Acquisition of antibiotic resistance in Staphylococcus aureus has been associated with loss of pathogenic fitness and also virulence potential, where this phenomenon has been observed in specific clinical and laboratory S. aureus strains [1–4]. Interestingly, this phenomenon of “inverse relationship between antibiotic resistance and virulence” was also observed in a general population of both methicillin-resistant and -susceptible S. aureus (MRSA and MSSA), when a molecular epidemiological study was carried out at our teaching hospital in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
The above study was done in 2009, where a total of 1,199 S. aureus isolates were recovered from various wards of our hospital. Three hundred and nineteen (26.6 %) and 880 (73.4 %) isolates were identified to be MRSA and MSSA, respectively. Most isolates were recovered from tissue and pus swabs.
As per hospital diagnostic laboratory requirement, all 1,199 isolates were subjected to antibiotic susceptibility tests, where the antibiograms were determined by disk diffusion method on Mueller-Hinton agar according to the Clinical Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) recommendations [5]. Most MRSA isolates in our study were found to be multi-drug resistant: 89.0, 88.1, 83.1 and 100.0 % were resistant to ciprofloxacin, erythromycin, gentamicin, and cefoxitine, respectively. Interestingly, about 81.5 % of the MRSA isolates remain susceptible to fucidic acid. No isolate was found to be resistant to vancomycin. In contrast, most MSSA isolates were susceptible to the above mentioned antibiotics: 91.8, 88.9, 85.8, 97.1 and 100.0 % were susceptible to ciprofloxacin, erythromycin, fucidic acid, gentamicin, and cefoxitine, respectively. The only antibiotic which they were usually resistant to was penicillin B (79.1 % of the isolates). All MSSA isolates showed susceptibility to cefoxitine and vancomycin.
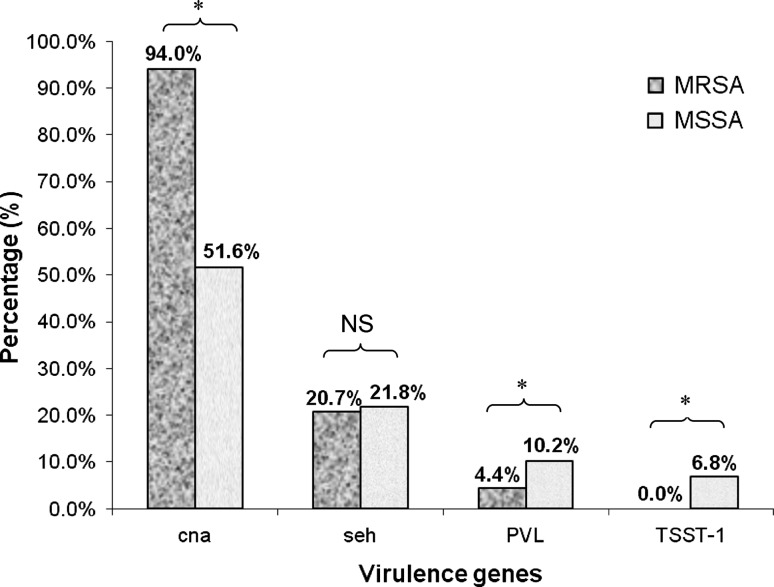
To further characterize our study isolates, we had proceeded to determine the prevalence of four staphylococcal virulence genes: collagen adhesin (cna), staphylococcal enterotoxin-H (seh), Panton-Valentine Leukocidin (PVL) and Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin-1 (TSST-1) in the isolates, using a modified multiplex PCR protocol [6, 7]. We found cna to be ubiquitously present in most MRSA isolates (94.0 %), and it was also the most prevalent toxin gene among the four to be harboured by our MSSA isolates (51.6 %). Intriguingly, the more virulent PVL and TSST-1 genes were more frequently found in MSSA than in MRSA, and there were significant differences (P < 0.05) in the frequency of three virulence genes (cna, PVL, TSST-1) found in MSSA compared to MRSA (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
The prevalence of four virulence genes (cna, seh, PVL and TSST-1) in S. aureus strains isolated from UKMMC in 2009. * indicates P < 0.05; NS indicates not significant
Apart from this report, Jimenez et al. [8] also reported more diverse and frequent virulence genes in MSSA compared to MRSA. Taking it all together with previous findings on this phenomenon with specific S. aureus strains, we suspect that an inverse relationship between antibiotic resistance and virulence exists in S. aureus, where multidrug resistant MRSA tend to harbour fewer virulence genes, whereas MSSA are more virulent but remain susceptible to many antibiotics. Down regulation of virulence determinants by S. aureus might be a strategy to evade immune system detection [4], this perhaps will give the bacteria more time in acquiring mutations crucial to generate antibiotic resistance. In addition, as antibiotic resistance is associated with fitness cost [9], minimizing the carriage of virulence determinants might be an MRSA strategy designed to compensate the cost.
In conclusion, possible explanations for the observed inverse relationship between antibiotic resistance and virulence in S. aureus are still largely hypothetical; more structured and detailed investigations will be needed for this purpose. Clarification of the dynamics of this inverse relationship will be important to elucidate the pathological and evolutionary importance of S. aureus in acquiring antibiotic resistance and virulence.
Acknowledgments
This research is supported by Research University Grant: UKM-GUP-TKP-08-19-067 and UKMMC Fundamental Research Grant: FF-001-2012.
Disclosure
All authors have no conflict of interest.
References
- 1.Cameron DR, Howden BP, Peleg AY. The interface between antibiotics resistance and virulence in Staphylococcus aureus and its impact upon clinical outcomes. Clin Infect Dis. 2011;53:576–582. doi: 10.1093/cid/cir473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gill SR, Fouts DE, Archer GL, Mongodin EF, Deboy RT, Ravel J, Paulsen IT, Kolonay JF, Brinkac L, Beanan M, Dodson RJ, Daugherty SC, Madupu R, Angiuoli SV, Durkin AS, Haft DH, Vamathevan J, Khouri H, Utterback T, Lee C, Dimitrov G, Jiang L, Qin H, Weidman J, Tran K, Kang K, Hance IR, Nelson KE, Fraser CM. Insights on evolution of virulence and resistance from the complete genome analysis of an early methicillin-resistant Staphylococcusaureus strain and a biofilm-producing methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis strain. J Bacteriol. 2005;187:2426–2438. doi: 10.1128/JB.187.7.2426-2438.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Neoh H, Yuzawa H, Cui L, Takeuchi F, Matsuo M, Hiramatsu K. Mutated response regulator graR is responsible for phenotypic conversion of Staphylococcus aureus from heterogeneous vancomycin-intermediate resistance to vancomycin-intermediate resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008;52:45–53. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00534-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gardete S, Kim C, Hartmann BM, Mwangi M, Roux CM, Dunman PM, Chambers HF, Tomasz A. Genetic pathway in acquisition and loss of vancomycin resistance in a methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) strain of clonal type USA300. PLoS Pathog. 2012;8:e1002505. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) (2012) Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; 22nd informational supplement, M100–S22. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA
- 6.Ma XX, Galiana A, Pedreira W, Mowszowicz M, Christophersen I, Machiavello S, Lope L, Benaderet S, Buela F, Vincentino W, Albini M, Bertaux O, Constenla I, Bagnulo H, Llosa L, Ito T, Hiramatsu K. Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Uruguay. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005;11:973–976. doi: 10.3201/eid1106.041059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hassriana Fazilla S, Nurul Azirah MS, Ainihayati N, Neoh H, Salasawati H. Virulence gene typing of methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) isolates in Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre (UKMMC) Asia Pac J Mol Med. 2011;1(1):1–4. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Jimenez JN, Ocampo AM, Vanegas JM, Rodriguez EA, Garces CG, Patino LA, Ospina S, Correa MM. Characterisation of virulence genes in methicillin susceptible and resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from a paediatric population in a university hospital of Medellín, Colombia. Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz Rio de Janeiro. 2011;106:980–985. doi: 10.1590/s0074-02762011000800013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Anderson DI, Levin BR. The biological cost of antibiotic resistance. Curr Opin Microbiol. 1999;2:489–493. doi: 10.1016/S1369-5274(99)00005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]