Abstract
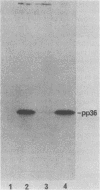
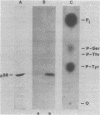
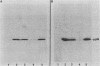
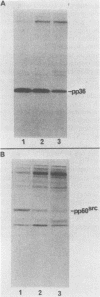
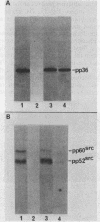
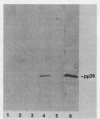
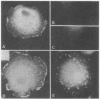
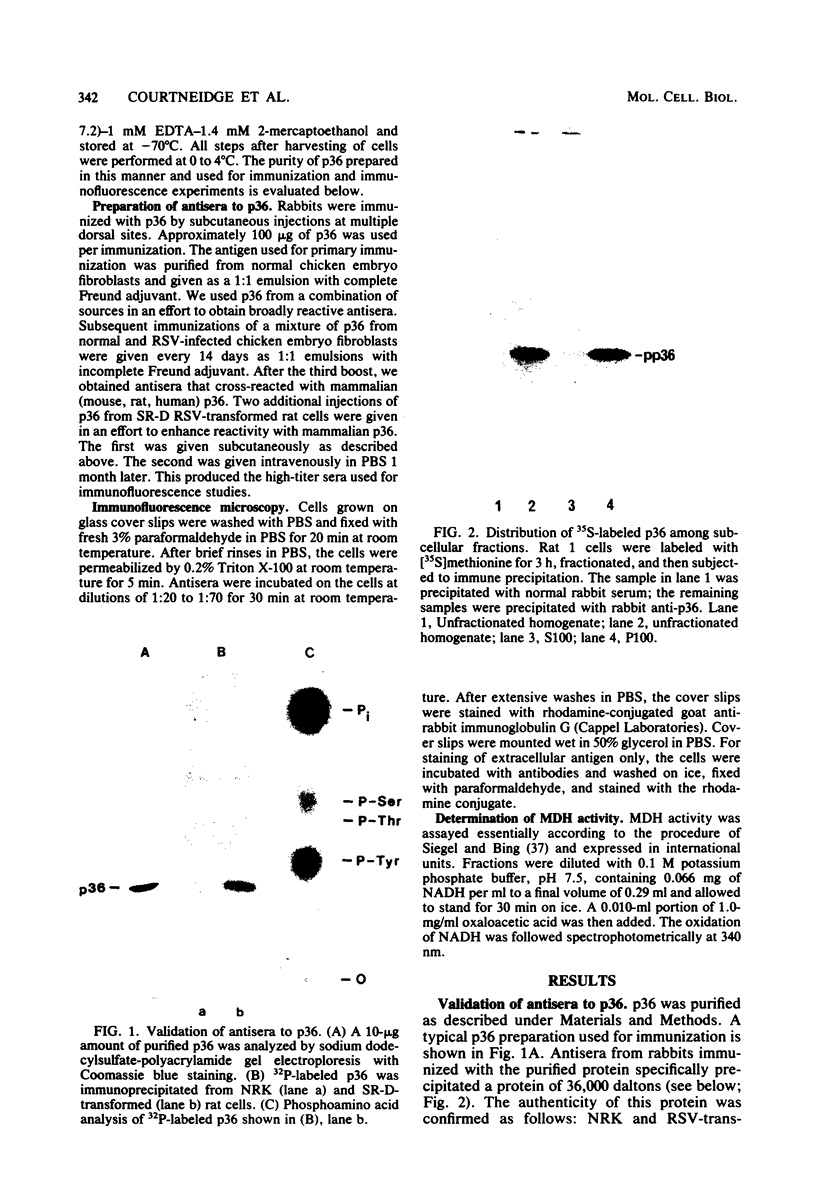
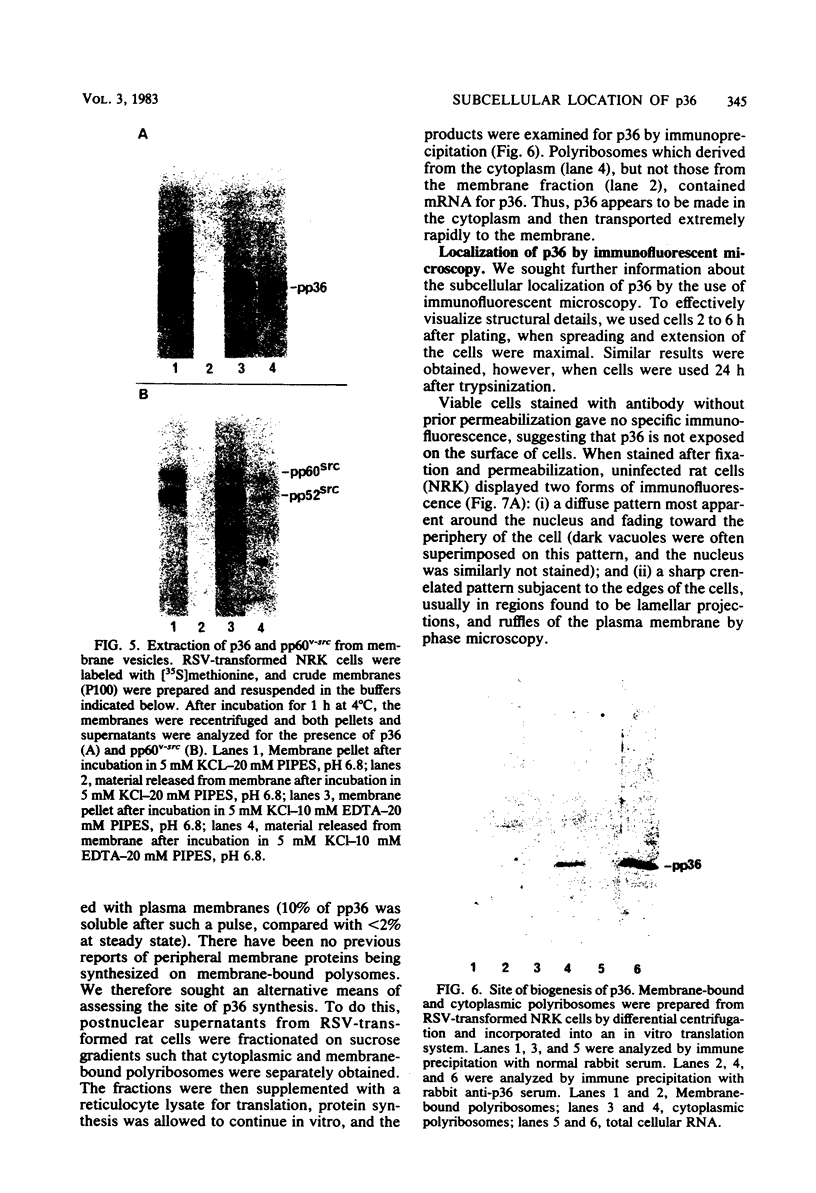
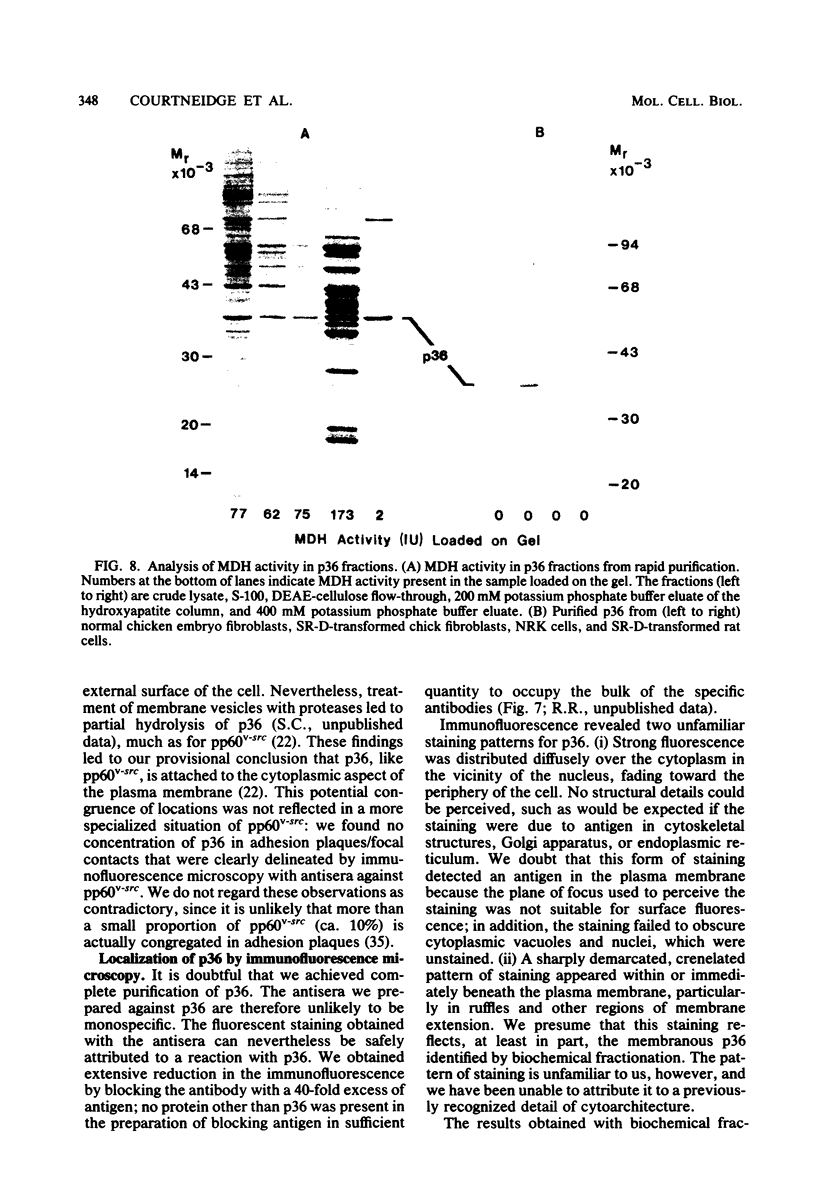
A 36,000-dalton cellular protein (p36) has been identified previously as an abundant substrate for phosphorylation by tyrosine-specific protein kinases. Since several of the responsible kinases are associated with the plasma membrane, we explored the subcellular distribution of p36. Biochemical fractionations located p36 on the plasma membrane of both normal and retrovirus-transformed cells. Approximately half of the p36 was bound to the membrane with the affinity of a peripheral membrane protein; the remainder was even more tightly bound. The distribution of p36 among subcellular fractions and its affinity for the plasma membrane were not affected by tyrosine phosphorylation. We determined that p36 is synthesized in the soluble compartment of the cell and then moves rapidly to the membranous compartment. Immunofluorescence microscopy with antibodies directed against p36 revealed two distinct distributions of the antigen: (i) a sharply demarcated crenelated pattern within or immediately beneath the plasma membrane, which we presume to be a correlary of the distribution of p36 in biochemical fractionations; and (ii) diffuse staining in a cytoplasmic location that could not be attributed to a specific feature of cytoarchitecture and could not be easily reconciled with the results of biochemical fractionations. Efforts to detect the secretion of p36 were unsuccessful. No evidence was obtained for exposure of p36 on the cell surface, and no changes in localization were observed as a consequence of neoplastic transformation. During the course of this study, we had the opportunity to pursue a previous report that p36 is a component of the enzyme malate dehydrogenase (Rubsamen et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79:228-232, 1982). We were unable to substantiate this claim. We conclude that at least a substantial fraction of p36 is located on the cytoplasmic aspect of the plasma membrane, where it could be well situated to serve as a substrate for several identified tyrosine-specific kinases. But the function of p36 and its role, if any, in neoplastic transformation of cells by retroviruses possessing tyrosine-specific kinases remain enigmatic.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ben-Ze'ev A., Duerr A., Solomon F., Penman S. The outer boundary of the cytoskeleton: a lamina derived from plasma membrane proteins. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):859–865. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90326-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boss M. A., Dreyfuss G., Baltimore D. Localization of the Abelson murine leukemia virus protein in a detergent-insoluble subcellular matrix: architecture of the protein. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):472–481. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.472-481.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branton D., Cohen C. M., Tyler J. Interaction of cytoskeletal proteins on the human erythrocyte membrane. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):24–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90497-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. S., Chen L. B. Detection of phosphotyrosine-containing 34,000-dalton protein in the framework of cells transformed with Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2388–2392. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Carpenter G., King L., Jr Epidermal growth factor-receptor-protein kinase interactions. Co-purification of receptor and epidermal growth factor-enhanced phosphorylation activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4834–4842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Erikson R. L. Protein kinase activity associated with the avian sarcoma virus src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):2021–2024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Purchio A. F., Erikson R. L. Avian sarcoma virus-transforming protein, pp60src shows protein kinase activity specific for tyrosine. Nature. 1980 May 15;285(5761):167–169. doi: 10.1038/285167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Four different classes of retroviruses induce phosphorylation of tyrosines present in similar cellular proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 May;1(5):394–407. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.5.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Similarities and differences between the effects of epidermal growth factor and Rous sarcoma virus. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):878–883. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Levinson A. D., Bishop J. M. The protein encoded by the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus (pp60src) and a homologous protein in normal cells (pp60proto-src) are associated with the plasma membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3783–3787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl H. H., Dickson C. Cell-free synthesis of mouse mammary tumor virus Pr77 from virion and intracellular mRNA. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):1131–1141. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.1131-1141.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Identification of a cellular protein substrate phosphorylated by the avian sarcoma virus-transforming gene product. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):829–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90446-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson R. L., Collett M. S., Erikson E., Purchio A. F. Evidence that the avian sarcoma virus transforming gene product is a cyclic AMP-independent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6260–6264. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmer T. M., Erikson R. L. Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein, p60src, expressed in E. coli, functions as a protein kinase. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):771–773. doi: 10.1038/294771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Epidermal growth factor induces rapid tyrosine phosphorylation of proteins in A431 human tumor cells. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90100-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. G., Wang E., Goldberg A. R. Evidence that the src gene product of Rous sarcoma virus is membrane associated. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):25–40. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90480-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Courtneidge S. A., Bishop J. M. Structural and functional domains of the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein (pp60src). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1624–1628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Oppermann H., Levintow L., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Evidence that the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus encodes a protein kinase associated with a phosphoprotein. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):561–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Oppermann H., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. The purified product of the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11973–11980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maness P. F., Engeser H., Greenberg M. E., O'Farrell M., Gall W. E., Edelman G. M. Characterization of the protein kinase activity of avian sarcoma virus src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5028–5032. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. P., Levinson A. D. Bacterial expression of an enzymatically active protein encoded by RSV src gene. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):423–425. doi: 10.1038/295423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mescher M. F., Jose M. J., Balk S. P. Actin-containing matrix associated with the plasma membrane of murine tumour and lymphoid cells. Nature. 1981 Jan 15;289(5794):139–144. doi: 10.1038/289139a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T. G. Site of synthesis of membrane and nonmembrane proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6955–6962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K. D., Weber M. J. Phosphorylation of a 36,000 Mr cellular protein in cells infected with partial transformation mutants of rous sarcoma virus. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):147–153. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann H., Levinson A. D., Levintow L., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Kawai S. Two cellular proteins that immunoprecipitate with the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):736–751. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90202-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Gilmore T., Martin G. S. Transformation by Rous sarcoma virus: a cellular substrate for transformation-specific protein phosphorylation contains phosphotyrosine. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):821–828. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90445-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radke K., Martin G. S. Transformation by Rous sarcoma virus: effects of src gene expression on the synthesis and phosphorylation of cellular polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5212–5216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrschneider L. R. Adhesion plaques of Rous sarcoma virus-transformed cells contain the src gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3514–3518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrschneider L. R. Immunofluorescence on avian sarcoma virus-transformed cells: localization of the src gene product. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90183-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrschneider L., Rosok M., Shriver K. Mechanism of transformation by Rous sarcoma virus: events within adhesion plaques. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 2):953–965. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rübsamen H., Saltenberger K., Friis R. R., Eigenbrodt E. Cytosolic malic dehydrogenase activity is associated with a putative substrate for the transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):228–232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIEGEL A., BING R. J. Plasma enzyme activity in myocardial infarction in dog and man. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Apr;91(4):604–607. doi: 10.3181/00379727-91-22344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J. The molecular organization of membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1974;43(0):805–833. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.43.070174.004105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Jay G., Pastan I. Localization of the ASV src gene product to the plasma membrane of transformed cells by electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90361-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte O. N., Rosenberg N., Baltimore D. Preparation of syngeneic tumor regressor serum reactive with the unique determinants of the Abelson murine leukemia virus-encoded P120 protein at the cell surface. J Virol. 1979 Sep;31(3):776–784. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.3.776-784.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]