Abstract
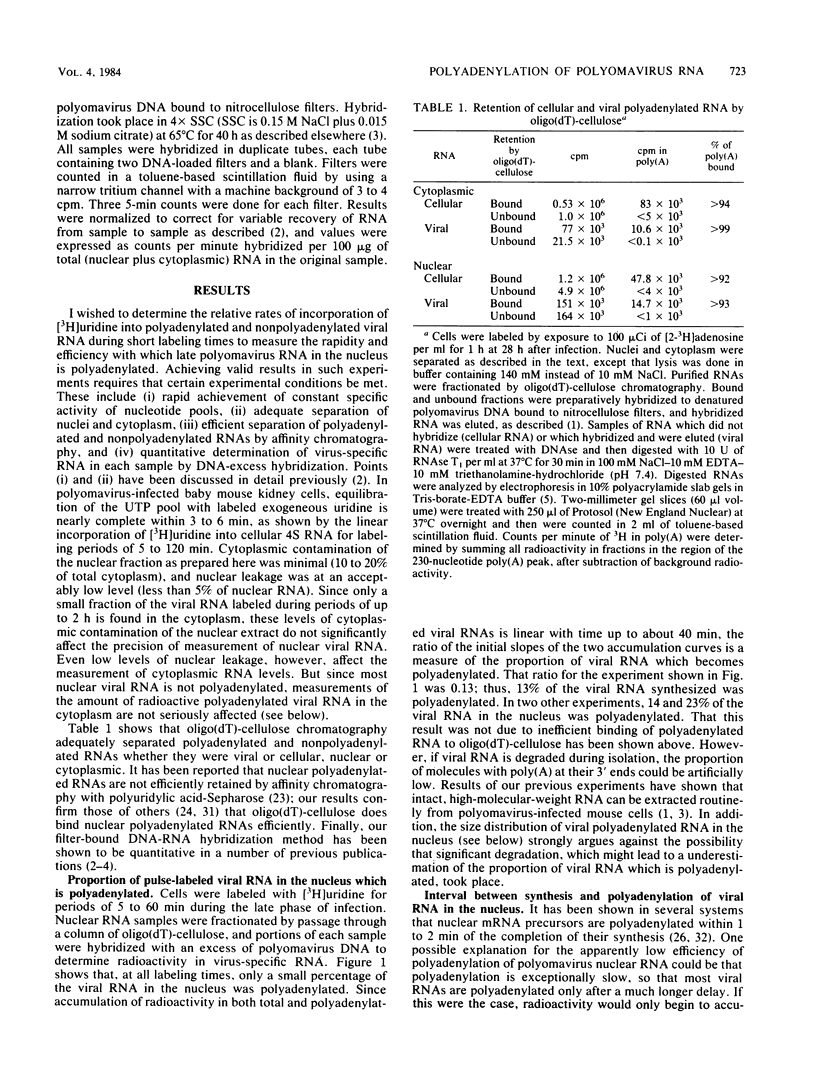
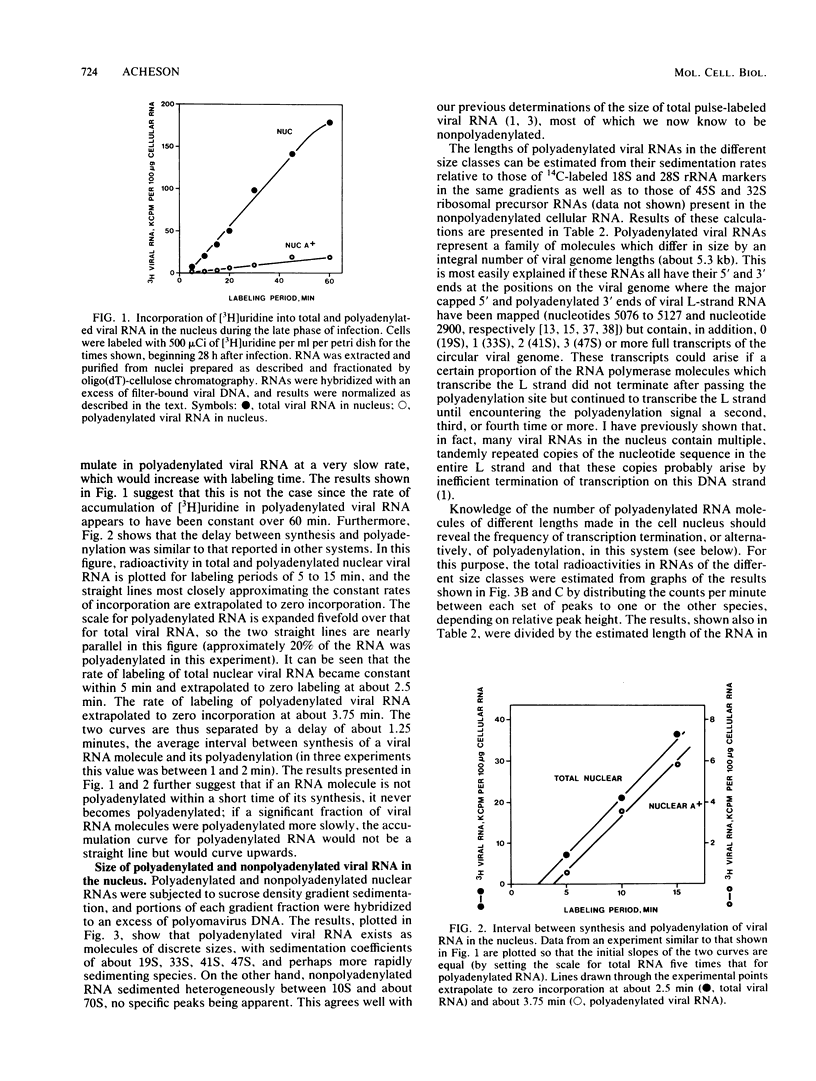
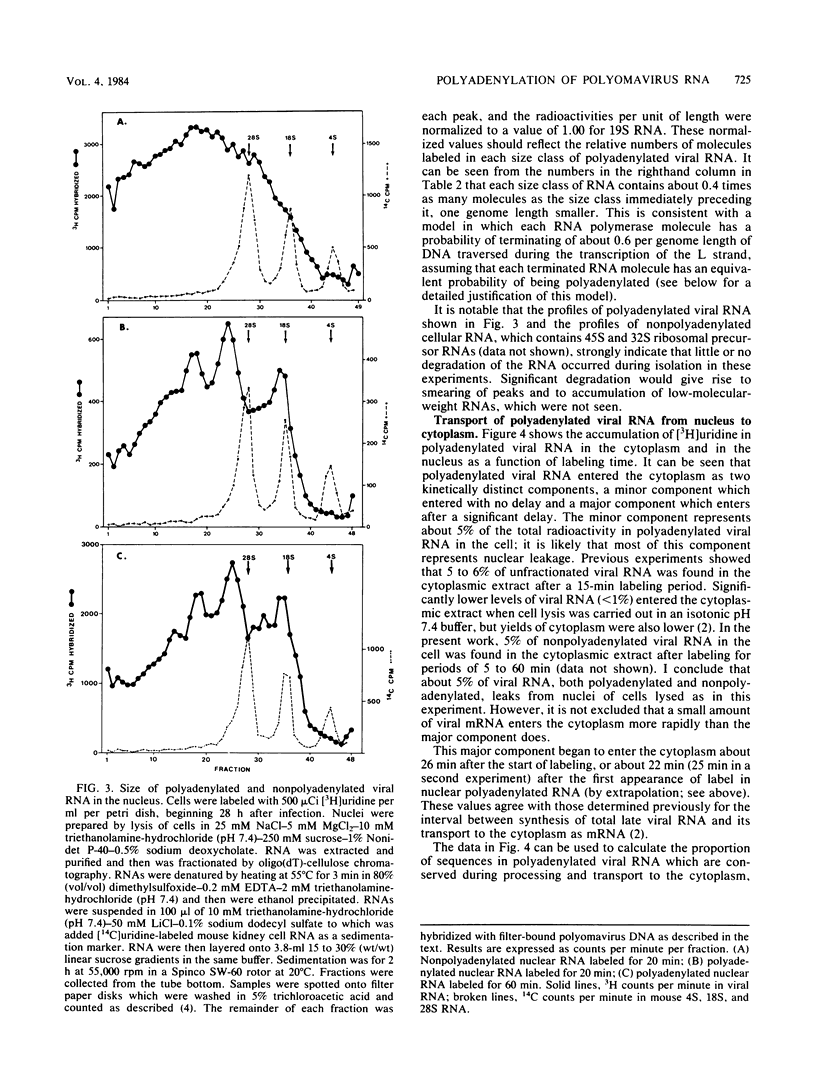
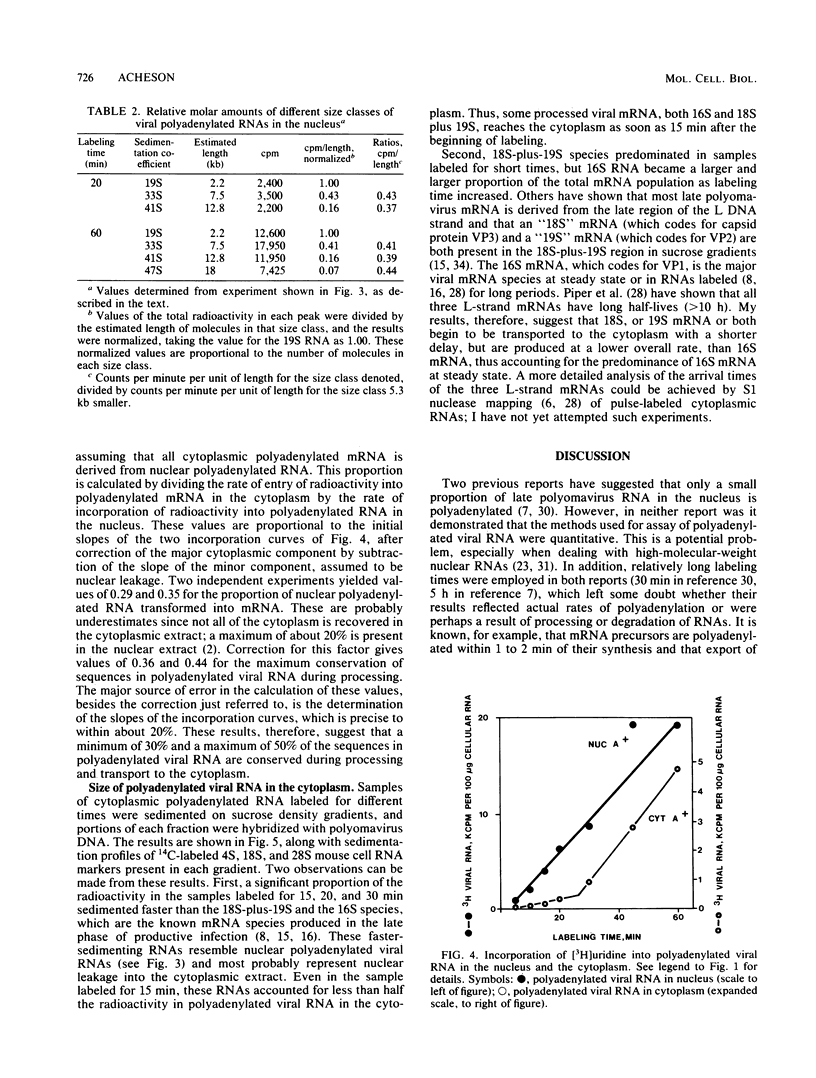
The rate and efficiency of polyadenylation of late polyomavirus RNA in the nucleus of productively infected mouse kidney cells were determined by measuring incorporation of [3H]uridine into total and polyadenylated viral RNAs fractionated by oligodeoxythymidylic acid-cellulose chromatography. Polyadenylation is rapid: the average delay between synthesis and polyadenylation of viral RNA in the nucleus is 1 to 2 min. However, only 10 to 25% of viral RNA molecules become polyadenylated. Polyadenylated RNAs in the nucleus are a family of molecules which differ in size by an integral number of viral genome lengths (5.3 kilobases). These RNAs are generated by repeated passage of RNA polymerase around the circular viral DNA, accompanied by addition of polyadenylic acid to a unique 3' end situated 2.2 + n(5.3) kilobases from the 5' end of the RNAs (n can be an integer from 0 to at least 3). Between 30 and 50% of the sequences in nuclear polyadenylated RNA are conserved during processing and transport to the cytoplasm as mRNA. This is consistent with the molar ratios of nuclear polyadenylated RNAs in the different size classes, and it suggests that most polyadenylated nuclear RNA is efficiently processed to mRNA. Thus, the low overall conservation of viral RNA sequences between nucleus and cytoplasm is explained by (i) low efficiency of polyadenylation of nuclear RNA and (ii) removal of substantial parts of polyadenylated RNAs during splicing. The correlation between inefficient termination of transcription and inefficient polyadenylation of transcripts suggests that these two events may be causally linked.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acheson N. H., Buetti E., Scherrer K., Weil R. Transcription of the polyoma virus genome: synthesis and cleavage of giant late polyoma-specific RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2231–2235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acheson N. H. Efficiency of processing of viral RNA during the early and late phases of productive infection by polyoma virus. J Virol. 1981 Feb;37(2):628–635. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.2.628-635.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acheson N. H., Miéville F. Extent of transcription of the E strand of polyoma virus DNA during the early phase of productive infection. J Virol. 1978 Dec;28(3):885–894. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.3.885-894.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Acheson N. H. Polyoma virus giant RNAs contain tandem repeats of the nucleotide sequence of the entire viral genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4754–4758. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adesnik M., Darnell J. E. Biogenesis and characterization of histone messenger RNA in HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90458-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birg F., Favaloro J., Kamen R. Analysis of polyoma virus nuclear RNA by mini-blot hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3138–3142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buetti E. Characterization of late polyoma mRNA. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):249–260. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.249-260.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu N. H., Radonovich M. F., Thoren M. M., Salzman N. P. Selective degradation of newly synthesized nonmessenger simian virus 40 transcripts. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):590–599. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.590-599.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Jr Variety in the level of gene control in eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1982 Jun 3;297(5865):365–371. doi: 10.1038/297365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deninger P. L., Esty A., LaPorte P., Hsu H., Friedmann T. The nucleotide sequence and restriction enzyme sites of the polyoma genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Feb 25;8(4):855–860. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford J. P., Hsu M. T. Transcription pattern of in vivo-labeled late simian virus 40 RNA: equimolar transcription beyond the mRNA 3' terminus. J Virol. 1978 Dec;28(3):795–801. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.3.795-801.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heiser W. C., Eckhart W. Polyoma virus early and late mRNAs in productively infected mouse 3T6 cells. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):175–188. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.175-188.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofer E., Hofer-Warbinek R., Darnell J. E., Jr Globin RNA transcription: a possible termination site and demonstration of transcriptional control correlated with altered chromatin structure. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):887–893. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90450-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamen R., Favaloro J., Parker J. Topography of the three late mRNA's of polyoma virus which encode the virion proteins. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):637–651. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.637-651.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legon S., Flavell A. J., Cowie A., Kamen R. Amplification in the leader sequence of late polyoma virus mRNAs. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):373–388. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki R., Roeder W., Traunecker A., Sidman C., Wabl M., Raschke W., Tonegawa S. The role of DNA rearrangement and alternative RNA processing in the expression of immunoglobulin delta genes. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):353–365. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90325-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L. Accurate and specific polyadenylation of mRNA precursors in a soluble whole-cell lysate. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):595–605. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90440-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. Rna synthesis in isolated nuclei processing of adenovirus serotype 2 late messenger rna precursors. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 25;159(4):581–599. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90102-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manor H., Wu M., Baran N., Davidson N. Electron microscopic mapping of RNA transcribed from the late region of polyoma virus DNA. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):293–303. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.293-303.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller T. J., Stephens D. L., Mertz J. E. Kinetics of accumulation and processing of simian virus 40 RNA in Xenopus laevis oocytes injected with simian virus 40 DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Dec;2(12):1581–1594. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.12.1581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakazato H., Edmonds M. Purification of messenger RNA and heterogeneous nuclear RNA containing poly(a) sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1974;29:431–443. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)29035-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Blanchard J. M., Darnell J. E., Jr Transcription units of adenovirus type 2. Termination of transcription beyond the poly(A) addition site in early regions 2 and 4. J Mol Biol. 1980 Dec 15;144(3):377–386. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90096-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Steps in the processing of Ad2 mRNA: poly(A)+ nuclear sequences are conserved and poly(A) addition precedes splicing. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1477–1493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R., Wilson M. C. Regulation of adenovirus-2 gene expression at the level of transcriptional termination and RNA processing. Nature. 1981 Mar 12;290(5802):113–118. doi: 10.1038/290113a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper P., Wardale J., Crew F. Splicing of the late mRNAs of polyoma virus does not occur in the cytoplasm of the infected cell. Nature. 1979 Dec 13;282(5740):686–691. doi: 10.1038/282686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal L. J. Isolation and characterization of poly(A)-containing polyoma "early" and "late" messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 Mar;3(3):661–676. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.3.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal L. J., Salomon C., Weil R. Isolation and characterization of poly(A)-containing intranuclear polyoma-specific "giant" RNA'S. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 May;3(5):1167–1183. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.5.1167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salditt-Georgieff M., Darnell J. E., Jr Further evidence that the majority of primary nuclear RNA transcripts in mammalian cells do not contribute to mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;2(6):701–707. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.6.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salditt-Georgieff M., Harpold M., Sawicki S., Nevins J., Darnell J. E., Jr Addition of poly(A) to nuclear RNA occurs soon after RNA synthesis. J Cell Biol. 1980 Sep;86(3):844–848. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.3.844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw A. R., Ziff E. B. Transcripts from the adenovirus-2 major late promoter yield a single early family of 3' coterminal mRNAs and five late families. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):905–916. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90568-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddell S. G., Smith A. E. Polyoma virus has three late mRNA's: one for each virion protein. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):427–431. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.427-431.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeda E., Arrand J. R., Smolar N., Walsh J. E., Griffin B. E. Coding potential and regulatory signals of the polyoma virus genome. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):445–453. doi: 10.1038/283445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tosi M., Young R. A., Hagenbüchle O., Schibler U. Multiple polyadenylation sites in a mouse alpha-amylase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 May 25;9(10):2313–2323. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.10.2313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R. Characterisation of polyoma late mRNA leader sequences by molecular cloning and DNA sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 11;8(21):4867–4888. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.21.4867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Kamen R. Structure of polyoma virus late nuclear RNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 25;148(3):273–301. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90539-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson M. C., Sawicki S. G., Salditt-Georgieff M., Darnell J. E. Adenovirus type 2 mRNA in transformed cells: map positions and difference in transport time. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):97–103. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.97-103.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



