Abstract
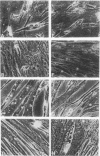
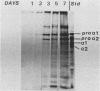
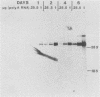
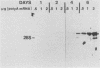
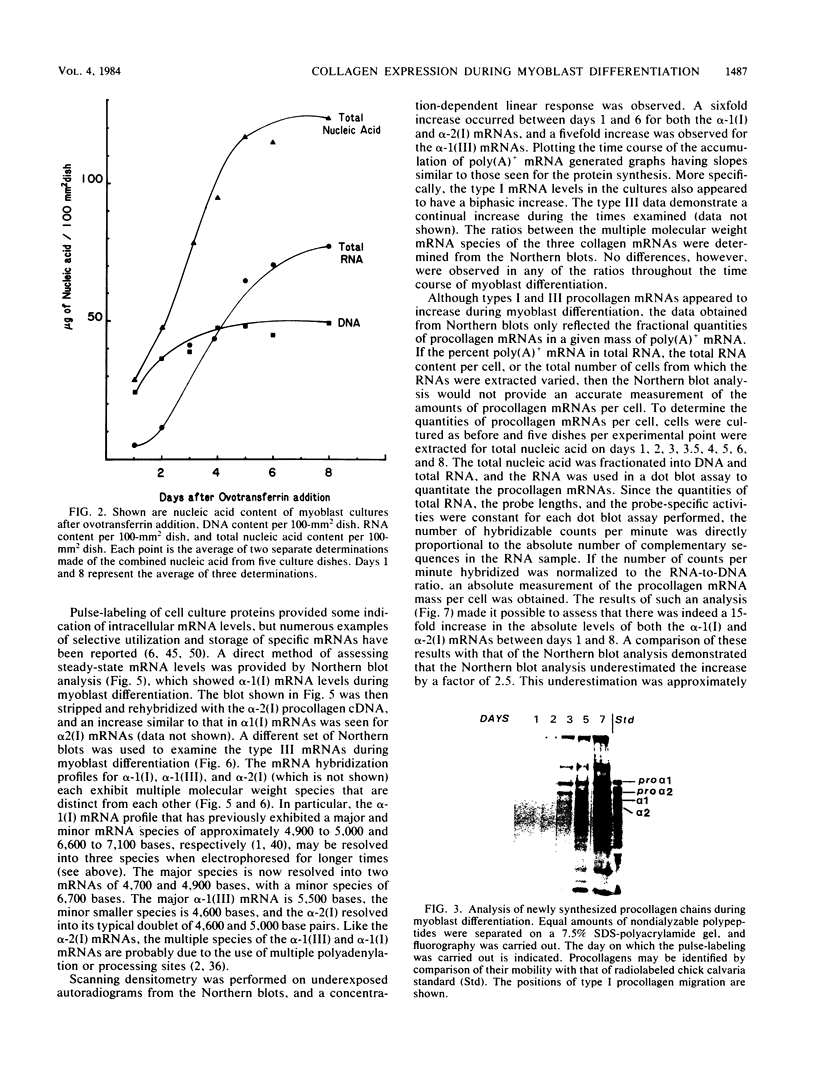
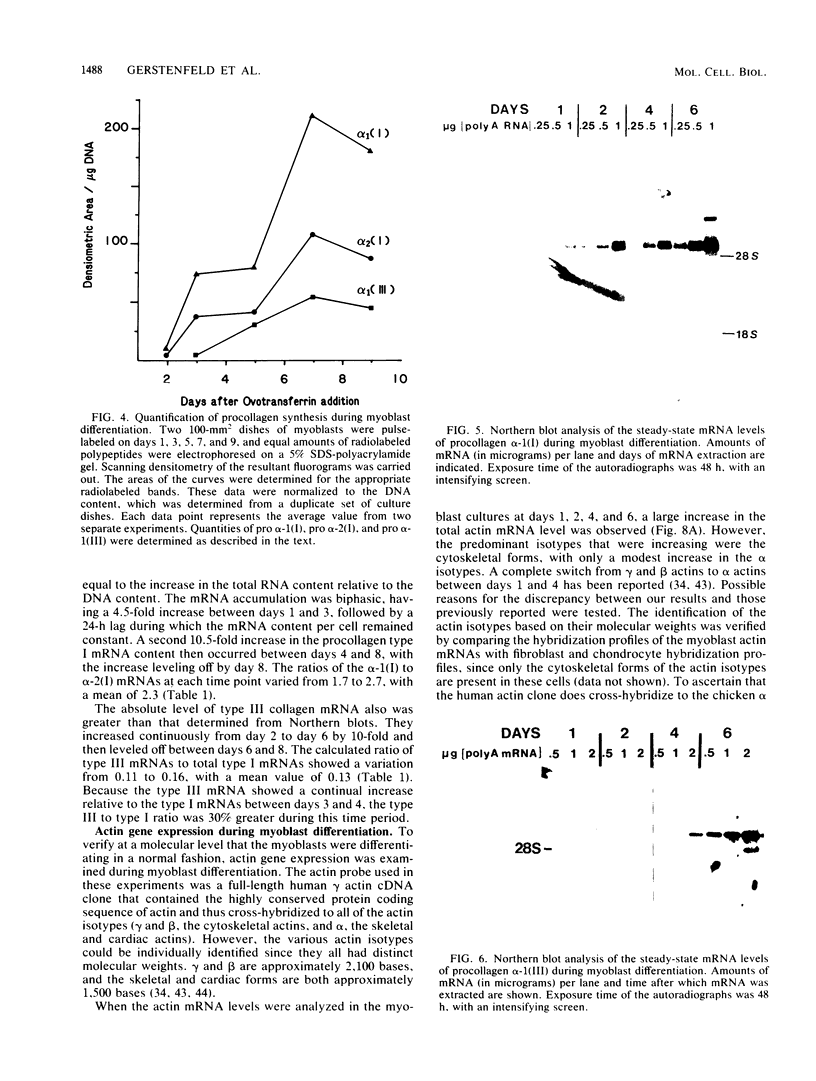
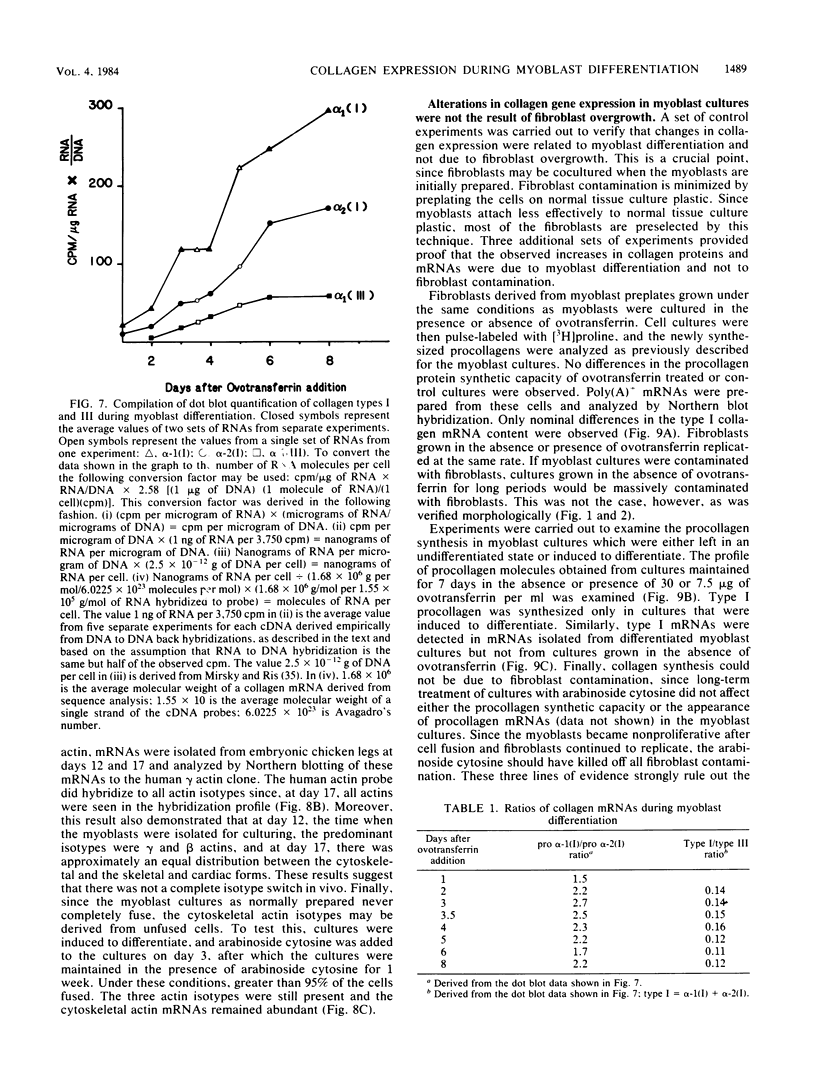
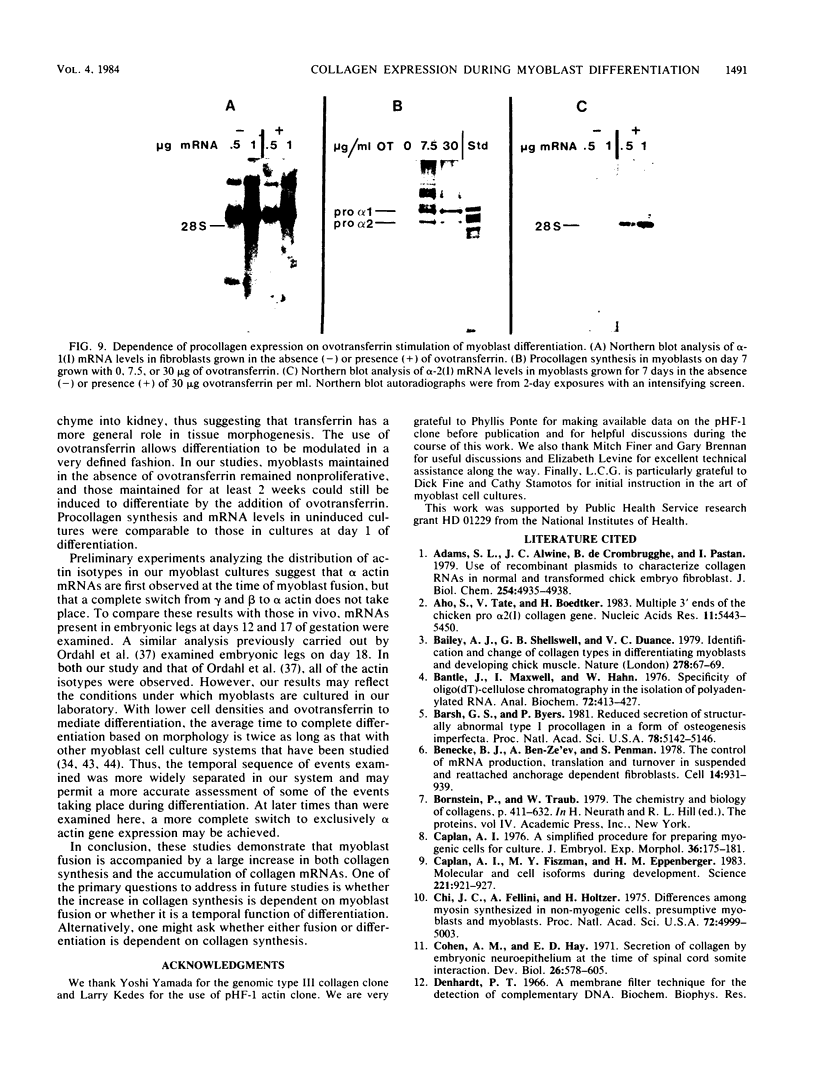
Expression of type I and III procollagen genes was studied in embryonic chicken myoblast cell cultures, obtained from thigh muscles of 11-day-old embryos. Differentiation initiated by the addition of ovotransferrin (30 micrograms/ml) was followed visually by phase-contrast microscopy. Myoblast fusion and myotube formation were detected by day 3 and appeared to be complete by day 7. The synthesis of procollagens was monitored by labeling cell cultures for 1 h with [3H]proline and determining the radioactivity in procollagen chains by scanning densitometry of the fluorograms of the sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. A 10- to 20-fold increase in the rate of pro alpha-1(I), pro alpha-2(I), and pro alpha-1(III) collagen synthesis was observed, with the greatest increase occurring between days 3 and 9. Collagen mRNA levels in the myoblast cultures were examined by Northern blot and dot blot hybridization assays. The 10- to 20-fold increased rate of protein synthesis was accompanied by a 15-fold increase in the steady-state levels of pro alpha-1(I) and pro alpha-2(I) mRNAs and a 10-fold increase in the steady-state levels of pro alpha-1(III). As a correlate to the studies of collagen expression during myoblast differentiation, the expression of actin mRNAs was examined. Although alpha actin could be detected by day 4, a complete switch from lambda and beta to alpha actin was not observed in the time periods examined. Similar results were obtained in the analysis of RNA extracted from embryonic legs at days 12 and 17 of gestation. Myoblast differentiation is manifested by the accumulation of both muscle-specific mRNAs, such as actin, and type I and III procollagen mRNAs.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. L., Alwine J. C., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Use of recombinant plasmids to characterize collagen RNAs in normal and transformed chick embryo fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 25;254(12):4935–4938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aho S., Tate V., Boedtker H. Multiple 3' ends of the chicken pro alpha 2(I) collagen gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5443–5450. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bailey A. J., Shellswell G. B., Duance V. C. Identification and change of collagen types in differentiating myoblasts and developing chick muscle. Nature. 1979 Mar 1;278(5699):67–69. doi: 10.1038/278067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bantle J. A., Maxwell I. H., Hahn W. E. Specificity of oligo (dT)-cellulose chromatography in the isolation of polyadenylated RNA. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:413–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90549-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barsh G. S., Byers P. H. Reduced secretion of structurally abnormal type I procollagen in a form of osteogenesis imperfecta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5142–5146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benecke B. J., Ben-Ze'ev A., Penman S. The control of mRNA production, translation and turnover in suspended and reattached anchorage-dependent fibroblasts. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):931–939. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90347-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan A. I. A simplified procedure for preparing myogenic cells for culture. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1976 Aug;36(1):175–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan A. I., Fiszman M. Y., Eppenberger H. M. Molecular and cell isoforms during development. Science. 1983 Sep 2;221(4614):921–927. doi: 10.1126/science.6348946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chi J. C., Fellini S. A., Holtzer H. Differences among myosins synthesized in non-myogenic cells, presumptive myoblasts, and myoblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4999–5003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A. M., Hay E. D. Secretion of collagen by embryonic neuroepithelium at the time of spinal cord--somite interaction. Dev Biol. 1971 Dec;26(4):578–605. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(71)90142-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duance V. C., Restall D. J., Beard H., Bourne F. J., Bailey A. J. The location of three collagen types in skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jul 15;79(2):248–252. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80797-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblom P., Thesleff I., Saxén L., Miettinen A., Timpl R. Transferrin as a fetal growth factor: acquisition of responsiveness related to embryonic induction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2651–2655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller F., Boedtker H. Sequence determination and analysis of the 3' region of chicken pro-alpha 1(I) and pro-alpha 2(I) collagen messenger ribonucleic acids including the carboxy-terminal propeptide sequences. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):996–1006. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerstenfeld L., Beldekas J. C., Franzblau C., Sonenshein G. E. Cell-free translation of calf type III collagen. Effect of magnesium on ribosome movement during elongation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):12058–12063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golob R., Chetsanga C. J., Doty P. The onset of collagen synthesis in sea urchin embryos. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Apr 27;349(1):135–141. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90017-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonnerman W. A., Goral A. B., Franzblau C. Use of soluble, collagenous peptides from medium of chick calvaria cultures as substrate for prolyl hydroxylase. Anal Biochem. 1980 Feb;102(1):8–12. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90308-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green H., Goldberg B., Schwartz M., Brown D. D. The synthesis of collagen during the development of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1968 Oct;18(4):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(68)90048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalcheim C., Vogel Z., Duksin D. Embryonic brain extract induces collagen biosynthesis in cultured muscle cells: involvement in acetylcholine receptor aggregation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3077–3081. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ketley J. N., Orkin R. W., Martin G. R. Collagen in developing chick muscle in vivo and in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1976 May;99(2):261–268. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90582-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman H. K., Klebe R. J., Martin G. R. Role of collagenous matrices in the adhesion and growth of cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Mar;88(3):473–485. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.3.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Frischauf A. M., Hanahan D., Wozney J., Fuller F., Boedtker H. Construction and characterization of pro alpha 1 collagen complementary deoxyribonucleic acid clones. Biochemistry. 1979 Jul 10;18(14):3146–3152. doi: 10.2196/47873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Frischauf A. M., Hanahan D., Wozney J., Fuller F., Crkvenjakov R., Boedtker H., Doty P. Construction and characterization of a 2.5-kilobase procollagen clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5417–5421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levenson R., Housman D. Commitment: how do cells make the decision to differentiate? Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90225-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIRSKY A. E., RIS H. The desoxyribonucleic acid content of animal cells and its evolutionary significance. J Gen Physiol. 1951 Mar 20;34(4):451–462. doi: 10.1085/jgp.34.4.451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manasek F. J. The extracellular matrix: a dynamic component of the developing embryo. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1975;10:35–102. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60038-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merlino G. T., McKeon C., de Crombrugghe B., Pastan I. Regulation of the expression of genes encoding types I, II, and III collagen during chick embryonic development. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10041–10048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A. J., Alonso S., Caravatti M., Buckingham M. E. A fetal skeletal muscle actin mRNA in the mouse and its identity with cardiac actin mRNA. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers J. C., Dickson L. A., de Wet W. J., Bernard M. P., Chu M. L., Di Liberto M., Pepe G., Sangiorgi F. O., Ramirez F. Analysis of the 3' end of the human pro-alpha 2(I) collagen gene. Utilization of multiple polyadenylation sites in cultured fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10128–10135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordahl C. P., Tilghman S. M., Ovitt C., Fornwald J., Largen M. T. Structure and developmental expression of the chick alpha-actin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 11;8(21):4989–5005. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.21.4989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky B., Diegelmann R. Use of a mixture of proteinase-free collagenases for the specific assay of radioactive collagen in the presence of other proteins. Biochemistry. 1971 Mar 16;10(6):988–994. doi: 10.1021/bi00782a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponte P., Gunning P., Blau H., Kedes L. Human actin genes are single copy for alpha-skeletal and alpha-cardiac actin but multicopy for beta- and gamma-cytoskeletal genes: 3' untranslated regions are isotype specific but are conserved in evolution. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Oct;3(10):1783–1791. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.10.1783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rave N., Crkvenjakov R., Boedtker H. Identification of procollagen mRNAs transferred to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper from formaldehyde agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3559–3567. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasse J., von der Mark H., Kühl U., Dessau W., von der Mark K. Origin of collagen types I, III, and V in cultures of avian skeletal muscle. Dev Biol. 1981 Apr 15;83(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(81)80010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnieke A., Harbers K., Jaenisch R. Embryonic lethal mutation in mice induced by retrovirus insertion into the alpha 1(I) collagen gene. 1983 Jul 28-Aug 3Nature. 304(5924):315–320. doi: 10.1038/304315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz R. J., Rothblum K. N. Gene switching in myogenesis: differential expression of the chicken actin multigene family. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 7;20(14):4122–4129. doi: 10.1021/bi00517a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shani M., Nudel U., Zevin-Sonkin D., Zakut R., Givol D., Katcoff D., Carmon Y., Reiter J., Frischauf A. M., Yaffe D. Skeletal muscle actin mRNA. Characterization of the 3' untranslated region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 11;9(3):579–589. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.3.579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenshein G. E., Brawerman G. Entry of mRNA into polyribosomes during recovery from starvation in mouse sarcoma 180 cells. Eur J Biochem. 1977 Feb 15;73(1):307–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11320.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stamatos C., Squicciarini J., Fine R. E. Chick embryo spinal cord neurons synthesize a transferrin-like myotrophic protein. FEBS Lett. 1983 Mar 21;153(2):387–390. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80649-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wozney J., Hanahan D., Morimoto R., Boedtker H., Doty P. Fine structural analysis of the chicken pro alpha 2 collagen gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):712–716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada Y., Mudryj M., Sullivan M., de Crombrugghe B. Isolation and characterization of a genomic clone encoding chick alpha 1 type III collagen. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2758–2761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zähringer J., Baliga B. S., Munro H. N. Novel mechanism for translational control in regulation of ferritin synthesis by iron. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):857–861. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet W. J., Chu M. L., Prockop D. J. The mRNAs for the pro-alpha 1(I) and pro-alpha 2(I) chains of type I procollagen are translated at the same rate in normal human fibroblasts and in fibroblasts from two variants of osteogenesis imperfecta with altered steady state ratios of the two mRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14385–14389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]