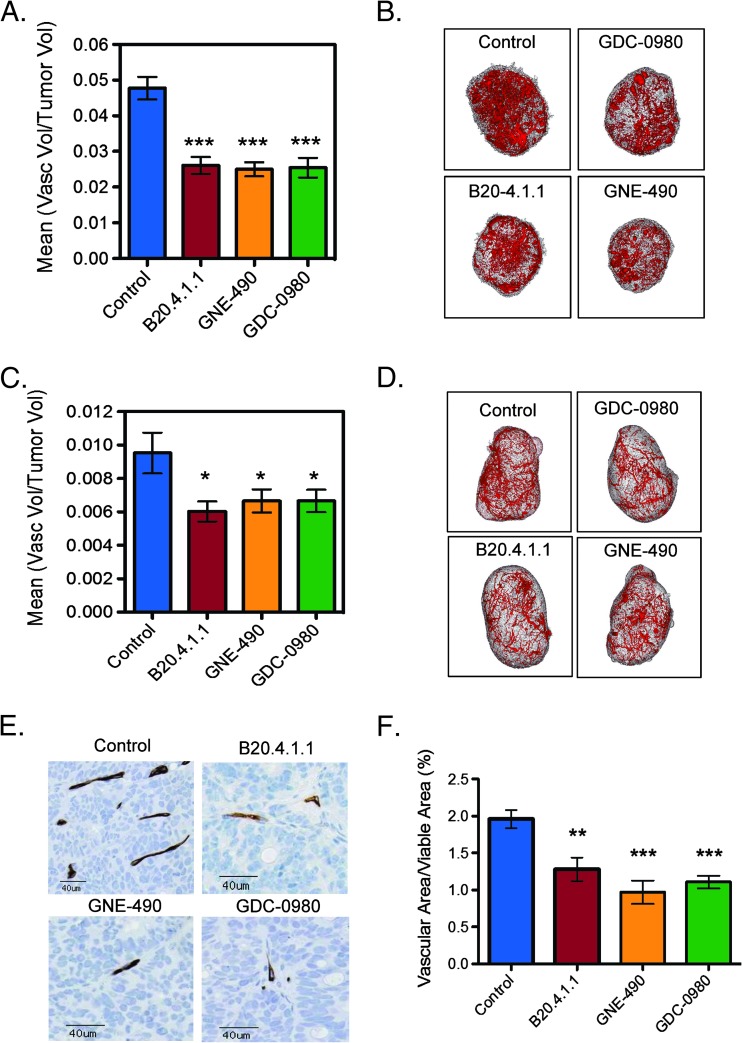
Figure 7.
Inhibition of PI3K is sufficient for reducing vascular density in HM-7 and NCI-PC3 xenograft models. (A) HM-7 xenograft model: micro-CT angiography results of mean vascular volume/tumor volume ± SEM 24 hours following a single dose of MCT vehicle (control), B20.4.1.1 (10 mg/kg), GNE-490 (30 mg/kg), or GDC-0980 (10 mg/kg) (HM-7 xenograft model). (B) Representative 3D renderings of the micro-CT-derived vascular skeleton (red) overlaid onto HM-7 tumor tissue (gray) from mice described in A. (C) NCI-PC3 xenograft model: micro-CT angiography results of mean vascular volume/tumor volume ± SEM 48 hours following a single dose of MCT vehicle (control), B20.4.1.1 (10 mg/kg), GNE-490 (30 mg/kg), or GDC-0980 (10 mg/kg). (D) Representative 3D renderings of the micro-CT-derived vascular skeleton (red) overlaid onto NCI-PC3 tumor tissue (gray) from mice described in C. (E) Representative IHC images of MECA-32-positive vessels contained in HM-7 tumors after 7 days of daily treatment with MCT vehicle (control), 10 mg/kg B20.4.1.1, 30 mg/kg GNE-490, or 10 mg/kg GDC-0980 and (F) the corresponding estimates for mean vascular fraction (%) = (vascular area/viable tumor area) x 100 ± SEM, n = 10/group. Comparisons to control were performed using Dunnett's method; *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001.