Abstract
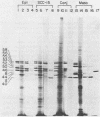
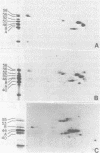
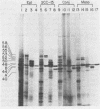
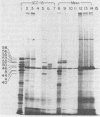
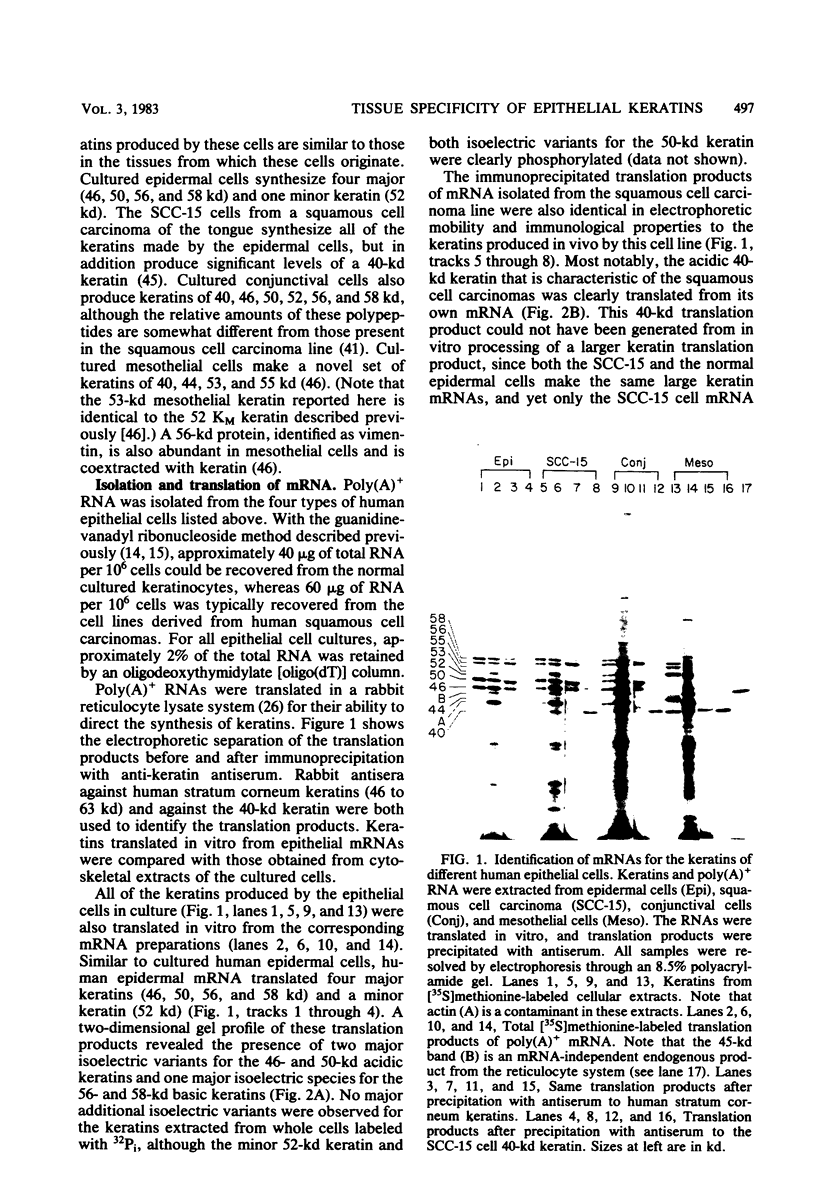
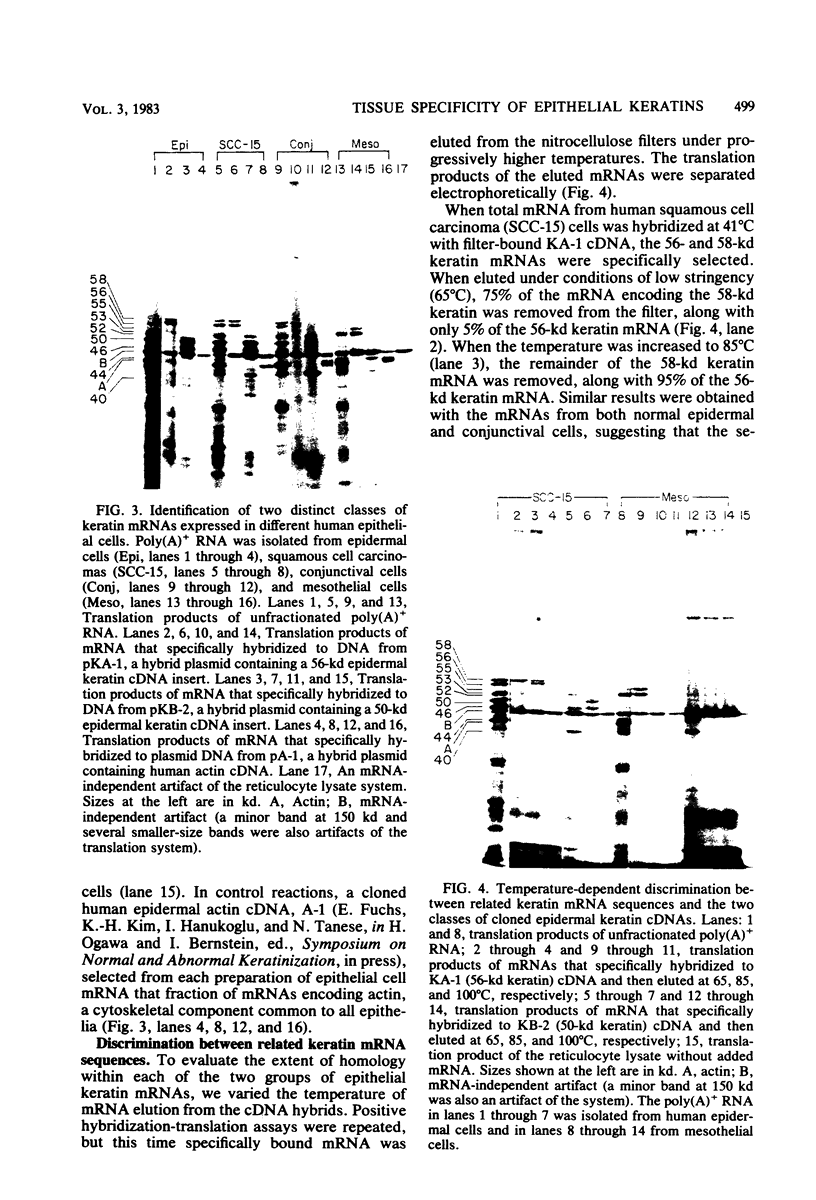
Human epithelial cells cultured from stratified and simple squamous tissues all produce keratins of 40,000 to 58,000 daltons, but within this range the number and sizes vary with different epithelial cells. We have shown that this tissue-specific variation in the keratins is not due to posttranslational modification or processing, but rather to the differential expression of a family of heterogeneous but closely related mRNAs. All of these epithelial keratin mRNAs can be further grouped into two distinct subfamilies by their ability to hybridize with either of two cloned epidermal keratin cDNAs. All of the keratin mRNAs hybridize to one or the other, but not both, of the two cloned cDNAs. However, the mRNAs within each group hybridize with varying degrees of stringency, indicating that they are of similar but not identical sequence. Both types of keratin mRNAs are always expressed in every epithelial cell line studied, suggesting that filament assembly is dependent on the presence of both types of keratins. Within each of these two groups, the slight sequence differences in each class may reflect subtle tissue-specific variations in the structural and functional requirements of the epithelial cytoskeleton.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes D., Sato G. Methods for growth of cultured cells in serum-free medium. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):255–270. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90151-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brysk M. M., Gray R. H., Bernstein I. A. Tonofilament protein from newborn rat epidermis. Isolation, localization, and biosynthesis of marker of epidermal differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):2127–2133. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Lopata M. A., MacDonald R. J., Cowan N. J., Rutter W. J., Kirschner M. W. Number and evolutionary conservation of alpha- and beta-tubulin and cytoplasmic beta- and gamma-actin genes using specific cloned cDNA probes. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90238-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culbertson V. B., Freedberg I. M. Mammalian epidermal keratin: isolation and characterization of the alpha-helical proteins from newborn rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jan 25;490(1):178–191. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90118-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale B. A., Stern I. B., Rabin M., Huang L. The identification of fibrous proteins in fetal rat epidermis by electrophoretic and immunologic techniques. J Invest Dermatol. 1976 Apr;66(4):230–235. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12482148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firtel R. A., Timm R., Kimmel A. R., McKeown M. Unusual nucleotide sequences at the 5' end of actin genes in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6206–6210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Moll R., Winter S., Schmid E., Engelbrecht I., Denk H., Krepler R., Platzer B. Diversity of cytokeratins. Differentiation specific expression of cytokeratin polypeptides in epithelial cells and tissues. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 25;153(4):933–959. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90460-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Weber K., Osborn M. HeLa cells contain intermediate-sized filaments of the prekeratin type. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Jan;118(1):95–109. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90587-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Weber K., Osborn M., Schmid E., Freudenstein C. Antibody to prekeratin. Decoration of tonofilament like arrays in various cells of epithelial character. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Oct 15;116(2):429–445. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90466-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E. V., Coppock S. M., Green H., Cleveland D. W. Two distinct classes of keratin genes and their evolutionary significance. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):75–84. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90362-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Green H. Changes in keratin gene expression during terminal differentiation of the keratinocyte. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):1033–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90094-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Green H. Multiple keratins of cultured human epidermal cells are translated from different mRNA molecules. Cell. 1979 Jul;17(3):573–582. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90265-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Green H. Regulation of terminal differentiation of cultured human keratinocytes by vitamin A. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):617–625. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90169-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs E., Green H. The expression of keratin genes in epidermis and cultured epidermal cells. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):887–897. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90273-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girvitz S. C., Bacchetti S., Rainbow A. J., Graham F. L. A rapid and efficient procedure for the purification of DNA from agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Aug;106(2):492–496. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90553-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanukoglu I., Fuchs E. The cDNA sequence of a human epidermal keratin: divergence of sequence but conservation of structure among intermediate filament proteins. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):243–252. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90424-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. D., Baden H. P. Organisation of the polypeptide chains in mammalian keratin. Nature. 1976 Nov 25;264(5584):377–379. doi: 10.1038/264377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciag T., Nemore R. E., Weinstein R., Gilchrest B. A. An endocrine approach to the control of epidermal growth: serum-free cultivation of human keratinocytes. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1452–1454. doi: 10.1126/science.6970413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstone L. M., McGuire J. Different polypeptides form the intermediate filaments in bovine hoof and esophageal epithelium and in aortic endothelium. J Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;88(2):312–316. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.2.312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Geiger B., Krepler R. The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rheinwald J. G., Beckett M. A. Tumorigenic keratinocyte lines requiring anchorage and fibroblast support cultured from human squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1981 May;41(5):1657–1663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rheinwald J. G., Green H. Epidermal growth factor and the multiplication of cultured human epidermal keratinocytes. Nature. 1977 Feb 3;265(5593):421–424. doi: 10.1038/265421a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rheinwald J. G., Green H. Serial cultivation of strains of human epidermal keratinocytes: the formation of keratinizing colonies from single cells. Cell. 1975 Nov;6(3):331–343. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(75)80001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rheinwald J. G. Serial cultivation of normal human epidermal keratinocytes. Methods Cell Biol. 1980;21A:229–254. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60769-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Miller J. S., Roberts B. E. Purification and mapping of specific mRNAs by hybridization-selection and cell-free translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4927–4931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor and a new derivative. Rapid isolation procedures and biological and chemical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7609–7611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Banks-Schlegel S., Pinkus G. S. Immunohistochemical localization of keratin in normal human tissues. Lab Invest. 1980 Jan;42(1):91–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweizer J., Goerttler K. Synthesis in vitro of keratin polypeptides directed by mRNA isolated from newborn and adult mouse epidermis. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Nov;112(2):243–249. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb07200.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skerrow D., Hunter I. Protein modifications during the keratinization of normal and psoriatic human epidermis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Dec 20;537(2):474–484. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90532-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Idler W. W. The polypeptide composition of bovine epidermal alpha-keratin. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;151(3):603–614. doi: 10.1042/bj1510603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Idler W. W., Zimmerman S. B. Self-assembly of bovine epidermal keratin filaments in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1976 Dec 15;108(3):547–567. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strohman R. C., Moss P. S., Micou-Eastwood J., Spector D., Przybyla A., Paterson B. Messenger RNA for myosin polypeptides: isolation from single myogenic cell cultures. Cell. 1977 Feb;10(2):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90220-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T. T., Green H. Cultured epithelial cells of cornea, conjunctiva and skin: absence of marked intrinsic divergence of their differentiated states. Nature. 1977 Oct 6;269(5628):489–493. doi: 10.1038/269489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T. T., Green H. Differentiation of the epidermal keratinocyte in cell culture: formation of the cornified envelope. Cell. 1976 Dec;9(4 Pt 1):511–521. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T. T., Green H. Keratin filaments of cultured human epidermal cells. Formation of intermolecular disulfide bonds during terminal differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 25;253(6):2053–2060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T. T., Shih C., Green H. Keratin cytoskeletons in epithelial cells of internal organs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2813–2817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseng S. C., Jarvinen M. J., Nelson W. G., Huang J. W., Woodcock-Mitchell J., Sun T. T. Correlation of specific keratins with different types of epithelial differentiation: monoclonal antibody studies. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):361–372. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90234-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde C. D., Crowther C. E., Cripe T. P., Gwo-Shu Lee M., Cowan N. J. Evidence that a human beta-tubulin pseudogene is derived from its corresponding mRNA. Nature. 1982 May 6;297(5861):83–84. doi: 10.1038/297083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Y. J., Parker L. M., Binder N. E., Beckett M. A., Sinard J. H., Griffiths C. T., Rheinwald J. G. The mesothelial keratins: a new family of cytoskeletal proteins identified in cultured mesothelial cells and nonkeratinizing epithelia. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(3 Pt 2):693–703. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90324-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Y. J., Rheinwald J. G. A new small (40 kd) keratin filament protein made by some cultured human squamous cell carcinomas. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):627–635. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90170-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]