Abstract
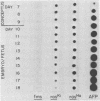
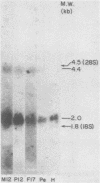
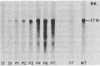
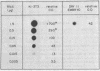
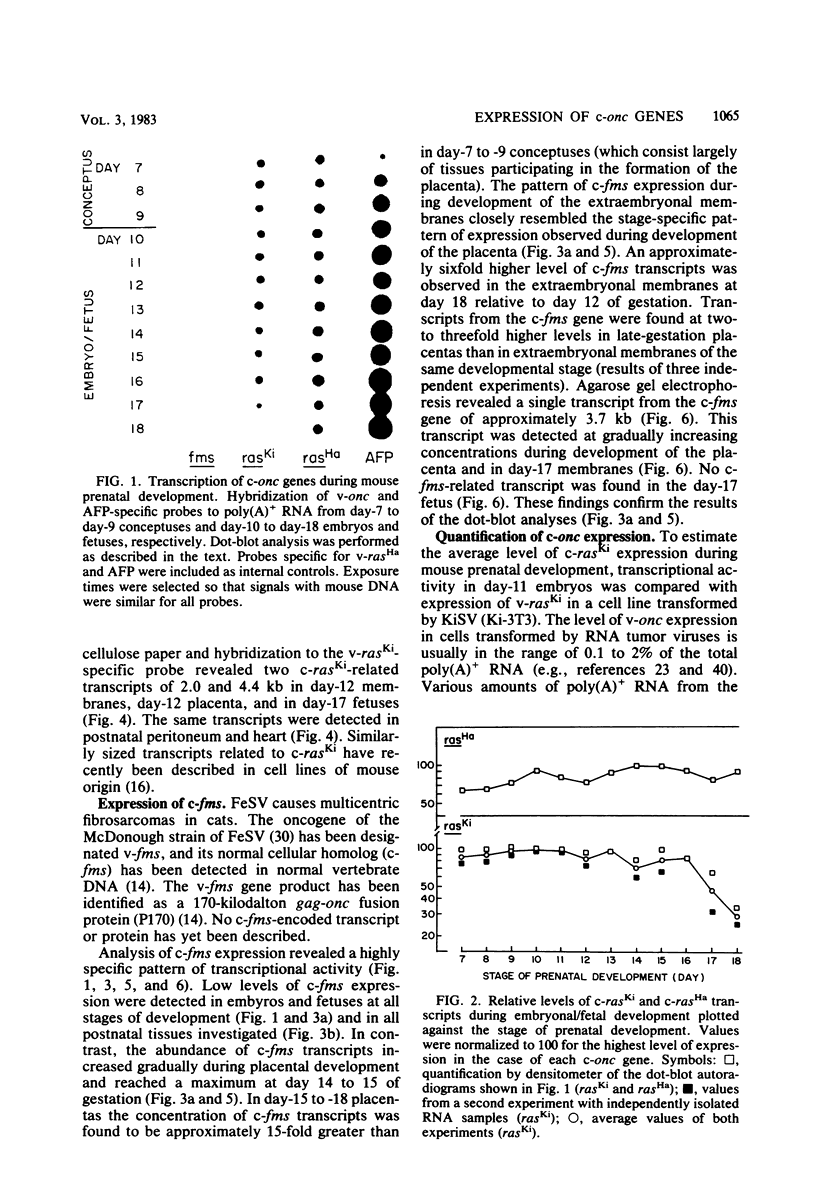
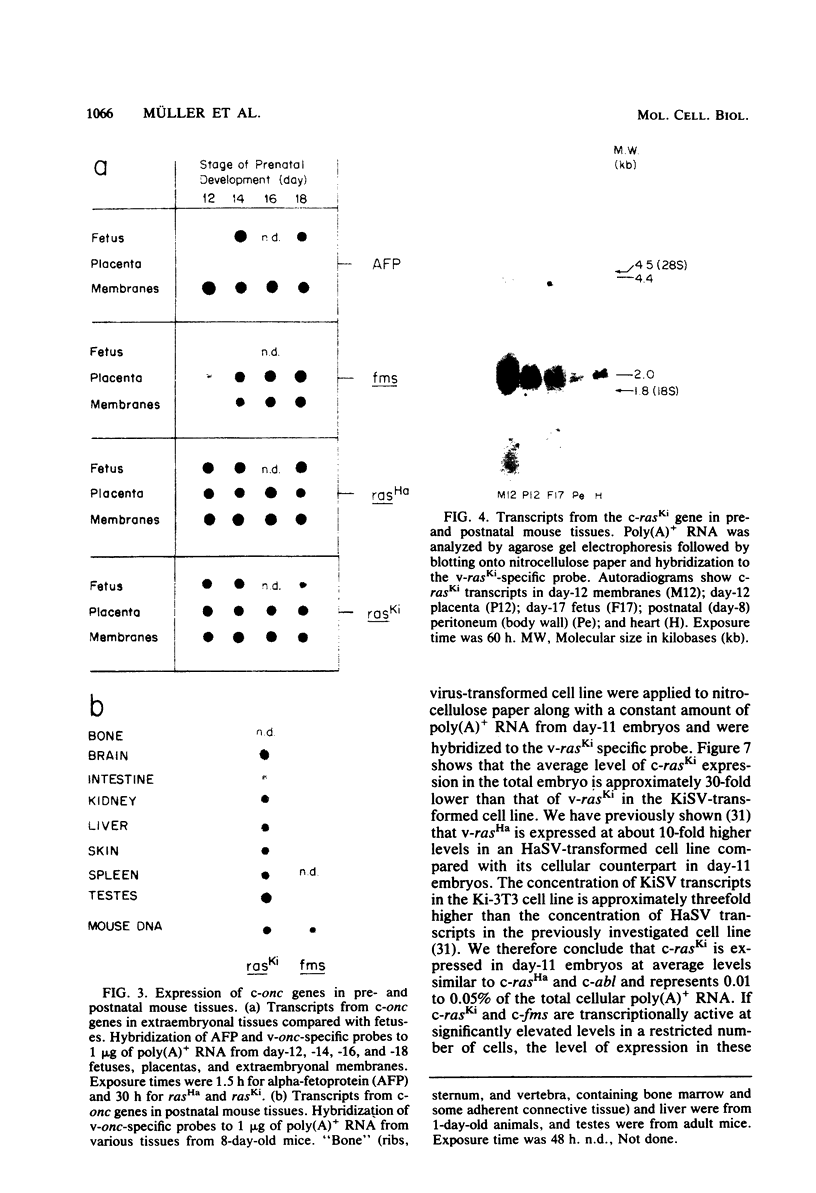
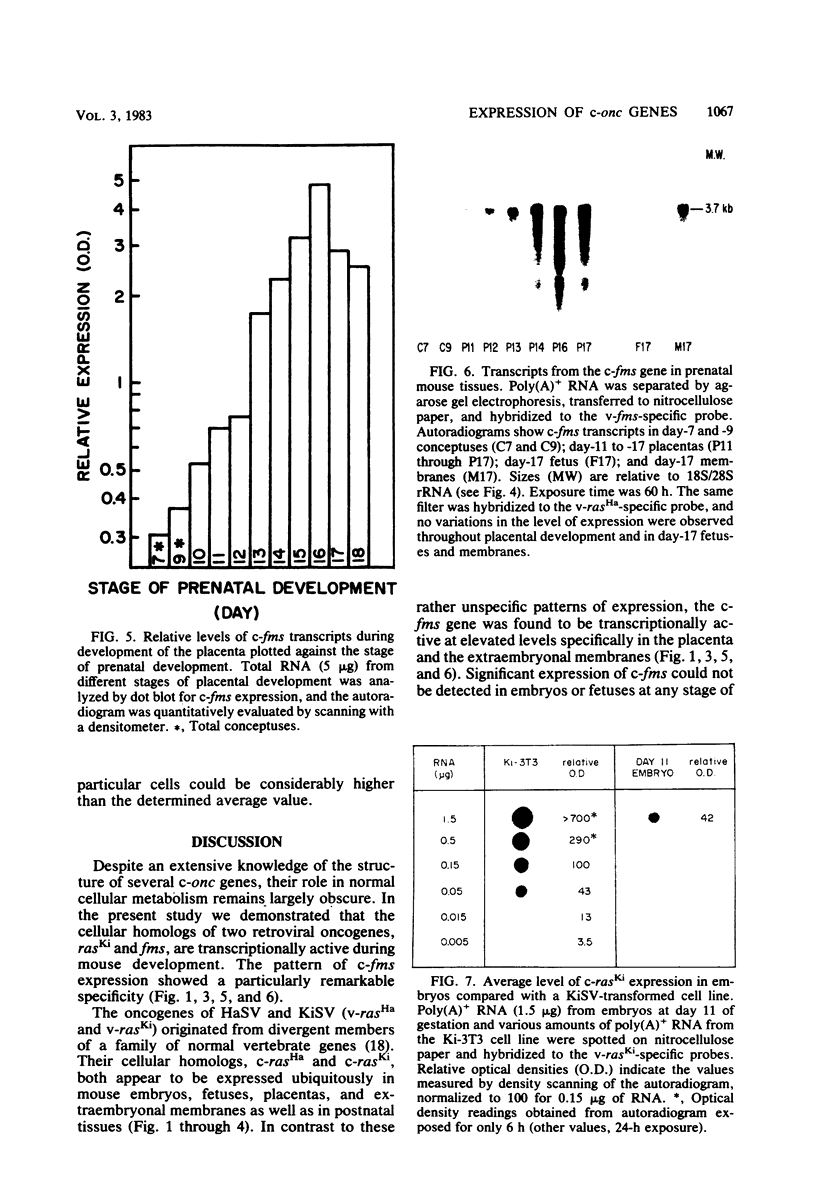
We investigated the expression of cellular sequences c-rasKi and c-fms, which are homologous to the oncogenes of Kirsten rat sarcoma virus and the McDonough strain of feline sarcoma virus, during murine development and in a variety of mouse tissues. The c-rasKi gene was found to be transcribed into two mRNA species of approximately 2.0 and 4.4 kilobases, whereas a single c-fms-related transcript of approximately 3.7 kilobases was identified. The c-rasKi gene appeared to be expressed ubiquitously, since similar levels of transcripts were observed in embryos, fetuses, extraembryonal structures, and a variety of postnatal tissues. In contrast, significant expression of c-fms was found to be confined to the placenta and extraembryonal membranes (i.e., combined yolk sac and amnion). The concentration of c-fms transcripts in the placenta increased approximately 15-fold (relative to day-7 to day-9 conceptuses) during development before reaching a plateau at day 14 to 15 of gestation. The time course of cfms expression in the extraembryonal membranes appeared to parallel the stage-specific pattern observed in the placenta. The level of c-fms transcripts in the extraembryonal tissues reached a level which was approximately 20- to 50-fold greater than that in the fetus. These findings suggest that the c-fms gene product may play a role in differentiation of extraembryonal structures or in transport processes occurring in these tissues. Our results indicate that the c-onc genes analyzed in the present study exert essentially different functions during mouse development.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Enemies within: the genesis of retrovirus oncogenes. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90263-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. G., Oskarsson M., Wood T. G., McClements W. L., Fischinger P. J., Vande Woude G. G. Activation of the transforming potential of a normal cell sequence: a molecular model for oncogenesis. Science. 1981 May 22;212(4497):941–943. doi: 10.1126/science.7233190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brahic M., Haase A. T. Detection of viral sequences of low reiteration frequency by in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6125–6129. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Chang E. H., Lander M. R., Ellis R. W., Scolnick E. M., Lowy D. R. Amplification and rearrangement of onc genes in mammalian species. Nature. 1982 Mar 25;296(5855):361–363. doi: 10.1038/296361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen I. S., Mak T. W., O'Rear J. J., Temin H. M. Characterization of reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T DNA and isolation of a novel variant of reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T by molecular cloning. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):800–811. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.800-811.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. H. Expression of endogenous avian myeloblastosis virus information in different chicken cells. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):162–170. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.162-170.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Brugge J. S., Erikson R. L. Characterization of a normal avian cell protein related to the avian sarcoma virus transforming gene product. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1363–1369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90061-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comings D. E. A general theory of carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3324–3328. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Peters G., Van Beveren C., Teich N. M., Verma I. M. FBJ murine osteosarcoma virus: identification and molecular cloning of biologically active proviral DNA. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):674–682. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.674-682.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFeo D., Gonda M. A., Young H. A., Chang E. H., Lowy D. R., Scolnick E. M., Ellis R. W. Analysis of two divergent rat genomic clones homologous to the transforming gene of Harvey murine sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3328–3332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner L., Fedele L. A., Garon C. F., Anderson S. J., Sherr C. J. McDonough feline sarcoma virus: characterization of the molecularly cloned provirus and its feline oncogene (v-fms). J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):489–500. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.489-500.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dziadek M., Adamson E. Localization and synthesis of alphafoetoprotein in post-implantation mouse embryos. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1978 Feb;43:289–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. W., DeFeo D., Furth M. E., Scolnick E. M. Mouse cells contain two distinct ras gene mRNA species that can be translated into a p21 onc protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;2(11):1339–1345. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.11.1339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. W., DeFeo D., Maryak J. M., Young H. A., Shih T. Y., Chang E. H., Lowy D. R., Scolnick E. M. Dual evolutionary origin for the rat genetic sequences of Harvey murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):408–420. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.408-420.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. W., Defeo D., Shih T. Y., Gonda M. A., Young H. A., Tsuchida N., Lowy D. R., Scolnick E. M. The p21 src genes of Harvey and Kirsten sarcoma viruses originate from divergent members of a family of normal vertebrate genes. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):506–511. doi: 10.1038/292506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. E., Fischinger P. J. Nucleotide sequences in mouse DNA and RNA specific for Moloney sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3705–3709. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. E., Gilbert J. H., Porzig K. J., Scolnick E. M., Aaronson S. A. Nature and distribution of feline sarcoma virus nucleotide sequences. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):821–827. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.821-827.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelmann E. P., Wong-Staal F., Kramer R. A., Gallo R. C. Molecular cloning and comparative analyses of the genomes of simian sarcoma virus and its associated helper virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3373–3377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. P., Gilboa E., Witte O. N., Baltimore D. Structure of the Abelson murine leukemia virus genome and the homologous cellular gene: studies with cloned viral DNA. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90554-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda T. J., Sheiness D. K., Bishop J. M. Transcripts from the cellular homologs of retroviral oncogenes: distribution among chicken tissues. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;2(6):617–624. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.6.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., Beug H. Avian leukemia viruses: interaction with their target cells in vivo and in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 17;516(3):269–299. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(78)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARVEY J. J. AN UNIDENTIFIED VIRUS WHICH CAUSES THE RAPID PRODUCTION OF TUMOURS IN MICE. Nature. 1964 Dec 12;204:1104–1105. doi: 10.1038/2041104b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M., Bosselman R. A., van der Hoorn F. A., Berns A., Fan H., Verma I. M. Identification and molecular cloning of Moloney mouse sarcoma virus-specific sequences from uninfected mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2651–2655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langbeheim H., Shih T. Y., Scolnick E. M. Identification of a normal vertebrate cell protein related to the p21 src of Harvey murine sarcoma virus. Virology. 1980 Oct 30;106(2):292–300. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90252-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathey-Prevot B., Hanafusa H., Kawai S. A cellular protein is immunologically crossreactive with and functionally homologous to the Fujinami sarcoma virus transforming protein. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):897–906. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonough S. K., Larsen S., Brodey R. S., Stock N. D., Hardy W. D., Jr A transmissible feline fibrosarcoma of viral origin. Cancer Res. 1971 Jul;31(7):953–956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Slamon D. J., Tremblay J. M., Cline M. J., Verma I. M. Differential expression of cellular oncogenes during pre- and postnatal development of the mouse. Nature. 1982 Oct 14;299(5884):640–644. doi: 10.1038/299640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppermann H., Levinson A. D., Varmus H. E., Levintow L., Bishop J. M. Uninfected vertebrate cells contain a protein that is closely related to the product of the avian sarcoma virus transforming gene (src). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1804–1808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oskarsson M., McClements W. L., Blair D. G., Maizel J. V., Vande Woude G. F. Properties of a normal mouse cell DNA sequence (sarc) homologous to the src sequence of Moloney sarcoma virus. Science. 1980 Mar 14;207(4436):1222–1224. doi: 10.1126/science.6243788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R. C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Cellular homologue (c-src) of the transforming gene of Rous sarcoma virus: isolation, mapping, and transcriptional analysis of c-src and flanking regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5842–5846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perbal B., Baluda M. A. Avian myeloblastosis virus transforming gene is related to unique chicken DNA regions separated by at least one intervening sequence. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):250–257. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.250-257.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel M., Saule S., Lagrou C., Rommens C., Beug H., Graf T., Stehelin D. Three new types of viral oncogene of cellular origin specific for haematopoietic cell transformation. Nature. 1979 Oct 11;281(5731):452–455. doi: 10.1038/281452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E. M., Weeks M. O., Shih T. Y., Ruscetti S. K., Dexter T. M. Markedly elevated levels of an endogenous sarc protein in a hemopoietic precursor cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Jan;1(1):66–74. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.1.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheiness D., Bishop J. M. DNA and RNA from uninfected vertebrate cells contain nucleotide sequences related to the putative transforming gene of avian myelocytomatosis virus. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):514–521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.514-521.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya M., Hanafusa H., Balduzzi P. C. Cellular sequences related to three new onc genes of avian sarcoma virus (fps, yes, and ros) and their expression in normal and transformed cells. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):143–152. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.143-152.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shilo B. Z., Weinberg R. A. DNA sequences homologous to vertebrate oncogenes are conserved in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6789–6792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Souza L. M., Strommer J. N., Hillyard R. L., Komaromy M. C., Baluda M. A. Cellular sequences are present in the presumptive avian myeloblastosis virus genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5177–5181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Smith K., Padgett T., McCombe P., Roulland-Dussoix D., Moscovici C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Uninfected avian cells contain RNA related to the transforming gene of avian sarcoma viruses. Cell. 1978 Feb;13(2):371–379. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90205-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Nucleotide sequences related to the transforming gene of avian sarcoma virus are present in DNA of uninfected vertebrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4102–4106. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stehelin D., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Vogt P. K. DNA related to the transforming gene(s) of avian sarcoma viruses is present in normal avian DNA. Nature. 1976 Mar 11;260(5547):170–173. doi: 10.1038/260170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilghman S. M., Kioussis D., Gorin M. B., Ruiz J. P., Ingram R. S. The presence of intervening sequences in the alpha-fetoprotein gene of the mouse. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 10;254(15):7393–7399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennström B., Bishop J. M. Isolation and characterization of chicken DNA homologous to the two putative oncogenes of avian erythroblastosis virus. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. Y., Hayward W. S., Hanafusa H. Genetic variation in the RNA transcripts of endogenous virus genes in uninfected chicken cells. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):64–73. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.64-73.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte O. N., Rosenberg N. E., Baltimore D. A normal cell protein cross-reactive to the major Abelson murine leukaemia virus gene product. Nature. 1979 Oct 4;281(5730):396–398. doi: 10.1038/281396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong-Staal F., Dalla-Favera R., Franchini G., Gelmann E. P., Gallo R. C. Three distinct genes in human DNA related to the transforming genes of mammalian sarcoma retroviruses. Science. 1981 Jul 10;213(4504):226–228. doi: 10.1126/science.6264598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida M., Kawai S., Toyoshima K. Unifected avian cells contain structurally unrelated progenitors of viral sarcoma genes. Nature. 1980 Oct 16;287(5783):653–654. doi: 10.1038/287653a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]