections |
| a = 9.8102 (6) Å | θ = 2.5–31.4° |
| b = 7.2915 (4) Å | µ = 2.15 mm−1 |
| c = 27.0162 (14) Å | T = 296 K |
| β = 92.942 (3)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 1929.95 (19) Å3 | 0.42 × 0.33 × 0.25 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker X8 APEXII area-detector diffractometer | 6371 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3830 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.044 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 31.4°, θmin = 2.5° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2009) | h = −14→14 |
| Tmin = 0.739, Tmax = 0.867 | k = −10→10 |
| 29996 measured reflections | l = −39→39 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.041 | Hydrogen site location: difference Fourier map |
| wR(F2) = 0.107 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.02 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0467P)2 + 0.2795P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 6371 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 253 parameters | Δρmax = 0.41 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.62 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against all reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on all data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.6173 (2) | 0.8274 (2) | −0.03898 (7) | 0.0377 (4) | |
| H1 | 0.6836 | 0.8688 | −0.0597 | 0.045* | |
| C2 | 0.4907 (2) | 0.7594 (2) | −0.05997 (7) | 0.0389 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.41574 (19) | 0.7044 (2) | 0.01713 (7) | 0.0363 (4) | |
| C4 | 0.3365 (2) | 0.6608 (2) | 0.05592 (7) | 0.0389 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.2478 | 0.6155 | 0.0539 | 0.047* | |
| C5 | 0.41646 (19) | 0.6987 (2) | 0.09908 (7) | 0.0345 (4) | |
| C6 | 0.64217 (19) | 0.8324 (2) | 0.01096 (7) | 0.0329 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.76984 (19) | 0.9055 (2) | 0.03730 (7) | 0.0366 (4) | |
| H7A | 0.7446 | 0.9745 | 0.0661 | 0.044* | |
| H7B | 0.8141 | 0.9894 | 0.0154 | 0.044* | |
| C8 | 0.87117 (19) | 0.7571 (2) | 0.05392 (7) | 0.0330 (4) | |
| C9 | 0.89437 (18) | 0.4831 (2) | 0.10641 (7) | 0.0332 (4) | |
| C10 | 0.89659 (19) | 0.4341 (2) | 0.15591 (7) | 0.0361 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.9568 (2) | 0.2718 (3) | 0.17291 (8) | 0.0422 (5) | |
| H11 | 0.9557 | 0.2416 | 0.2063 | 0.051* | |
| C12 | 1.0184 (2) | 0.1551 (3) | 0.14043 (8) | 0.0436 (5) | |
| C13 | 1.0160 (2) | 0.2037 (3) | 0.09087 (8) | 0.0432 (5) | |
| H13 | 1.0567 | 0.1265 | 0.0685 | 0.052* | |
| C14 | 0.9547 (2) | 0.3641 (3) | 0.07366 (8) | 0.0397 (4) | |
| H14 | 0.9538 | 0.3925 | 0.0401 | 0.048* | |
| C15 | 1.0869 (3) | −0.0203 (3) | 0.15829 (10) | 0.0691 (7) | |
| H15A | 1.1706 | 0.0085 | 0.1766 | 0.104* | |
| H15B | 1.1060 | −0.0955 | 0.1303 | 0.104* | |
| H15C | 1.0274 | −0.0854 | 0.1793 | 0.104* | |
| C16 | 0.4645 (2) | 0.7598 (3) | −0.11515 (8) | 0.0512 (5) | |
| H16C | 0.4995 | 0.8709 | −0.1287 | 0.077* | |
| H16A | 0.3680 | 0.7523 | −0.1229 | 0.077* | |
| H16B | 0.5091 | 0.6563 | −0.1292 | 0.077* | |
| C17 | 0.38277 (19) | 0.6745 (2) | 0.15115 (7) | 0.0361 (4) | |
| C18 | 0.2742 (2) | 0.5647 (3) | 0.16391 (9) | 0.0470 (5) | |
| H18 | 0.2209 | 0.5064 | 0.1392 | 0.056* | |
| C19 | 0.2447 (2) | 0.5415 (3) | 0.21290 (9) | 0.0541 (6) | |
| H19 | 0.1721 | 0.4670 | 0.2209 | 0.065* | |
| C20 | 0.3217 (2) | 0.6275 (3) | 0.25011 (9) | 0.0533 (6) | |
| H20 | 0.3013 | 0.6116 | 0.2831 | 0.064* | |
| C21 | 0.4294 (2) | 0.7376 (3) | 0.23797 (9) | 0.0518 (5) | |
| H21 | 0.4818 | 0.7966 | 0.2628 | 0.062* | |
| C22 | 0.4595 (2) | 0.7604 (3) | 0.18897 (8) | 0.0452 (5) | |
| H22 | 0.5326 | 0.8345 | 0.1812 | 0.054* | |
| N1 | 0.39309 (17) | 0.6994 (2) | −0.03282 (6) | 0.0405 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.54163 (15) | 0.7640 (2) | 0.08894 (6) | 0.0338 (3) | |
| N3 | 0.53930 (15) | 0.76798 (18) | 0.03862 (6) | 0.0317 (3) | |
| N4 | 0.82608 (16) | 0.6428 (2) | 0.08896 (6) | 0.0370 (4) | |
| H4A | 0.7499 | 0.6695 | 0.1016 | 0.044* | |
| O1 | 0.98349 (14) | 0.74725 (19) | 0.03713 (5) | 0.0453 (3) | |
| Br1 | 0.81300 (3) | 0.58958 (3) | 0.201758 (8) | 0.05961 (10) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0391 (11) | 0.0356 (9) | 0.0378 (10) | 0.0071 (8) | −0.0030 (9) | 0.0039 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0459 (12) | 0.0288 (8) | 0.0409 (11) | 0.0120 (8) | −0.0089 (9) | −0.0027 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0315 (10) | 0.0304 (8) | 0.0458 (12) | 0.0060 (7) | −0.0103 (9) | −0.0036 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0268 (10) | 0.0370 (9) | 0.0523 (12) | 0.0007 (8) | −0.0044 (9) | −0.0031 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0282 (10) | 0.0278 (8) | 0.0473 (11) | 0.0048 (7) | −0.0008 (8) | −0.0028 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0303 (10) | 0.0275 (8) | 0.0405 (10) | 0.0056 (7) | −0.0035 (8) | 0.0011 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0330 (10) | 0.0341 (9) | 0.0420 (11) | 0.0014 (8) | −0.0036 (8) | 0.0021 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0294 (10) | 0.0381 (9) | 0.0309 (9) | 0.0008 (7) | −0.0032 (8) | −0.0041 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0223 (9) | 0.0400 (9) | 0.0371 (10) | 0.0042 (7) | −0.0009 (8) | 0.0022 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0291 (10) | 0.0442 (10) | 0.0350 (10) | 0.0004 (8) | 0.0005 (8) | 0.0002 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0409 (12) | 0.0462 (10) | 0.0387 (11) | −0.0011 (9) | −0.0055 (9) | 0.0086 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0366 (11) | 0.0381 (9) | 0.0549 (13) | 0.0032 (8) | −0.0102 (10) | 0.0024 (9) |
| C13 | 0.0359 (11) | 0.0409 (10) | 0.0522 (13) | 0.0050 (8) | −0.0026 (9) | −0.0077 (9) |
| C14 | 0.0345 (11) | 0.0466 (10) | 0.0377 (11) | 0.0048 (8) | −0.0027 (9) | −0.0010 (8) |
| C15 | 0.0758 (19) | 0.0495 (12) | 0.0796 (18) | 0.0205 (13) | −0.0183 (15) | 0.0084 (12) |
| C16 | 0.0619 (15) | 0.0482 (11) | 0.0422 (12) | 0.0110 (10) | −0.0118 (11) | −0.0065 (9) |
| C17 | 0.0277 (10) | 0.0335 (9) | 0.0470 (12) | 0.0077 (7) | 0.0010 (8) | −0.0020 (8) |
| C18 | 0.0373 (12) | 0.0483 (11) | 0.0551 (13) | −0.0024 (9) | 0.0001 (10) | −0.0032 (9) |
| C19 | 0.0418 (13) | 0.0624 (13) | 0.0588 (15) | −0.0058 (11) | 0.0085 (11) | 0.0066 (11) |
| C20 | 0.0467 (14) | 0.0681 (14) | 0.0455 (13) | 0.0084 (11) | 0.0074 (11) | 0.0030 (10) |
| C21 | 0.0453 (13) | 0.0632 (13) | 0.0466 (13) | −0.0024 (11) | 0.0013 (10) | −0.0085 (10) |
| C22 | 0.0366 (11) | 0.0490 (11) | 0.0501 (13) | −0.0034 (9) | 0.0015 (10) | −0.0048 (9) |
| N1 | 0.0393 (10) | 0.0358 (8) | 0.0451 (10) | 0.0055 (7) | −0.0107 (8) | −0.0041 (7) |
| N2 | 0.0292 (8) | 0.0355 (7) | 0.0362 (9) | 0.0033 (6) | −0.0027 (7) | −0.0015 (6) |
| N3 | 0.0276 (8) | 0.0296 (7) | 0.0371 (9) | 0.0048 (6) | −0.0056 (7) | −0.0012 (6) |
| N4 | 0.0279 (9) | 0.0454 (8) | 0.0379 (9) | 0.0098 (7) | 0.0046 (7) | 0.0059 (7) |
| O1 | 0.0352 (8) | 0.0541 (8) | 0.0474 (8) | 0.0065 (6) | 0.0094 (7) | 0.0049 (6) |
| Br1 | 0.0728 (2) | 0.06541 (16) | 0.04192 (14) | 0.01753 (12) | 0.01561 (12) | 0.00091 (10) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| C1—C6 | 1.359 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.428 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.384 (3) |
| C1—H1 | 0.9300 | C12—C15 | 1.512 (3) |
| C2—N1 | 1.311 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.385 (3) |
| C2—C16 | 1.500 (3) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| C3—N1 | 1.357 (2) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.374 (3) | C15—H15A | 0.9600 |
| C3—N3 | 1.396 (2) | C15—H15B | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.399 (3) | C15—H15C | 0.9600 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C16—H16C | 0.9600 |
| C5—N2 | 1.358 (2) | C16—H16A | 0.9600 |
| C5—C17 | 1.472 (3) | C16—H16B | 0.9600 |
| C6—N3 | 1.369 (2) | C17—C22 | 1.387 (3) |
| C6—C7 | 1.506 (3) | C17—C18 | 1.390 (3) |
| C7—C8 | 1.521 (2) | C18—C19 | 1.380 (3) |
| C7—H7A | 0.9700 | C18—H18 | 0.9300 |
| C7—H7B | 0.9700 | C19—C20 | 1.377 (3) |
| C8—O1 | 1.215 (2) | C19—H19 | 0.9300 |
| C8—N4 | 1.353 (2) | C20—C21 | 1.380 (3) |
| C9—C10 | 1.383 (3) | C20—H20 | 0.9300 |
| C9—C14 | 1.393 (3) | C21—C22 | 1.381 (3) |
| C9—N4 | 1.412 (2) | C21—H21 | 0.9300 |
| C10—C11 | 1.390 (3) | C22—H22 | 0.9300 |
| C10—Br1 | 1.8962 (19) | N2—N3 | 1.359 (2) |
| C11—C12 | 1.384 (3) | N4—H4A | 0.8600 |
| C6—C1—C2 | 120.76 (19) | C13—C14—C9 | 120.30 (19) |
| C6—C1—H1 | 119.6 | C13—C14—H14 | 119.8 |
| C2—C1—H1 | 119.6 | C9—C14—H14 | 119.8 |
| N1—C2—C1 | 122.65 (18) | C12—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| N1—C2—C16 | 117.63 (19) | C12—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—C16 | 119.7 (2) | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| N1—C3—C4 | 133.01 (18) | C12—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| N1—C3—N3 | 121.12 (18) | H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—N3 | 105.85 (16) | H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 105.95 (17) | C2—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 127.0 | C2—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 127.0 | H16C—C16—H16A | 109.5 |
| N2—C5—C4 | 112.04 (17) | C2—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| N2—C5—C17 | 118.99 (17) | H16C—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—C17 | 128.97 (18) | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—N3 | 115.66 (17) | C22—C17—C18 | 118.12 (19) |
| C1—C6—C7 | 125.52 (18) | C22—C17—C5 | 120.65 (18) |
| N3—C6—C7 | 118.81 (16) | C18—C17—C5 | 121.24 (18) |
| C6—C7—C8 | 113.78 (14) | C19—C18—C17 | 120.7 (2) |
| C6—C7—H7A | 108.8 | C19—C18—H18 | 119.7 |
| C8—C7—H7A | 108.8 | C17—C18—H18 | 119.7 |
| C6—C7—H7B | 108.8 | C20—C19—C18 | 120.7 (2) |
| C8—C7—H7B | 108.8 | C20—C19—H19 | 119.7 |
| H7A—C7—H7B | 107.7 | C18—C19—H19 | 119.7 |
| O1—C8—N4 | 124.06 (17) | C19—C20—C21 | 119.3 (2) |
| O1—C8—C7 | 121.57 (17) | C19—C20—H20 | 120.4 |
| N4—C8—C7 | 114.36 (16) | C21—C20—H20 | 120.4 |
| C10—C9—C14 | 117.85 (17) | C20—C21—C22 | 120.1 (2) |
| C10—C9—N4 | 121.28 (16) | C20—C21—H21 | 119.9 |
| C14—C9—N4 | 120.76 (17) | C22—C21—H21 | 119.9 |
| C9—C10—C11 | 121.64 (18) | C21—C22—C17 | 121.1 (2) |
| C9—C10—Br1 | 119.42 (14) | C21—C22—H22 | 119.4 |
| C11—C10—Br1 | 118.93 (15) | C17—C22—H22 | 119.4 |
| C12—C11—C10 | 120.42 (19) | C2—N1—C3 | 117.42 (17) |
| C12—C11—H11 | 119.8 | C5—N2—N3 | 103.92 (14) |
| C10—C11—H11 | 119.8 | N2—N3—C6 | 125.34 (15) |
| C11—C12—C13 | 118.01 (18) | N2—N3—C3 | 112.24 (15) |
| C11—C12—C15 | 121.3 (2) | C6—N3—C3 | 122.38 (16) |
| C13—C12—C15 | 120.7 (2) | C8—N4—C9 | 125.11 (15) |
| C12—C13—C14 | 121.77 (19) | C8—N4—H4A | 117.4 |
| C12—C13—H13 | 119.1 | C9—N4—H4A | 117.4 |
| C14—C13—H13 | 119.1 |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N4—H4A···N2 | 0.86 | 2.17 | 2.927 (2) | 147 |
| C14—H14···O1i | 0.93 | 2.43 | 3.189 (2) | 139 |
Symmetry code: (i) −x+2, −y+1, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: RZ5060).
References
- Almansa, C. A., Alberto, F., Cavalcanti, F. L., Gomez, L. A., Miralles, A., Merlos, M., Garcia-Rafanell, J. & Forn, J. (2001). J. Med. Chem. 44, 350–361. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bassoude, I., Berteina-Raboin, S., Essassi, E. M., Guillaumet, G. & El Ammari, L. (2013a). Acta Cryst. E69, o740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bassoude, I., Berteina-Raboin, S., Essassi, E. M., Guillaumet, G. & El Ammari, L. (2013b). Acta Cryst. E69, o749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2009). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Chen, C., Wilcoxen, K. M., Huang, C. Q., Xie, Y.-F., McCarthy, J. R., Webb, T. R., Zhu, Y.-F., Saunders, J., Liu, X.-J., Chen, T.-K., Bozigian, H. & Grigoriadis, D. E. (2004). J. Med. Chem. 47, 4787–4798. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Selleri, S., Gratteri, P., Costagli, C., Bonaccini, C., Costanzo, A., Melani, F., Guerrini, G., Ciciani, G., Costa, B., Spinetti, F., Martini, C. & Bruni, F. (2005). Bioorg. Med. Chem. 13, 4821–4834. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M., Iwasaki, H., Fujikawa, Y., Sakashita, M., Kitahara, M. & Sakoda, R. (2001). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 11, 1285–1288. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2010). J. Appl. Cryst. 43, 920–925.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813011811/rz5060sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813011811/rz5060Isup2.hkl
Supplementary material file. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536813011811/rz5060Isup3.cml
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report