Abstract
Background:
Colonoscopy is a safe and effective means of visual inspection of the large bowel from the distal rectum to the caecum. It may be carried out for diagnostic and or therapeutic reasons. There is a paucity of data on this procedure in Nigeria. We, therefore, determined the indications, findings, and diagnostic yield in Nigerians at colonoscopy.
Materials and Methods:
This was a hospital-based cross-sectional study carried out at the Endoscopy unit of Crescent hospital, Ilorin from January 2010 to May, 2012. The endoscopy register was reviewed, and the biodata, indications and colonoscopic findings were recorded on a pro forma.
Results:
A total of 103 patients had colonoscopy. Seventy (68.0%) were males while 33 (32.0%) were females. The indications for colonoscopy were rectal bleeding 41 (39.8%), suspected colon cancer 32 (31.1%), chronic constipation and chronic diarrhoea nine each (8.7%), abdominal/anal pain five (4.9%), suspected anorectal cancer and enterocutaneous fistula two each (1.9%), faecal incontinence, occult gastrointestinal bleeding, post-colostomy for Hirschsprung disease one each (1.0%). Endoscopic findings were normal findings 21 (20.4%), diverticulosis 17 (16.5%), polyps 16 (15.5%), haemorrhoids 16 (15.5%), anorectal cancer 13 (12.6%), angiodysplasia 12 (11.7%), colon cancer eight (7.8%), colitis 7 (6.8%), anorectal ulcer 4 (3.9%), anal warts two (1.9%), anal fissure, caecal tumour, faecal impaction and proctitis one each (1.0%). The diagnostic yield was 79.6%.
Conclusions:
The commonest indication for colonoscopy was rectal bleeding, while the most frequent pathology was diverticulosis. The diagnostic yield was high.
Keywords: Colonoscopy, findings, indications, Nigerians, yield
INTRODUCTION
Colonoscopy is a safe and effective means of visual inspection of the large bowel from the distal rectum to the caecum. It may be carried out for diagnostic and or therapeutic reasons.1,2
Colonoscopy may be carried out for a variety of reasons such as to investigate the cause of gastrointestinal (GI) haemorrhage, abdominal pain, unexplained changes in bowel habit, suspicion of malignancy, or an abnormality found on abdominal ultrasound, colonic X-rays, barium enema or a computerised tomographic (CT) scan.2 Individuals with a previous history of polyps, colon cancer and those with a family history of non-colonic cancers or colonic disorders that may be associated with colon cancer may also undergo periodic colonoscopies.2,3
Even though the procedure is widely used in developed countries, it is not readily available in Nigeria.4–7 There is a paucity of data on the indications, endoscopic findings and diagnostic yield at colonoscopy in Nigerians.7 Diagnostic yield was defined as the ratio between significant findings detected on colonoscopy and the total number of procedures performed for that indication. In our study, the definition of significant findings was based on certain positive results on colonoscopy. A normal colonoscopy was not considered significant, although this may be relevant to patient care as it may rule out a serious disease in the colon during surveillance. We, therefore, determined the indications and endoscopic findings in Nigerians who underwent colonoscopy.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The setting of the study was at Crescent Hospital, Ilorin. It is a private hospital that runs a specialised gastroenterology clinic and GI endoscopic services. It receives referrals for gastroenterology consultations and lower GI endoscopy mainly from the University of Ilorin Teaching Hospital, Ilorin, other government-owned primary and secondary health facilities and other private hospitals in Ilorin and its environs. This is because this procedure is not available elsewhere in Ilorin. This was a hospital based cross-sectional study carried out at the Endoscopy unit of Crescent hospital, Ilorin from January 2010 to May, 2012. The endoscopy register was reviewed, and the biodata, indications and colonoscopic findings were noted and recorded on a pro forma.
All consenting patients, who required colonoscopy as part of their management, were recruited. All colonoscopies were performed with a Pentax video colonoscope with a light source EPM 3300. The patients usually had a 3-day bowel preparation through the use of laxatives comprising Bisacodyl (Dulcolax), Magnesium sulphate (Epsum) salt and lactulose syrup. They were also placed on liquid diet during the period. The patients had intravenous lines, and analgesia and sedation was carried with 10 mg of diazepam and 100 mg of tramadol. A digital rectal examination was done, and, thereafter, the Colonoscopy was carried out according to standard protocol.
RESULTS
A total of 103 patients had colonoscopy carried out on them during the period. Seventy (68.0%) were males while 33 (32.0%) were females, giving a male to female ratio of 2.1:1. Their ages ranged from 6 to 84 years, with a mean age of 53.4 ± 14.5 years. There was a steady increase in the age of the patients till the sixth decade i.e., 51-60 years; thereafter, there was a decline [Figure 1].
Figure 1.

Age and gender distribution of patients
The commonest indications for colonoscopy were rectal bleeding 41 (39.8%), suspected colon cancer 32 (31.1%), chronic constipation and chronic diarrhoea nine each (8.7%), abdominal/anal pain five (4.9%), suspected anorectal cancer and enterocutaneous fistula two each (1.9%), faecal incontinence, occult GI bleeding, post-colostomy for Hirschsprung disease one each (1.0%) [Figure 2].
Figure 2.
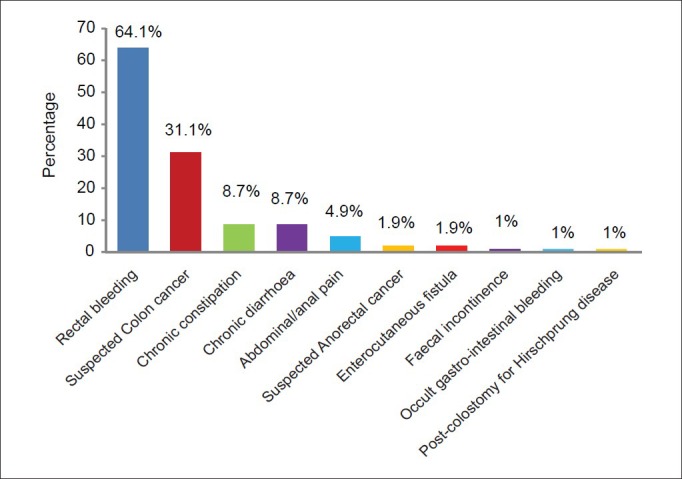
Indications for colonoscopy
Endoscopic findings were Normal findings 21 (20.4%), diverticulosis 17 (16.5%), polyps 16 (15.5%), haemorrhoids 16 (15.5%), anorectal cancer 13 (12.6%), angiodysplasia 12 (11.7%), colon cancer eight (7.8%), colitis 7 (6.8%), anorectal ulcer four (3.9%), anal warts two (1.9%), anal fissure, caecal tumour, faecal impaction and proctitis one each (1.0%) [Figure 3].
Figure 3.
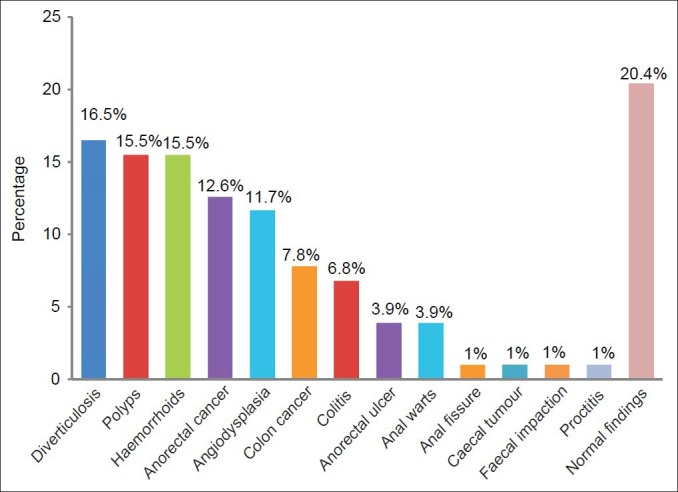
Endocopic findings
The diagnostic yield in this study was 82 out of 103 (79.6%) [Figure 4].
Figure 4.
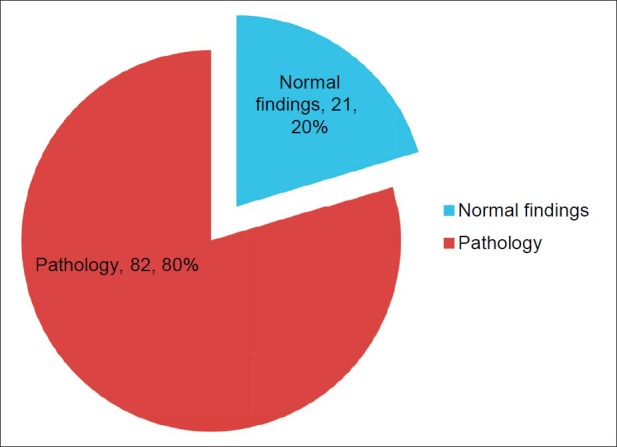
Diagnostic yield at colonoscopy
DISCUSSION
The main aim of our study was to determine the indications, findings and diagnostic yield at colonoscopy in Nigerians. Our study has shown an overall diagnostic yield of 79.6% at colonoscopy. This figure is similar to the 79.0% diagnostic yield found by Ismaila and Misauno in Jos, Nigeria.7 Studies in the West African sub-region carried out by Mbengue et al.,8 and Dakubo et al.,9 in Senegal and Ghana, respectively, revealed a similarly high diagnostic yield. However, the high diagnostic yield in our study contrasts with the 48.0% obtained by Sahu et al.,3 amongst their Indian patients and the 27.2% found by Siddique et al.,10 Furthermore, it is higher than the 21.0% diagnostic yield obtained by Al-shamali et al.,11 amongst the Saudis. The differences in the diagnostic yield may be due to varying sample sizes in the studies, the differences in the spectrum of colonic diseases seen in the different regions of the world, and the different selection criteria and indications for colonoscopy. Studies have shown that the highest diagnostic yield is found in patients having lower GI bleeding, mass lesions and polyps as demonstrated by Morini et al.,12 Kassa,13 Lee et al.,14 and Rex15 in their work. Rex, in his study amongst Americans, demonstrated that colonoscopy for bleeding indications such as positive faecal occult blood test, emergent or non-emergent rectal bleeding, melaena with a negative upper GI endoscopy and iron deficiency anaemia has a substantial yield for cancers.15
The availability and the cost of colonoscopy may also be a factor. The more expensive the cost of the procedure, the more stringent the selection criteria is.
From our study, the commonest indications for colonoscopy were rectal bleeding, suspected colorectal cancer and an unexplained change in bowel habit. These were also the indications for colonoscopy in the works carried out by Berkowitz and Kaplan,1 Sahu et al.,3 and Kassa13 in their South African, Indian and Ethiopian patients, respectively.
The commonest pathologies seen at colonoscopy in our study were cancer of the colon and anorectal regions 20.4%, diverticulosis 16.5%, polyps, haemorrhoids 15.5% and angiodysplasia 11.7%. This spectrum of pathologies is similar to that found by Irabor6 in Ibadan, Nigeria and Lee et al.,14 in their Jamaican patients, whereas, Ismaila and Misauno7 found haemorrhoids to be the commonest lesion. Ismaila and Misauno7 also reported that polyps and colorectal cancers are rare. This rarity may be due to the small sample size of their study, and a selection bias which was acknowledged by them in their work.
The main cause of colonic diseases in our study contrasts with the findings of El-Batea et al.,16 amongst Egyptians, that of Al-Nakib et al.,17 amongst Kuwaitis and that of Al-Shamali et al.,11 amongst Saudis who all found ulcerative colitis to be the most common pathology at colonoscopy. Furthermore, Sahu et al.,3 found ulcerative colitis to be the most frequent pathology in Indians. The main reason for the differences in the spectrum of findings at colonoscopy may be due to racial differences, geographical variations, life style and environmental, behavioural and dietary factors. It has been established that inflammatory bowel disease is common in Europe, Scandinavia and the US but rare in the black populations of sub-Saharan Africa.18–20 This may account for the rarity of ulcerative colitis in our study.
In conclusion, the diagnostic yield at colonoscopy was high. The commonest indication for colonoscopy was rectal bleeding, while the most frequent pathology seen was diverticulosis.
In view of the aforementioned benefits and the diagnostic yield from colonoscopy, the practice of colonoscopy deserves to be developed further in Nigeria.
Footnotes
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
REFERENCES
- 1.Berkowitz I, Kaplan M. Indications for colonoscopy. An analysis based on indications and diagnostic yield. S Afr Med J. 1993;83:245–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Grassini M, Verna C, Niola P, Navino M, Battaglia E, Bassotti G. Appropriateness of colonoscopy: Diagnostic yield and safety in guidelines. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13:1816–9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i12.1816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sahu SK, Husain M, Sachan PK. Clinical spectrum and diagnostic yield of lower gastrointestinal endoscopy at a tertiary centre. Internet J Surg. 2009:18. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Arigbabu AO, Odesanmi WO. Colonoscopy. First experience in Nigeria. Dis Colon Rectum. 1985;28:728–31. doi: 10.1007/BF02560287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Arigbabu AO, Badejo OA, Akinola DO. Colonoscopy in the emergency treatment of colonic volvulus in Nigeria. Dis Colon Rectum. 1985;28:795–8. doi: 10.1007/BF02555478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Irabor DO. Surgical gastrointestinal endoscopy in Ibadan, Nigeria. Nigerian J Surg Res. 2006;8:161–2. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ismaila BO, Misauno MO. Colonoscopy in a tertiary hospital in Nigeria. J Med Trop. 2011;13:172–4. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mbengue M, Dia D, Diouf ML, Bassène ML, Fall S, Diallo S, et al. Contribution of colonoscopy to diagnosis of rectal bleeding in Dakar (Sénégal) Med Trop (Mars) 2009;69:286–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dakubo J, Kumoji R, Naaeder S, Clegg-Lamptey J. Endoscopic evaluation of the colorectum in patients presenting with haematochaezia in at Korle-Bu Teaching Hospital Accra. Ghana Med J. 2008;42:33–7. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Siddique I, Mohan K, Hasan F, Memon A, Patty I, Al-Nakib B. Appropriateness of indication and diagnostic yield of colonoscopy: First report based on the 2000 guidelines of the American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11:7007–13. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i44.7007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Al-Shamali MA, Kalaoui M, Hasan F, Khajah A, Siddiqe I, Al-Nakeeb B. Colonoscopy: Evaluating indications and diagnostic yield. Ann Saudi Med. 2001;21:304–7. doi: 10.5144/0256-4947.2001.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Morini S, Hassan C, Meucci G, Toldi A, Zullo A, Minoli G. Diagnostic yield of open access colonoscopy according to appropriateness. Gastrointest Endosc. 2001;54:175–9. doi: 10.1067/mge.2001.116565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kassa E. Colonoscopy in the investigation of colonic disease. East Afr Med J. 1996;73:741–5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lee MG, Martin A, Terry SI. Colonoscopy in Jamaica- a 12 year experience. West Indian Med J. 1989;38:213–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Rex DK. Colonoscopy: A review of its yield for cancers and adenomas by indication. Am J Gastroenterol. 1995;90:353–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Elbatea H, Enaba M, Elkassas G, El-Kalla F, Elfert AA. Indications and outcomes of colonoscopy in the middle of Nile delta of Egypt. Dig Dis Sci. 2011;56:2120–3. doi: 10.1007/s10620-010-1538-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Nakib BA, Jacob GS, Liddawi HA, Bayoumi A. Fiberoptic colonoscopy: A report of findings in 481 patients from Kuwait. Dis Colon Rectum. 1983;26:236–8. doi: 10.1007/BF02562485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Segal I, Tim LO, Hamilton DG, Walker AR. The rarity of ulcerative colitis in South African blacks. Am J Gastroenterol. 1980;74:332–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Karlinger K, Györke T, Makö E, Mester A, Tarján Z. The epidemiology and the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. Eur J Radiol. 2000;35:154–67. doi: 10.1016/s0720-048x(00)00238-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sandler RS, Golder AL. Epidemiology of Crohn's disease. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1986;8:160–5. doi: 10.1097/00004836-198604000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


