Abstract
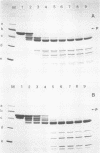
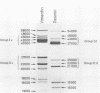
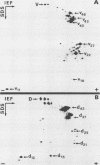
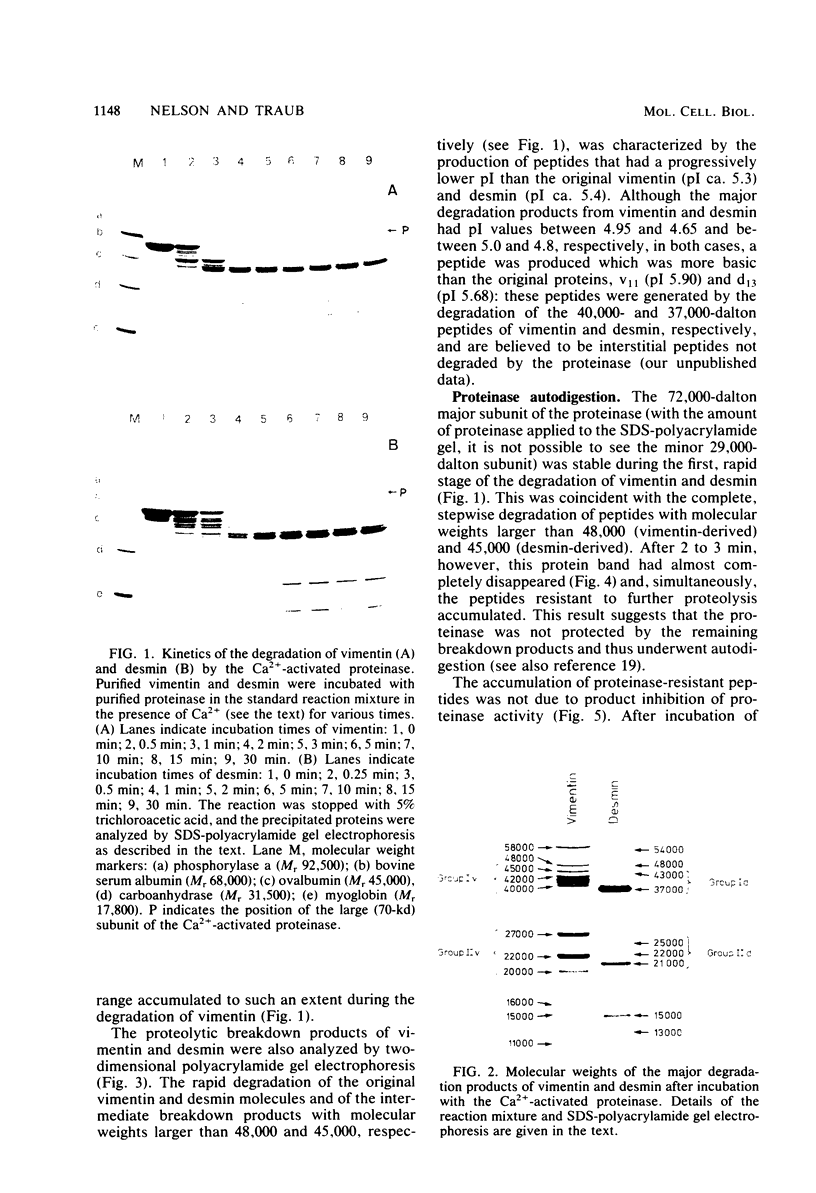
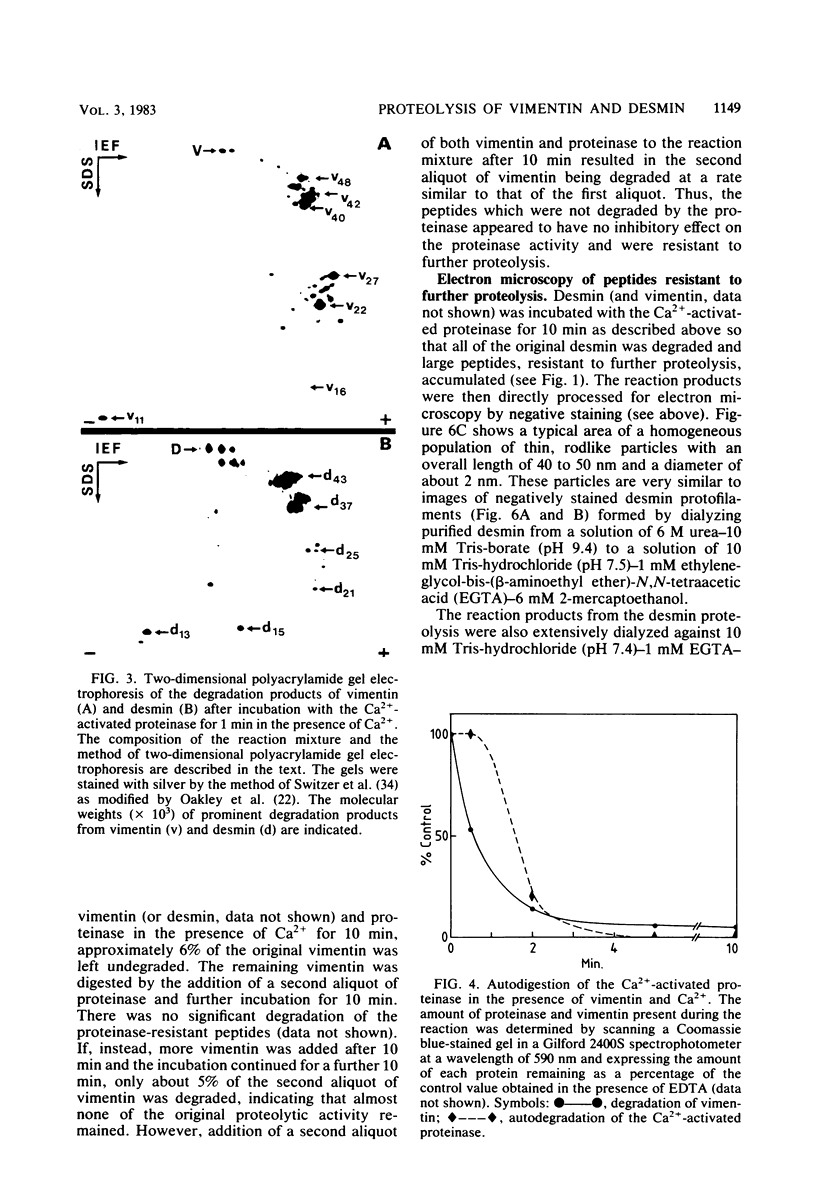
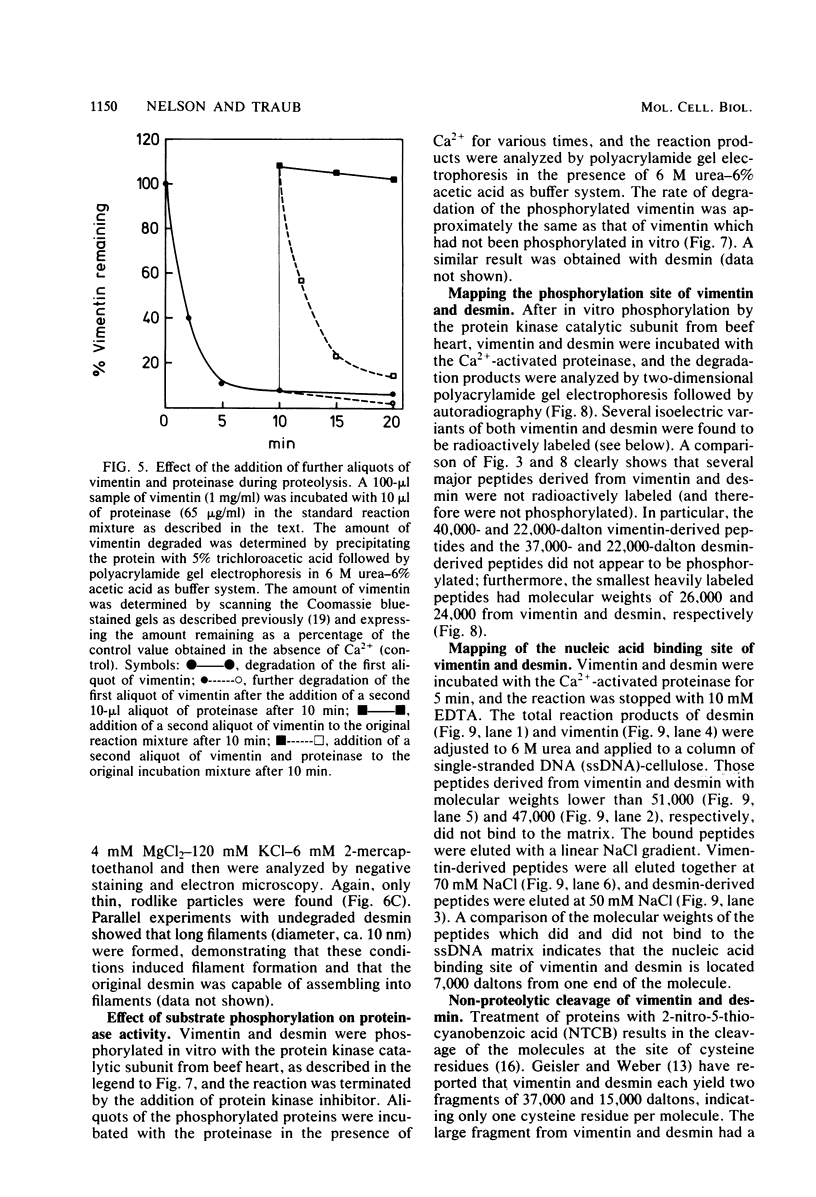
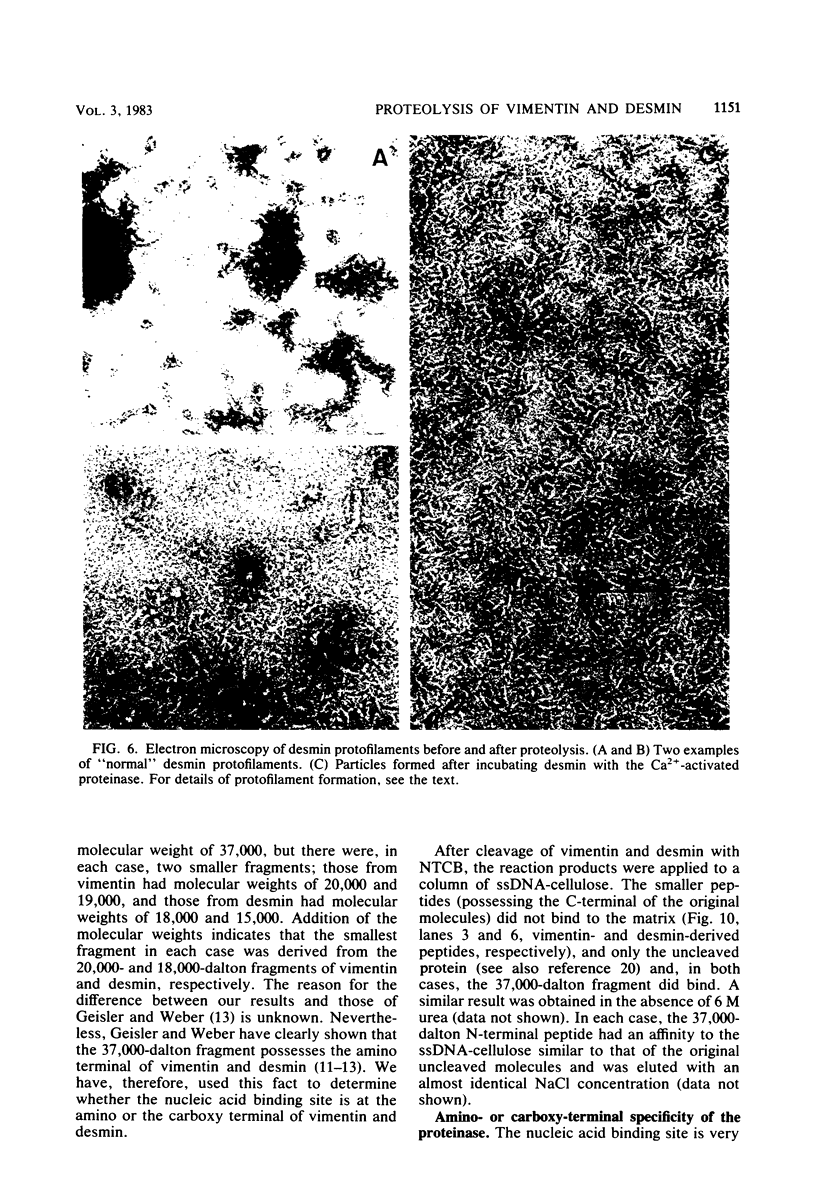
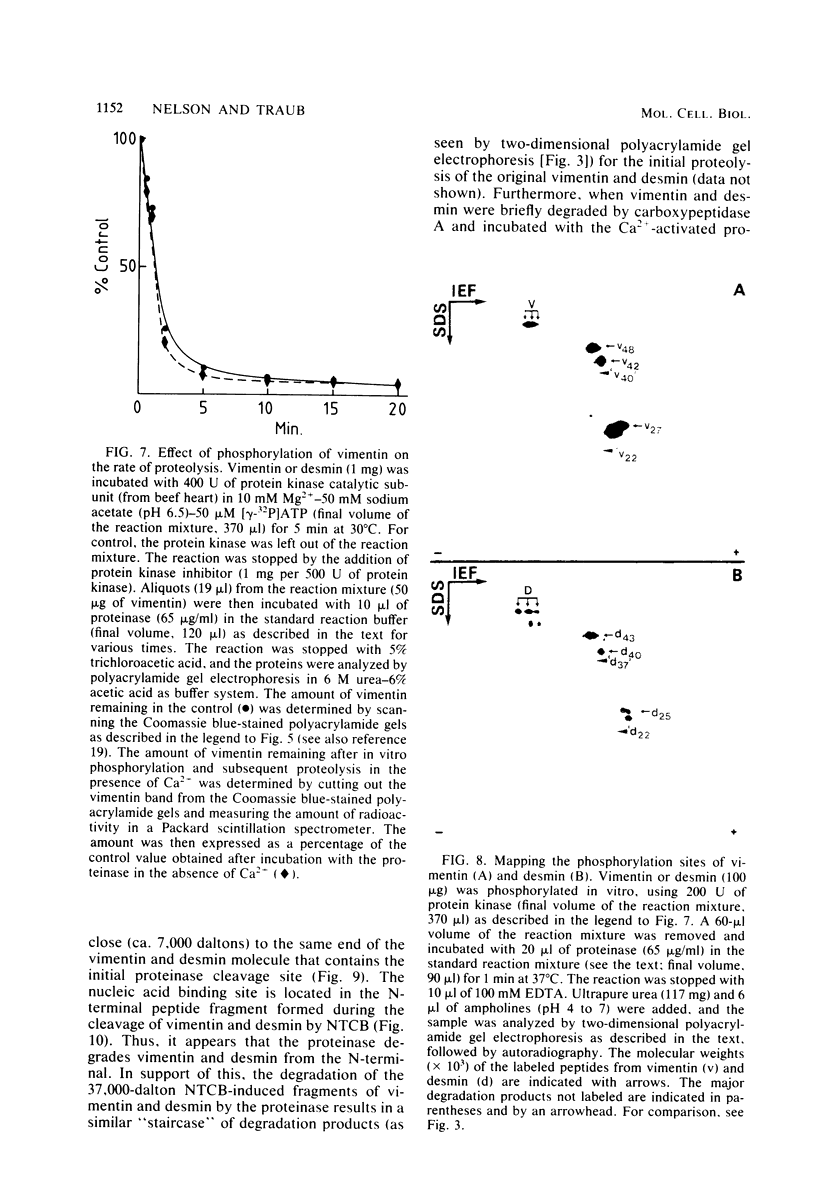
The degradation of vimentin and desmin by the Ca2+-activated proteinase specific for these intermediate filament proteins proceeds in two stages in the form of a limited proteolysis. At first, the reaction is very rapid, with the stepwise and complete removal of a peptide (ca. 9,000 daltons) from the N-terminal of vimentin and desmin. This results in the production of a characteristic "staircase" of degradation products, as seen in two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The second stage of proteolysis is characterized by the accumulation of peptides which are resistant to further proteolysis; this is due not to product inhibition but to the fact that these peptides are not substrates for the proteinase and therefore do not protect the latter from inactivation (autodigestion). In vitro phosphorylation of the substrates does not affect proteinase activity, probably because the phosphorylation site is located towards the C-terminal of the molecules. The specific and limited proteolysis of vimentin and desmin results in the deletion of the nucleic acid binding and filament assembly site of these proteins, indicating that the Ca2+-activated proteinase plays a role in regulating the function(s) of these intermediate filament proteins, rather than their simple turnover during the cell cycle.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderton B. H. Intermediate filaments: a family of homologous structures. J Muscle Res Cell Motil. 1981 Jun;2(2):141–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00711866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett G. S., Fellini S. A., Croop J. M., Otto J. J., Bryan J., Holtzer H. Differences among 100-A filamentilament subunits from different cell types. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4364–4368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borenfreund E., Schmid E., Bendich A., Franke W. W. Constitutive aggregates of intermediate-sized filaments of the vimentin and cytokeratin type in cultured hepatoma cells and their dispersal by butyrate. Exp Cell Res. 1980 May;127(1):215–235. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90428-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabral F., Gottesman M. M., Zimmerman S. B., Steinert P. M. Intermediate filaments from Chinese hamster ovary cells contain a single protein. Comparison with more complex systems from baby hamster kidney and mouse epidermal cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 10;256(3):1428–1431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fey S. J., Bravo R., Larsen P. M., Bellatin J., Celis J. E. [35S]-methionine labelled polypeptides from secondary mouse kidney fibroblasts: coordinates and one dimensional peptide maps of some major polypeptides. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1981 May;5(5):491–500. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(81)90176-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Osborn M., Weber K. Different intermediate-sized filaments distinguished by immunofluorescence microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5034–5038. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. Permanently proliferating rat vascular smooth muscle cell with maintained expression of smooth muscle characteristics, including actin of the vascular smooth muscle type. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):594–600. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Schmid E., Winter S., Chaponnier C., de Ckhastonay C., Vandekerckhove J., Weber K., Franke W. W. Vascular smooth muscle cells differ from other smooth muscle cells: predominance of vimentin filaments and a specific alpha-type actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):298–302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gard D. L., Bell P. B., Lazarides E. Coexistence of desmin and the fibroblastic intermediate filament subunit in muscle and nonmuscle cells: identification and comparative peptide analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3894–3898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Kaufmann E., Weber K. Proteinchemical characterization of three structurally distinct domains along the protofilament unit of desmin 10 nm filaments. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):277–286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Plessmann U., Weber K. Related amino acid sequences in neurofilaments and non-neural intermediate filaments. Nature. 1982 Apr 1;296(5856):448–450. doi: 10.1038/296448a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Comparison of the proteins of two immunologically distinct intermediate-sized filaments by amino acid sequence analysis: desmin and vimentin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4120–4123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granger B. L., Lazarides E. Desmin and vimentin coexist at the periphery of the myofibril Z disc. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1053–1063. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90218-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson B. W., Grund C., Winter S., Franke W. W., Illmensee K. Formation of cytoskeletal elements during mouse embryogenesis. II. Epithelial differentiation and intermediate-sized filaments in early postimplantation embryos. Differentiation. 1981;20(3):203–216. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1981.tb01177.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson G. R., Schaffer M. H., Stark G. R., Vanaman T. C. Specific chemical cleavage in high yield at the amino peptide bonds of cysteine and cystine residues. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6583–6591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Intermediate filaments as mechanical integrators of cellular space. Nature. 1980 Jan 17;283(5744):249–256. doi: 10.1038/283249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. J., Traub P. Intermediate (10 nm) filament proteins and the Ca2+-activated proteinase specific for vimentin and desmin in the cells from fish to man: an example of evolutionary conservation. J Cell Sci. 1982 Oct;57:25–49. doi: 10.1242/jcs.57.1.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. J., Traub P. Properties of Ca2+-activated protease specific for the intermediate-sized filament protein vimentin in Ehrlich-ascites-tumour cells. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May;116(1):51–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05299.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. J., Traub P. Purification and further characterization of the Ca2+-activated proteinase specific for the intermediate filament proteins vimentin and desmin. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5544–5553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. J., Traub P. Purification of the intermediate filament protein vimentin from Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 25;257(10):5536–5543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor C. M., Balzer D. R., Jr, Lazarides E. Phosphorylation of subunit proteins of intermediate filaments from chicken muscle and nonmuscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):819–823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea J. M., Robson R. M., Huiatt T. W., Hartzer M. K., Stromer M. H. Purified desmin from adult mammalian skeletal muscle: a peptide mapping comparison with desmins from adult mammalian and avian smooth muscle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Aug 13;89(3):972–980. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91873-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakley B. R., Kirsch D. R., Morris N. R. A simplified ultrasensitive silver stain for detecting proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):361–363. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90470-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochs D. C., McConkey E. H., Guard N. L. Vimentin-derived proteins: differences between normal human fibroblasts and transformed human cells. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Oct;135(2):355–362. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90171-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Franke W., Weber K. Direct demonstration of the presence of two immunologically distinct intermediate-sized filament systems in the same cell by double immunofluorescence microscopy. Vimentin and cytokeratin fibers in cultured epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Jan;125(1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90186-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paetau A., Virtanen I., Stenman S., Kurki P., Linder E., Vaheri A., Westermark B., Dahl D., Haltia M. Glial fibrillary acidic protein and intermediate filaments in human glioma cells. Acta Neuropathol. 1979 Jun 15;47(1):71–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00698276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss R. M., Mirsky R., Raff M. C., Thorpe R., Dowding A. J., Anderton B. H. All classes of intermediate filaments share a common antigenic determinant defined by a monoclonal antibody. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):419–428. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90383-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoeman R. L., Schweiger H. G. Gene expression in Acetabularia. I. Calibration of wheat germ cell-free translation system proteins as internal references for two-dimensional electrophoresis. J Cell Sci. 1982 Dec;58:23–33. doi: 10.1242/jcs.58.1.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J. V., Sobieszek A. Studies on the function and composition of the 10-NM(100-A) filaments of vertebrate smooth muscle. J Cell Sci. 1977 Feb;23:243–268. doi: 10.1242/jcs.23.1.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Idler W. W., Cabral F., Gottesman M. M., Goldman R. D. In vitro assembly of homopolymer and copolymer filaments from intermediate filament subunits of muscle and fibroblastic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3692–3696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Idler W. W., Goldman R. D. Intermediate filaments of baby hamster kidney (BHK-21) cells and bovine epidermal keratinocytes have similar ultrastructures and subunit domain structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4534–4538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Zimmerman S. B., Starger J. M., Goldman R. D. Ten-nanometer filaments of hamster BHK-21 cells and epidermal keratin filaments have similar structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):6098–6101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.6098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switzer R. C., 3rd, Merril C. R., Shifrin S. A highly sensitive silver stain for detecting proteins and peptides in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1979 Sep 15;98(1):231–237. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(79)90732-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub P., Boeckmann G. High-resolution polyacrylamide gradient slab gel electrophoresis of histones H1, H3 and H4. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1978 May;359(5):571–579. doi: 10.1515/bchm.1978.359.1.571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub P., Nelson W. J. Interaction of the intermediate filament protein vimentin with ribosomal subunits and ribosomal RNA in vitro. Mol Biol Rep. 1982 Nov 30;8(4):239–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00776586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub P., Nelson W. J., Kühn S., Vorgias C. E. The interaction in vitro of the intermediate filament protein vimentin with naturally occurring RNAs and DNAs. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1456–1466. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub P., Nelson W. J. Occurrence in various mammalian cells and tissues of the Ca 2+ activated protease specific for the intermediate-sized filament proteins vimentin and desmin. Eur J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;26(1):61–67. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]