Abstract
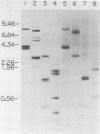
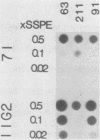
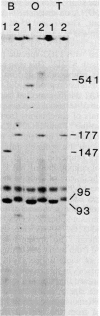
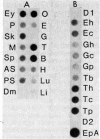
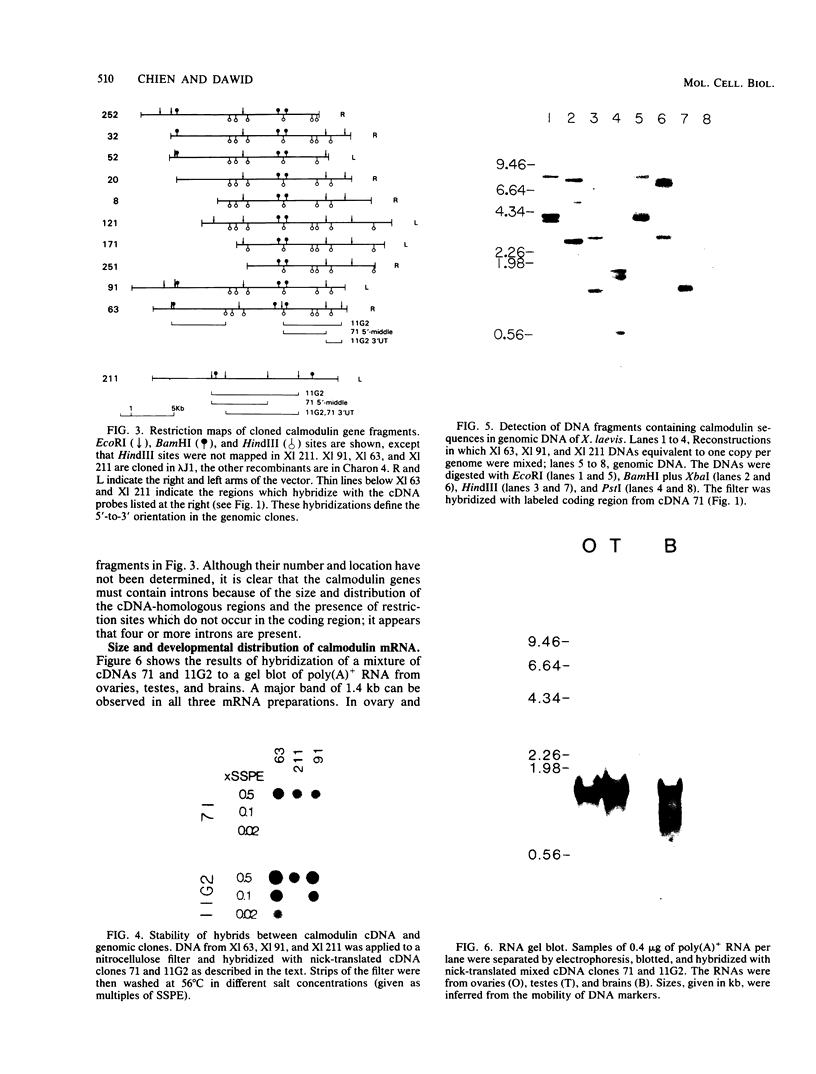
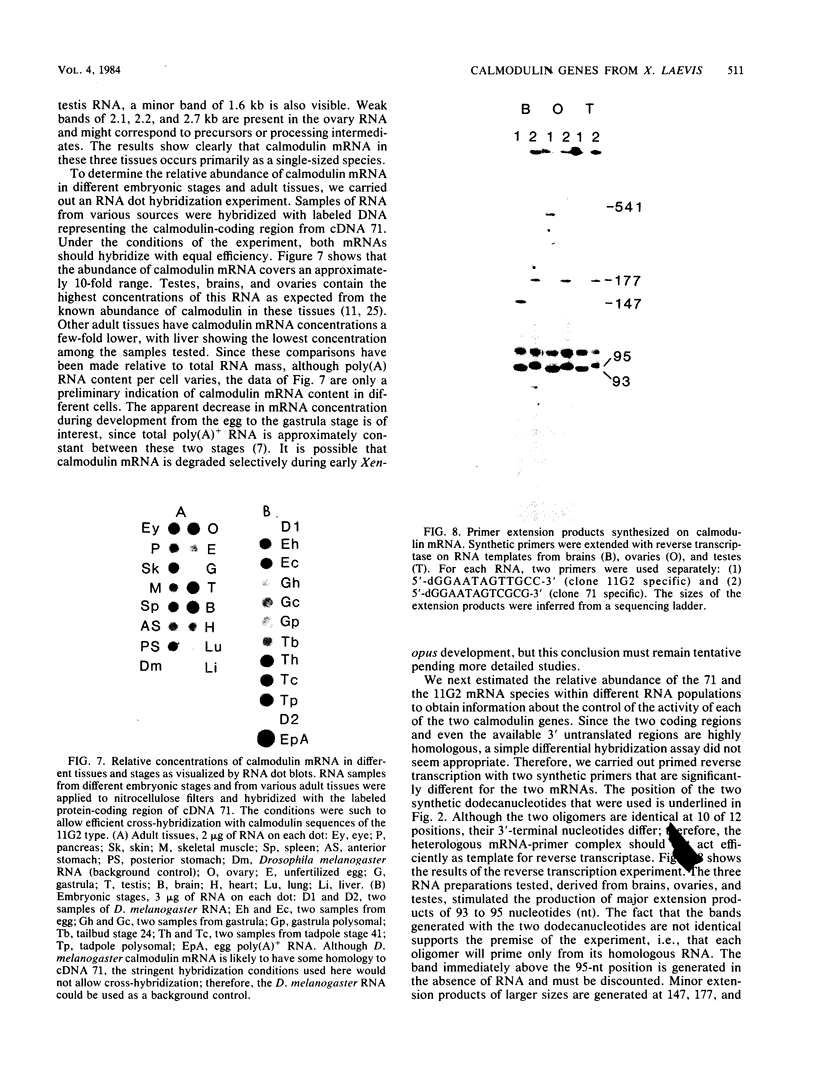
Two cDNAs derived from Xenopus laevis calmodulin mRNA have been cloned. Both cDNAs contain the complete protein-coding region and various lengths of untranslated segments. The two cDNAs encode an identical protein but differ from each other by 5% nucleotide substitutions. The 5' and 3' untranslated regions, to the extent available, are highly homologous between the two cDNAs. The predicted sequence of X. laevis calmodulin is identical to that of vertebrate calmodulins from mammals and chickens and shows one substitution compared with electric eel calmodulin. Genomic DNA sequences homologous to each of the two cDNA clones have been isolated and were shown to account for the major calmodulin-coding DNA sequences in X. laevis. These data suggest that X. laevis carries two active, nonallelic calmodulin genes. Although no complete analysis has been carried out, it appears that the X. laevis calmodulin genes are interrupted by at least four introns. The relative concentrations of calmodulin mRNA have been estimated in different embryonic stages and adult tissues and found to vary by up to a factor of 10. The highest levels of calmodulin mRNA were found in ovaries, testes, and brains. In these three tissues, the two calmodulin genes appear to be expressed at approximately equal levels.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. M., Richter J. D., Chamberlin M. E., Price D. H., Britten R. J., Smith L. D., Davidson E. H. Sequence organization of the poly(A) RNA synthesized and accumulated in lampbrush chromosome stage Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Mol Biol. 1982 Mar 5;155(3):281–309. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90006-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisbee C. A., Baker M. A., Wilson A. C., Haji-Azimi I., Fischberg M. Albumin phylogeny for clawed frogs (Xenopus). Science. 1977 Feb 25;195(4280):785–787. doi: 10.1126/science.65013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartaud A., Ozon R., Walsh M. P., Haiech J., Demaille J. G. Xenopus laevis oocyte calmodulin in the process of meiotic maturation. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9404–9408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabtree G. R., Kant J. A. Molecular cloning of cDNA for the alpha, beta, and gamma chains of rat fibrinogen. A family of coordinately regulated genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Sep 25;256(18):9718–9723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enea V., Zinder N. D. Guanidinium-CsCl density gradients for isopycnic analysis of nucleic acids. Science. 1975 Nov 7;190(4214):584–586. doi: 10.1126/science.1188358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosbach H. A., Wyler T., Weber R. The Xenopus laevis globin gene family: chromosomal arrangement and gene structure. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):45–53. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90495-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Vanaman T. C. Calmodulin. Adv Protein Chem. 1982;35:213–321. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60470-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagacé L., Chandra T., Woo S. L., Means A. R. Identification of multiple species of calmodulin messenger RNA using a full length complementary DNA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1684–1688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May F. E., Weber R., Westley B. R. Isolation and characterisation of the Xenopus laevis albumin genes: loss of 74K albumin gene sequences by library amplification. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2791–2807. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munjaal R. P., Chandra T., Woo S. L., Dedman J. R., Means A. R. A cloned calmodulin structural gene probe is complementary to DNA sequences from diverse species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putkey J. A., Ts'ui K. F., Tanaka T., Lagacé L., Stein J. P., Lai E. C., Means A. R. Chicken calmodulin genes. A species comparison of cDNA sequences and isolation of a genomic clone. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11864–11870. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sargent T. D., Dawid I. B. Differential gene expression in the gastrula of Xenopus laevis. Science. 1983 Oct 14;222(4620):135–139. doi: 10.1126/science.6688681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasagawa T., Ericsson L. H., Walsh K. A., Schreiber W. E., Fischer E. H., Titani K. Complete amino acid sequence of human brain calmodulin. Biochemistry. 1982 May 11;21(10):2565–2569. doi: 10.1021/bi00539a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. P., Munjaal R. P., Lagace L., Lai E. C., O'Malley B. W., Means A. R. Tissue-specific expression of a chicken calmodulin pseudogene lacking intervening sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6485–6489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Eldik L. J., Zendegui J. G., Marshak D. R., Watterson D. M. Calcium-binding proteins and the molecular basis of calcium action. Int Rev Cytol. 1982;77:1–61. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62463-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W., Dawid I. B. Isolation of two closely related vitellogenin genes, including their flanking regions, from a Xenopus laevis gene library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1437–1441. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W., Dawid I. B., Ryffel G. U., Weber R. Vitellogenesis and the vitellogenin gene family. Science. 1981 Apr 17;212(4492):298–304. doi: 10.1126/science.7209528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahli W., Dawid I. B., Wyler T., Jaggi R. B., Weber R., Ryffel G. U. Vitellogenin in Xenopus laevis is encoded in a small family of genes. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):535–549. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watterson D. M., Sharief F., Vanaman T. C. The complete amino acid sequence of the Ca2+-dependent modulator protein (calmodulin) of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1980 Feb 10;255(3):962–975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]