Abstract
Relatively little is known about the damage suffered by transfected DNA molecules during their journey from outside the cell into the nucleus. To follow selectively the minor subpopulation that completes this journey, we devised a genetic approach using simian virus 40 DNA transfected with DEAE-dextran. We investigated this active subpopulation in three ways: (i) by assaying reciprocal pairs of mutant linear dimers which differed only in the arrangement of two mutant genomes; (ii) by assaying a series of wild-type oligomers which ranged from 1.1 to 2.0 simian virus 40 genomes in length; and (iii) by assaying linear monomers of simian virus 40 which were cleaved within a nonessential region to leave either sticky, blunt, or mismatched ends. We conclude from these studies that transfected DNA molecules in the active subpopulation are moderately damaged by fragmentation and modification of ends. As a whole, the active subpopulation suffers about one break per 5 to 15 kilobases, and about 15 to 20% of the molecules have one or both ends modified. Our analysis of fragmentation is consistent with the random introduction of double-strand breaks, whose cause and exact nature are unknown. Our analysis of end modification indicated that the most prevalent form of damage involved deletion or addition of less than 25 base pairs. In addition we demonstrated directly that the efficiencies of joining sticky, blunt, or mismatched ends are identical, verifying the apparent ability of cells to join nearly any two DNA ends and suggesting that the efficiency of joining approaches 100%. The design of these experiments ensured that the detected damage preceded viral replication and thus should be common to all DNAs transfected with DEAE-dextran and not specific for viral DNA. These measurements of damage within transfected DNA have important consequences for studies of homologous and nonhomologous recombination in somatic cells as is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R. A., Krakauer T., Camerini-Otero R. D. DNA-mediated gene transfer: recombination between cotransferred DNA sequences and recovery of recombinants in a plasmid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2748–2752. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Cancer genes come of age. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1018–1020. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90284-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botchan M., Stringer J., Mitchison T., Sambrook J. Integration and excision of SV40 DNA from the chromosome of a transformed cell. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):143–152. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90242-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calos M. P., Lebkowski J. S., Botchan M. R. High mutation frequency in DNA transfected into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3015–3019. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler V. L., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. DNA sequences bound specifically by glucocorticoid receptor in vitro render a heterologous promoter hormone responsive in vivo. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):489–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowley C. W., Liu C. C., Levinson A. D. Plasmid-directed synthesis of hepatitis B surface antigen in monkey cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;3(1):44–55. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.1.44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierks P., van Ooyen A., Cochran M. D., Dobkin C., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Three regions upstream from the cap site are required for efficient and accurate transcription of the rabbit beta-globin gene in mouse 3T6 cells. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):695–706. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folger K. R., Wong E. A., Wahl G., Capecchi M. R. Patterns of integration of DNA microinjected into cultured mammalian cells: evidence for homologous recombination between injected plasmid DNA molecules. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;2(11):1372–1387. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.11.1372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Construction of influenza haemagglutinin genes that code for intracellular and secreted forms of the protein. Nature. 1982 Dec 16;300(5893):598–603. doi: 10.1038/300598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodenow R. S., McMillan M., Nicolson M., Sher B. T., Eakle K., Davidson N., Hood L. Identification of the class I genes of the mouse major histocompatibility complex by DNA-mediated gene transfer. Nature. 1982 Nov 18;300(5889):231–237. doi: 10.1038/300231a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutai M. W., Nathans D. Evolutionary variants of simian virus 40: Cellular DNA sequences and sequences at recombinant joints of substituted variants. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 5;126(2):275–288. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90363-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D., Lane D., Lipsich L., Wigler M., Botchan M. Characteristics of an SV40-plasmid recombinant and its movement into and out of the genome of a murine cell. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):127–139. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90120-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard B. V., Estes M. K., Pagano J. S. The uptake of SV40 DNA by nonpermissive cells in the presence of DEAE-dextran. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Jan 1;228(1):105–116. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(71)90550-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israel M. A., Byrne J. C., Martin M. A. Biologic activity of oligomeric forms of SV40 DNA. Virology. 1978 Jun 15;87(2):239–246. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90129-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaenisch R., Levine A. J. Infection of primary African green monkey cells with SV40 monomeric and dimeric DNA. J Mol Biol. 1971 Nov 14;61(3):735–738. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90076-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury G., Gruss P. Enhancer elements. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):313–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90410-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kratzer P. G., Chapman V. M., Lambert H., Evans R. E., Liskay R. M. Differences in the DNA of the inactive X chromosomes of fetal and extraembryonic tissues of mice. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):37–42. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90332-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. J., Nathans D. A map of temperature-sensitive mutants of simian virus 40. Virology. 1975 Jul;66(1):70–81. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90179-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebeurier G., Hirth L., Hohn B., Hohn T. In vivo recombination of cauliflower mosaic virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2932–2936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loyter A., Scangos G. A., Ruddle F. H. Mechanisms of DNA uptake by mammalian cells: fate of exogenously added DNA monitored by the use of fluorescent dyes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):422–426. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCutchan J. H., Pagano J. S. Enchancement of the infectivity of simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid with diethylaminoethyl-dextran. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1968 Aug;41(2):351–357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. K., Temin H. M. High-efficiency ligation and recombination of DNA fragments by vertebrate cells. Science. 1983 May 6;220(4597):606–609. doi: 10.1126/science.6301012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Factors governing the expression of a bacterial gene in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 May;1(5):449–459. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.5.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neff N. F., Thomas J. H., Grisafi P., Botstein D. Isolation of the beta-tubulin gene from yeast and demonstration of its essential function in vivo. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):211–219. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90350-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perucho M., Hanahan D., Wigler M. Genetic and physical linkage of exogenous sequences in transformed cells. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):309–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90178-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pipas J. M., Peden K. W., Nathans D. Mutational analysis of simian virus 40 T antigen: isolation and characterization of mutants with deletions in the T-antigen gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):203–213. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulciani S., Santos E., Lauver A. V., Long L. K., Aaronson S. A., Barbacid M. Oncogenes in solid human tumours. Nature. 1982 Dec 9;300(5892):539–542. doi: 10.1038/300539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Razzaque A., Mizusawa H., Seidman M. M. Rearrangement and mutagenesis of a shuttle vector plasmid after passage in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3010–3014. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy E. P., Reynolds R. K., Santos E., Barbacid M. A point mutation is responsible for the acquisition of transforming properties by the T24 human bladder carcinoma oncogene. Nature. 1982 Nov 11;300(5888):149–152. doi: 10.1038/300149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins D. M., Ripley S., Henderson A. S., Axel R. Transforming DNA integrates into the host chromosome. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):29–39. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90267-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruley H. E., Fried M. Clustered illegitimate recombination events in mammalian cells involving very short sequence homologies. Nature. 1983 Jul 14;304(5922):181–184. doi: 10.1038/304181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santangelo G. M., Cole C. N. Preparation of a "functional library" of African green monkey DNA fragments which substitute for the processing/polyadenylation signal in the herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):643–653. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W. Direct transfer of cloned genes from bacteria to mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2163–2167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small J., Scangos G. Recombination during gene transfer into mouse cells can restore the function of deleted genes. Science. 1983 Jan 14;219(4581):174–176. doi: 10.1126/science.6294829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer J. R. DNA sequence homology and chromosomal deletion at a site of SV40 DNA integration. Nature. 1982 Mar 25;296(5855):363–366. doi: 10.1038/296363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer J. R. Integrated simian virus 40 DNA: nucleotide sequences at cell-virus recombinant junctions. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):671–679. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.671-679.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramani S., Berg P. Homologous and nonhomologous recombination in monkey cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1040–1052. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian K. N. Segments of simian virus 40 DNA spanning most of the leader sequence of the major late viral messenger RNA are dispensable. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2556–2560. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2556. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabin C. J., Bradley S. M., Bargmann C. I., Weinberg R. A., Papageorge A. G., Scolnick E. M., Dhar R., Lowy D. R., Chang E. H. Mechanism of activation of a human oncogene. Nature. 1982 Nov 11;300(5888):143–149. doi: 10.1038/300143a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis: the viral replicon. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):591–598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.591-598.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upcroft P., Carter B., Kidson C. Analysis of recombination in mammalian cells using SV40 genome segments having homologous overlapping termini. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jun 25;8(12):2725–2736. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.12.2725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upcroft P., Carter B., Kidson C. Mammalian cell function mediating recombination of genetic elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5835–5844. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkert F. C., Young C. S. The genetic analysis of recombination using adenovirus overlapping terminal DNA fragments. Virology. 1983 Feb;125(1):175–193. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake C. T., Wilson J. H. Defined oligomeric SV40 DNA: a sensitive probe of general recombination in somatic cells. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90121-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wake C. T., Wilson J. H. Simian virus 40 recombinants are produced at high frequency during infection with genetically mixed oligomeric DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2876–2880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. A dominant role for DNA secondary structure in forming hypersensitive structures in chromatin. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1191–1203. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90302-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
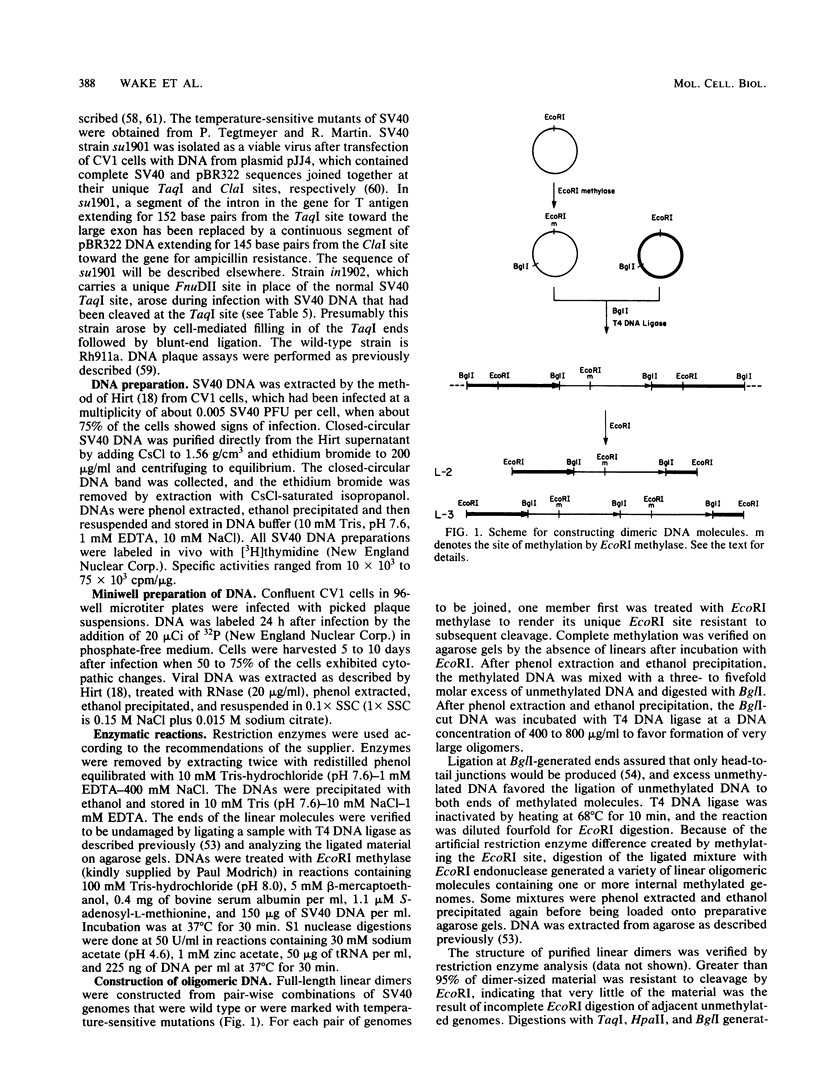
- Wieringa B., Meyer F., Reiser J., Weissmann C. Unusual splice sites revealed by mutagenic inactivation of an authentic splice site of the rabbit beta-globin gene. Nature. 1983 Jan 6;301(5895):38–43. doi: 10.1038/301038a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M. H. The inheritance of methylation patterns in vertebrates. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):285–286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90317-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. H., Berget P. B., Pipas J. M. Somatic cells efficiently join unrelated DNA segments end-to-end. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;2(10):1258–1269. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.10.1258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. H., DePamphilis M., Berg P. Simian virus 40-permissive cell interactions: selection and characterization of spontaneously arising monkey cells that are resistant to simian virus 40 infection. J Virol. 1976 Nov;20(2):391–399. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.2.391-399.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. H. Genetic analysis of host range mutant viruses suggests an uncoating defect in simian virus 40-resistant monkey cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3503–3507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. H. Interference in SV40 DNA infections: a possible basis for cellular competence. Virology. 1978 Dec;91(2):380–388. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90385-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winocour E., Keshet I. Indiscriminate recombination in simian virus 40-infected monkey cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4861–4865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodworth-Gutai M. Recombination in SV40-infected cells: viral DNA sequences at sites of circularization of transfecting linear DNA. Virology. 1981 Mar;109(2):353–365. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90506-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Saint Vincent B. R., Wahl G. M. Homologous recombination in mammalian cells mediates formation of a functional gene from two overlapping gene fragments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):2002–2006. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]