Abstract
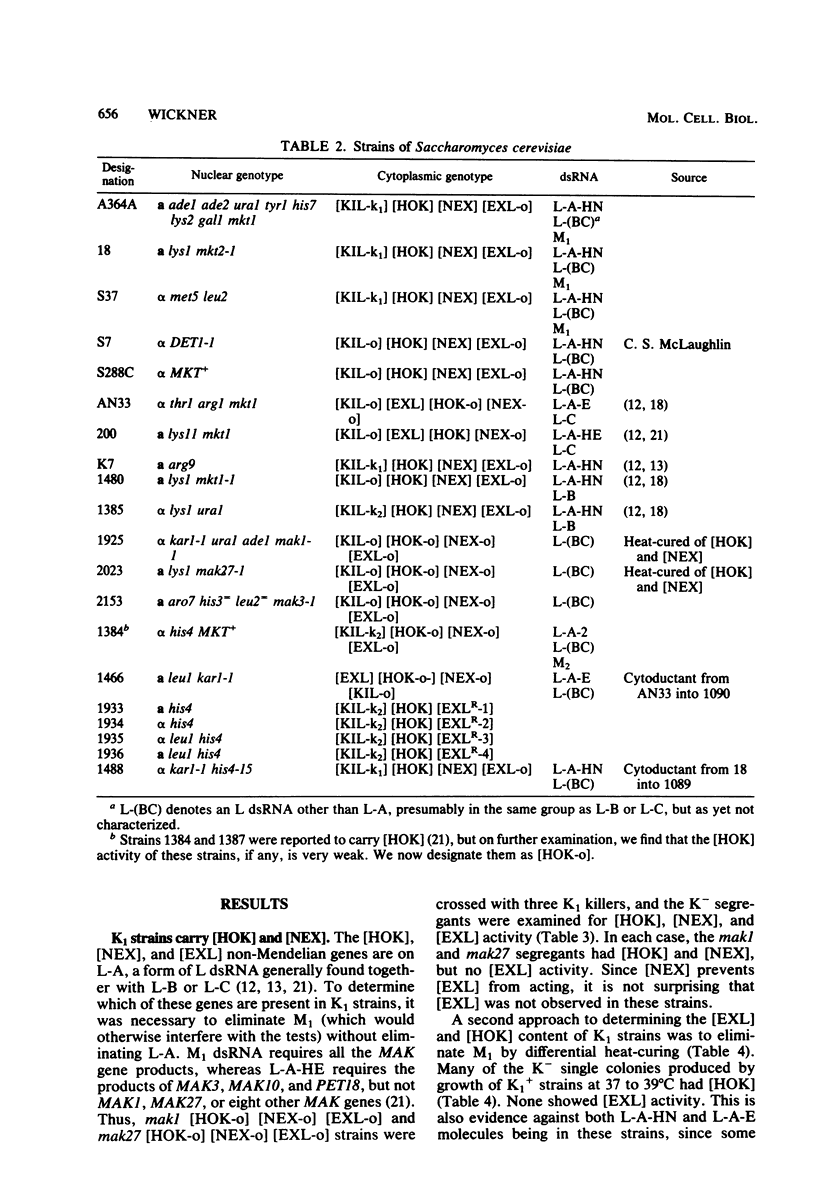
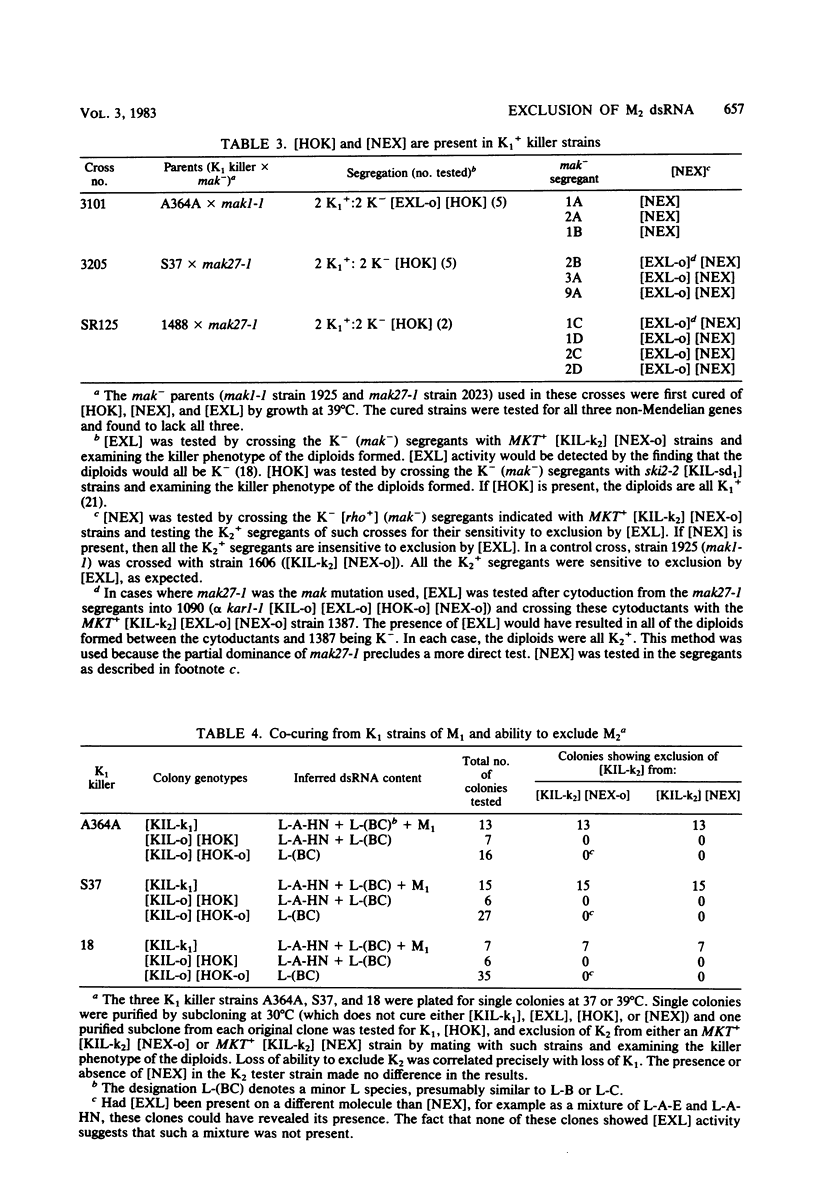
M1 and M2 double-stranded RNAs (dsRNAs) code for the K1R1 and K2R2 killer toxin and resistance functions, respectively. Natural variants of a larger dsRNA (L-A) carry various combinations of the [EXL], [HOK], and [NEX] genes, which affect the K1 and K2 killer systems. Other dsRNAs, the same size as L-A, called L-B and L-C, are often present with L-A. We show that K1 killer strains have [HOK] and [NEX] but not [EXL] on their L-A (in disagreement with Field et al., Cell 31:193-200, 1982). These strains also carry other L-size molecules detectable after heat-curing has eliminated L-A. The exclusion of M2 dsRNA observed on mating K2 strains with K1 strains is due to the M1 dsRNA (not the L-A dsRNA as claimed by Field et al.) in the K1 strains. Four independent mutants of a [KIL-k2] [NEX-o] [HOK-o] strain were selected for resistance to [EXL] exclusion of M2 ([EXLR] phenotype). The [EXLR] phenotype showed non-Mendelian inheritance in each case, and these mutants had simultaneously each acquired [HOK]. The mutations were located on L-A and not on M2, and did not confer resistance to M1 exclusion of M2.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bevan E. A., Herring A. J., Mitchell D. J. Preliminary characterization of two species of dsRNA in yeast and their relationship to the "killer" character. Nature. 1973 Sep 14;245(5420):81–86. doi: 10.1038/245081b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostian K. A., Hopper J. E., Rogers D. T., Tipper D. J. Translational analysis of the killer-associated virus-like particle dsRNA genome of S. cerevisiae: M dsRNA encodes toxin. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):403–414. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90514-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennan V. E., Field L., Cizdziel P., Bruenn J. A. Sequences at the 3' ends of yeast viral dsRNAs: proposed transcriptase and replicase initiation sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 25;9(16):4007–4021. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.16.4007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bussey H. Physiology of killer factor in yeast. Adv Microb Physiol. 1981;22:93–122. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60326-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conde J., Fink G. R. A mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae defective for nuclear fusion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3651–3655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field L. J., Bobek L. A., Brennan V. E., Reilly J. D., Bruenn J. A. There are at least two yeast viral double-stranded RNAs of the same size: an explanation for viral exclusion. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):193–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90419-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried H. M., Fink G. R. Electron microscopic heteroduplex analysis of "killer" double-stranded RNA species from yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4224–4228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper J. E., Bostian K. A., Rowe L. B., Tipper D. J. Translation of the L-species dsRNA genome of the killer-associated virus-like particles of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 25;252(24):9010–9017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. J., Herring A. J., Bevan E. A. The genetic control of DS-RNA virus-like particles associated with Saccharomyces cerevisiae killer yeast. Heredity (Edinb) 1976 Aug;37(1):129–134. doi: 10.1038/hdy.1976.71. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumova G. I., Naumova T. I. Sravitel'naia genetika drozhzhei. Soobshchenie XIII. Sravitel'noe izuchenie sakharomitsetov-ubiits iz razlichnykh kollektsii. Genetika. 1973 Nov;9(11):140–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palfree R. G., Bussey H. Yeast killer toxin: purification and characterisation of the protein toxin from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Feb 1;93(3):487–493. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer S. S., Wickner R. B. Co-curing of plasmids affecting killer double-stranded RNAs of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: [HOK], [NEX], and the abundance of L are related and further evidence that M1 requires L. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):545–551. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.545-551.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer S. S., Wickner R. B. Yeast L dsRNA consists of at least three distinct RNAs; evidence that the non-Mendelian genes [HOK], [NEX] and [EXL] are on one of these dsRNAs. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):429–441. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toh-E A., Wickner R. B. A mutant killer plasmid whose replication depends on a chromosomal "superkiller" mutation. Genetics. 1979 Apr;91(4):673–682. doi: 10.1093/genetics/91.4.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vodkin M., Katterman F., Fink G. R. Yeast killer mutants with altered double-stranded ribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):681–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.681-686.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh J. D., Leibowitz M. J. Localization of genes for the double-stranded RNA killer virus of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):786–789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner R. B. "Killer character" of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: curing by growth at elevated temperature. J Bacteriol. 1974 Mar;117(3):1356–1357. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.3.1356-1357.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner R. B., Leibowitz M. J. Chromosomal genes essential for replication of a double-stranded RNA plasmid of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: the killer character of yeast. J Mol Biol. 1976 Aug 15;105(3):427–443. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90102-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner R. B. Plasmids controlled exclusion of the K2 killer double-stranded RNA plasmid of yeast. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):217–226. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90129-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner R. B., Toh-e A. [HOK], a new yeast non-Mendelian trait, enables a replication-defective killer plasmid to be maintained. Genetics. 1982 Feb;100(2):159–174. doi: 10.1093/genetics/100.2.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




