Abstract
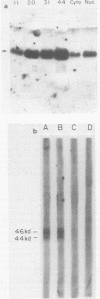
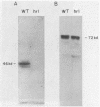
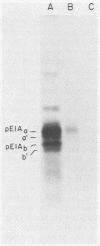
The function of the adenovirus E1Aa protein (the product of the 13S E1A mRNA) during a productive viral infection is to activate transcription of the six early viral transcription units. To study the mechanism of action of this protein, a peptide which was 13 amino acids long and had a sequence unique to the protein product of the adenovirus 13S E1A mRNA (pE1Aa) was coupled to keyhole limpet hemocyanin and used to raise an antibody in rabbits. The resulting antiserum was specific to this protein and did not react with the protein product of the 12S E1A mRNA, which shares considerable sequence with the E1Aa protein. This antiserum was used to probe for the E1Aa protein in situ by indirect immunofluorescence and in extracts of infected HeLa cells. We found that the protein was associated with large cellular structures both in the nucleus and in the cytoplasm. The nuclear form of the protein was analyzed further and was found to purify with the nuclear matrix.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiello L., Guilfoyle R., Huebner K., Weinmann R. Adenovirus 5 DNA sequences present and RNA sequences transcribed in transformed human embryo kidney cells (HEK-Ad-5 or 293). Virology. 1979 Apr 30;94(2):460–469. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90476-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babich A., Nevins J. R. The stability of early adenovirus mRNA is controlled by the viral 72 kd DNA-binding protein. Cell. 1981 Nov;26(3 Pt 1):371–379. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90206-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Lee F., Harrison T., Williams J., Sharp P. A. Pre-early adenovirus 5 gene product regulates synthesis of early viral messenger RNAs. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):935–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Structure of the adenovirus 2 early mRNAs. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):695–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90252-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Erikson E., Erikson R. L. The specific interaction of the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein, pp60src, with two cellular proteins. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):363–372. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C., Simmons D. T., Martin M. A., Mora P. T. Identification and partial characterization of new antigens from simian virus 40-transformed mouse cells. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):463–471. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.463-471.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow L. T., Broker T. R., Lewis J. B. Complex splicing patterns of RNAs from the early regions of adenovirus-2. J Mol Biol. 1979 Oct 25;134(2):265–303. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R., Brazell I. A. Mapping sequences in loops of nuclear DNA by their progressive detachment from the nuclear cage. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jul 11;8(13):2895–2906. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.13.2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esche H., Mathews M. B., Lewis J. B. Proteins and messenger RNAs of the transforming region of wild-type and mutant adenoviruses. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 25;142(3):399–417. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90279-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman L. T., Imperiale M. J., Nevins J. R. Activation of early adenovirus transcription by the herpesvirus immediate early gene: evidence for a common cellular control factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4952–4956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher P. A., Berrios M., Blobel G. Isolation and characterization of a proteinaceous subnuclear fraction composed of nuclear matrix, peripheral lamina, and nuclear pore complexes from embryos of Drosophila melanogaster. J Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;92(3):674–686. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.3.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert D. N., Raskas H. J. Tryptic and chymotryptic methionine peptide analysis of the in vitro translation products specified by the transforming region of adenovirus type 2. Virology. 1982 Jan 30;116(2):406–418. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90135-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halbert D. N., Spector D. J., Raskas H. J. In vitro translation products specified by the transforming region of adenovirus type 2. J Virol. 1979 Sep;31(3):621–629. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.3.621-629.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison T., Graham F., Williams J. Host-range mutants of adenovirus type 5 defective for growth in HeLa cells. Virology. 1977 Mar;77(1):319–329. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90428-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harter M. L., Lewis J. B. Adenovirus type 2 early proteins synthesized in vitro and in vivo: identification in infected cells of the 38,000- to 50,000- molecular-weight protein encoded by the left end of the adenovirus type 2 genome. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):736–749. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.736-749.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. An adenovirus type 5 early gene function regulates expression of other early viral genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3665–3669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., Persson H., Philipson L. Control of adenovirus early gene expression: posttranscriptional control mediated by both viral and cellular gene products. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;1(9):807–813. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.9.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitchingman G. R., Westphal H. The structure of adenovirus 2 early nuclear and cytoplasmic RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1980 Feb 15;137(1):23–48. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90155-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kress M., May E., Cassingena R., May P. Simian virus 40-transformed cells express new species of proteins precipitable by anti-simian virus 40 tumor serum. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):472–483. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.472-483.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Crawford L. V. T antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):261–263. doi: 10.1038/278261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Levine A. J. Characterization of a 54K dalton cellular SV40 tumor antigen present in SV40-transformed cells and uninfected embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F. T., Zinnecker M., Hamaoka T., Katz D. H. New procedures for preparation and isolation of conjugates of proteins and a synthetic copolymer of D-amino acids and immunochemical characterization of such conjugates. Biochemistry. 1979 Feb 20;18(4):690–693. doi: 10.1021/bi00571a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupker J. H., Davis A., Jochemsen H., van der Eb A. J. In vitro synthesis of adenovirus type 5 T antigens. I. Translation of early region 1-specific rna from lytically infected cells. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):524–529. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.524-529.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrogan M., Spector D. J., Goldenberg C. J., Halbert D., Raskas H. J. Purification of specific adenovirus 2 RNAs by preparative hybridization and selective thermal elution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Feb;6(2):593–607. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.2.583. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Fisher E. F., Caruthers M. H., Berk A. J. Resolving the functions of overlapping viral genes by site-specific mutagenesis at a mRNA splice site. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):380–384. doi: 10.1038/295380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelkin B. D., Pardoll D. M., Vogelstein B. Localization of SV40 genes within supercoiled loop domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5623–5633. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Adenovirus gene expression: control at multiple steps of mRNA biogenesis. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):1–2. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90366-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Definition and mapping of adenovirus 2 nuclear transcription. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):768–785. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Ginsberg H. S., Blanchard J. M., Wilson M. C., Darnell J. E., Jr Regulation of the primary expression of the early adenovirus transcription units. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):727–733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.727-733.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Mechanism of activation of early viral transcription by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90304-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Winkler J. J. Regulation of early adenovirus transcription: a protein product of early region 2 specifically represses region 4 transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1893–1897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perricaudet M., Akusjärvi G., Virtanen A., Pettersson U. Structure of two spliced mRNAs from the transforming region of human subgroup C adenoviruses. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):694–696. doi: 10.1038/281694a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Philipson L. Regulation of adenovirus gene expression. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;97:157–203. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68318-3_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Jones R. L., Cepko C. L., Sharp P. A., Roberts B. E. Expression of early adenovirus genes requires a viral encoded acidic polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6121–6125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson S. I., Nelkin B. D., Vogelstein B. The ovalbumin gene is associated with the nuclear matrix of chicken oviduct cells. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):99–106. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90379-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross S. R., Levine A. J., Galos R. S., Williams J., Shenk T. Early viral proteins in HeLa cells infected with adenovirus type 5 host range mutants. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):475–492. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90205-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenk T., Jones N., Colby W., Fowlkes D. Functional analysis of adenovirus-5 host-range deletion mutants defective for transformation of rat embryo cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):367–375. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart J. E., Lewis J. B., Mathews M. B., Harter M. L., Anderson C. W. Adenovirus type 2 early proteins: assignment of the early region 1A proteins synthesized in vivo and in vitro to specific mRNAs. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):703–713. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90315-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. E., Smith R., Paucha E. Characterization of different tumor antigens present in cells transformed by simian virus 40. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):335–346. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. J., McGrogan M., Raskas H. J. Regulation of the appearance of cytoplasmic RNAs from region 1 of the adenovirus 2 genome. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 15;126(3):395–414. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90048-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutcliffe J. G., Shinnick T. M., Green N., Liu F. T., Niman H. L., Lerner R. A. Chemical synthesis of a polypeptide predicted from nucleotide sequence allows detection of a new retroviral gene product. Nature. 1980 Oct 30;287(5785):801–805. doi: 10.1038/287801a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ormondt H., Maat J., De Waard A., Van der Eb A. J. The nucleotide sequence of the transforming HpaI-E fragment of adenovirus type 5 DNA. Gene. 1978 Dec;4(4):309–328. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90048-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall R., Philipson L., Darnell J. E. Processing of adenovirus specific nuclear RNA during virus replication. Virology. 1972 Oct;50(1):27–34. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90342-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Younghusband H. B., Maundrell K. Adenovirus DNA is associated with the nuclear matrix of infected cells. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):705–713. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.705-713.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeevi M., Nevins J. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Newly formed mRNA lacking polyadenylic acid enters the cytoplasm and the polyribosomes but has a shorter half-life in the absence of polyadenylic acid. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 May;2(5):517–525. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.5.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziff E. B. Transcription and RNA processing by the DNA tumour viruses. Nature. 1980 Oct 9;287(5782):491–499. doi: 10.1038/287491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]