Abstract
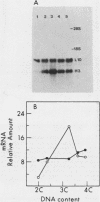
The mechanisms responsible for the periodic accumulation and decay of histone mRNA in the mammalian cell cycle were investigated in mouse erythroleukemia cells, using a cloned mouse H3 histone gene probe that hybridizes with most or all H3 transcripts. Exponentially growing cells were fractionated into cell cycle-specific stages by centrifugal elutriation, a method for purifying cells at each stage of the cycle without the use of treatments that arrest growth. Measurements of H3 histone mRNA content throughout the cell cycle show that the mRNA accumulates gradually during S phase, achieving its highest value in mid-S phase when DNA synthesis is maximal. The mRNA content then decreases as cells approach G2. These results demonstrate that the periodic synthesis of histones during S phase is due to changes in the steady-state level of histone mRNA. They are consistent with the conventional view in which histone synthesis is regulated coordinately with DNA synthesis in the cell cycle. The periodic accumulation and decay of H3 histone mRNA appear to be controlled primarily by changes in the rate of appearance of newly synthesized mRNA in the cytoplasm, determined by pulse-labeling whole cells with [3H]uridine. Measurements of H3 mRNA turnover by pulse-chase experiments with cells in S and G2 did not provide evidence for changes in the cytoplasmic stability of the mRNA during the period of its decay in late S and G2. Furthermore, transcription measurements carried out by brief pulse-labeling in vivo and by in vitro transcription in isolated nuclei indicate that the rate of H3 gene transcription changes to a much smaller extent than the steady-state levels of the mRNA or the appearance of newly synthesized mRNA in the cytoplasm. The results suggest that post-transcriptional processes make an important contribution to the periodic accumulation and decay of histone mRNA and that these processes may operate within the nucleus.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borun T. W., Gabrielli F., Ajiro K., Zweidler A., Baglioni C. Further evidence of transcriptional and translational control of histone messenger RNA during the HeLa S3 cycle. Cell. 1975 Jan;4(1):59–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90134-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borun T. W., Scharff M. D., Robbins E. Rapidly labeled, polyribosome-associated RNA having the properties of histone messenger. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):1977–1983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. H., Schildkraut C. L. Perturbation of growth and differentiation of Friend murine erythroleukemia cells by 5-bromodeoxyuridine incorporation in early S phase. J Cell Physiol. 1979 May;99(2):261–278. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040990213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. B., Mueller G. C. Control of histone synthesis in HeLa cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 4;294(1):481–496. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90104-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conscience J. F., Ruddle F. H., Skoultchi A., Darlington G. J. Somatic cell hybrids between Friend erythroleukemia cells and mouse hepatoma cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1977 Mar;3(2):157–172. doi: 10.1007/BF01551812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman E., Krauter K., Walling L., Weinberger C., Ray M., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcriptional control in the production of liver-specific mRNAs. Cell. 1981 Mar;23(3):731–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90436-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Detke S., Lichtler A., Phillips I., Stein J., Stein G. Reassessment of histone gene expression during cell cycle in human cells by using homologous H4 histone cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4995–4999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Mueller G. C. Histone synthesis in vitro on HeLa cell microsomes. The nature of the coupling to deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 10;244(21):5947–5952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groppi V. E., Jr, Coffino P. G1 and S phase mammalian cells synthesize histones at equivalent rates. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):195–204. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90127-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Sive H. L., Roeder R. G. Regulation of human histone gene expression: kinetics of accumulation and changes in the rate of synthesis and in the half-lives of individual histone mRNAs during the HeLa cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):539–550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Zernik M., Roeder R. G. The structure of the human histone genes: clustered but not tandemly repeated. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):661–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90092-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L., Bromley S., Osley M. A. Periodic transcription of yeast histone genes. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):305–310. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90036-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofer E., Darnell J. E., Jr The primary transcription unit of the mouse beta-major globin gene. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):585–593. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90154-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiung N., Roginski R. S., Henthorn P., Smithies O., Kucherlapati R., Skoultchi A. I. Introduction and expression of a fetal human globin gene in mouse fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;2(4):401–411. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.4.401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jelinek W., Leinwand L. Low molecular weight RNAs hydrogen-bonded to nuclear and cytoplasmic poly(A)-terminated RNA from cultured Chinese hamster ovary cells. Cell. 1978 Sep;15(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90095-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melli M. Clustering of the DNA sequences complementary to repetitive nuclear RNA of HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1975 Mar 25;93(1):23–38. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90357-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melli M., Spinelli G., Arnold E. Synthesis of histone messenger RNA of HeLa cells during the cell cycle. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):167–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90194-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyuhas O., Perry R. P. Construction and identification of cDNA clones for mouse ribosomal proteins: application for the study of r-protein gene expression. Gene. 1980 Jul;10(2):113–129. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90129-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta Y., Tanaka M., Terada M., Miller O. J., Bank A., Marks P., Rifkind R. A. Erythroid cell differentiation: murine erythroleukemia cell variant with unique pattern of induction by polar compounds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1232–1236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumb M., Stein J., Stein G. Coordinate regulation of multiple histone mRNAs during the cell cycle in HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2391–2410. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott D. M. The cell cycle and the control of cellular reproduction. Adv Genet. 1976;18:99–177. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60438-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickles R., Marashi F., Sierra F., Clark S., Wells J., Stein J., Stein G. Analysis of histone gene expression during the cell cycle in HeLa cells by using cloned human histone genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):749–753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins E., Borun T. W. The cytoplasmic synthesis of histones in hela cells and its temporal relationship to DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Feb;57(2):409–416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J., Lau L. F., Bahl C. P., Narang S. A., Wu R. Synthetic adaptors for cloning DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:98–109. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sittman D. B., Chiu I. M., Pan C. J., Cohn R. H., Kedes L. H., Marzluff W. F. Isolation of two clusters of mouse histone genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4078–4082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sittman D. B., Graves R. A., Marzluff W. F. Histone mRNA concentrations are regulated at the level of transcription and mRNA degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1849–1853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeiro R., Darnell J. E. Competition hybridization by "pre-saturation" of HeLa cell DNA. J Mol Biol. 1969 Sep 28;44(3):551–562. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90379-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein G. S., Stein J. L., Park W. D., Detke S., Lichtler A. C., Shephard E. A., Jansing R. L., Phillips I. R. Regulation of histone gene expression in HeLa S3 cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 2):1107–1120. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volloch V., Housman D. Stability of globin mRNA in terminally differentiating murine erythroleukemia cells. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):509–514. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90146-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J., Jelinek W., Darnell J. E., Jr The definition of a large viral transcription unit late in Ad2 infection of HeLa cells: mapping of nascent RNA molecules labeled in isolated nuclei. Cell. 1977 Apr;10(4):611–616. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90093-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R. S., Bonner W. M. Separation of basal histone synthesis from S-phase histone synthesis in dividing cells. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90415-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]