Abstract
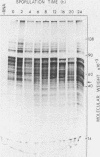
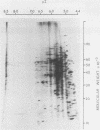
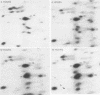
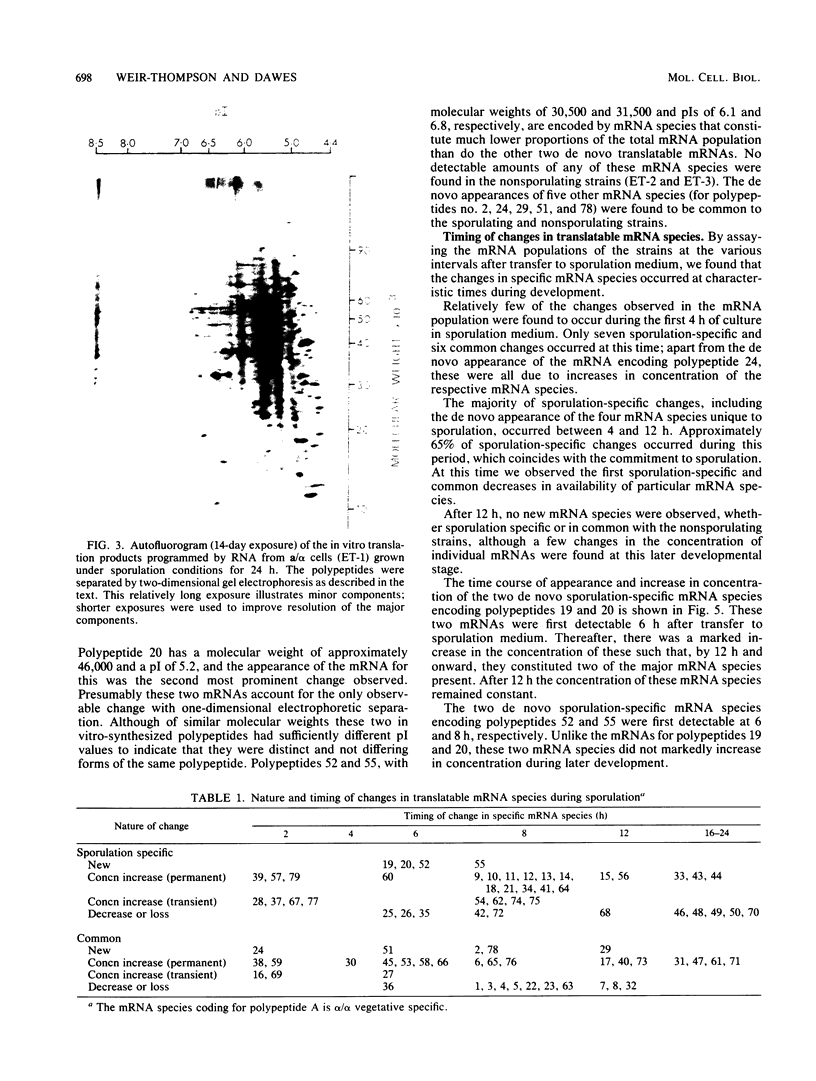
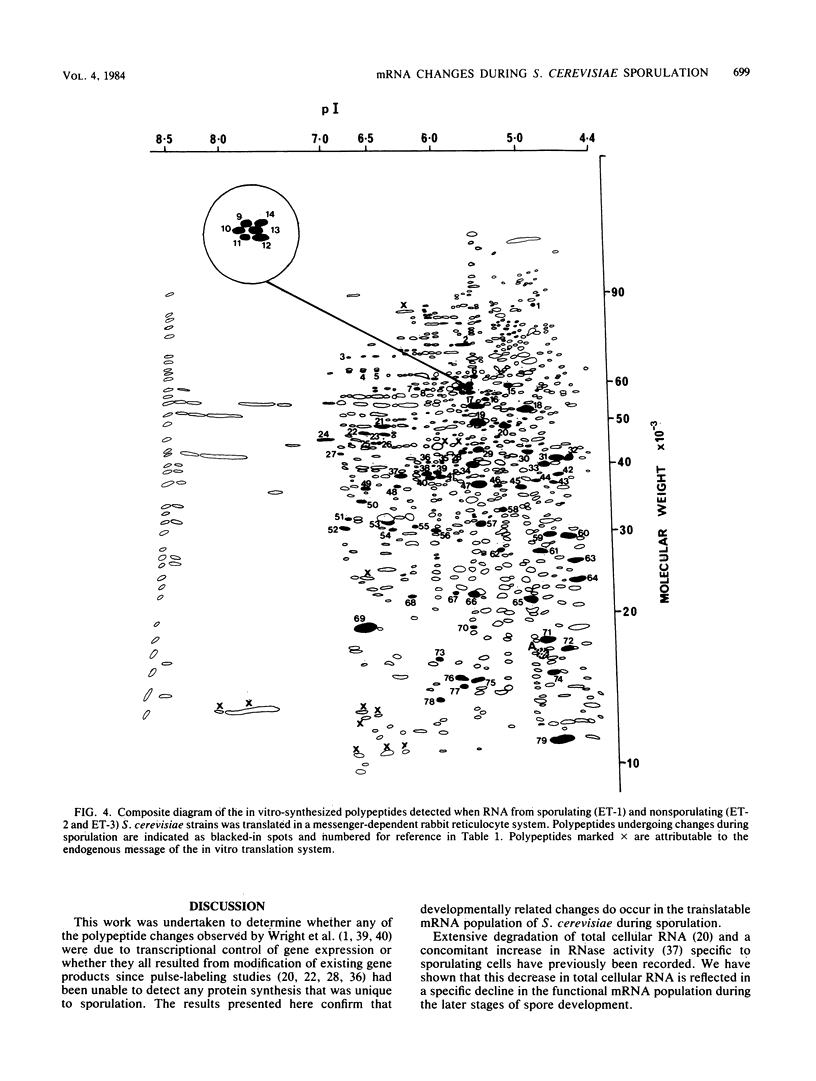
During Saccharomyces cerevisiae sporulation distinct changes in translatable mRNA species have been detected by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of the polypeptides produced in a messenger-dependent, cell-free rabbit reticulocyte lysate primed with RNA prepared from a/alpha, a/a, and alpha/alpha isogenic diploids at different stages of sporulation. The availability of functional mRNA increased by about 25% during the first 4 h after transfer of either sporulating (a/alpha), or nonsporulating (a/a and alpha/alpha) diploids to sporulation medium. Thereafter functional mRNA decreased such that in the a/alpha strain after 24 h there was only about 50% of the amount in vegetative cells; a less marked decrease was observed in the a/a and alpha/alpha strains. Of 750 mRNA species detected, 43 underwent alterations only during sporulation in the a/alpha strain, whereas 36 changes were common to all three strains and one mRNA specific to alpha/alpha vegetative cells was detected. Only four of the sporulation-specific changes were due to the de novo appearance of translatable species, and two of these became predominant species of the total population. The majority of the specific changes were due to either permanent or transient increases in the concentration of individual mRNA species; 11 decreases were found. Changes were found at most stages of sporulation, although many occurred in either of two stages, one early (before 2 h) and the other later (between 6 and 8 h) when commitment to meiotic segregation was beginning. The results provide evidence for both quantitative and, to a lesser extent, qualitative transcriptional control of gene expression during sporulation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beckett A., Illingworth R. F., Rose A. H. Ascospore wall development in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):1054–1057. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.1054-1057.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briley M. S., Illingworth R. F., Rose A. H., Fisher D. J. Evidence for a surface protein layer on the Saccharomyces cerevisiae ascospore. J Bacteriol. 1970 Oct;104(1):588–589. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.1.588-589.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaffin W. L., Sogin S. J., Halvorson H. O. Nature of ribonucleic acid synthesis during early sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1974 Nov;120(2):872–879. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.2.872-879.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen A. W., Miller J. J. Proteolytic activity of intact yeast cells during sporulation. Can J Microbiol. 1968 Sep;14(9):957–963. doi: 10.1139/m68-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy M. J., Buten-Magee B., Straight D. J., Kennedy A. L., Partridge R. M., Magee P. T. Isolation of genes expressed preferentially during sporulation in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3000–3004. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clancy M. J., Smith L. M., Magee P. T. Developmental regulation of a sporulation-specific enzyme activity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Feb;2(2):171–178. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.2.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonna W. J., Magee P. T. Glycogenolytic enzymes in sporulating yeast. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):844–853. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.844-853.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croes A. F. Duplication of DNA during meiosis in baker's yeast. Exp Cell Res. 1966 Feb;41(2):452–454. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(66)80151-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawes I. W., Donaldson S., Edwards R., Dawes J. Synthesis of a spore-specific surface antigen during sporulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Gen Microbiol. 1983 Apr;129(4):1103–1108. doi: 10.1099/00221287-129-4-1103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito M. S., Esposito R. E., Arnaud M., Halvorson H. O. Acetate utilization and macromolecular synthesis during sporulation of yeast. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):180–186. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.180-186.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito R. E., Esposito M. S. Genetic recombination and commitment to meiosis in Saccharomyces. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3172–3176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esposito R. E., Frink N., Bernstein P., Esposito M. S. The genetic control of sporulation in Saccharomyces. II. Dominance and complementation of mutants of meiosis and spore formation. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;114(3):241–248. doi: 10.1007/BF01788893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fast D. Sporulation synchrony of Saccharomyces cerevisiae grown in various carbon sources. J Bacteriol. 1973 Nov;116(2):925–930. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.2.925-930.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guth E., Hashimoto T., Conti S. F. Morphogenesis of ascospores in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):869–880. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.869-880.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopper A. K., Magee P. T., Welch S. K., Friedman M., Hall B. D. Macromolecule synthesis and breakdown in relation to sporulation and meiosis in yeast. J Bacteriol. 1974 Aug;119(2):619–628. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.2.619-628.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klar A. J., Halvorson H. O. Proteinase activities of Saccharomyces cerevisiae during sporulation. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):863–869. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.863-869.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraig E., Haber J. E. Messenger ribonucleic acid and protein metabolism during sporulation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1980 Dec;144(3):1098–1112. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.3.1098-1112.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee P. T., Hopper A. K. Protein synthesis in relation to sporulation and meiosis in yeast. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):952–960. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.952-960.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schild D., Byers B. Meiotic effects of DNA-defective cell division cycle mutations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Chromosoma. 1978 Dec 21;70(1):109–130. doi: 10.1007/BF00292220. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shilo V., Simchen G., Shilo B. Initiation of meiosis in cell cycle initiation mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Mar 15;112(2):241–248. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90206-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simchen G. Are mitotic functions required in meiosis? Genetics. 1974 Apr;76(4):745–753. doi: 10.1093/genetics/76.4.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simchen G., Piñon R., Salts Y. Sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: premeiotic DNA synthesis, readiness and commitment. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Nov;75(1):207–218. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90538-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider I. J., Miller J. J. A serological comparison of vegetative cell and ascus walls and the spore coat of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Can J Microbiol. 1966 Jun;12(3):485–488. doi: 10.1139/m66-070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathern J., Hicks J., Herskowitz I. Control of cell type in yeast by the mating type locus. The alpha 1-alpha 2 hypothesis. J Mol Biol. 1981 Apr 15;147(3):357–372. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90488-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trew B. J., Friesen J. D., Moens P. B. Two-dimensional protein patterns during growth and sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1979 Apr;138(1):60–69. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.1.60-69.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuboi M. Correlation among turnover of nucleic acids, ribonuclease activity and sporulation ability of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch Microbiol. 1976 Dec 1;111(1-2):13–19. doi: 10.1007/BF00446544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wejksnora P. J., Haber J. E. Ribonucleoprotein particle appearing during sporulation in yeast. J Bacteriol. 1978 Apr;134(1):246–260. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.1.246-260.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. F., Ajam N., Dawes I. W. Nature and timing of some sporulation-specific protein changes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Oct;1(10):910–918. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.10.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Rey F., Santos T., García-Acha I., Nombela C. Synthesis of beta-glucanases during sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: formation of a new, sporulation-specific 1,3-beta-glucanase. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):621–627. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.621-627.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]