Abstract
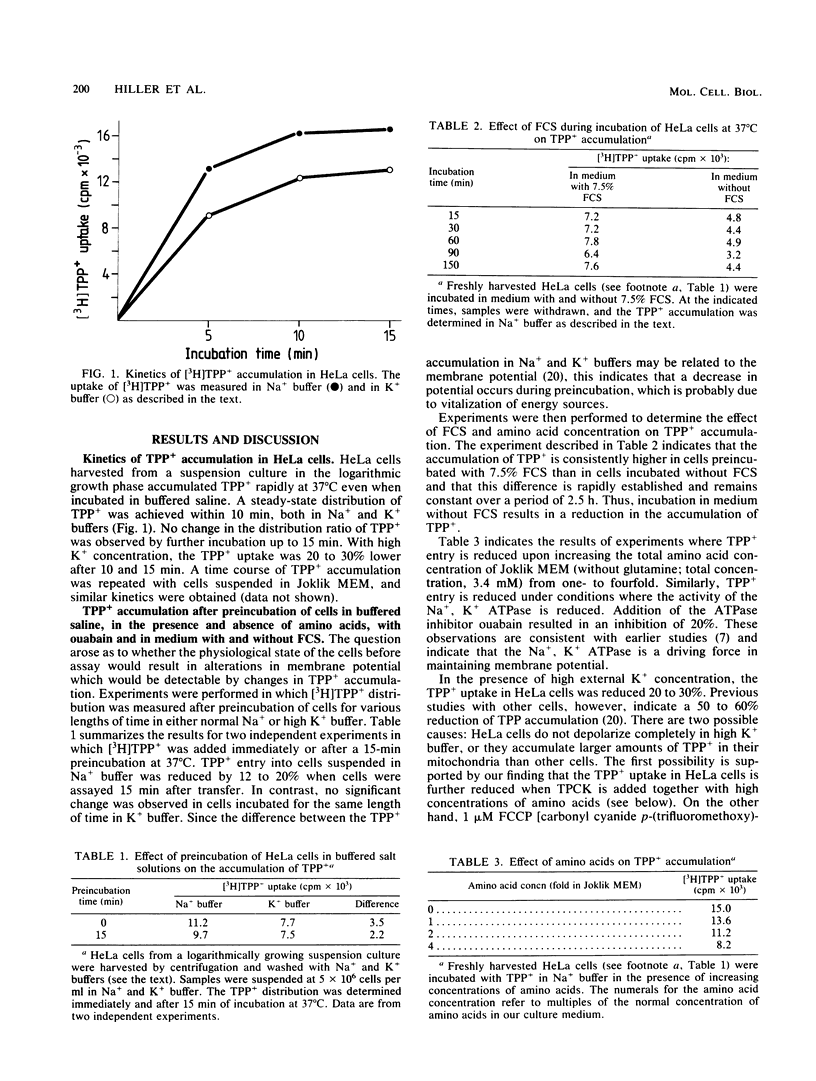
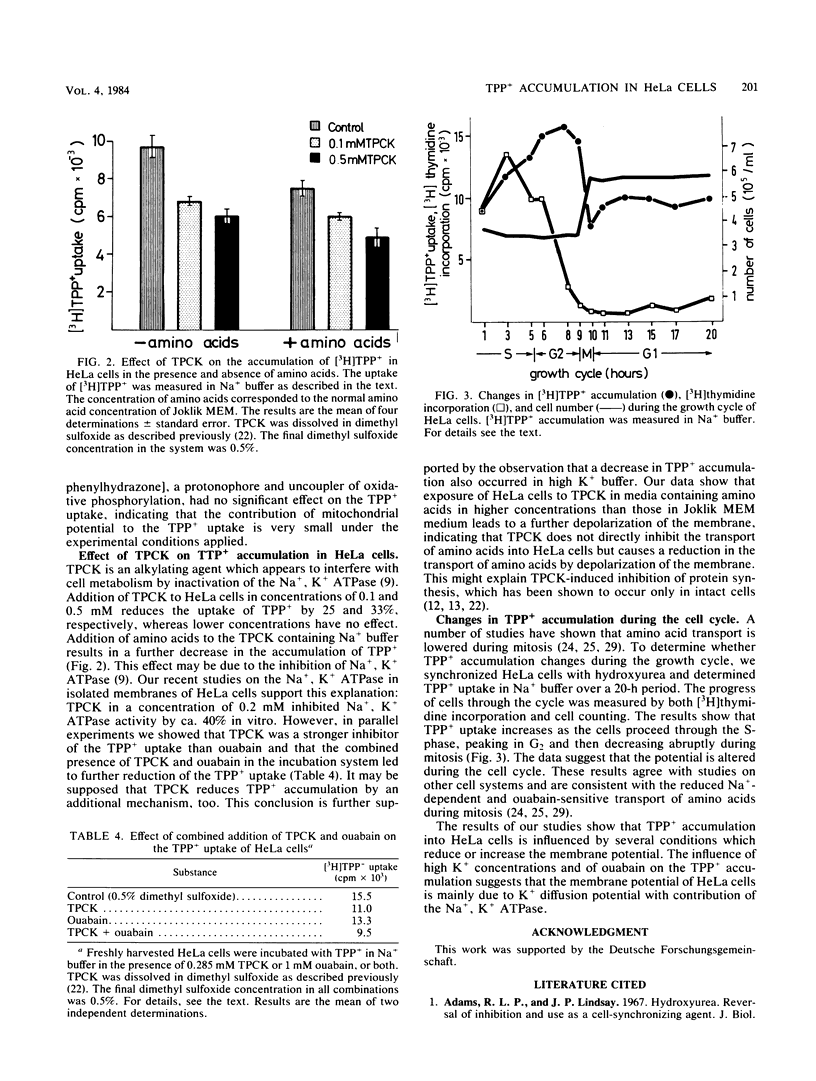
Exposure of HeLa cells to tetraphenylphosphonium cation (TPP+) results in a rapid accumulation intracellularly, and a steady-state level is reached within 10 min. Accumulation of [3H]TPP+ in HeLa cells is reduced under the following conditions: (i) after preincubation of cells in buffered saline or in medium containing two- to fourfold higher concentrations of amino acids, (ii) exposure to the alkylating agent L-1-tosylamido-2-phenyl-ethylchloromethyl ketone, (iii) ouabain-mediated inhibition of the Na+, K+ ATPase, and (iv) high external K+ concentrations. In contrast, addition of serum increases the uptake of TPP+. In synchronized cells, intracellular levels of TPP+ differ at various stages of cell cycle and are lowest in mitosis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Christensen H. N. On the development of amino acid transport systems. Fed Proc. 1973 Jan;32(1):19–28. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone C. D., Jr Unified theory on the basic mechanism of normal mitotic control and oncogenesis. J Theor Biol. 1971 Jan;30(1):151–181. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(71)90042-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felle H., Porter J. S., Slayman C. L., Kaback H. R. Quantitative measurements of membrane potential in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1980 Jul 22;19(15):3585–3590. doi: 10.1021/bi00556a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinius L. L., Jasaitis A. A., Kadziauskas Y. P., Liberman E. A., Skulachev V. P., Topali V. P., Tsofina L. M., Vladimirova M. A. Conversion of biomembrane-produced energy into electric form. I. Submitochondrial particles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 4;216(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90153-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinz E., Geck P., Pietrzyk C. Driving forces of amino acid transport in animal cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Dec 30;264:428–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb31501.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holz R. W. Measurement of membrane potential of chromaffin granules by the accumulation of triphenylmethylphosphonium cation. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6703–6709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihlenfeldt M., Gantner G., Harrer M., Puschendorf B., Putzer H., Grunicke H. Interaction of the alkylating antitumor agent 2,3,5-tris(ethyleneimino)benzoquinone with the plasma membrane of Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1981 Jan;41(1):289–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Electrochemical ion gradients and active transport. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;339:53–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb15968.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiefer H., Blume A. J., Kaback H. R. Membrane potential changes during mitogenic stimulation of mouse spleen lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2200–2204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch G., Bilello J. A., Kruppa J., Koch F., Oppermann H. Amplification of translational control by membrane-mediated events: a pleiotropic effect on cellular and viral gene expression. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;339:280–306. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb15984.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch G., Oppermann H., Bilello P., Koch F., Nuss D. Control of peptide chain initiation in uninfected and virus infected cells by membrane mediated events. Hamatol Bluttransfus. 1976;19:541–555. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-87524-3_51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korchak H. M., Weissmann G. Changes in membrane potential of human granulocytes antecede the metabolic responses to surface stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3818–3822. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroki M., Satoh H., Kamo N., Kobatake Y. Contribution to the membrane potential of the electrogenic Na+, K+-pump in guinea pig polymorphonuclear leukocytes. FEBS Lett. 1981 Jan 26;123(2):177–180. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lever J. E. Active amino acid transport in plasma membrane vesicles from Simian virus 40-transformed mouse fibroblasts. Characteristics of electrochemical Na+ gradient-stimulated uptake. J Biol Chem. 1977 Mar 25;252(6):1990–1997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lever J. E. Membrane potential and neutral amino acid transport in plasma membrane vesicles from Simian virus 40 transformed mouse fibroblasts. Biochemistry. 1977 Sep 20;16(19):4328–4334. doi: 10.1021/bi00638a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtshtein D., Dunlop K., Kaback H. R., Blume A. J. Mechanism of monensin-induced hyperpolarization of neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid NG108-15. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2580–2584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtshtein D., Kaback H. R., Blume A. J. Use of a lipophilic cation for determination of membrane potential in neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid cell suspensions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):650–654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloff B. L., Scordilis S. P., Tedeschi H. Membrane potential of mitochondrial measured with microelectrodes. Science. 1977 Mar 4;195(4281):898–900. doi: 10.1126/science.841317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pong S. S., Nuss D. L., Koch G. Inhibition of initiation of protein synthesis in mammalian tissue culture cells by L-1-tosylamido-2-phenylethyl chloromethyl ketone. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 10;250(1):240–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos S., Grollman E. F., Lazo P. S., Dyer S. A., Habig W. H., Hardegree M. C., Kaback H. R., Kohn L. D. Effect of tetanus toxin on the accumulation of the permeant lipophilic cation tetraphenylphosphonium by guinea pig brain synaptosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4783–4787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs H. G., Stambrook P. J., Ebert J. D. Changes in membrane potential during the cell cycle. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Feb;83(2):362–366. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90350-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander G., Pardee A. B. Transport changes in synchronously growing CHO and L cells. J Cell Physiol. 1972 Oct;80(2):267–271. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040800214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuldiner S., Kaback H. R. Membrane potential and active transport in membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1975 Dec 16;14(25):5451–5461. doi: 10.1021/bi00696a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert M. Reversible inhibition of the division of Crithidia luciliae by hydroxyurea and its use for obtaining synchronized cultures. FEBS Lett. 1969 Nov 29;5(4):291–294. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80371-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tupper J. T., Mills B., Zorgniotti F. Membrane transport in synchronized Ehrlich ascites tumor cells: uptake of amino acids by the A and L system during the cell cycle. J Cell Physiol. 1976 May;88(1):77–87. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040880110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilereal M. L., Cook J. S. Role of the membrane potential in serum-stimulated uptake of amino acid in a diploid human fibroblast. J Supramol Struct. 1977;6(2):179–189. doi: 10.1002/jss.400060204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waggoner A. Optical probes of membrane potential. J Membr Biol. 1976 Jun 30;27(4):317–334. doi: 10.1007/BF01869143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



