Abstract
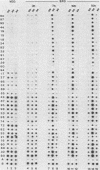
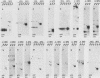
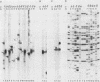
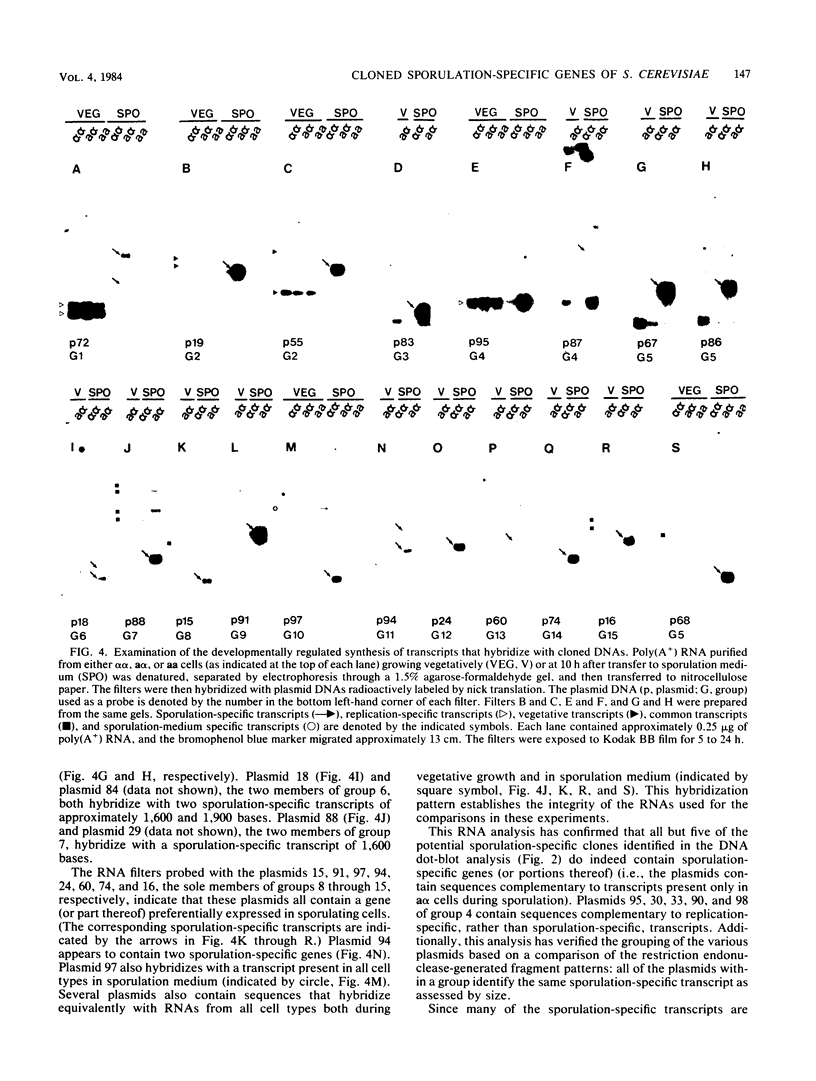
A differential hybridization screen has been used to identify genes cloned from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae that are expressed preferentially during sporulation. Duplicate copies of a partial Sau3A yeast DNA library prepared in the vector pBR322 were hybridized with radioactive cDNA probes representing the mRNA populations of sporulating a alpha cells and asporogenous alpha alpha cells at various times after transfer to sporulation medium. Thirty-eight clones showed an enhanced hybridization signal with the a alpha sporulation probe relative to the alpha alpha control cDNA probe. A comparison of the array of fragments produced by restriction endonuclease digestion of these plasmids suggested that 15 different sequences had been cloned. An RNA blot analysis using these cloned DNAs to probe RNAs purified from aa, a alpha, and alpha alpha cells harvested either during vegetative growth or at 10 h after transfer to sporulation medium indicated that 14 different sporulation-specific genes had been identified. Transcripts complementary to these genes are present only in a alpha cells after transfer to sporulation medium. Three of these clones contain two sporulation-specific genes. Three genes have been identified that are expressed in all cell types during vegetative growth and only in a alpha cells in sporulation medium.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy M. J., Buten-Magee B., Straight D. J., Kennedy A. L., Partridge R. M., Magee P. T. Isolation of genes expressed preferentially during sporulation in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3000–3004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy M. J., Smith L. M., Magee P. T. Developmental regulation of a sporulation-specific enzyme activity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):171–178. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer D. R., Eccleshall R., Marmur J. Isolation of yeast DNA. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;12:39–44. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60950-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godson G. N., Vapnek D. A simple method of preparing large amounts of phiX174 RF 1 supercoiled DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Apr 11;299(4):516–520. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90223-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Meselson M. Plasmid screening at high colony density. Gene. 1980 Jun;10(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L. M., Rosbash M. Number and distribution of polyadenylated RNA sequences in yeast. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):453–462. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90032-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L., Fahrner K., Woolford J., Jr, Rosbash M., Kaback D. B. Isolation of yeast histone genes H2A and H2B. Cell. 1979 Dec;18(4):1261–1271. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90237-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper A. K., Hall B. D. Mating type and sporulation in yeast. I. Mutations which alter mating-type control over sporulation. Genetics. 1975 May;80(1):41–59. doi: 10.1093/genetics/80.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper A. K., Magee P. T., Welch S. K., Friedman M., Hall B. D. Macromolecule synthesis and breakdown in relation to sporulation and meiosis in yeast. J Bacteriol. 1974 Aug;119(2):619–628. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.2.619-628.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraig E., Haber J. E. Messenger ribonucleic acid and protein metabolism during sporulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):1098–1112. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.1098-1112.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee P. T., Hopper A. K. Protein synthesis in relation to sporulation and meiosis in yeast. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):952–960. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.952-960.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangiarotti G., Chung S., Zuker C., Lodish H. F. Selection and analysis of cloned developmentally-regulated Dictyostelium discoideum genes by hybridization-competition. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 25;9(4):947–963. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.4.947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Jeffrey A., Kleid D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1184–1188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. A., Reed S. I. Isolation of genes by complementation in yeast: molecular cloning of a cell-cycle gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2119–2123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng R., Abelson J. Isolation and sequence of the gene for actin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3912–3916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rave N., Crkvenjakov R., Boedtker H. Identification of procollagen mRNAs transferred to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper from formaldehyde agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3559–3567. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- St John T. P., Davis R. W. Isolation of galactose-inducible DNA sequences from Saccharomyces cerevisiae by differential plaque filter hybridization. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):443–452. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trew B. J., Friesen J. D., Moens P. B. Two-dimensional protein patterns during growth and sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1979 Apr;138(1):60–69. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.1.60-69.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. F., Ajam N., Dawes I. W. Nature and timing of some sporulation-specific protein changes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;1(10):910–918. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.10.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis using M13-derived vectors: an efficient and general procedure for the production of point mutations in any fragment of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6487–6500. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]