Abstract
In mouse Ltk- cells that were transfected with recombinant bacteriophage DNA containing a complete proviral copy of an integrated endogenous mouse mammary tumor virus (MMTV) with its flanking cellular sequences, the newly acquired MMTV proviruses were transcribed in a glucocorticoid-responsive fashion. After hormone treatment of selected cell clones in culture we isolated the nuclei, elongated the nascent RNA chains in vitro, and determined the number of RNA polymerase II molecules on the transcribed MMTV DNA as well as on the flanking mouse DNA sequences. We found that the specific increase in the polymerase loading after hormone treatment is proportional to the increase in the amount of stable MMTV mRNA. When the DNA sequences which are responsible for hormone-receptor binding and for the increased MMTV mRNA levels were deleted, no increase in RNA polymerase II loading on MMTV DNA was observed. Nuclear RNA chains which were transcribed in response to hormone treatment were detected not only from the transfected MMTV DNA but also from the mouse DNA sequences adjacent to the 3' end of the provirus.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buetti E., Diggelmann H. Cloned mouse mammary tumor virus DNA is biologically active in transfected mouse cells and its expression is stimulated by glucocorticoid hormones. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):335–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90129-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buetti E., Diggelmann H. Glucocorticoid regulation of mouse mammary tumor virus: identification of a short essential DNA region. EMBO J. 1983;2(8):1423–1429. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01601.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chandler V. L., Maler B. A., Yamamoto K. R. DNA sequences bound specifically by glucocorticoid receptor in vitro render a heterologous promoter hormone responsive in vivo. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):489–499. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. F. Quantitation of elongating form A and B RNA polymerases in chick oviduct nuclei and effects of estradiol. Cell. 1976 Mar;7(3):455–465. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90176-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox R. F. Transcription of high-molecular-weight RNA from hen-oviduct chromatin by bacterial and endogenous form-B RNA polymerases. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Nov 1;39(1):49–61. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diggelmann H., Vessaz A. L., Buetti E. Cloned endogenous mouse mammary tumor virus DNA is biologically active in transfected mouse cells and its expression is stimulated by glucocorticoid hormones. Virology. 1982 Oct 30;122(2):332–341. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90233-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fasel N., Pearson K., Buetti E., Diggelmann H. The region of mouse mammary tumor virus DNA containing the long terminal repeat includes a long coding sequence and signals for hormonally regulated transcription. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):3–7. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01115.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gariglio P., Bellard M., Chambon P. Clustering of RNA polymerase B molecules in the 5' moiety of the adult beta-globin gene of hen erythrocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 11;9(11):2589–2598. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.11.2589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisse S., Scheidereit C., Westphal H. M., Hynes N. E., Groner B., Beato M. Glucocorticoid receptors recognize DNA sequences in and around murine mammary tumour virus DNA. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1613–1619. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01363.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Govindan M. V., Spiess E., Majors J. Purified glucocorticoid receptor-hormone complex from rat liver cytosol binds specifically to cloned mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeats in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5157–5161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudine M., Peretz M., Weintraub H. Transcriptional regulation of hemoglobin switching in chicken embryos. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;1(3):281–288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.3.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewish D. R., Burgoyne L. A. Chromatin sub-structure. The digestion of chromatin DNA at regularly spaced sites by a nuclear deoxyribonuclease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 May 15;52(2):504–510. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90740-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. L., Ostrowski M. C., Berard D., Hager G. L. Glucocorticoid regulation of the Ha-MuSV p21 gene conferred by sequences from mouse mammary tumor virus. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90408-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes N., van Ooyen A. J., Kennedy N., Herrlich P., Ponta H., Groner B. Subfragments of the large terminal repeat cause glucocorticoid-responsive expression of mouse mammary tumor virus and of an adjacent gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3637–3641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
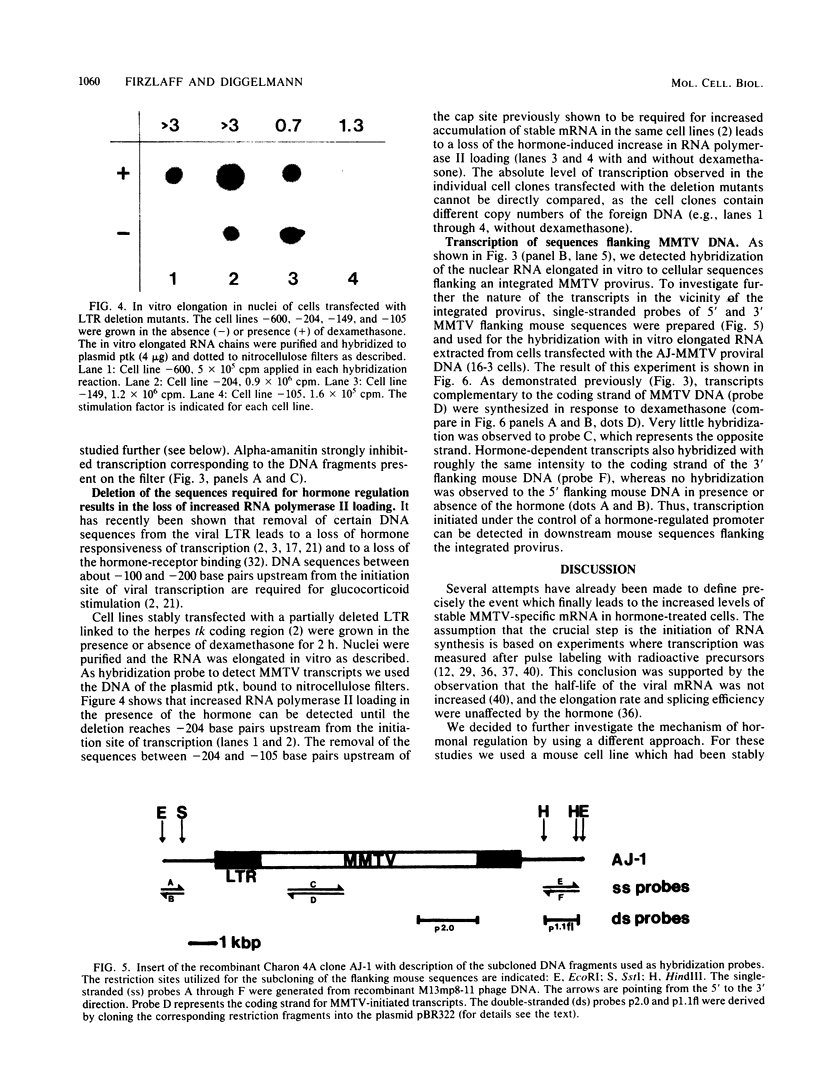
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasfargues E. Y., Vaidya A. B., Lasfargues J. C., Moore D. H. In vitro susceptibility of mink lung cells to the mouse mammary tumor virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Aug;57(2):447–449. doi: 10.1093/jnci/57.2.447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F., Mulligan R., Berg P., Ringold G. Glucocorticoids regulate expression of dihydrofolate reductase cDNA in mouse mammary tumour virus chimaeric plasmids. Nature. 1981 Nov 19;294(5838):228–232. doi: 10.1038/294228a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASTER R. W. POSSIBLE SYNTHESIS OF POLYRIBONUCLEOTIDES OF KNOWN BASE-TRIPLET SEQUENCES. Nature. 1965 Apr 3;206:93–93. doi: 10.1038/206093b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majors J., Varmus H. E. A small region of the mouse mammary tumor virus long terminal repeat confers glucocorticoid hormone regulation on a linked heterologous gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5866–5870. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. Enhancer elements activated by steroid hormones? Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):687–688. doi: 10.1038/304687a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parks W. P., Scolnick E. M., Kozikowski E. H. Dexamethasone stimulation of murine mammary tumor virus expression: a tissue culture source of virus. Science. 1974 Apr 12;184(4133):158–160. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4133.158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payvar F., Wrange O., Carlstedt-Duke J., Okret S., Gustafsson J. A., Yamamoto K. R. Purified glucocorticoid receptors bind selectively in vitro to a cloned DNA fragment whose transcription is regulated by glucocorticoids in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6628–6632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfahl M. Specific binding of the glucocorticoid-receptor complex to the mouse mammary tumor proviral promoter region. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):475–482. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90140-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringold G. M., Cardiff R. D., Varmus H. E., Yamamoto K. R. Infection of cultured rat hepatoma cells by mouse mammary tumor virus. Cell. 1977 Jan;10(1):11–18. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90134-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringold G. M., Yamamoto K. R., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Glucocorticoid-stimulated accumulation of mouse mammary tumor virus RNA: increased rate of synthesis of viral RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2879–2883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringold G. M., Yamamoto K. R., Tomkins G. M., Bishop M., Varmus H. E. Dexamethasone-mediated induction of mouse mammary tumor virus RNA: a system for studying glucocorticoid action. Cell. 1975 Nov;6(3):299–305. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Geisse S., Westphal H. M., Beato M. The glucocorticoid receptor binds to defined nucleotide sequences near the promoter of mouse mammary tumour virus. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):749–752. doi: 10.1038/304749a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schibler U., Hagenbüchle O., Wellauer P. K., Pittet A. C. Two promoters of different strengths control the transcription of the mouse alpha-amylase gene Amy-1a in the parotid gland and the liver. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):501–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90431-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E. M., Young H. A., Parks W. P. Biochemical and physiological mechanisms in glucocorticoid hormone induction of mouse mammary tumor virus. Virology. 1976 Jan;69(1):148–156. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90202-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ucker D. S., Firestone G. L., Yamamoto K. R. Glucocorticoids and chromosomal position modulate murine mammary tumor virus transcription by affecting efficiency of promoter utilization. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Apr;3(4):551–561. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.4.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ucker D. S., Ross S. R., Yamamoto K. R. Mammary tumor virus DNA contains sequences required for its hormone-regulated transcription. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):257–266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90409-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaidya A. B., Lasfargues E. Y., Heubel G., Lasfargues J. C., Moore D. H. Murine mammary tumor virus: characterization of infection of nonmurine cells. J Virol. 1976 Jun;18(3):911–917. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.3.911-917.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkie N. M., Clements J. B., Boll W., Mantei N., Lonsdale D., Weissmann C. Hybrid plasmids containing an active thymidine kinase gene of Herpes simplex virus 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Oct 25;7(4):859–877. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.4.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young H. A., Shih T. Y., Scolnick E. M., Parks W. P. Steroid induction of mouse mammary tumor virus: effect upon synthesis and degradation of viral RNA. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):139–146. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.139-146.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]