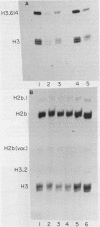
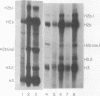
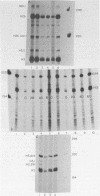
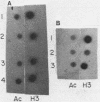
Abstract
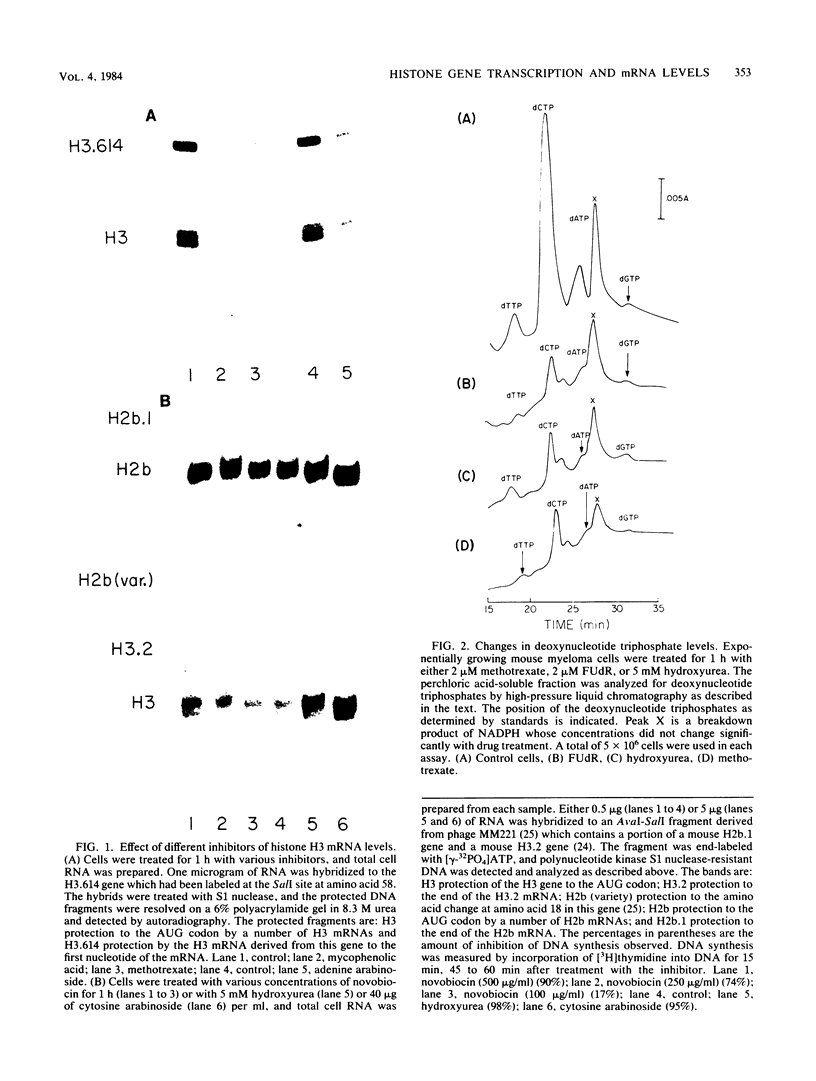
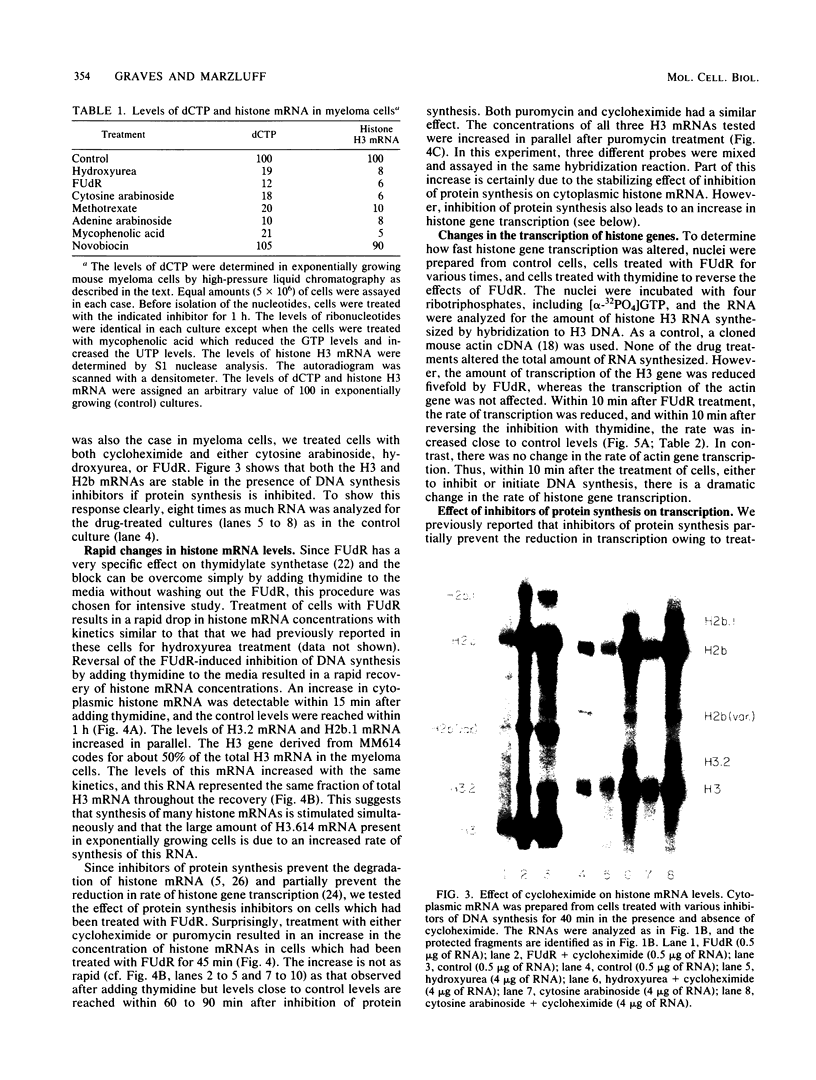
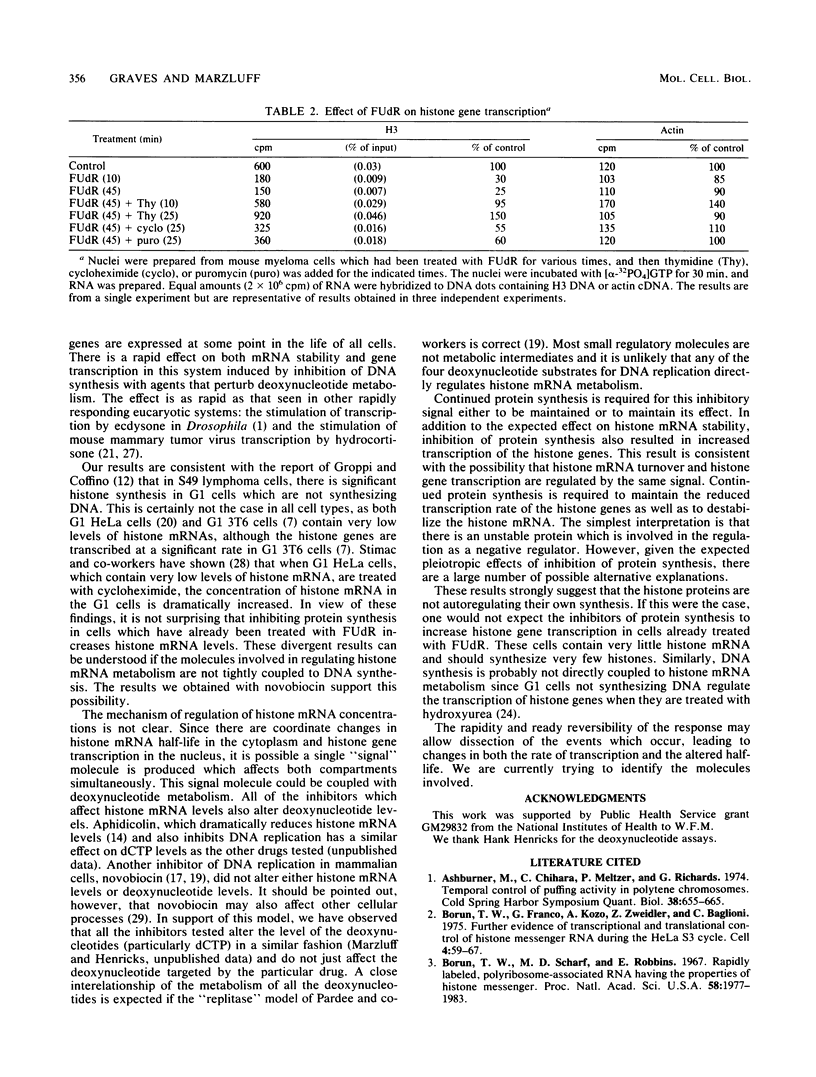
The levels of histone mRNAs are reduced 90 to 95% after treatment of mouse myeloma cells with inhibitors of DNA synthesis which disrupt deoxynucleotide metabolism. In contrast, novobiocin, which inhibits DNA synthesis but does not alter deoxynucleotide metabolism, did not alter histone mRNA levels. Upon reversing the inhibition by fluorodeoxyuridine by feeding with thymidine, histone mRNA levels are restored to control levels within 40 to 60 min. The rate of histone gene transcription is reduced 75 to 80% within 10 min after treatment with fluorodeoxyuridine and increased to control levels within 10 min after refeeding with thymidine. Inhibition of protein synthesis with cycloheximide or puromycin in cells which had been treated with fluorodeoxyuridine resulted in an increase of histone mRNA levels. This was partly due to an increase in the rate of transcription. The data indicate that both transcription and mRNA degradation are linked to deoxynucleotide metabolism. Continued protein synthesis is necessary for maintaining the inhibition of histone gene transcription.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashburner M., Chihara C., Meltzer P., Richards G. Temporal control of puffing activity in polytene chromosomes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:655–662. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borun T. W., Gabrielli F., Ajiro K., Zweidler A., Baglioni C. Further evidence of transcriptional and translational control of histone messenger RNA during the HeLa S3 cycle. Cell. 1975 Jan;4(1):59–67. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90134-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borun T. W., Scharff M. D., Robbins E. Rapidly labeled, polyribosome-associated RNA having the properties of histone messenger. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):1977–1983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breindl M., Gallwitz D. On the translational control of histone synthesis. Quantitation of biologically active histone mRNA from synchronized HeLa cells and its translation in different cell-free systems. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jun 1;45(1):91–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03533.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler W. B., Mueller G. C. Control of histone synthesis in HeLa cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 4;294(1):481–496. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(73)90104-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. B., Maybaum J., Sadee W. Guanine nucleotide depletion and toxicity in mouse T lymphoma (S-49) cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8713–8717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLisle A. J., Graves R. A., Marzluff W. F., Johnson L. F. Regulation of histone mRNA production and stability in serum-stimulated mouse 3T6 fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):1920–1929. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.1920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklin S. G., Zweidler A. Non-allelic variants of histones 2a, 2b and 3 in mammals. Nature. 1977 Mar 17;266(5599):273–275. doi: 10.1038/266273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D. Kinetics of inactivation of histone mRNA in the cytoplasm after inhibition of DNA replication in synchronised HeLa cells. Nature. 1975 Sep 18;257(5523):247–248. doi: 10.1038/257247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Mueller G. C. Histone synthesis in vitro on HeLa cell microsomes. The nature of the coupling to deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 10;244(21):5947–5952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett C., Santi D. V. A rapid and sensitive high pressure liquid chromatography assay for deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates in cell extracts. Anal Biochem. 1979 Nov 1;99(2):268–273. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(79)80005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groppi V. E., Jr, Coffino P. G1 and S phase mammalian cells synthesize histones at equivalent rates. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):195–204. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90127-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurley L. R., Walters R. A., Tobey R. A. The metabolism of histone fractions. IV. Synthesis of histones during the G1-phase of the mammalian life cycle. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Feb;148(2):633–641. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90182-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N., Sive H. L., Roeder R. G. Regulation of human histone gene expression: kinetics of accumulation and changes in the rate of synthesis and in the half-lives of individual histone mRNAs during the HeLa cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):539–550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluff W. F., Jr, Murphy E. C., Jr, Huang R. C. Transcription of ribonucleic acid in isolated mouse myeloma nuclei. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 28;12(18):3440–3446. doi: 10.1021/bi00742a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marzluff W. F., Jr Transcription of RNA in isolated nuclei. Methods Cell Biol. 1978;19:317–332. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60032-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattern M. R., Painter R. B. Dependence of mammalian DNA replication on DNA supercoiling. II. Effects of novobiocin on DNA synthesis in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Jul 26;563(2):306–312. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(79)90049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A. J., Caravatti M., Robert B., Cohen A., Daubas P., Weydert A., Gros F., Buckingham M. E. Mouse actin messenger RNAs. Construction and characterization of a recombinant plasmid molecule containing a complementary DNA transcript of mouse alpha-actin mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):1008–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi H., Prem veer Reddy G., Pardee A. B. Rapid incorporation of label from ribonucleoside disphosphates into DNA by a cell-free high molecular weight fraction from animal cell nuclei. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):443–451. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90464-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rickles R., Marashi F., Sierra F., Clark S., Wells J., Stein J., Stein G. Analysis of histone gene expression during the cell cycle in HeLa cells by using cloned human histone genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):749–753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringold G. M., Yamamoto K. R., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Glucocorticoid-stimulated accumulation of mouse mammary tumor virus RNA: increased rate of synthesis of viral RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2879–2883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santi D. V., McHenry C. S., Sommer H. Mechanism of interaction of thymidylate synthetase with 5-fluorodeoxyuridylate. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 29;13(3):471–481. doi: 10.1021/bi00700a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sittman D. B., Chiu I. M., Pan C. J., Cohn R. H., Kedes L. H., Marzluff W. F. Isolation of two clusters of mouse histone genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4078–4082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sittman D. B., Graves R. A., Marzluff W. F. Histone mRNA concentrations are regulated at the level of transcription and mRNA degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1849–1853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sittman D. B., Graves R. A., Marzluff W. F. Structure of a cluster of mouse histone genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Oct 11;11(19):6679–6697. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.19.6679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H., Gallwitz D. Fate of histone messenger RNA in synchronized HeLa cells in the absence of initiation of protein synthesis. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Jan;72(2):385–392. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11263.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stallcup M. R., Ring J., Yamamoto K. R. Synthesis of mouse mammary tumor virus ribonucleic acid in isolated nuclei from cultured mammary tumor cells. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 18;17(8):1515–1521. doi: 10.1021/bi00601a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimac E., Groppi V. E., Coffino P. Increased histone mRNA levels during inhibition of protein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jul 18;114(1):131–137. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91604-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright H. T., Nurse K. C., Goldstein D. J. Nalidixic acid, oxolinic acid, and novobiocin inhibit yeast glycyl- and leucyl-transfer RNA synthetases. Science. 1981 Jul 24;213(4506):455–456. doi: 10.1126/science.7017932. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu R. S., Bonner W. M. Separation of basal histone synthesis from S-phase histone synthesis in dividing cells. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90415-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]