Abstract
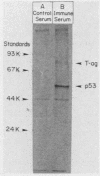
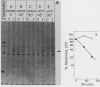
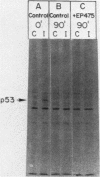
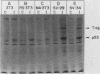
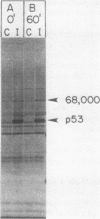
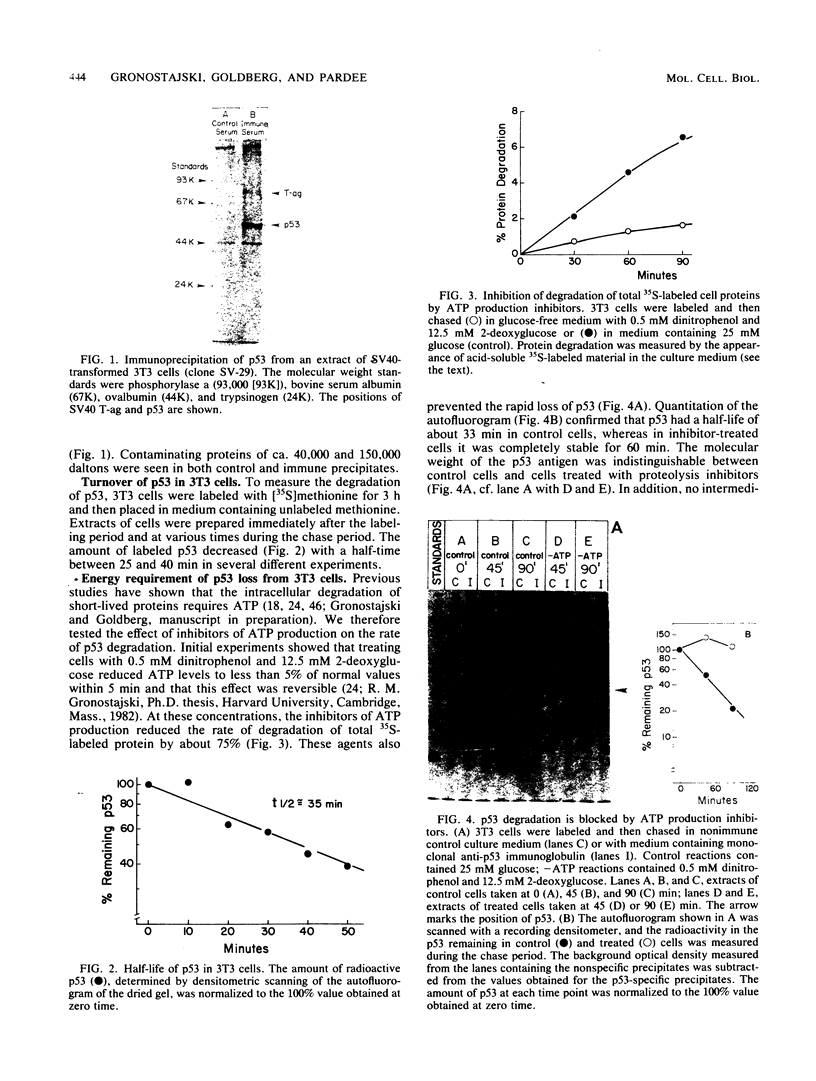
A 53,000-dalton protein (p53) present in large amounts in several types of tumorigenic cells was rapidly degraded in nontumorigenic BALB/c 3T3 fibroblasts (t 1/2, approximately 0.5 h) but not in tumorigenic methylcholanthrene-induced mouse sarcoma cells (t 1/2, greater than 2 h). In 3T3 cells, dinitrophenol and 2-deoxyglucose, agents which reduce ATP production, inhibited the rapid degradation of p53 and the slower breakdown of total cell protein. After removal of these agents, the degradation of both p53 and total cell proteins resumed at their normal rates. Inhibitors of intralysosomal proteolysis (Ep475 and chloroquine) did not reduce the rate of degradation of p53. Thus, in 3T3 cells, p53 appears to be degraded by a nonlysosomal, ATP-dependent proteolytic system similar to that previously shown to degrade short- and long-lived proteins in growing fibroblasts. The immunoreactive p53 which remained in ATP-depleted cells had the same molecular weight as the p53 in the control cells. No intermediate products of p53 degradation were detected by immunoprecipitation in either ATP-depleted or control cells. Hence, ATP seems to be required for an initial step in the degradation of p53. Although the amount of labeled p53 was increased in simian virus 40-transformed and methylcholanthrene-induced mouse sarcoma cells, the amount of p53 labeled during a 3-h pulse in Moloney virus- and Rous sarcoma virus-transformed cells and untransformed 3T3 cells was similar. Thus, an increased net rate of p53 accumulation is not a common feature of transformed tumorigenic cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson S. A., Rowe S. P. Nonproducer clones of murine sarcoma virus transformed BALB-3T3 cells. Virology. 1970 Sep;42(1):9–19. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90233-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett A. J., Kembhavi A. A., Hanada K. E-64 [L-trans-epoxysuccinyl-leucyl-amido(4-guanidino)butane] and related epoxides as inhibitors of cysteine proteinases. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1981;40(10-11):1513–1517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benchimol S., Pim D., Crawford L. Radioimmunoassay of the cellular protein p53 in mouse and human cell lines. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1055–1062. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01296.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botbol V., Scornik O. A. Degradation of abnormal proteins in intact mouse reticulocytes: accumulation of intermediates in the presence of bestatin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):710–713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Botbol V., Scornik O. A. Intermediates in the degradation of abnormal globin. Bestatin permits the accumulation of the same peptides in cell-free extracts as in intact reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 25;254(22):11254–11257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campisi J., Medrano E. E., Morreo G., Pardee A. B. Restriction point control of cell growth by a labile protein: evidence for increased stability in transformed cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):436–440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandrasekaran K., McFarland V. W., Simmons D. T., Dziadek M., Gurney E. G., Mora P. T. Quantitation and characterization of a species-specific and embryo stage-dependent 55-kilodalton phosphoprotein also present in cells transformed by simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6953–6957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Phillips A. H. Evidence for rapid turnover of hepatic endoplasmic reticulum and its possible relationship to secretion. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):3103–3111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke G. D., Stoker M. G., Ludlow A., Thornton M. Requirement of serum for DNA synthesis in BHK 21 cells: effects of density, suspension and virus transformation. Nature. 1970 Aug 22;227(5260):798–801. doi: 10.1038/227798a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Weissman I. L. A monoclonal antibody that recognizes B cells and B cell precursors in mice. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):269–279. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford L. V., Pim D. C., Gurney E. G., Goodfellow P., Taylor-Papadimitriou J. Detection of a common feature in several human tumor cell lines--a 53,000-dalton protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):41–45. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford L., Leppard K., Lane D., Harlow E. Cellular proteins reactive with monoclonal antibodies directed against simian virus 40 T-antigen. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):612–620. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.612-620.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croy R. G., Pardee A. B. Enhanced synthesis and stabilization of Mr 68,000 protein in transformed BALB/c-3T3 cells: candidate for restriction point control of cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4699–4703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLeo A. B., Jay G., Appella E., Dubois G. C., Law L. W., Old L. J. Detection of a transformation-related antigen in chemically induced sarcomas and other transformed cells of the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2420–2424. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLeo A. B., Shiku H., Takahashi T., John M., Old L. J. Cell surface antigens of chemically induced sarcomas of the mouse. I. Murine leukemia virus-related antigens and alloantigens on cultured fibroblasts and sarcoma cells: description of a unique antigen on BALB/c Meth A sarcoma. J Exp Med. 1977 Sep 1;146(3):720–734. doi: 10.1084/jem.146.3.720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etlinger J. D., Goldberg A. L. A soluble ATP-dependent proteolytic system responsible for the degradation of abnormal proteins in reticulocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):54–58. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrels J. I. Two dimensional gel electrophoresis and computer analysis of proteins synthesized by clonal cell lines. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7961–7977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. L., St John A. C. Intracellular protein degradation in mammalian and bacterial cells: Part 2. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:747–803. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney E. G., Harrison R. O., Fenno J. Monoclonal antibodies against simian virus 40 T antigens: evidence for distinct sublcasses of large T antigen and for similarities among nonviral T antigens. J Virol. 1980 Jun;34(3):752–763. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.3.752-763.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harlow E., Pim D. C., Crawford L. V. Complex of simian virus 40 large-T antigen and host 53,000-molecular-weight protein in monkey cells. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):564–573. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.564-573.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashida S., Towatari T., Kominami E., Katunuma N. Inhibitions by E-64 derivatives of rat liver cathepsin B and cathepsin L in vitro and in vivo. J Biochem. 1980 Dec;88(6):1805–1811. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Eytan E., Ciechanover A., Haas A. L. Immunochemical analysis of the turnover of ubiquitin-protein conjugates in intact cells. Relationship to the breakdown of abnormal proteins. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):13964–13970. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershko A., Tomkins G. M. Studies on the degradation of tyrosine aminotransferase in hepatoma cells in culture. Influence of the composition of the medium and adenosine triphosphate dependence. J Biol Chem. 1971 Feb 10;246(3):710–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemes Y., Etlinger J. D., Goldberg A. L. Properties of abnormal proteins degraded rapidly in reticulocytes. Intracellular aggregation of the globin molecules prior to hydrolysis. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8436–8444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowit J. D., Goldberg A. L. Intermediate steps in the degradation of a specific abnormal protein in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1977 Dec 10;252(23):8350–8357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Crawford L. V. T antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):261–263. doi: 10.1038/278261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Hoeffler W. K. SV40 large T shares an antigenic determinant with a cellular protein of molecular weight 68,000. Nature. 1980 Nov 13;288(5787):167–170. doi: 10.1038/288167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Levine A. J. Characterization of a 54K dalton cellular SV40 tumor antigen present in SV40-transformed cells and uninfected embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Maltzman W., Levine A. J. Characterization of a murine cellular SV40 T antigen in SV40-transformed cells and uninfected embryonal carcinoma cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):215–224. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Maltzman W., Levine A. J. The SV40 A gene product is required for the production of a 54,000 MW cellular tumor antigen. Virology. 1979 Oct 30;98(2):308–318. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90554-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick F., Harlow E. Association of a murine 53,000-dalton phosphoprotein with simian virus 40 large-T antigen in transformed cells. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):213–224. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.213-224.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medrano E. E., Pardee A. B. Prevalent deficiency in tumor cells of cycloheximide-induced cycle arrest. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4123–4126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer W. E., Nelson D., DeLeo A. B., Old L. J., Baserga R. Microinjection of monoclonal antibody to protein p53 inhibits serum-induced DNA synthesis in 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6309–6312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milman G., Portnoff L. S., Tiemeier D. C. Immunochemical evidence for glutamine-mediated degradation of glutamine synthetase in cultured Chinese hamster cells. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1393–1399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mora P. T., Chandrasekaran K., Hoffman J. C., McFarland V. W. Quantitation of a 55K cellular protein: similar amount and instability in normal and malignant mouse cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jul;2(7):763–771. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.7.763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mora P. T., Chandrasekaran K., McFarland V. W. An embryo protein induced by SV40 virus transformation of mouse cells. Nature. 1980 Dec 25;288(5792):722–724. doi: 10.1038/288722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neff N. T., DeMartino G. N., Goldberg A. L. The effect of protease inhibitors and decreased temperature on the degradation of different classes of proteins in cultured hepatocytes. J Cell Physiol. 1979 Dec;101(3):439–457. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041010311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren M., Maltzman W., Levine A. J. Post-translational regulation of the 54K cellular tumor antigen in normal and transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;1(2):101–110. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.2.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren M., Reich N. C., Levine A. J. Regulation of the cellular p53 tumor antigen in teratocarcinoma cells and their differentiated progeny. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;2(4):443–449. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.4.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oshiro Y., DiPaolo J. A. Changes in the uptake of 2-deoxy-D-glucose in BALB-3T3 cells chemically transformed in culture. J Cell Physiol. 1974 Apr;83(2):193–201. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040830205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. A restriction point for control of normal animal cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1286–1290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B., Campisi J., Croy R. G. Differences in growth regulation of normal and tumor cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982 Dec 10;397:121–129. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb43422.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prouty W. F. Degradation of abnormal proteins in HeLa cells. J Cell Physiol. 1976 Jul;88(3):371–382. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040880313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prouty W. F. Ornithine decarboxylase inactivation in HeLa cells. J Cell Physiol. 1976 Sep;89(1):65–76. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040890107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossow P. W., Riddle V. G., Pardee A. B. Synthesis of labile, serum-dependent protein in early G1 controls animal cell growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4446–4450. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter V., Boss M. A., Baltimore D. Increased concentration of an apparently identical cellular protein in cells transformed by either Abelson murine leukemia virus or other transforming agents. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):336–346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.336-346.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter V. p53, a transformation-related cellular-encoded protein, can be used as a biochemical marker for the detection of primary mouse tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2613–2617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscetti S. K., Scolnick E. M. Expression of a transformation-related protein (p53) in the malignant stage of Friend virus-induced diseases. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):1022–1026. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.1022-1026.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarnow P., Ho Y. S., Williams J., Levine A. J. Adenovirus E1b-58kd tumor antigen and SV40 large tumor antigen are physically associated with the same 54 kd cellular protein in transformed cells. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):387–394. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90356-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scher C. D., Nelson-Rees W. A. Direct isolation and characterization of "flat" SV40-transformed cells. Nat New Biol. 1971 Oct 27;233(43):263–265. doi: 10.1038/newbio233263a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider E. L., Stanbridge E. J., Epstein C. J. Incorporation of 3H-uridine and 3H-uracil into RNA: a simple technique for the detection of mycoplasma contamination of cultured cells. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Mar 15;84(1):311–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90411-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman C., Potash M. J., Köhler G. Roles of protein and carbohydrate in glycoprotein processing and secretion. Studies using mutants expressing altered IgM mu chains. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 25;256(24):13180–13187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sompayrac L. M., Gurney E. G., Danna K. J. Stabilization of the 53,000-dalton nonviral tumor antigen is not required for transformation by simian virus 40. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):290–296. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., De Larco J. E., Cohen S. Transformation by murine and feline sarcoma viruses specifically blocks binding of epidermal growth factor to cells. Nature. 1976 Nov 4;264(5581):26–31. doi: 10.1038/264026a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]