Abstract
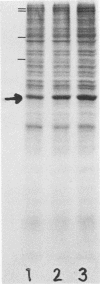
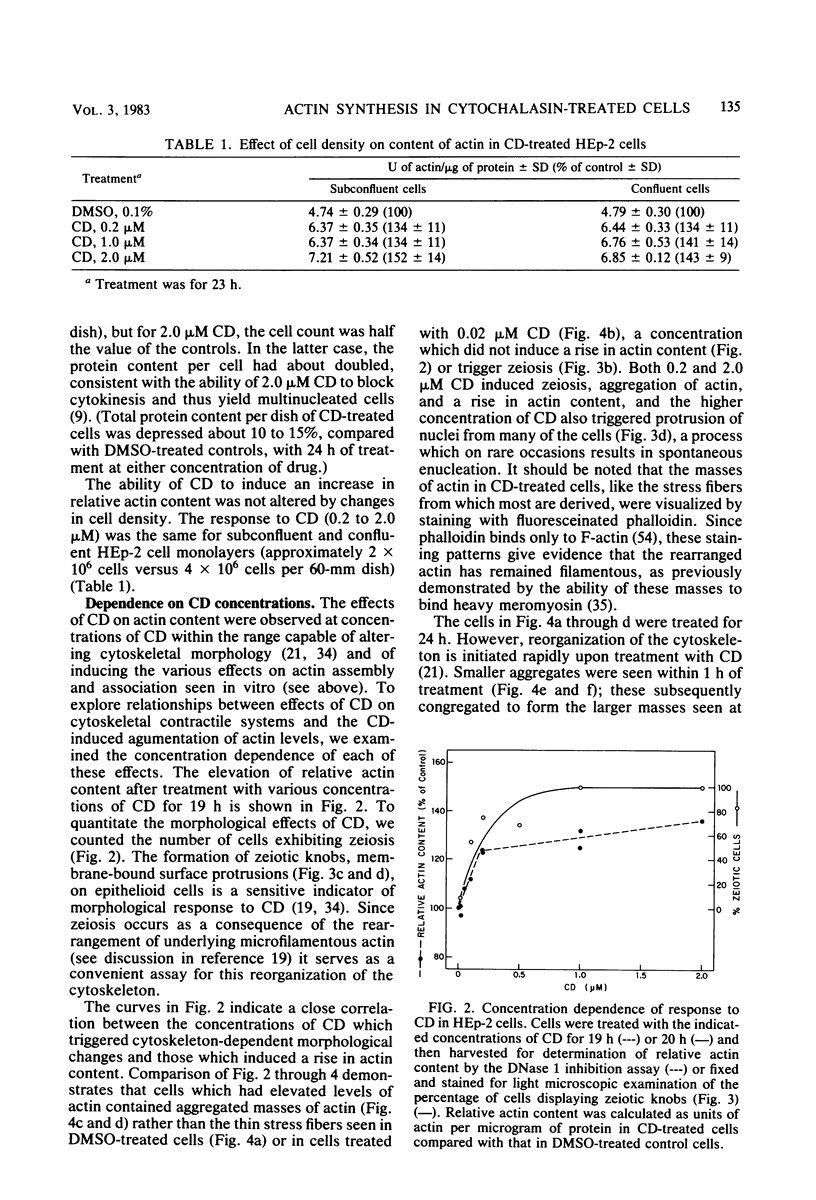
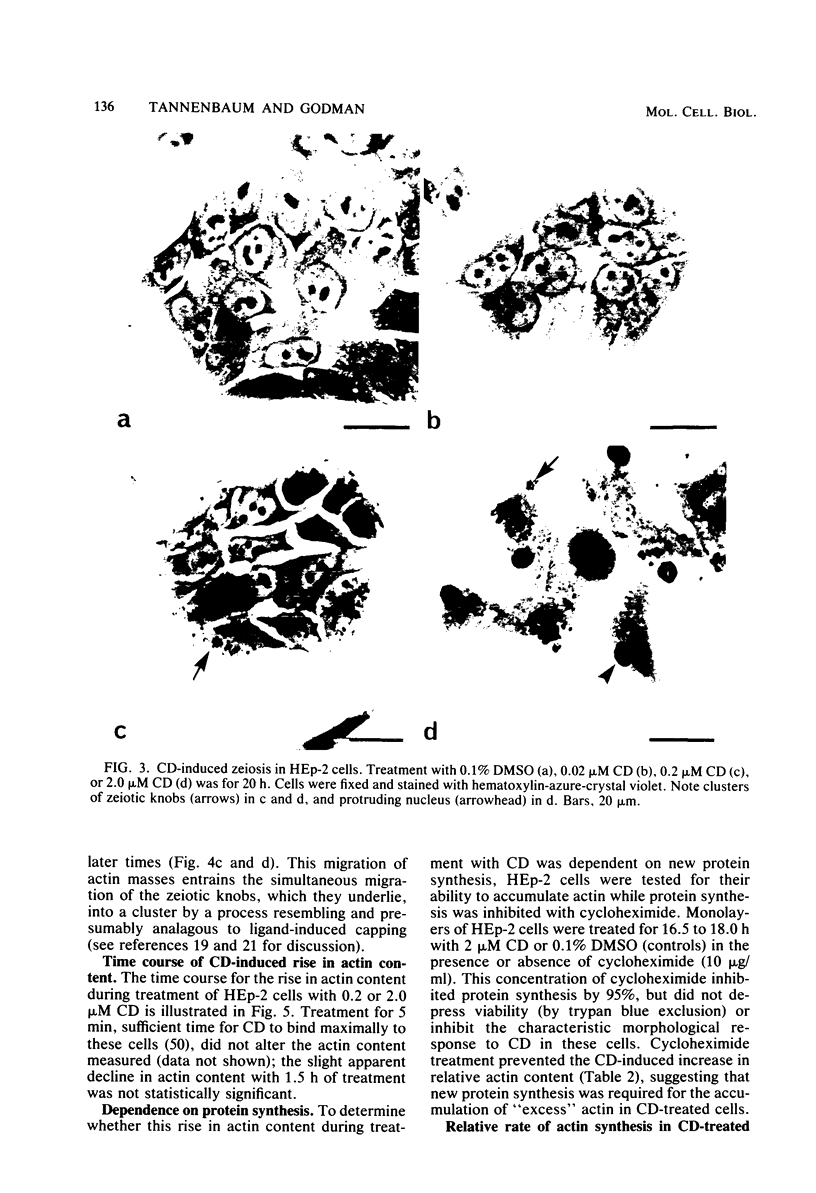
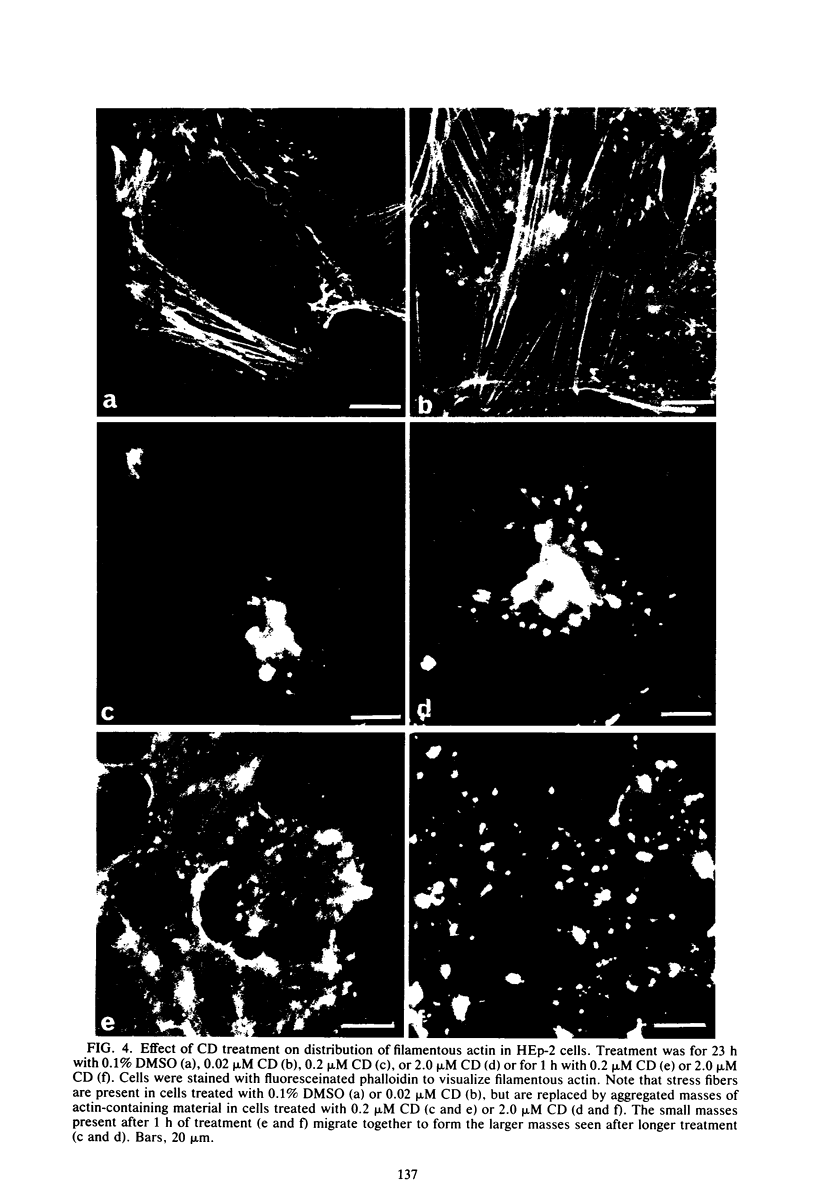
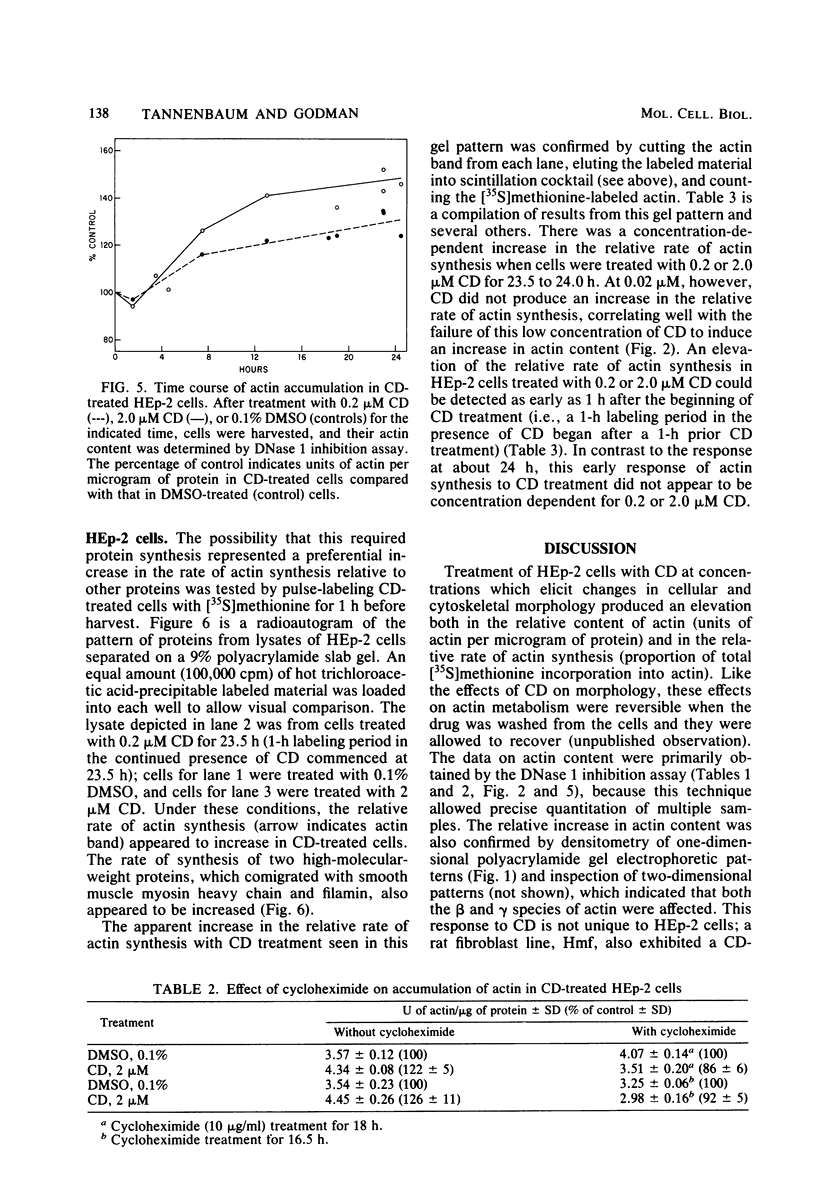
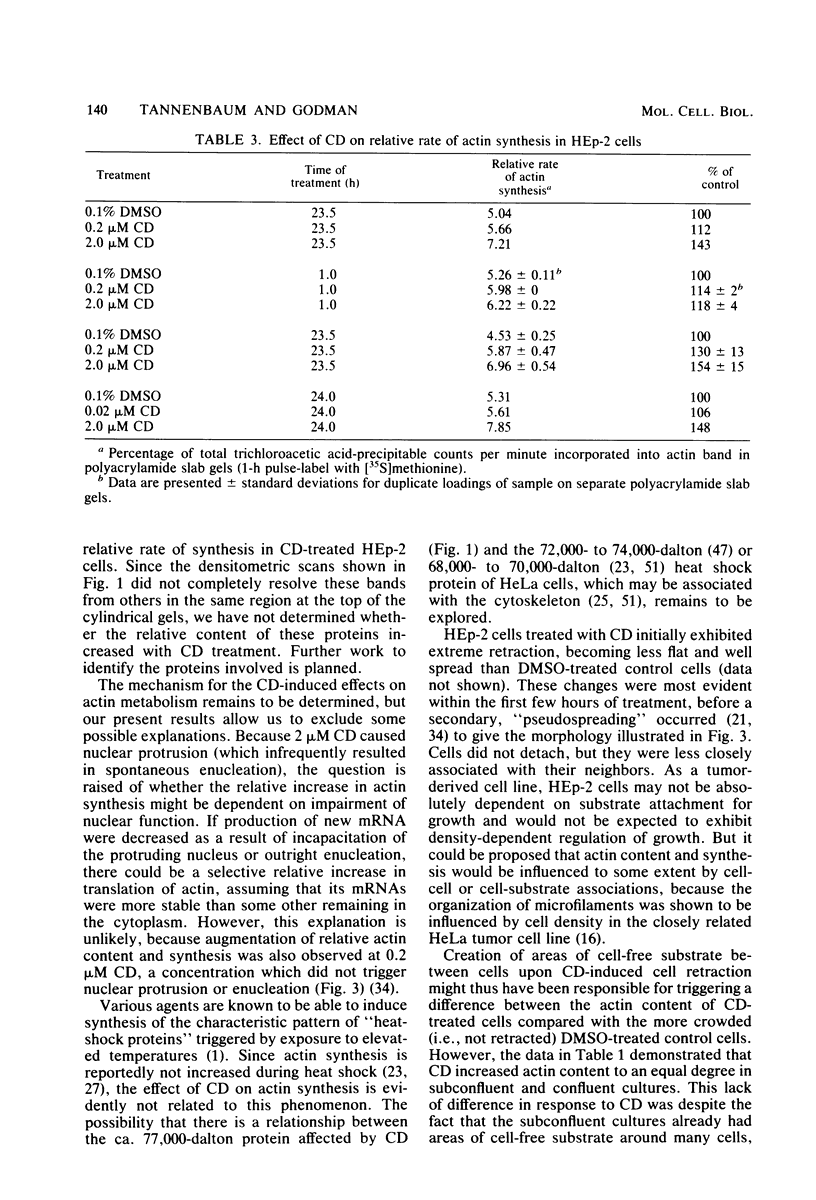
In HEp-2 cells treated with 0.2 to 2.0 microM cytochalasin D (CD) for 7.5 to 24 h there was a 20 to 50% relative increase in actin content (units of actin per microgram of total cell protein). This augmentation, which was concentration and time dependent, was prevented by treatment with cycloheximide during exposure to CD. A 15 to 20% increase in the relative rate of actin synthesis in CD-treated HEp-2 cells (0.2 to 2.0 microM CD) was detectable after 1 h of treatment and increased to 30 to 50% by 24 h. This increased rate of actin synthesis was apparently responsible for the higher actin content of CD-treated HEp-2 cells. The concentration dependence of these effects of CD on actin metabolism correlated with the pattern seen for CD-triggered changes in cellular morphology and the underlying rearrangements of the actin-containing cytoskeletal structures, suggesting that the effects on metabolism and morphology were interrelated. Since the rapidly occurring cytoskeletal reorganization preceded the effects of CD on actin metabolism, it is proposed that actin synthesis is induced by the cytoskeletal rearrangement resulting from exposure to CD.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashburner M., Bonner J. J. The induction of gene activity in drosophilia by heat shock. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):241–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90150-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benecke B. J., Ben-Ze'ev A., Penman S. The control of mRNA production, translation and turnover in suspended and reattached anchorage-dependent fibroblasts. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):931–939. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90347-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blikstad I., Carlsson L. On the dynamics of the microfilament system in HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):122–128. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blikstad I., Markey F., Carlsson L., Persson T., Lindberg U. Selective assay of monomeric and filamentous actin in cell extracts, using inhibition of deoxyribonuclease I. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):935–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90277-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Celis J. E. A search for differential polypeptide synthesis throughout the cell cycle of HeLa cells. J Cell Biol. 1980 Mar;84(3):795–802. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.3.795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner S. L., Korn E. D. Substoichiometric concentrations of cytochalasin D inhibit actin polymerization. Additional evidence for an F-actin treadmill. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):9982–9985. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. S., Spudich J. A. Cytochalasin inhibits the rate of elongation of actin filament fragments. J Cell Biol. 1979 Dec;83(3):657–662. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.3.657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheitlin R., Ramachandran J. Regulation of actin in rat adrenocortical cells by corticotropin. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3156–3158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crain W. R., Jr, Durica D. S., Van Doren K. Actin gene expression in developing sea urchin embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;1(8):711–720. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.8.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farmer S. R., Ben-Ze'av A., Benecke B. J., Penman S. Altered translatability of messenger RNA from suspended anchorage-dependent fibroblasts: reversal upon cell attachment to a surface. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):627–637. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90031-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine R. E., Taylor L. Decreased actin and tubulin synthesis in 3T3 cells after transformation by SV40 virus. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Oct 1;102(1):162–168. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90311-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan M. D., Lin S. Cytochalasins block actin filament elongation by binding to high affinity sites associated with F-actin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):835–838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara K., Pollard T. D. Fluorescent antibody localization of myosin in the cytoplasm, cleavage furrow, and mitotic spindle of human cells. J Cell Biol. 1976 Dec;71(3):848–875. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.3.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrels J. I., Gibson W. Identification and characterization of multiple forms of actin. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 2):793–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90142-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godman G. C., Miranda A. F. Cellular contractility and the visible effects of cytochalasin. Front Biol. 1978;46:277–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godman G. C., Miranda A. F., Deitch A. D., Tanenbaum S. W. Action of cytochalasin D on cells of established lines. III. Zeiosis and movements at the cell surface. J Cell Biol. 1975 Mar;64(3):644–667. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.3.644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
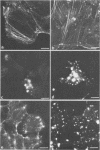
- Godman G., Woda B., Kolberg R., Berl S. Redistribution of contractile and cytoskeletal components induced by cytochalasin. II. In HeLa and HEp2 cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 1980 Oct;22(2):745–754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwig J. H., Stossel T. P. Cytochalasin B and the structure of actin gels. J Mol Biol. 1979 Nov 5;134(3):539–553. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90366-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey E. D., Weber L. A. Modulation of heat-shock polypeptide synthesis in HeLa cells during hyperthermia and recovery. Biochemistry. 1982 Mar 30;21(7):1513–1521. doi: 10.1021/bi00536a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman-Liebermann B., Sachs L. Regulation of actin and other proteins in the differentiation of myeloid leukemic cells. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):825–834. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90338-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes E. N., August J. T. Coprecipitation of heat shock proteins with a cell surface glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2305–2309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Infante A. A., Heilmann L. J. Distribution of messenger ribonucleic acid in polysomes and nonpolysomal particles of sea urchin embryos: translational control of actin synthesis. Biochemistry. 1981 Jan 6;20(1):1–8. doi: 10.1021/bi00504a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley P. M., Schlesinger M. J. The effect of amino acid analogues and heat shock on gene expression in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1277–1286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin D. C., Lin S. Actin polymerization induced by a motility-related high-affinity cytochalasin binding complex from human erythrocyte membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2345–2349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLean-Fletcher S., Pollard T. D. Mechanism of action of cytochalasin B on actin. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):329–341. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90619-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Hartwig J. H., Stossel T. P. Cytochalasin B and the structure of actin gels. II. Further evidence for the splitting of F-actin by cytochalasin B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Dec 16;626(2):494–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mely-Goubert B., Bellgrau D. Actin content in lymphocytes: a proposed correlation with their recirculating properties. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):399–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milcarek C., Zahn K. The synthesis of ninety proteins including actin throughout the HeLa cell cycle. J Cell Biol. 1978 Dec;79(3):833–838. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.3.833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
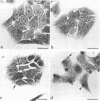
- Miranda A. F., Godman G. C., Deitch A. D., Tanenbaum S. W. Action of cytochalasin D on cells of established lines. I. Early events. J Cell Biol. 1974 May;61(2):481–500. doi: 10.1083/jcb.61.2.481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miranda A. F., Godman G. C., Tanenbaum S. W. Action of cytochalasin D on cells of established lines. II. Cortex and microfilaments. J Cell Biol. 1974 Aug;62(2):406–423. doi: 10.1083/jcb.62.2.406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A., Tannenbaum J. Cytochalasin D does not produce net depolymerization of actin filaments in HEp-2 cells. Nature. 1980 Oct 16;287(5783):637–639. doi: 10.1038/287637a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata K., Sagara J., Ichikawa Y. Changes in contractile proteins during differentiation of myeloid leukemia cells. I. Polymerization of actin. J Cell Biol. 1980 May;85(2):273–282. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palatnik C. M., Storti R. V., Jacobson A. Partial purification of a developmentally regulated messenger RNA from Dictyostelium discoideum by thermal elution from poly(U)-sepharose. J Mol Biol. 1981 Aug 15;150(3):389–398. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90554-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddle V. G., Dubrow R., Pardee A. B. Changes in the synthesis of actin and other cell proteins after stimulation of serum-arrested cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1298–1302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riddle V. G., Pardee A. B. Quiescent cells but not cycling cells exhibit enhanced actin synthesis before they synthesize DNA. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Apr;103(1):11–15. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041030103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin R. W., Warren R. H., Lukeman D. S., Clements E. Actin content and organization in normal and transformed cells in culture. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jul;78(1):28–35. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.1.28. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schliwa M. Action of cytochalasin D on cytoskeletal networks. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):79–91. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selden L. A., Gershman L. C., Estes J. E. A proposed mechanism of action of cytochalasin D on muscle actin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Aug 29;95(4):1854–1860. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(80)80115-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu R. S. Two-dimensional electrophoretic analyses of proteins synthesized during differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):11111–11118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson P. A., Spudich J. A. ATP-driven steady-state exchange of monomeric and filamentous actin from Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4610–4613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater A., Cato A. C., Sillar G. M., Kioussis J., Burdon R. H. The pattern of protein synthesis induced by heat shock of HeLa cells. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Jul;117(2):341–346. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb06343.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannenbaum J., Rich A. An isoelectric focusing study of plasma membrane actin. Anal Biochem. 1979 May;95(1):236–244. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannenbaum J., Tanenbaum S. W., Lo L. W., Godman G. C., Miranda A. F. Binding and subcellular localization of tritiated cytochalasin D. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Mar 1;91(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90139-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C., Gomer R. H., Lazarides E. Heat shock proteins are methylated in avian and mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3531–3535. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Rathke P. C., Osborn M., Franke W. W. Distribution of actin and tubulin in cells and in glycerinated cell models after treatment with cytochalasin B (CB). Exp Cell Res. 1976 Oct 15;102(2):285–297. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wulf E., Deboben A., Bautz F. A., Faulstich H., Wieland T. Fluorescent phallotoxin, a tool for the visualization of cellular actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4498–4502. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries J., Wieland T. Influence of phallotoxins and metal ions on the rate of proteolysis of actin. Biochemistry. 1978 May 16;17(10):1965–1968. doi: 10.1021/bi00603a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]