Abstract
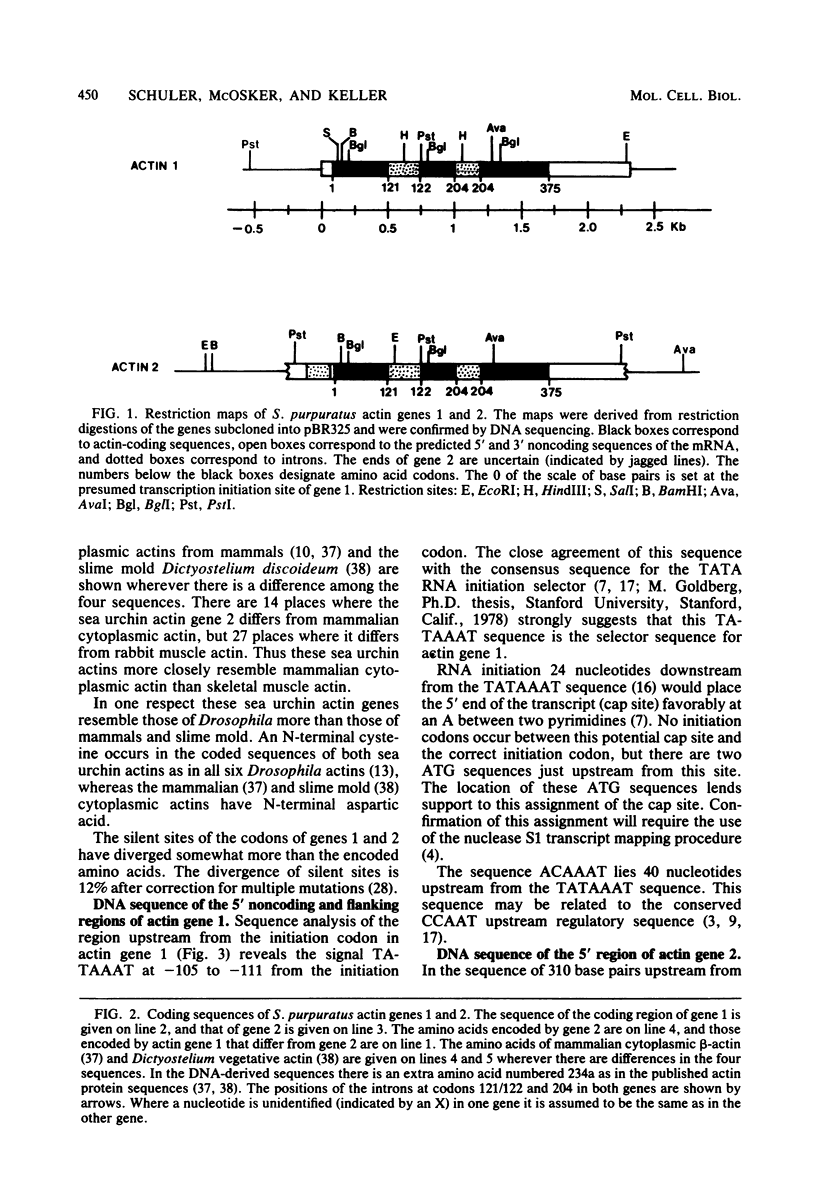
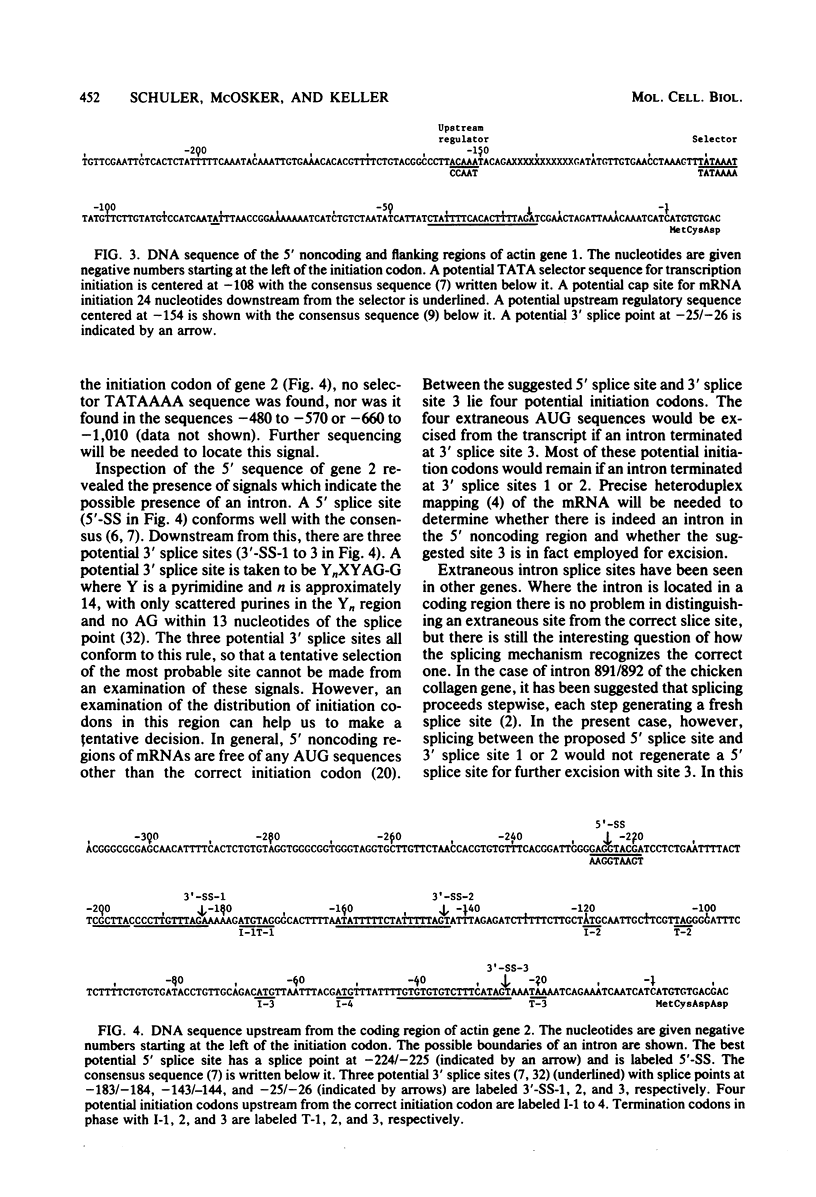
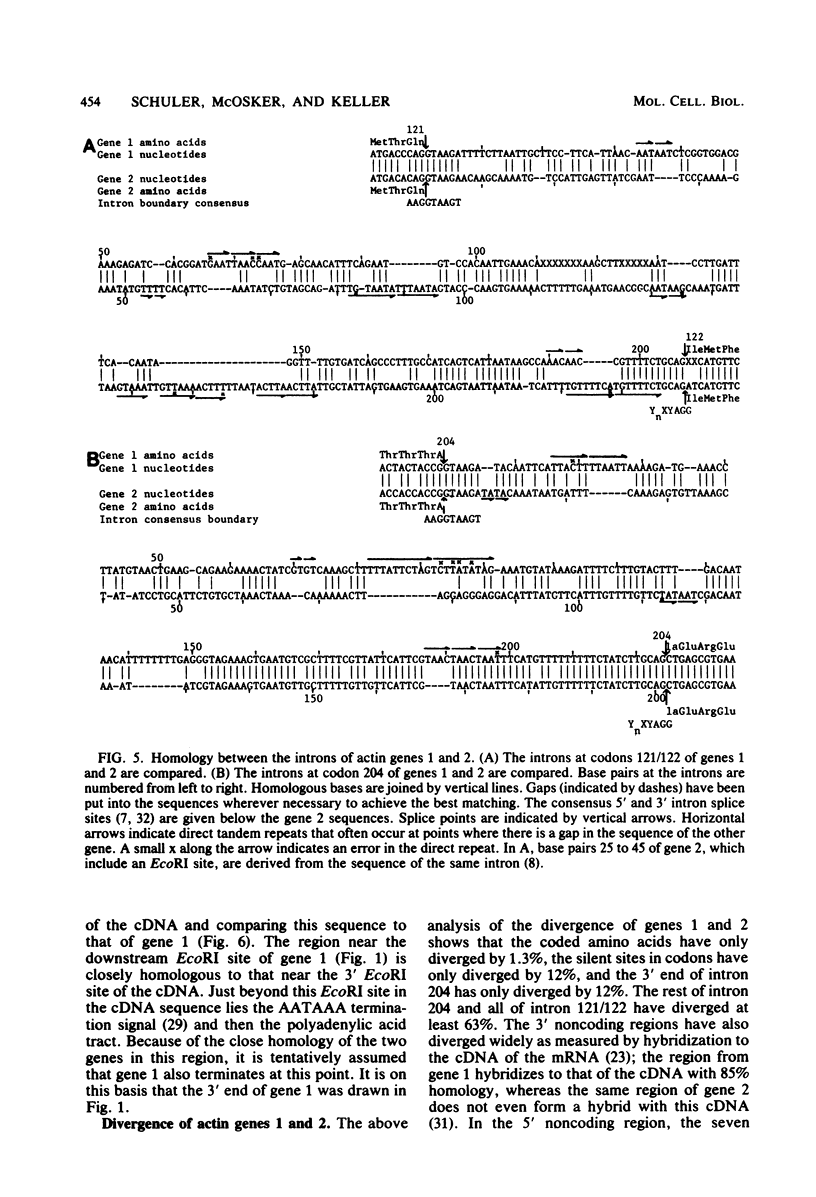
DNA sequences have been determined for two actin genes which are closely linked in the genome of the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus purpuratus. The two genes have the same 5'-3' orientation; they were apparently formed originally by tandem gene duplication. The amino acids encoded by the two genes closely resemble those of cytoplasmic actins of mammals and slime molds and differ somewhat from those of mammalian muscle actin. Actin gene 1 had been tentatively identified earlier as the gene for an embryonic cytoplasmic actin by the homology of the 3' noncoding region with that of the cDNA of an embryonic actin mRNA from S. purpuratus. The DNA sequence of gene 1 shows presumptive signals for the initiation and termination of transcription which would govern the formation of a mature mRNA of 1.9 kilobases. Both actin genes 1 and 2 have introns in their coding regions at codons 121/122 and 204. These positions for actin introns have been reported so far only in the rat, not in lower organisms. The divergence of the sequences of these coding-region introns in the two actin genes is 66%, suggesting that the genes diverged about 90 million years ago. By contrast to the introns, the coding regions have been highly conserved; the amino acids of the two genes differ by only 1.3%, and the silent sites of the codons differ by only 12%.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. M., Scheller R. H., Posakony J. W., McAllister L. B., Trabert S. G., Beall C., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Repetitive sequences of the sea urchin genome. Distribution of members of specific repetitive families. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jan 5;145(1):5–28. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90332-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avvedimento V. E., Vogeli G., Yamada Y., Maizel J. V., Jr, Pastan I., de Crombrugghe B. Correlation between splicing sites within an intron and their sequence complementarity with U1 RNA. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):689–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90432-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., O'Hare K., Breathnach R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene-sequence of putative control regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):127–142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. III. Derivatives of plasmid pBR322 carrying unique Eco RI sites for selection of Eco RI generated recombinant DNA molecules. Gene. 1978 Oct;4(2):121–136. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Benoist C., O'Hare K., Gannon F., Chambon P. Ovalbumin gene: evidence for a leader sequence in mRNA and DNA sequences at the exon-intron boundaries. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4853–4857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durica D. S., Schloss J. A., Crain W. R., Jr Organization of actin gene sequences in the sea urchin: molecular cloning of an intron-containing DNA sequence coding for a cytoplasmic actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5683–5687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Posakony J. W., Maniatis T., Lawn R. M., O'Connell C., Spritz R. A., DeRiel J. K., Forget B. G., Weissman S. M., Slightom J. L. The structure and evolution of the human beta-globin gene family. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):653–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90429-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farabaugh P. J., Schmeissner U., Hofer M., Miller J. H. Genetic studies of the lac repressor. VII. On the molecular nature of spontaneous hotspots in the lacI gene of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):847–857. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90023-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firtel R. A., Timm R., Kimmel A. R., McKeown M. Unusual nucleotide sequences at the 5' end of actin genes in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6206–6210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrberg E. A., Bond B. J., Hershey N. D., Mixter K. S., Davidson N. The actin genes of Drosophila: protein coding regions are highly conserved but intron positions are not. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):107–116. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90506-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Sures I. Structure of a split yeast gene: complete nucleotide sequence of the actin gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2546–2550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W. Why genes in pieces? Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):501–501. doi: 10.1038/271501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y., Sambrook J. F., Frisque R. J. Expression of early genes of origin-defective mutants of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3898–3902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. Identification of regulatory sequences in the prelude sequences of an H2A histone gene by the study of specific deletion mutants in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1432–1436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaine B. P., Spear B. B. Nucleotide sequence of a macronuclear gene for actin in Oxytricha fallax. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):430–432. doi: 10.1038/295430a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. How do eucaryotic ribosomes select initiation regions in messenger RNA? Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1109–1123. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeown M., Firtel R. A. Differential expression and 5' end mapping of actin genes in Dictyostelium. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):799–807. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlino G. T., Water R. D., Chamberlain J. P., Jackson D. A., El-Gewely M. R., Kleinsmith L. J. Cloning of sea urchin actin gene sequences for use in studying the regulation of actin gene transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):765–769. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlino G. T., Water R. D., Moore G. P., Kleinsmith L. J. Change in expression of the actin gene family during early sea urchin development. Dev Biol. 1981 Jul 30;85(2):505–508. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90280-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng R., Abelson J. Isolation and sequence of the gene for actin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3912–3916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka Y., Leder A., Leder P. Unusual alpha-globin-like gene that has cleanly lost both globin intervening sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2806–2809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudel U., Katcoff D., Zakut R., Shani M., Carmon Y., Finer M., Czosnek H., Ginsburg I., Yaffe D. Isolation and characterization of rat skeletal muscle and cytoplasmic actin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2763–2767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perler F., Efstratiadis A., Lomedico P., Gilbert W., Kolodner R., Dodgson J. The evolution of genes: the chicken preproinsulin gene. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):555–566. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90641-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J., Brownlee G. G. 3' non-coding region sequences in eukaryotic messenger RNA. Nature. 1976 Sep 16;263(5574):211–214. doi: 10.1038/263211a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheller R. H., McAllister L. B., Crain W. R., Jr, Durica D. S., Posakony J. W., Thomas T. L., Britten R. J., Davidson E. H. Organization and expression of multiple actin genes in the sea urchin. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;1(7):609–628. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.7.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuler M. A., Keller E. B. The chromosomal arrangement of two linked actin genes in the sea urchin S. purpuratus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 11;9(3):591–604. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.3.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seif I., Khoury G., Dhar R. BKV splice sequences based on analysis of preferred donor and acceptor sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jul 25;6(10):3387–3398. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.10.3387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shah D. M., Hightower R. C., Meagher R. B. Complete nucleotide sequence of a soybean actin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1022–1026. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. R., Calvo J. M. Nucleotide sequence of the E coli gene coding for dihydrofolate reductase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2255–2274. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streisinger G., Okada Y., Emrich J., Newton J., Tsugita A., Terzaghi E., Inouye M. Frameshift mutations and the genetic code. This paper is dedicated to Professor Theodosius Dobzhansky on the occasion of his 66th birthday. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:77–84. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. Actin amino-acid sequences. Comparison of actins from calf thymus, bovine brain, and SV40-transformed mouse 3T3 cells with rabbit skeletal muscle actin. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Oct 16;90(3):451–462. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12624.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. At least six different actins are expressed in a higher mammal: an analysis based on the amino acid sequence of the amino-terminal tryptic peptide. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):783–802. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. Vegetative Dictyostelium cells containing 17 actin genes express a single major actin. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):475–477. doi: 10.1038/284475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



