Abstract
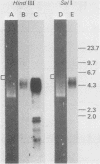
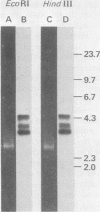
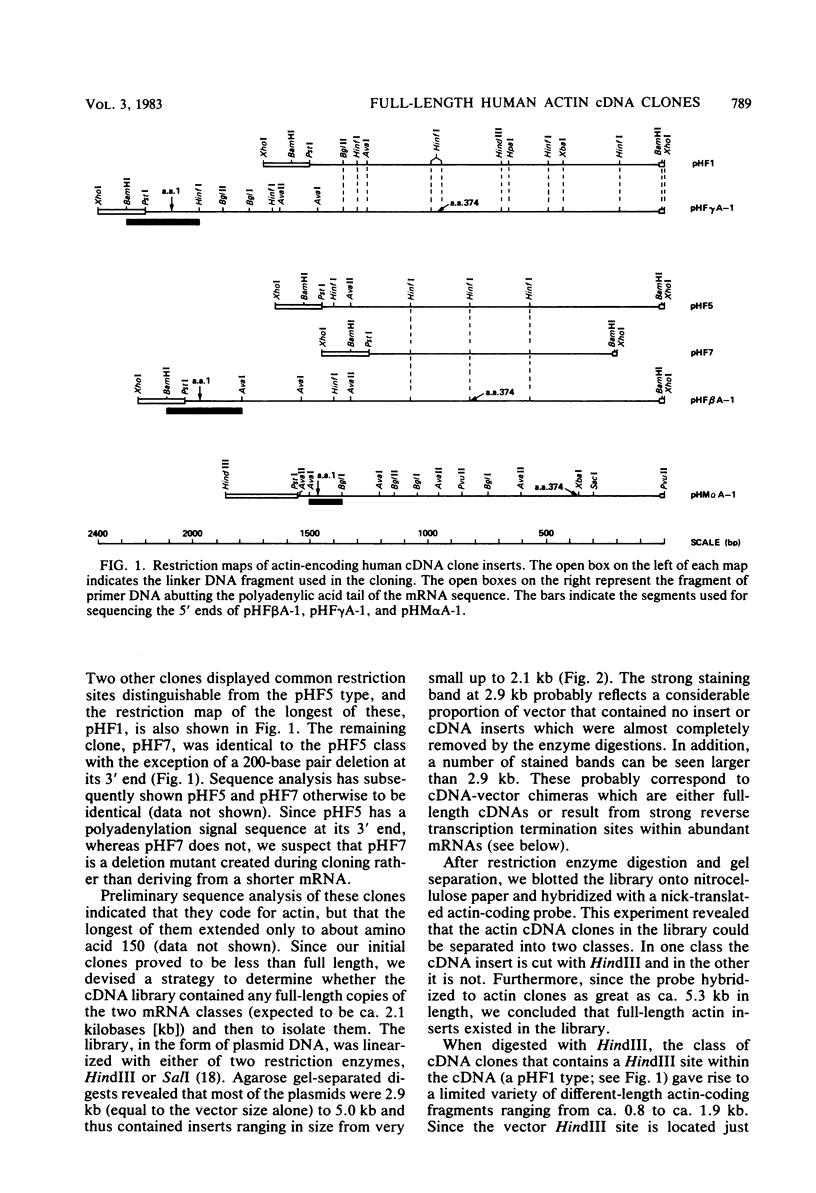
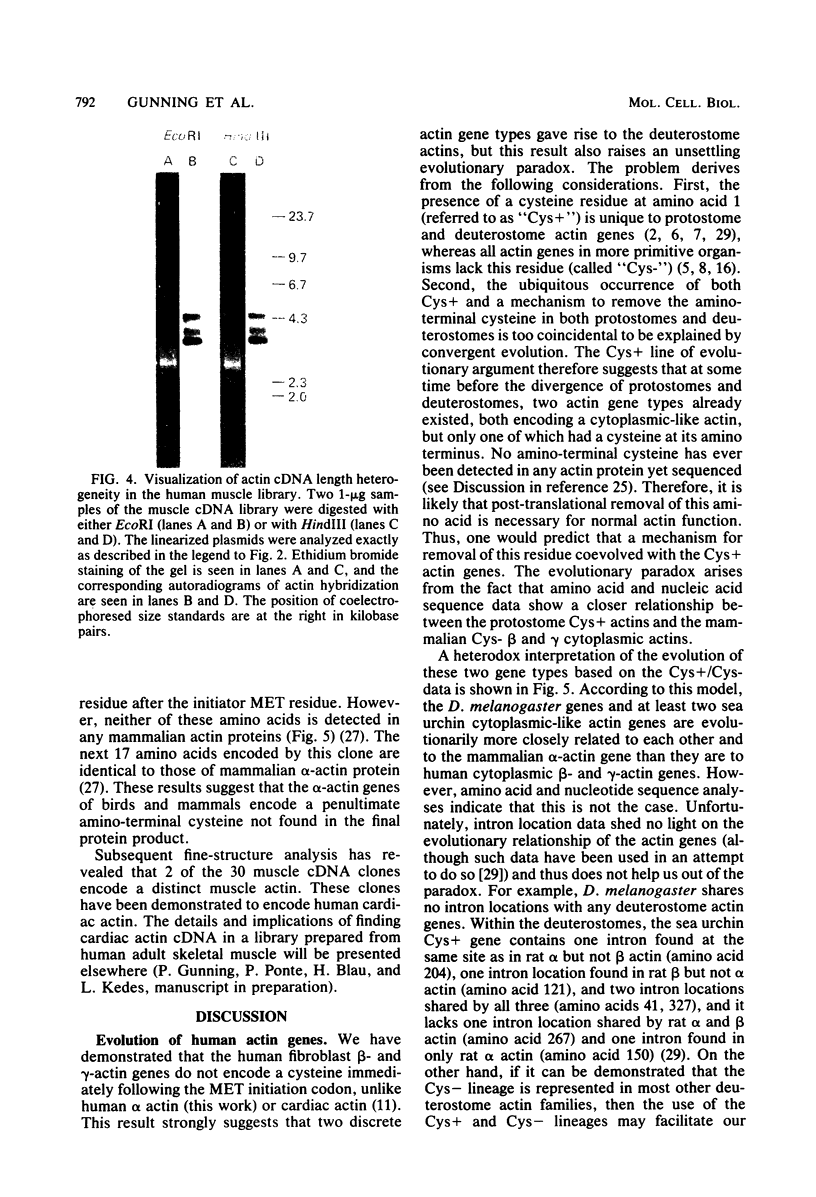
cDNA clones encoding three classes of human actins have been isolated and characterized. The first two classes (gamma and beta, cytoplasmic actins) were obtained from a cDNA library constructed from simian virus 40-transformed human fibroblast mRNA, and the third class (alpha, muscle actin) was obtained from a cDNA library constructed from adult human muscle mRNA. A new approach was developed to enrich for full-length cDNAs. The human fibroblast cDNA plasmid library was linearized with restriction enzymes that did not cut the inserts of interest; it was then size-fractionated on gels, and the chimeric molecules of optimal length were selected for retransformation of bacteria. When the resulting clones were screened for actin-coding sequences it was found that some full-length cDNAs were enriched as much as 50- to 100-fold relative to the original frequency of full-length clones in the total library. Two types of clones were distinguished. One of these clones encodes gamma actin and contains 100 base pairs of 5' untranslated region, the entire protein coding region, and the 3' untranslated region. The second class encodes beta actin, and the longest such clone contains 45 base pairs of 5' untranslated region plus the remainder of the mRNA extending to the polyadenylic acid tail. A third class, obtained from the human muscle cDNA library, encodes alpha actin and contains 100 base pairs of 5' untranslated region, the entire coding region, and the 3' untranslated region. Analysis of the DNA sequences of the 5' end of the clones demonstrated that although beta- and gamma-actin genes start with a methionine codon (MET-Asp-Asp-Asp and MET-Glu-Glu-Glu, respectively), the alpha-actin gene starts with a methionine codon followed by a cysteine codon (MET-CYS-Asp-Glu-Asp-Glu). Since no known actin proteins start with a cysteine, it is likely that post-translational removal of cysteine in addition to methionine accompanies alpha-actin synthesis but not beta- and gamma-actin synthesis. This observation has interesting implications both for actin function and actin gene regulation and evolution.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper A. D., Crain W. R., Jr Complete nucleotide sequence of a sea urchin actin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 10;10(13):4081–4092. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.13.4081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J. N., Gunning P. W., Kedes L. Isolation and characterization of human actin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):4674–4678. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.4674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J., Gunning P., Kedes L. Human cytoplasmic actin proteins are encoded by a multigene family. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;2(6):674–684. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.6.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Firtel R. A., Timm R., Kimmel A. R., McKeown M. Unusual nucleotide sequences at the 5' end of actin genes in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6206–6210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornwald J. A., Kuncio G., Peng I., Ordahl C. P. The complete nucleotide sequence of the chick a-actin gene and its evolutionary relationship to the actin gene family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jul 10;10(13):3861–3876. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.13.3861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrberg E. A., Bond B. J., Hershey N. D., Mixter K. S., Davidson N. The actin genes of Drosophila: protein coding regions are highly conserved but intron positions are not. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):107–116. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90506-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Sures I. Structure of a split yeast gene: complete nucleotide sequence of the actin gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2546–2550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada H., Petrino M. G., Kakunaga T. Molecular structure and evolutionary origin of human cardiac muscle actin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5901–5905. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Possible role of flanking nucleotides in recognition of the AUG initiator codon by eukaryotic ribosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5233–5252. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A. J., Alonso S., Caravatti M., Buckingham M. E. A fetal skeletal muscle actin mRNA in the mouse and its identity with cardiac actin mRNA. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng R., Abelson J. Isolation and sequence of the gene for actin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3912–3916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):161–170. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Magnesium precipitation of ribonucleoprotein complexes. Expedient techniques for the isolation of undergraded polysomes and messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 13;13(17):3606–3615. doi: 10.1021/bi00714a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pollard T. D., Weihing R. R. Actin and myosin and cell movement. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1974 Jan;2(1):1–65. doi: 10.3109/10409237409105443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shani M., Zevin-Sonkin D., Saxel O., Carmon Y., Katcoff D., Nudel U., Yaffe D. The correlation between the synthesis of skeletal muscle actin, myosin heavy chain, and myosin light chain and the accumulation of corresponding mRNA sequences during myogenesis. Dev Biol. 1981 Sep;86(2):483–492. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90206-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith H. O., Birnstiel M. L. A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Sep;3(9):2387–2398. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.9.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutoh K. Identification of myosin-binding sites on the actin sequence. Biochemistry. 1982 Jul 20;21(15):3654–3661. doi: 10.1021/bi00258a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Franke W. W., Weber K. Diversity of expression of non-muscle actin in amphibia. J Mol Biol. 1981 Oct 25;152(2):413–426. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90251-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. At least six different actins are expressed in a higher mammal: an analysis based on the amino acid sequence of the amino-terminal tryptic peptide. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):783–802. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. The complete amino acid sequence of actins from bovine aorta, bovine heart, bovine fast skeletal muscle, and rabbit slow skeletal muscle. A protein-chemical analysis of muscle actin differentiation. Differentiation. 1979;14(3):123–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1979.tb01021.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. Vegetative Dictyostelium cells containing 17 actin genes express a single major actin. Nature. 1980 Apr 3;284(5755):475–477. doi: 10.1038/284475a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakut R., Shani M., Givol D., Neuman S., Yaffe D., Nudel U. Nucleotide sequence of the rat skeletal muscle actin gene. Nature. 1982 Aug 26;298(5877):857–859. doi: 10.1038/298857a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]