Abstract
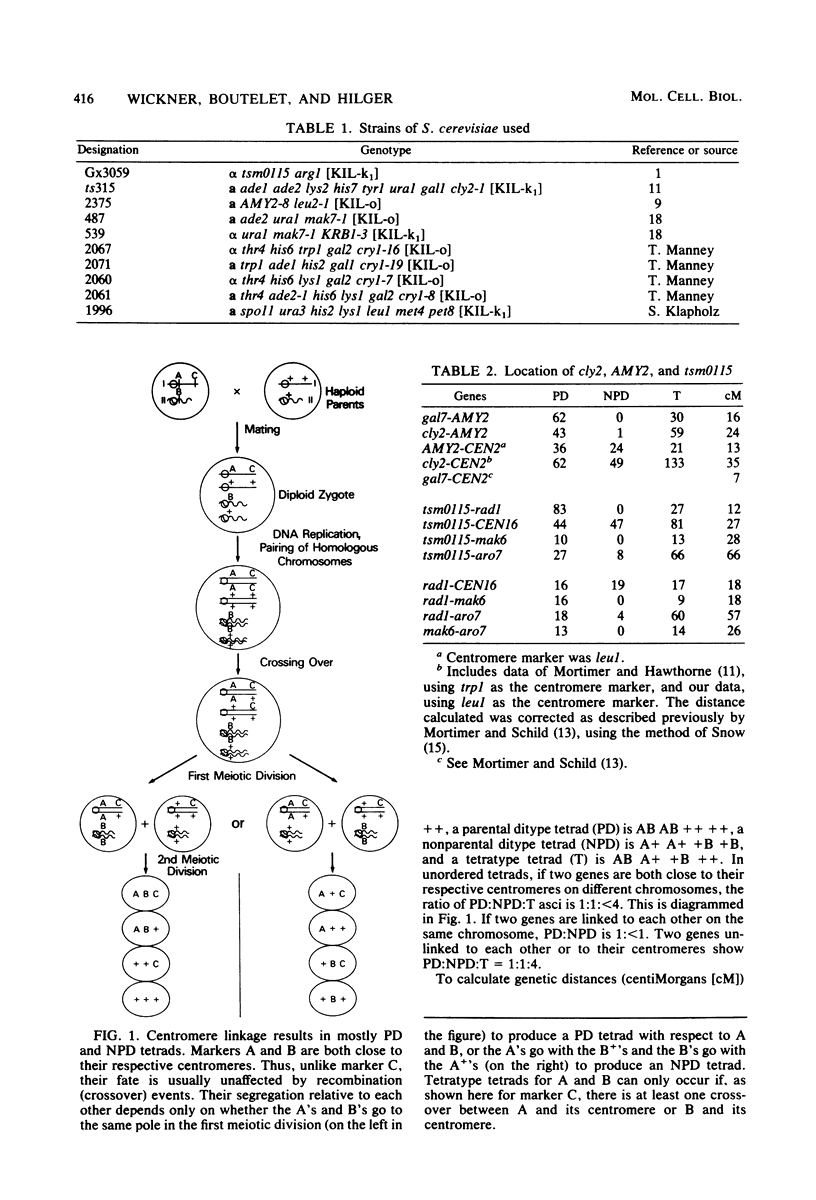
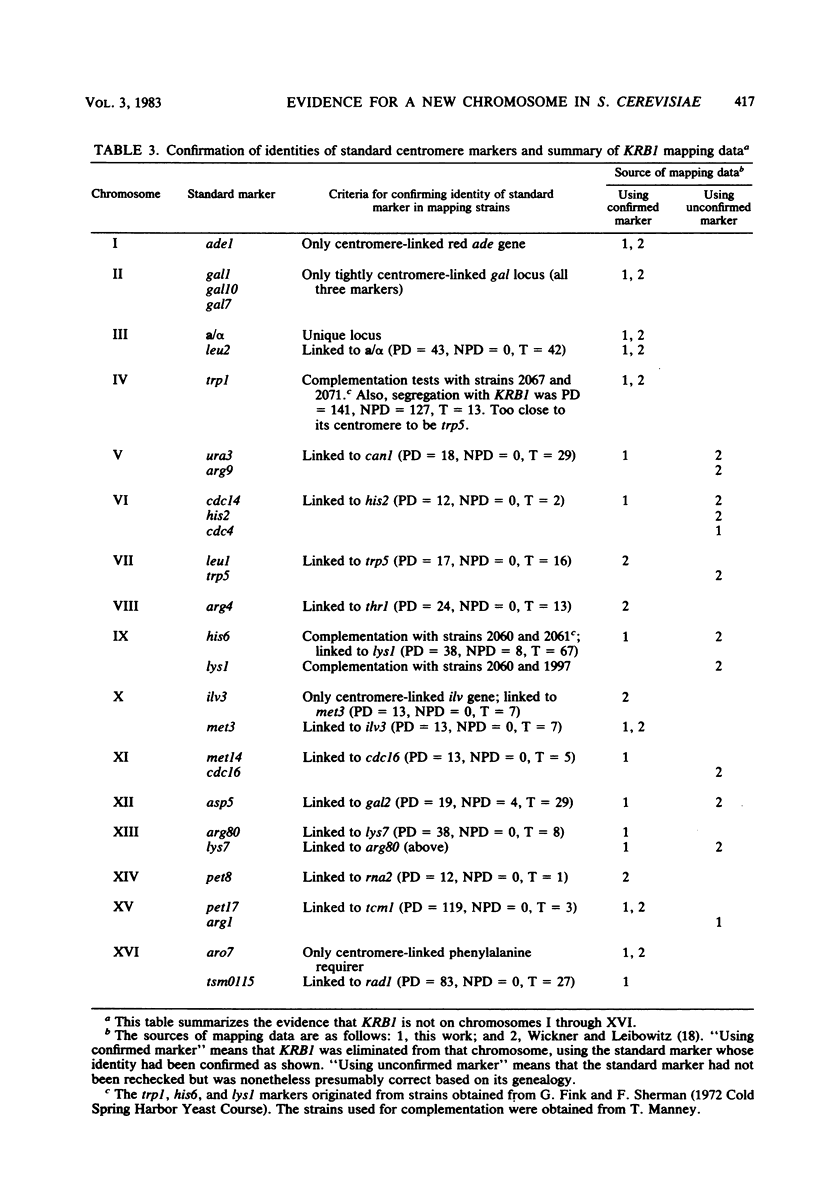
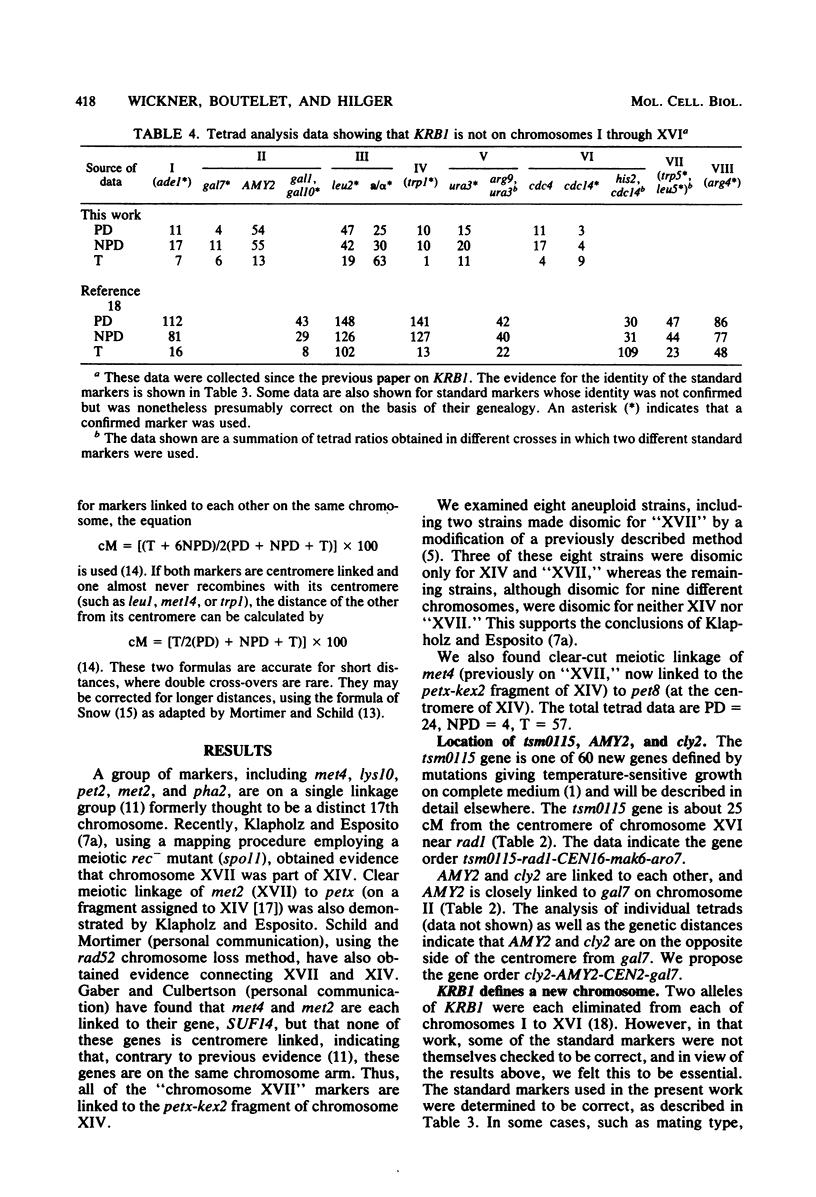
The current yeast map has 16 chromosomes, each originally defined by a centromere-linked gene unlinked to previously defined centromere markers. We examined four genes, cly2, KRB1, AMY2, and tsm0115, each centromere linked, but previously thought to be not on chromosomes I to XVI. We found that AMY2 is linked to cly2, and both are on chromosome II. tsm0115 is on the left arm of chromosome XVI. We confirm the earlier evidence that KRB1 is not on chromosomes I through XVI. This gene thus defines a new chromosome XVII. We also report meiotic linkage of met4 and pet8 (on chromosome XIV), confirming the connection between the petx-kex2 fragment of XIV and the centromere of XIV.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Byers B., Goetsch L. Electron microscopic observations on the meiotic karyotype of diploid and tetraploid Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5056–5060. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HWANG Y. L., LINDEGREN G., LINDEGREN C. C. MAPPING THE ELEVENTH CENTROMERE IN SACCHAROMYCES. Can J Genet Cytol. 1963 Sep;5:290–298. doi: 10.1139/g63-040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HWANG Y. L., LINDEGREN G., LINDEGREN C. C. THE TWELFTH CHROMOSOME OF SACCHAROMYCES. Can J Genet Cytol. 1964 Sep;6:373–380. doi: 10.1139/g64-047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawthorne D C, Mortimer R K. Chromosome Mapping in Saccharomyces: Centromere-Linked Genes. Genetics. 1960 Aug;45(8):1085–1110. doi: 10.1093/genetics/45.8.1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawthorne D. C., Mortimer R. K. Genetic mapping of nonsense suppressors in yeast. Genetics. 1968 Dec;60(4):735–742. doi: 10.1093/genetics/60.4.735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilger F., Mortimer R. K. Genetic mapping of arg1 and arg8 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by trisomic analysis combined with interallelic complementation. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jan;141(1):270–274. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.1.270-274.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klapholz S., Esposito R. E. Chromosomes XIV and XVII of Saccharomyces cerevisiae constitute a single linkage group. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;2(11):1399–1409. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.11.1399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDEGREN C. C., LINDEGREN G., SHULT E., HWANG Y. L. Centromeres, sites of affinity and gene loci on the chromosomes of Saccharomyces. Nature. 1962 Apr 21;194:260–265. doi: 10.1038/194260a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucchini G., Carbone M. L., Cocucci M., Sensi M. L. Nuclear inheritance of resistance to antimycin A in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1979;177(1):139–143. doi: 10.1007/BF00267263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer R. K., Hawthorne D. C. Genetic Mapping in Saccharomyces IV. Mapping of Temperature-Sensitive Genes and Use of Disomic Strains in Localizing Genes. Genetics. 1973 May;74(1):33–54. doi: 10.1093/genetics/74.1.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer R. K., Hawthorne D. C. Genetic mapping in Saccharomyces. Genetics. 1966 Jan;53(1):165–173. doi: 10.1093/genetics/53.1.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer R. K., Hawthorne D. C. Genetic mapping in yeast. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;11:221–233. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60325-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer R. K., Schild D. Genetic map of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1980 Dec;44(4):519–571. doi: 10.1128/mr.44.4.519-571.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins D. D. Biochemical Mutants in the Smut Fungus Ustilago Maydis. Genetics. 1949 Sep;34(5):607–626. doi: 10.1093/genetics/34.5.607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow R. Maximum likelihood estimation of linkage and interference from tetrad data. Genetics. 1979 May;92(1):231–245. doi: 10.1093/genetics/92.1.231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner R. B., Leibowitz M. J. Dominant chromosomal mutation bypassing chromosomal genes needed for killer RNA plasmid replication in yeast. Genetics. 1977 Nov;87(3):453–469. doi: 10.1093/genetics/87.3.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner R. B., Leibowitz M. J. Two chromosomal genes required for killing expression in killer strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1976 Mar 25;82(3):429–442. doi: 10.1093/genetics/82.3.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner R. B. Plasmids controlled exclusion of the K2 killer double-stranded RNA plasmid of yeast. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):217–226. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90129-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


