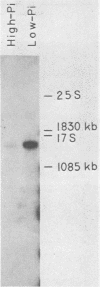
Abstract
Two EcoRI restriction fragments carrying Saccharomyces cerevisiae repressible acid phosphatase genes were analyzed. Transcripts were mapped by restriction endonuclease cleavage of glyoxal-stabilized R-loops and by gel blot hybridizations to cDNA. Homology between the two fragments was examined by gel blots and heteroduplex analysis. Each fragment carried a region of about 1.5 kilobases that coded for a repressible acid phosphatase, and these regions showed homology to one another. In addition, one fragment carried a second region of somewhat lower homology that probably codes for the so-called constitutive acid phosphatase.
Full text
PDF



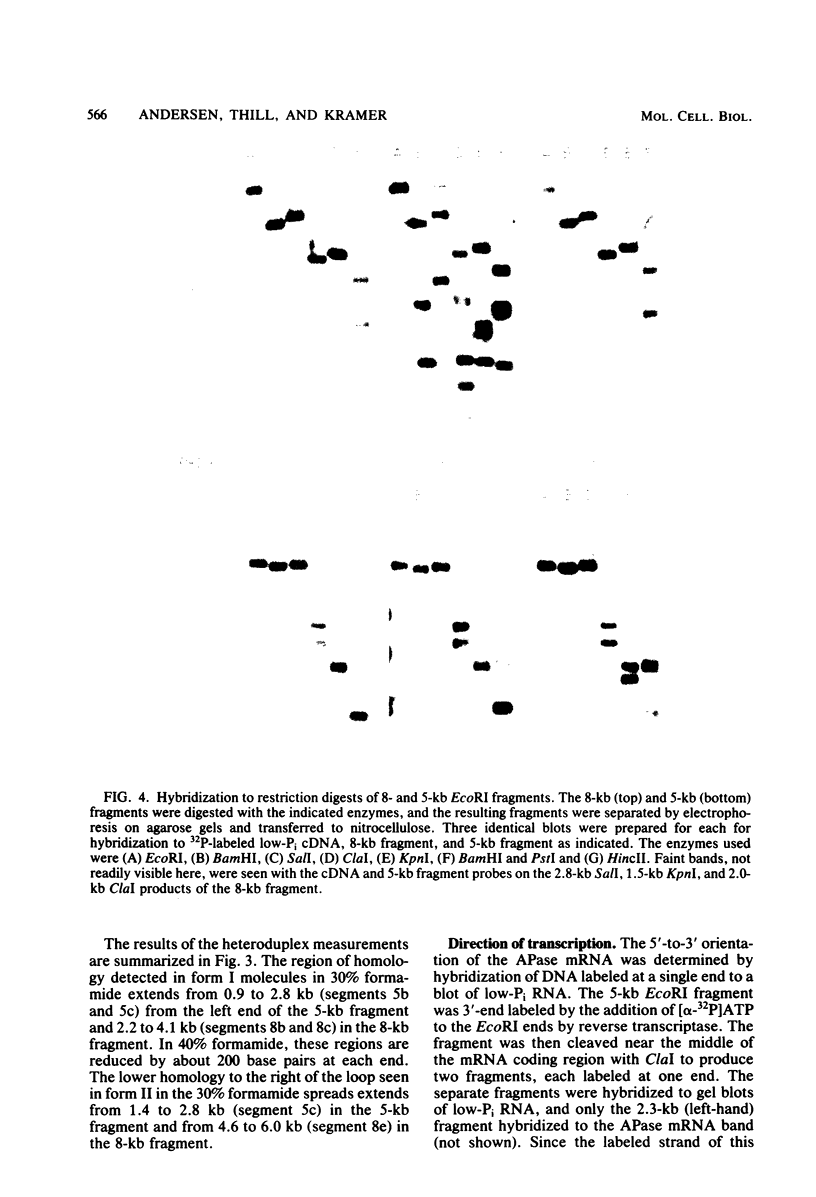
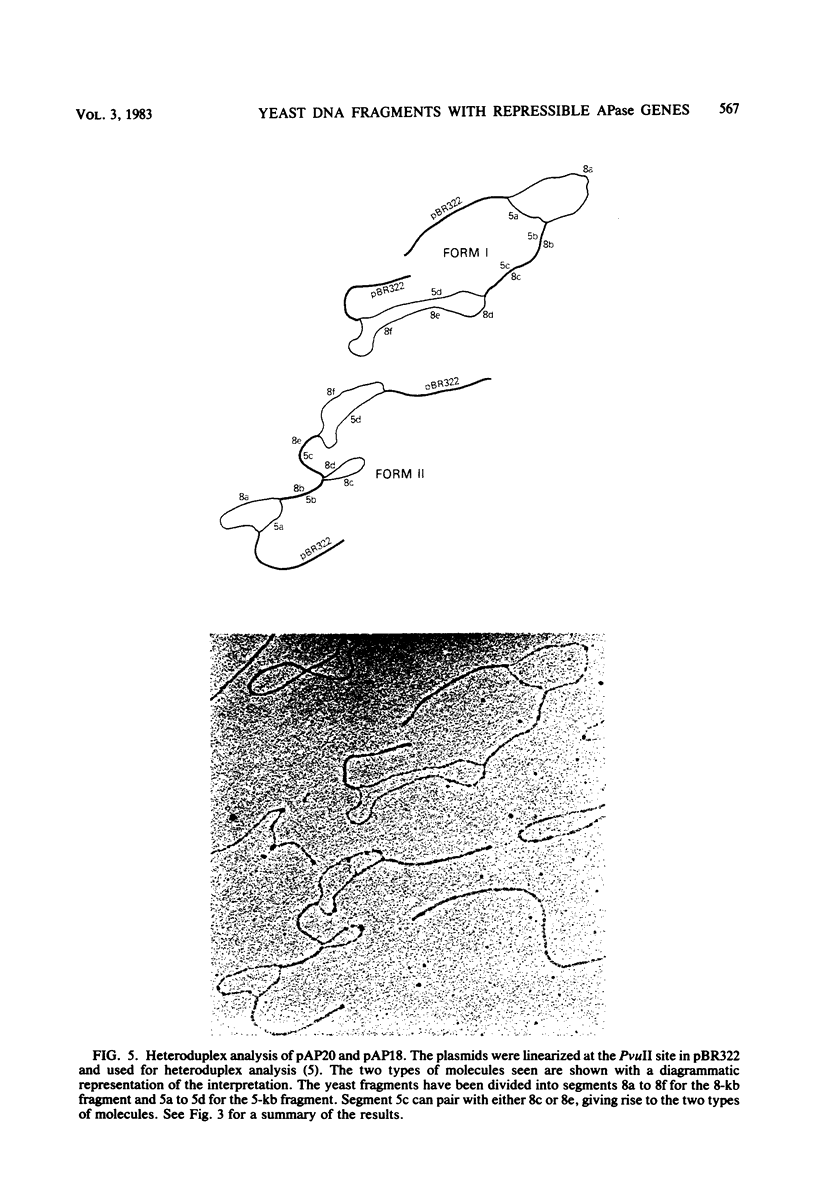


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostian K. A., Hopper J. E., Rogers D. T., Tipper D. J. Translational analysis of the killer-associated virus-like particle dsRNA genome of S. cerevisiae: M dsRNA encodes toxin. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):403–414. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90514-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostian K. A., Lemire J. M., Cannon L. E., Halvorson H. O. In vitro synthesis of repressible yeast acid phosphatase: identification of multiple mRNAs and products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4504–4508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback D. B., Angerer L. M., Davidson N. Improved methods for the formation and stabilization of R-loops. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jun 11;6(7):2499–2317. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.7.2499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer R. A., Andersen N. Isolation of yeast genes with mRNA levels controlled by phosphate concentration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Nov;77(11):6541–6545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.11.6541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonell M. W., Simon M. N., Studier F. W. Analysis of restriction fragments of T7 DNA and determination of molecular weights by electrophoresis in neutral and alkaline gels. J Mol Biol. 1977 Feb 15;110(1):119–146. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80102-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J., Wintersberger E. Adenylic acid-rich sequences in messenger RNA from yeast polysomes. FEBS Lett. 1973 Jun 1;32(2):213–217. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80835-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers D. T., Lemire J. M., Bostian K. A. Acid phosphatase polypeptides in Saccharomyces cerevisiae are encoded by a differentially regulated multigene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2157–2161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurr A., Yagil E. Regulation and characterization of acid and alkaline phosphatase in yeast. J Gen Microbiol. 1971 Mar;65(3):291–303. doi: 10.1099/00221287-65-3-291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thill G. P., Kramer R. A., Turner K. J., Bostian K. A. Comparative analysis of the 5'-end regions of two repressible acid phosphatase genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):570–579. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M., White R. L., Davis R. W. Hybridization of RNA to double-stranded DNA: formation of R-loops. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2294–2298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- To-E A., Ueda Y., Kakimoto S. I., Oshima Y. Isolation and characterization of acid phosphatase mutants in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):727–738. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.727-738.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh-e A., Kakimoto S. Genes coding for the structure of the acid phosphatases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Dec 30;143(1):65–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00269421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh-e A., Kobayashi S., Oshima Y. Disturbance of the machinery for the gene expression by acidic pH in the repressible acid phosphatase system of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1978 Jun 14;162(2):139–149. doi: 10.1007/BF00267870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolford J. L., Jr, Rosbash M. The use of R-looping for structural gene identification and mRNA purification. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Jun 11;6(7):2483–2497. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.7.2483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]