Abstract
Aim:
To share our experience of doing tubularized incised plate urethroplasty with modifications.
Materials and Methods:
This is a single surgeon personal series from 2004 to 2009. One hundred patients of distal hypospadias were subjected for Snodgrass urethroplasty with preputioplasty. The age range was 1 to 5 year with mean age of 2.7 years. Selection criteria were good urethral plate, without chordee and torsion needing complete degloving. Main technical modification from original Snodgrass procedure was spongioplasty, preputioplasty, and dorsal slit when inability to retract prepuce during surgery.
Results:
Average follow-up period is 23 months. Seven (7%) patients developed fistula and one patient had complete preputial dehiscence. Phimosis developed in three (3%) patients and required circumcision. Dorsal slit was required in seven patients. One patient developed meatal stenosis in postoperative period. All other patients are passing single urinary stream and have cosmesis that is acceptable.
Conclusions:
Modified tubularized incised plate urethroplasty with preputioplasty effectively gives cosmetically normal looking penis with low complications.
Keywords: Preputioplasty, Snodgrass, spongioplasty, urethroplasty
INTRODUCTION
Snodgrass urethroplasty[1] for distal hypospadias is a common procedure and accepted worldwide. It is a landmark in the history of hypospadias repair. It has lowest reported incidence of urethral fistula and meatal stenosis but at the same time gives circumcised penis. To address the increased demand of preserving prepuce in India, we decided to do preputioplasty along with tubularized incised plate urethroplasty. We made some modifications in the tubularized incised plate urethroplasty as described originally by Snodgrass. This study reports the experience of a single surgeon over period of 5 years.
MATERIAL AND METHODS
A total number of 100 hypospadias repair with preputioplasty have been done over a period of 5 years from 2004 to 2009. The age range was 1 year to 5 years with a mean age of 2.7 years. All patients had distal hypospadias. The patients with severe chordee, torsion as well as those patients with narrow urethral plate were not considered for this type of repair. Only those patients whose parents demanded preputioplasty were considered for the preputioplasty.
Surgical technique
All patients were given general anesthesia and caudal block. A vertical stay suture was taken on the tip of glans with prolene 5-0. Urethra was catheterized with an infant feeding tube. Tourniquet was applied in all cases at the base of penis over the skin. Two stay sutures were taken at the edge of the prepuce on lateral most part. A “U”-shaped incision was given around the meatal opening and extended on either side along the edge of the prepuce. Care was taken not to damage the spongiosum while taking skin incision. Cases where the perimeatal skin is thin and hypoplastic, U-shaped incision was taken, which starts from skin over normal ventral spongiosum so as to avoid damage to the underlying urethra.
Ventral skin was dissected proximally till we see the normal spongiosum. In cases where urethra was thin and hypoplastic, it was cut till normal urethra with normal corpus spongiosum. Then ventral dartos fascia was dissected on lateral aspect from the Buck's fascia and was left with the outer skin [Figure 1]. Corpus spongiosum which was splayed on either side [Figure 2] was dissected laterally from the Buck's fascia so as to get easy approximation of the corpus spongiosum in the midline. Keeping close to the margin of the urethral plate, glans wings were raised distally till the midglans level.
Figure 1.
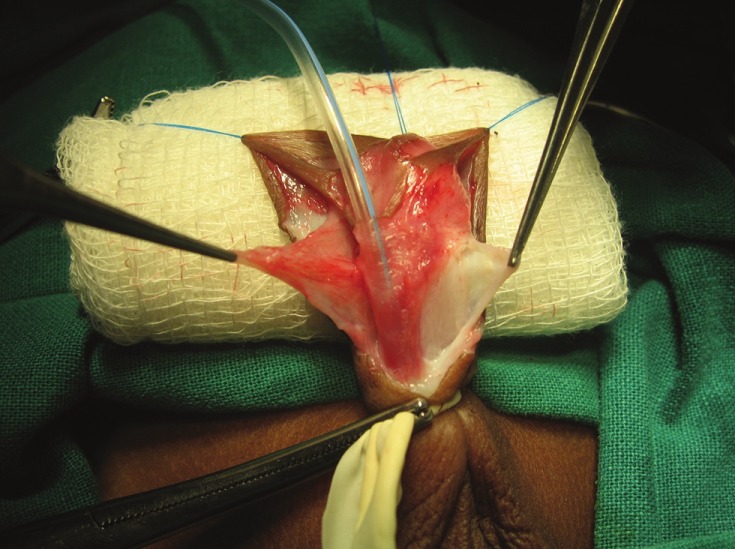
Ventral dartos fascia was dissected
Figure 2.

Splayed corpus spongiosum on either side
Stay suture was taken on either side of the urethral plate about 5 mm proximal to distal end of urethral plate [Figure 3]. This helps to stretch urethral plate on either side and is also a marker for distal limit to construct urethral tube. With the knife a midline incision is taken on the urethral plate. Care was taken not to extend this incision up to tip of urethra distally. Proximally this incision is extended across urethral meatus on the normal urethra.
Figure 3.

Stay taken on urethral plate about 5 mm proximal to distal end of urethral plate
We start approximating corpus spongiosum in midline, starting few millimeters proximal to urethral meatus (to avoid narrowing of normal urethra at this level, midline urethral plate incision is extended within the normal urethra). While approximating corpus spongiosum in the midline with 6-0 polyglycolic acid continuous and locking sutures, edges of the urethral plate gets inverted. Special care was taken to avoid going through the edges of urethral plate [Figure 4]. Corpus spongiosum is approximated in the midline till 5 mm proximal to distal end of urethral plate [Figure 4]. Last suture at urethral plate was kept long after tying a knot.
Figure 4.

Spongioplasty by avoiding to go through the edges of urethral plate
Glansplasty was done in two layers. Initially distal stitch was taken and its knot is tied with left over suture of urethral plate. This stitch will fix the glans over the newly created urethral meatus.
Second layer of glansplasty done with vertical mattress sutures using 6-0 polyglycolic acid. Proximally raised glans wings were fixed from inside laterally on either side with corporal body, while taking this stitch, ventral dartos fascia is put within the proximal glans. This will avoid the retraction of glans and will take care of the bleeding from the raised glans wings.
After doing glansplasty preputial skin comes in midline. First inner prepuce was sutured in the midline by subcuticular continuous suture; then outer prepuce was approximated in the midline. Ventral dartos fascia was sutured in the midline to cover the urethral repair, which will act as a barrier layer to prevent fistula formation. Finally ventral penile skin is sutured in the midline, tourniquet was released. At the end, reconstructed prepuce was retracted over the glans, in case of difficulty in retracting the prepuce over glans, dorsal midline vertical skin incision was taken and then it was sutured transversely [Figure 5]. This dorsal slit incision prevents phimosis and allowed easy retraction of prepuce over glans. The mean operating time is 45 minutes.
Figure 5.

Dorsal midline incision taken and sutured transversely
Compression dressing using Elastoplast was given for 10 days. Dressing and catheter removed on 10th postoperative day. After removing the dressing, preputial edema becomes more in first week and then generally subsides by second week. Once edema subsided parents are advised to retract the prepuce slowly over the glans. Over the period of time, it gives an appearance of normal, uncircumcised prepuce [Figure 6].
Figure 6.
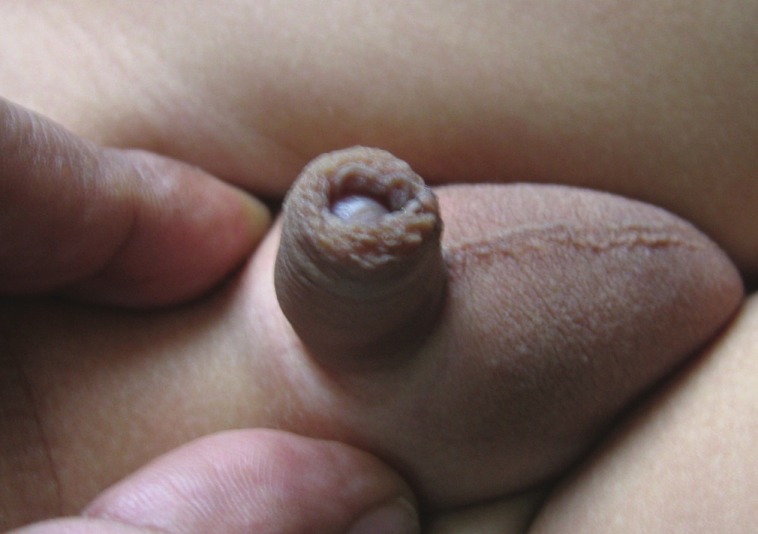
Prepuce after 6 months of preputioplasty
RESULTS
The follow-up period is between 3 months and 4 years (3 months to 48 months, average 23 months). In one case, there was complete dehiscence of prepuce. Fistula has developed in seven patients (sub glanular-1, sub coronal-3, mid penile-3) who required operative closure. In three patients, retraction of prepuce was not possible in the postoperative period so required circumcision. These were the cases, which were done in earlier period of the experience when we did not make the dorsal slit incision. Intraoperatively seven patients required dorsal slit. In cases having difficulty in retracting prepuce, application of steroid ointment helped in retracting the prepuce. One patient developed meatal stenosis. A total of 38 patients required steroid ointment application containing hydrocortisone (1% ointment). Whenever the urinary stream was thin, parents were asked to do meatal calibration with the infant feeding tube by a size less than what was used for urethral tubularization. Meatal calibration was done in 32 patients. Cosmetic appearance was acceptable. In patients with dorsal slit after a follow up of 6 months, a dorsal slit is visualized as a minor cleft dorsally in the prepuce but glans was well covered by prepuce all over giving an appearance of normal prepuce covering glans.
DISCUSSION
Since its introduction in 1994, tubularized incised plate urethroplasty by Snodgrass[1] is a most widely done procedure for distal penile hypospadias. We did some modifications in the original procedure reported by Snodgrass to address the issue of reported high incidence of meatal stenosis and to have uncircumcised prepuce.
When planning for preputioplasty, patient selection is very important. It is better to avoid preputioplasty for patients having significant penile torsion, which needs degloving to correct the torsion. While correcting penile torsion it is necessary to deglove the penis till the base; and after degloving, it is difficult to do preputioplasty and one may face more complications like preputial breakdown. Most of the distal hypospadias without chordee can be repaired by the Snodgrass technique and also subjected for preputioplasty.
In this Snodgrass urethroplasty with preputioplasty, there is no dorsal dissection; hence, dorsal dartos fascia cannot be used to cover the urethral repair as a barrier layer to prevent fistula formation. Snodgrass has also not reported increased incidence of fistula with preputioplasty.[2] We have experienced meatal stenosis in earlier part of practice where midline urethral plate incision was extended up to the tip of urethral plate. Nguyen[3] has addressed this problem by making the TIP incision first which is not extended up to the meatus; he incises that portion of urethral plate which is little narrow. Jayanti[4] tubularized urethra from distal to proximal. Preputioplasty has been done in three to four layers by different surgeons.[2,5–7] We have sutured prepuce in two layers with subcuticular sutures of vicryl 6-0. At the end of preputioplasty, if we find difficult to retract newly constructed prepuce over the glans then dorsal midline silt incision is given on the prepuce and it is sutured transversely. This has reduced postoperative phimosis and difficulty in retracting the prepuce. Some have advocated retraction of prepuce after 3 to 10 weeks[2] depending upon the healing of sutures. Application of steroid-based ointment helps to reduce the edema and it also helps to retract the prepuce easily over the glans. We recommend application of steroid-based ointment in all patients after 2 weeks and advocate retraction of prepuce after 3 weeks once preputial edema settles. Overall preputioplasty gives an uncircumcised normal looking penis, as desired by parents.
We feel meatal stenosis can be reduced by: (1) not extending the midline urethral plate incision up to the distal end of urethral plate, one should never go across urethral plate on to the distal glans. (2) Raising the glans wings only up to the mid glans level. (3) While converting urethral plate into the tube, stop at least 5 mm proximal from the tip, do not convert urethral plate into a tube up to its distal end.
Corpus spongiosum being good vascular and thick structure, it is easy to take good suture bites to approximate spongiosum in midline. Suturing corpus spongiosum alone without taking edges of urethral plate is enough to roll urethral plate into a tube. By this technique we had fistula rate comparable to series reported by Snodgrass where he has used dorsal dartos fascia to cover urethral repair.
CONCLUSIONS
Midline approximation of corpus spongiosum is enough to convert urethral plate into a tube, without taking actual sutures through the edges of urethral plate. Modified tubularized incised plate urethroplasty with preputioplasty effectively gives cosmetically normal looking penis with low complications. However, long-term follow-up and double blind trial will establish the results.
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: No
REFERENCES
- 1.Snodgrass W. Tubularized, incised plate urethroplasty for distal hypospadias. J Urol. 1994;151:464–5. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)34991-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Snodgrass W, Koyle M, Baskin L, Caldamone A. Foreskin preservation in penile surgery. J Urol. 2006;176:711–4. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2006.03.082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Nguyen MT, Snodgrass WT, Zaontz Effect of urethral plate characteristics on tubularized incised plate urethroplasty. J Urol. 2004;171:1260–2. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000110426.32005.91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Jayanthi VR. The modified Snodgrass hypospadias repair: Reducing the risk of fistula and meatal stenosis. J Urol. 2003;170:1603–5. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000085260.52825.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Erdenetsetseg G, Dewan PA. Reconstruction of the hypospadiac hooded prepuce. J Urol. 2003;169:1822–4. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000062320.34774.09. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Johnson D, Coleman DJ. The selective use of a single stage and a two stage technique for hypospadias correction in 157 consecutive cases with aim of normal appearance and function. Br J Plast Surg. 1998;51:195–201. doi: 10.1016/s0007-1226(98)80009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Klijn AJ, Dik P, De Jong TP. Results of Preputial reconstruction in 77 boys with distal hypospadias. J Urol. 2001;165:1255–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


